Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acc 111 Week 6-7 Notes
Acc 111 Week 6-7 Notes
Uploaded by
Jennifer NardoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acc 111 Week 6-7 Notes
Acc 111 Week 6-7 Notes
Uploaded by
Jennifer NardoCopyright:
Available Formats
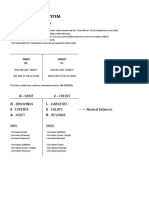
For the next following weeks the coverage is to know the adjusting entries and how to prepare it.
Accrual- under the accrual we have accrued income and accrued expense.
It means: you bought something but, it is still not paid. It is the same way other round when you
already gave your services but your customer has not paid yet.
While…
Deferral- is the other way around, under deferral we have pre- collected income and prepaid
expense.
It means: you already paid for something but, not yet received and customer already paid the item
but it has yet to be rendered.
Depreciation- is the devaluation of an asset over time. Example of an asset that depreciates are:
machines, buildings, service vehicles and etc.
Uncollectible Accounts or Doubtful accounts- this is the allotted amount of money that is possible
not to collect due to some circumstances like when a borrower/ client dies or unexpectedly
unreachable.
Solvency- it shows the company’s ableness to pay it’s long term debts and other financial needs
Liquidity- liquidity is the opposite of solvency. Liquidity is the ableness to pay the company’s short
term debts specially bills that are due.
Profitability- is when a company can make use of their money to help them generate an income.
Reversing Entry- a technique in bookkeeping that is simplified.
Salvage Value- is the full use of depreciated asset until it’s last use of life.
Salvage has it’s own formula which is:
SALVAGE VALUE= purchase price – (depreciation x useful life)
Adjusting entries are prepared dated December 31. Adjusting entries is useful to measure the profit
and to balance the accounts. When failed to recognize any of this accounts it is expected that the
financial position can be wrong.
You might also like
- Intermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandIntermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Chapter 3Document5 pagesFinancial Accounting Chapter 3NiraniyaNo ratings yet
- Current and Noncurrent AssetsDocument19 pagesCurrent and Noncurrent AssetsMylene SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Accounting Terms - Basic DefinitionsDocument7 pagesAccounting Terms - Basic DefinitionsSourav JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Amodia - Notes (SIM 3)Document2 pagesAmodia - Notes (SIM 3)CLUVER AEDRIAN AMODIANo ratings yet
- Actg 1 Module 3Document5 pagesActg 1 Module 3Mae BertilloNo ratings yet
- The Accounts and The Double-Entry SystemDocument14 pagesThe Accounts and The Double-Entry SystemLOURIE JANE GULLEMNo ratings yet
- Accounting Training: Confidential PresentationDocument74 pagesAccounting Training: Confidential Presentationzee_iitNo ratings yet
- BFAR 09 - 09 - 2022 Double Entry SystemDocument5 pagesBFAR 09 - 09 - 2022 Double Entry SystemSheryl cornelNo ratings yet
- Finance TermsDocument7 pagesFinance TermsTanveer HussainNo ratings yet
- HandoutDocument4 pagesHandoutZack CullenNo ratings yet
- AssetsDocument7 pagesAssetsarchie demesaNo ratings yet
- Name: Ezy Tri Agustina NPM: C1C020028 Class: 2 A Accounting Resume CH 7Document4 pagesName: Ezy Tri Agustina NPM: C1C020028 Class: 2 A Accounting Resume CH 7EzyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Accounting: Concepts and PrinciplesDocument25 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Accounting: Concepts and Principlesd_hambrettNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Audit of Receivable and SalesDocument7 pagesUnit 3 Audit of Receivable and Salessolomon adamuNo ratings yet
- FABMDocument11 pagesFABMDennis N. IndigNo ratings yet
- Fabm 2 ReviewerDocument5 pagesFabm 2 Reviewerlun3l1ght18No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Accounting 1 CDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Accounting 1 CAle EalNo ratings yet
- Bsba Acctg 111Document2 pagesBsba Acctg 111Hansel UngartNo ratings yet
- The Accounting EquationDocument5 pagesThe Accounting EquationHuskyNo ratings yet
- Accounting 1 - Module 7Document38 pagesAccounting 1 - Module 7CATHNo ratings yet
