Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Essentials Strength Training Conditioning National Strength and Conditioning Association Third Edition PDF Free 1 656 26
Essentials Strength Training Conditioning National Strength and Conditioning Association Third Edition PDF Free 1 656 26
Uploaded by
LR Santana0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views1 pageProprioceptors are specialized sensory receptors that provide the central nervous system with information about muscle tone and coordinated movement. Muscle spindles are proprioceptors that consist of modified muscle fibers enclosed in a sheath and detect muscle length and rate of change of length. When a muscle is stretched, the muscle spindles activate sensory neurons that signal motor neurons to contract the muscle. Golgi tendon organs located in tendons also provide information about muscle tension to the central nervous system.
Original Description:
Kgujnbjnhuhbhh
Original Title
pdfcoffee.com_essentials-strength-training-conditioning-national-strength-and-conditioning-association-third-edition-pdf-free-1-656-26
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentProprioceptors are specialized sensory receptors that provide the central nervous system with information about muscle tone and coordinated movement. Muscle spindles are proprioceptors that consist of modified muscle fibers enclosed in a sheath and detect muscle length and rate of change of length. When a muscle is stretched, the muscle spindles activate sensory neurons that signal motor neurons to contract the muscle. Golgi tendon organs located in tendons also provide information about muscle tension to the central nervous system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views1 pageEssentials Strength Training Conditioning National Strength and Conditioning Association Third Edition PDF Free 1 656 26
Essentials Strength Training Conditioning National Strength and Conditioning Association Third Edition PDF Free 1 656 26
Uploaded by
LR SantanaProprioceptors are specialized sensory receptors that provide the central nervous system with information about muscle tone and coordinated movement. Muscle spindles are proprioceptors that consist of modified muscle fibers enclosed in a sheath and detect muscle length and rate of change of length. When a muscle is stretched, the muscle spindles activate sensory neurons that signal motor neurons to contract the muscle. Golgi tendon organs located in tendons also provide information about muscle tension to the central nervous system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
12 ■ Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning
opment of strength early in the range of motion,
especially at high velocities (13, 14, 19). Sensory neuron
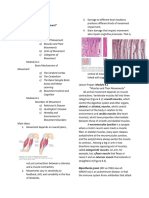
Proprioception Intrafusal fiber
Proprioceptors are specialized sensory receptors
located within joints, muscles, and tendons. Because
these receptors are sensitive to pressure and tension,
they relay information concerning muscle dynam- Motor
ics to the conscious and subconscious parts of the neuron
Muscle
central nervous system. The brain is thus provided spindle
with information concerning kinesthetic sense, or
conscious appreciation of the position of body parts
with respect to gravity. Most of this proprioceptive
information, however, is processed at subconscious Extrafusal fiber
levels so we do not have to dedicate conscious
activity toward tasks such as maintaining posture
or position of body parts. Figure 1.7 Muscle spindle. When a muscle is stretched,
deformation of the muscle spindle activates the sensory
neuron, which sends an impulse to the spinal cord, where it
Proprioceptors are specialized sensory receptors synapses with aE3392/NSCA/Fig.1.7/301144/GK/R1
motor neuron, causing the muscle to con-
that provide the central nervous system with information tract.
needed to maintain muscle tone and perform complex
coordinated movements.
vates the sensory neuron of the spindle, which sends
an impulse to the spinal cord, where it synapses
Muscle Spindles (connects) with motor neurons. This results in the
Muscle spindles are proprioceptors that consist of activation of motor neurons that innervate the same
several modified muscle fibers enclosed in a sheath muscle. Spindles thus indicate the degree to which
of connective tissue (figure 1.7). These modified the muscle must be activated in order to overcome
fibers, called intrafusal fibers, run parallel to the a given resistance. As a load increases, the muscle
normal, or extrafusal, fibers. Muscle spindles pro- is stretched to a greater extent, and engagement of
vide information concerning muscle length and the muscle spindles results in greater activation of the
rate of change in length. When the muscle length- muscle. Muscles that perform precise movements
ens, spindles are stretched. This deformation acti- have many spindles per unit of mass to help ensure
exact control of their contractile activity. A simple
example of muscle spindle activity is the knee jerk
reflex. Tapping on the tendon of the knee extensor
How Can Athletes Improve muscle group below the patella stretches the muscle
Force Production? spindle fibers. This causes activation of extrafusal
muscle fibers in the same muscle. There is a knee
°°Recruit large muscles or muscle groups jerk as these fibers actively shorten. This, in turn,
during an activity. shortens the intrafusal fibers and causes their dis-
°°Increase the cross-sectional area of mus- charge to cease.
cles involved in the desired activity.