- General Journal (Record) Check Voucher Trial Balance (Prepare) General Ledger (Post)Document10 pagesGeneral Journal (Record) Check Voucher Trial Balance (Prepare) General Ledger (Post)Teajay BautistaNo ratings yet
- All Basic Terms of AccountingDocument20 pagesAll Basic Terms of AccountingpoornapavanNo ratings yet
- Debet and Credit 1Document23 pagesDebet and Credit 1Jemal SeidNo ratings yet
- Reviewer On Basic AccountingDocument8 pagesReviewer On Basic AccountingPRINCESS JOY BALAISNo ratings yet
- Accounts or Real AccountsDocument3 pagesAccounts or Real AccountsKrystel Gay GanaganagNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting Terminology: Tangible AssetsDocument4 pagesBasic Accounting Terminology: Tangible Assetskavya guptaNo ratings yet
- FABM 1 - Contextualized LAS - Week 4Document7 pagesFABM 1 - Contextualized LAS - Week 4Sheila Marie Ann Magcalas-GaluraNo ratings yet
- Key Financial Terms - Business - Gov.auDocument10 pagesKey Financial Terms - Business - Gov.auSantosh AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Account Titles and ExplanationDocument4 pagesAccount Titles and ExplanationKaye VillaflorNo ratings yet
- Financial BookletDocument7 pagesFinancial Bookletneelashi maruNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Elements of FsDocument53 pagesLesson 8 Elements of FsSoothing BlendNo ratings yet
- Acfm Unit 4Document47 pagesAcfm Unit 4begumayesha7366No ratings yet
- Updated Lecture Partnership and CorporationDocument10 pagesUpdated Lecture Partnership and CorporationAppleNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Accounting Exam BreakdownDocument9 pagesGrade 11 Accounting Exam BreakdownAli SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Andriod 3Document5 pagesAndriod 3Mark Ghever PopuliNo ratings yet
- Book KeepingDocument11 pagesBook KeepingRocket SinghNo ratings yet
- The Statement of Financial PositionDocument6 pagesThe Statement of Financial PositionMA. ANGELA NISSI QUIROZNo ratings yet
- Accounts Payble and Receivable.Document8 pagesAccounts Payble and Receivable.haris123786No ratings yet
- Accounting Equation Powerpoint NotesDocument28 pagesAccounting Equation Powerpoint NotespsrikanthmbaNo ratings yet
- (ACCT 317) Chapter 8 - Reporting and Analyzing ReceivablesDocument1 page(ACCT 317) Chapter 8 - Reporting and Analyzing Receivablesp.a.No ratings yet
- Accounts ReceivableDocument5 pagesAccounts ReceivableCaila RamosNo ratings yet
- Major Account TitleDocument63 pagesMajor Account TitleElla RamosNo ratings yet
- Assorted GlossaryDocument3 pagesAssorted GlossaryOmkumarNo ratings yet
- ADIMINSTER SUBISIDIRY&CONTROLING DOCUMENTS Levell IIIDocument17 pagesADIMINSTER SUBISIDIRY&CONTROLING DOCUMENTS Levell IIIembaendo27uNo ratings yet
- 02 Administer Subsidiary Accounts and Ledgers Level IIIDocument40 pages02 Administer Subsidiary Accounts and Ledgers Level IIIkejela75% (4)
- MYOB Glossary of Accounting TermsDocument14 pagesMYOB Glossary of Accounting TermsSyirleen Adlyna OthmanNo ratings yet
- Types and Effects Of: Transacti ONSDocument62 pagesTypes and Effects Of: Transacti ONSJeremy MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Accounting Basics: Debits and Credits vs. Account TypesDocument16 pagesAccounting Basics: Debits and Credits vs. Account TypeskazrobNo ratings yet
- Elements of Financial StatementsDocument6 pagesElements of Financial StatementsAdelina AquinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Statement of Financial Position (Part 1)Document10 pagesLesson 5 - Statement of Financial Position (Part 1)yana jungNo ratings yet
- Rev BusacctgDocument2 pagesRev BusacctgeliNo ratings yet
- Elements of Financial StatementsDocument3 pagesElements of Financial StatementsMargNo ratings yet
- English For Accounting: Module Session 3 - Accounting Terms by Yulia Sulianti Se - Ak, M.IkomDocument3 pagesEnglish For Accounting: Module Session 3 - Accounting Terms by Yulia Sulianti Se - Ak, M.IkomWulan AyuNo ratings yet
- Key Financial TermsDocument9 pagesKey Financial TermsHoney VermaNo ratings yet
- Entrep SSLM Q2 - WK 8Document12 pagesEntrep SSLM Q2 - WK 8Micca Jade HernanNo ratings yet
- Glossary For Accounting For ManagersDocument6 pagesGlossary For Accounting For ManagersSaurav TomarNo ratings yet
- Afar NotesDocument24 pagesAfar NotesCoreen ElizaldeNo ratings yet
- Fabm 2 Reviewer 1Document7 pagesFabm 2 Reviewer 1lun3l1ght18No ratings yet