°°Preload a muscle just before a concentric Golgi Tendon Organs
action to enhance force production during
Golgi tendon organs (GTOs) are proprioceptors
the subsequent muscle action.
located in tendons near the myotendinous junction
°°Use preloading during training to develop
and are in series, that is, attached end to end, with
strength early in the range of motion.
Accommodating-resistance apparatus, extrafusal muscle fibers (figure 1.8). Golgi tendon
such as isokinetic, hydraulic, and friction- organs are activated when the tendon attached to
modulated systems, do not load the muscle an active muscle is stretched. As tension in the
prior to contraction. muscle increases, discharge of the GTOs increases.
The sensory neuron of the GTO synapses with an
You might also like
- Complete Calisthenics Skills List - GravgearDocument1 pageComplete Calisthenics Skills List - GravgearAyoubNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tone - Spinal RefelxesDocument17 pagesMuscle Tone - Spinal RefelxesLaw YouNo ratings yet
- Reflex DR Arpana HazarikaDocument126 pagesReflex DR Arpana HazarikaDorin Pathak100% (1)
- Ch3 - Skeletal Muscle MechanicsDocument13 pagesCh3 - Skeletal Muscle MechanicsLinh Chi NguyễnNo ratings yet
- OtotDocument4 pagesOtotRiskayati LatiefNo ratings yet
- Muscle Spindle: Name: Rishbha Tiku Year:3 Semester:6Document9 pagesMuscle Spindle: Name: Rishbha Tiku Year:3 Semester:6Rishbha TikuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5.3Document29 pagesChapter 5.3FtnysmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Control of MovementDocument6 pagesChapter 8 - Control of MovementManilyn DacoNo ratings yet
- Spinal ReflexesDocument4 pagesSpinal Reflexesjp100% (1)
- Muscle Stretch ReflexDocument6 pagesMuscle Stretch ReflexNasreen SultanaNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous System - Movement - BritannicaDocument15 pagesHuman Nervous System - Movement - Britannicasalamy amourNo ratings yet
- LiệtDocument19 pagesLiệtChan Vinz KysNo ratings yet
- Material Arco ReflejoDocument3 pagesMaterial Arco ReflejoV PrNo ratings yet
- MovementDocument6 pagesMovementRaven SandaganNo ratings yet
- Motor SystemDocument116 pagesMotor SystemKhalid AlhemyariNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy and Physiology of The Masticatory System: MAJ Joseph Lowe October 15, 2010Document76 pagesNeuroanatomy and Physiology of The Masticatory System: MAJ Joseph Lowe October 15, 2010joeylowetylerNo ratings yet
- 035 Motor System Spinal MechanismDocument6 pages035 Motor System Spinal MechanismZeyad AmrNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13: Motor Control: Psychology 110: Biological PsychologyDocument32 pagesLecture 13: Motor Control: Psychology 110: Biological Psychologyamyle37No ratings yet
- Reflexes, Cardiac and Smooth Muscles - PhysiologyDocument35 pagesReflexes, Cardiac and Smooth Muscles - Physiologyworldwide handsomeNo ratings yet
- Muscular ConsiderationsDocument59 pagesMuscular ConsiderationsThor ManlangitNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tone PhysiologyDocument5 pagesMuscle Tone PhysiologyfatimaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 08 May 2023Document6 pagesAdobe Scan 08 May 2023Fayeez AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Nelson VCE PEDocument23 pagesNelson VCE PEPNo ratings yet
- Muscle Physiology - Muscle SpindlesDocument6 pagesMuscle Physiology - Muscle SpindlesRadwan BourjiNo ratings yet
- Golgi Tendon Reflux - 0Document4 pagesGolgi Tendon Reflux - 0AanNo ratings yet
- The Human Fascial System by L Stecco J A Day HandoutsDocument4 pagesThe Human Fascial System by L Stecco J A Day Handoutsnyaniso rahotepNo ratings yet
- The Stretch ReflexDocument3 pagesThe Stretch Reflexsungmin kimNo ratings yet
- 6 - Muscular SystemDocument48 pages6 - Muscular SystemCarl Vincent VingnoNo ratings yet
- Week 41-SCI PDFDocument3 pagesWeek 41-SCI PDFJaimie Charlotte Marie LangilleNo ratings yet
- Muscle SystemDocument2 pagesMuscle Systemapi-428138727No ratings yet
- Key Terms or Topic, Etymology, (Example), Steps in A Chapter 7: MovementDocument4 pagesKey Terms or Topic, Etymology, (Example), Steps in A Chapter 7: MovementShekaina NatadNo ratings yet
- 7.reflex Regulation of Physiological Function PDFDocument2 pages7.reflex Regulation of Physiological Function PDFNektarios TsakalosNo ratings yet
- Muscular System ReviewerDocument16 pagesMuscular System ReviewerNicole ZaputNo ratings yet
- 2-Skeletal Muscles Team441Document17 pages2-Skeletal Muscles Team441Bujeng BardaNo ratings yet
- 2009 - ProprioceptionDocument7 pages2009 - ProprioceptionMariana NannettiNo ratings yet
- Muscle Spindle - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesMuscle Spindle - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediamarcoserasmoNo ratings yet
- CHP 11Document71 pagesCHP 11Sophia YounNo ratings yet
- PNF BasicsDocument38 pagesPNF Basicsbpt2100% (3)
- PDF CrackDocument12 pagesPDF Crackdj_reaverNo ratings yet
- Involuntary MovementDocument17 pagesInvoluntary Movementfatimanasir2266No ratings yet
- Physio Lab 1-3Document6 pagesPhysio Lab 1-3Allison Eunice Servando100% (1)
- Skeletal Motor Control HierarchyDocument16 pagesSkeletal Motor Control HierarchyHapy ArdiaNo ratings yet
- Apps Functional Anatomy Lecture 3Document11 pagesApps Functional Anatomy Lecture 3joshNo ratings yet
- D.muscular System PDFDocument8 pagesD.muscular System PDFJohn Lawrence YbanezNo ratings yet
- Module 2 SkeletalDocument26 pagesModule 2 SkeletalJerome JanNo ratings yet
- Ankles Knees Hip Trunk Elbows Shoulders: Netball Goal ShootingDocument18 pagesAnkles Knees Hip Trunk Elbows Shoulders: Netball Goal ShootingJess Zausa MasulaNo ratings yet
- Donald A. Neumann - Kinesiology of The Musculoskeletal System 3rd Edition (2018, ELSEVIER) - Libgen - Li-P Íginas-4Document28 pagesDonald A. Neumann - Kinesiology of The Musculoskeletal System 3rd Edition (2018, ELSEVIER) - Libgen - Li-P Íginas-4ritaalmeida98No ratings yet
- ReflexesDocument18 pagesReflexesjolilarmatarNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle PhysiologyDocument26 pagesSkeletal Muscle Physiologypuchio100% (1)
- The Nervous System, Structure and Control of MovementDocument33 pagesThe Nervous System, Structure and Control of Movementarham mujahidNo ratings yet
- AnaKines NotesDocument3 pagesAnaKines NotesLorenzSantosHernandezNo ratings yet
- MonosynaptocDocument24 pagesMonosynaptocSaad IsmailNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of MusclesDocument58 pagesBiomechanics of MusclesAsad Chaudhary100% (2)
- The Rood Approach TheraExDocument8 pagesThe Rood Approach TheraExLall Jingerppang100% (1)
- Unit - 6 Muscular SystemDocument17 pagesUnit - 6 Muscular SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 6 - Spinal Reflexes - Source MaterialDocument19 pagesLecture - 6 - Spinal Reflexes - Source MaterialAmr KasemNo ratings yet
- Basic Background in Reflex PhysiologyDocument8 pagesBasic Background in Reflex PhysiologyMamta KungaliNo ratings yet
- Brain Breakthrough: The Art of Neurological Rehabilitation: Easy and Innovative Techniques, #1From EverandBrain Breakthrough: The Art of Neurological Rehabilitation: Easy and Innovative Techniques, #1No ratings yet
- Official Hand Signal1Document8 pagesOfficial Hand Signal1Anime TV'sNo ratings yet
- Taste and SmellDocument22 pagesTaste and SmellabdirizakNo ratings yet
- Group Iv - Urinary Elimination PDFDocument96 pagesGroup Iv - Urinary Elimination PDFMeshezabel AsentistaNo ratings yet
- SkeletalDocument11 pagesSkeletalJharaNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics - Question PapersDocument22 pagesBiomechanics - Question PapersHey GoogleNo ratings yet
- Muscular EduranceDocument3 pagesMuscular EduranceMarc Jalen ReladorNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Surgery Case ReportsDocument6 pagesInternational Journal of Surgery Case ReportsErikNo ratings yet
- Git AnatomyDocument62 pagesGit AnatomyBimo HarmajiNo ratings yet
- Tennis Warmup GuideDocument20 pagesTennis Warmup GuideAbdelRahman BahieldinNo ratings yet
- Leg Resistance Band WorkoutDocument10 pagesLeg Resistance Band WorkoutJulemar LucasNo ratings yet
- Journal Benjolan Di LeherDocument9 pagesJournal Benjolan Di LeherStase IPD SoedarsoNo ratings yet
- Tooth Eruption and Its Disorders Pediatric DentistryDocument157 pagesTooth Eruption and Its Disorders Pediatric DentistryIlich GarayNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Pearls PDFDocument2 pagesOrthodontic Pearls PDFortho123No ratings yet
- Project Yogi 3Document141 pagesProject Yogi 3Mukesh kannan MahiNo ratings yet
- 36 Reading RapoffDocument11 pages36 Reading RapoffFanica ScarlatNo ratings yet
- SGD 3 Elbow and Hand ANA LAB PDFDocument4 pagesSGD 3 Elbow and Hand ANA LAB PDFim. EliasNo ratings yet
- TRX Mobility WorkoutDocument4 pagesTRX Mobility WorkoutShaoYenNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Nerve Block (Other Techniques)Document24 pagesMandibular Nerve Block (Other Techniques)daw022100% (2)
- Cardiovascular System NotesDocument43 pagesCardiovascular System Notestruefriends0809No ratings yet
- Cancer of LarynxDocument46 pagesCancer of LarynxVIDYANo ratings yet
- 13 - Daftar Pustaka NewDocument3 pages13 - Daftar Pustaka NewalfianiNo ratings yet
- Muscle Deprogramming - An Orthodontist's Perspective: Batra Laxman Ra Angshuman B LlachDocument5 pagesMuscle Deprogramming - An Orthodontist's Perspective: Batra Laxman Ra Angshuman B LlachJulio Cesar AlvearNo ratings yet
- 5 6156903161471696955 PDFDocument281 pages5 6156903161471696955 PDFHarish ShindeNo ratings yet
- Upper LimbDocument33 pagesUpper LimbchiokemuteonwuezobeNo ratings yet
- SGBAU B.Pharm 1 SEM Human-Anatomy-n-Physiology-I 2018Document2 pagesSGBAU B.Pharm 1 SEM Human-Anatomy-n-Physiology-I 2018Abhay DeulkarNo ratings yet
- Penatalaksanaan Fisioterapi Pada Kondisi Bell'S: Palsy Dextra Di Rsud Dr. Soehadi PrijonegoroDocument14 pagesPenatalaksanaan Fisioterapi Pada Kondisi Bell'S: Palsy Dextra Di Rsud Dr. Soehadi PrijonegoroNurul AzizahNo ratings yet
- Nimhans Mock 1 (DM) Mock Exam Explanatory KeyDocument28 pagesNimhans Mock 1 (DM) Mock Exam Explanatory KeySoman PillaiNo ratings yet
- SN 2Document2 pagesSN 2ELYA MAISARAH BINTI MAZLAN MoeNo ratings yet
- AKI CASE NishaDocument64 pagesAKI CASE NishaSurkhali Bipana100% (1)