Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 viewsSuraj 2111933
Suraj 2111933
Uploaded by
Ajit KumarThe document provides steps to troubleshoot network connectivity issues between PCs connected to the same network. It involves checking the IP address settings, releasing and renewing the IP address if it is invalid, using ping and tracert commands to test connectivity to the router and internet, and determining if the issue is local to the network or farther in the connection.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Huawei HCIA-IoT v. 2.5 Evaluation QuestionsDocument77 pagesHuawei HCIA-IoT v. 2.5 Evaluation Questionstest oneNo ratings yet
- Diy Microcontroller Projects For Hobbyists The Ultimate Project Based Guide To Building Real World Embedded Applications in C and C Programming 1nbsped 9781800564138 - CompressDocument320 pagesDiy Microcontroller Projects For Hobbyists The Ultimate Project Based Guide To Building Real World Embedded Applications in C and C Programming 1nbsped 9781800564138 - Compressbeck67% (3)
- ASSEMBLY AND PARTS ALBUM - Kipor Power Systems - KDE16STA PDFDocument1 pageASSEMBLY AND PARTS ALBUM - Kipor Power Systems - KDE16STA PDFracso0% (1)
- Ansys User Programmable Features (UPFs) .Document167 pagesAnsys User Programmable Features (UPFs) .kiran_wakchaure100% (1)
- How To Configure Peer To Peer Workgroup Network Step by Step GuideDocument62 pagesHow To Configure Peer To Peer Workgroup Network Step by Step GuiderezhabloNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Principles and Practices of Maintenance Planning KVNDocument23 pagesUnit 1 Principles and Practices of Maintenance Planning KVNVenkadeshwaran KuthalingamNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Doesn't Have A Valid IP Configuration: Try To Restart Your Machine First Thing FirstDocument4 pagesEthernet Doesn't Have A Valid IP Configuration: Try To Restart Your Machine First Thing FirstMuntaha ZyanNo ratings yet
- Postupak Kada IP Adresa Nije ValidnaDocument47 pagesPostupak Kada IP Adresa Nije ValidnajovanicmarijaNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Dynamic Ip ArticleDocument4 pagesEthernet Dynamic Ip ArticleMuntaha ZyanNo ratings yet
- Questions CeragonDocument3 pagesQuestions CeragonAndrei ZebreniucNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Troubleshooting ToolsDocument10 pagesTCP/IP Troubleshooting ToolsLoredel Doria LueteNo ratings yet
- WR-854 - B - Manual-01202004Document45 pagesWR-854 - B - Manual-01202004Alexis MedinaNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Fundamentals of Troubleshooting The NetworkDocument9 pages2.0 Fundamentals of Troubleshooting The NetworkAmsalu SeteyNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Computer Network System: By: Alyssa Joi Viloria Tracy Mae Quizon Jerico RayoDocument30 pagesTroubleshooting Computer Network System: By: Alyssa Joi Viloria Tracy Mae Quizon Jerico RayoDanilo AggabaoNo ratings yet
- EXPARIMENT # 9 and 10 DCNDocument20 pagesEXPARIMENT # 9 and 10 DCNSaad AliNo ratings yet
- Network DebugDocument5 pagesNetwork DebugFERNANDONo ratings yet
- TLE-Presentation 9-BAUTISTADocument7 pagesTLE-Presentation 9-BAUTISTAruzzel cedrick g zaballeroNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2-LAB 2-Understanding Network CommandsDocument10 pagesWEEK 2-LAB 2-Understanding Network CommandsAbu SufyanNo ratings yet
- HOWTO ResetWin7NetworkConnections NewDocument7 pagesHOWTO ResetWin7NetworkConnections NewAlexandro MarquesNo ratings yet
- Internet IssuuesDocument7 pagesInternet IssuuesMilind MehtaNo ratings yet
- TD-8840T QigDocument18 pagesTD-8840T QigChu Văn Nam100% (1)
- W6-Network Checking Procedures and TechniquesDocument6 pagesW6-Network Checking Procedures and TechniquesEchelle OgatisNo ratings yet
- Airlink Wireless Router Rt210wDocument4 pagesAirlink Wireless Router Rt210wdonsterthemonsterNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 1.6Document11 pagesLab Activity 1.6amna mukhtarNo ratings yet
- For VistaDocument2 pagesFor VistaSyafiqah ZahariNo ratings yet
- TD w8151n QigDocument18 pagesTD w8151n Qigtotos20100% (1)
- Computer N LabbbbbDocument13 pagesComputer N LabbbbbNoman saddiqueNo ratings yet
- AC6-How To Setup Static IP ModeDocument9 pagesAC6-How To Setup Static IP ModeawakkoNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing and Troubleshooting Wireless NetworkDocument5 pagesDiagnosing and Troubleshooting Wireless NetworkJudy Ann T. UchiNo ratings yet
- User'S Guide Speedtouch 511EDocument7 pagesUser'S Guide Speedtouch 511EsohailsamarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document26 pagesExperiment 4kumarjigar4727No ratings yet
- Lab No # 03 Network Basic Commands Objective:: Computer System Command PromptDocument10 pagesLab No # 03 Network Basic Commands Objective:: Computer System Command Promptaftab_sweet3024No ratings yet
- CCN Lab Manual # 1: Networking Basic CommandsDocument10 pagesCCN Lab Manual # 1: Networking Basic CommandsTanveer KhadimNo ratings yet
- Resnet: Resetting Network Connections For Windows 7: Basic TroubleshootingDocument7 pagesResnet: Resetting Network Connections For Windows 7: Basic TroubleshootingperoslawNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5Document2 pagesExperiment 5mk9995236No ratings yet
- RouterDocument18 pagesRoutersaipratapbecNo ratings yet
- IPCONFIG Command PDFDocument3 pagesIPCONFIG Command PDFCharles CaadanNo ratings yet
- Setup Peer To Peer NetworkDocument3 pagesSetup Peer To Peer NetworkDan AvergonzadoNo ratings yet
- LAB 3 DEC30023 NewDocument14 pagesLAB 3 DEC30023 NewFirdausNo ratings yet
- Recovering From An IP Address ChangeDocument4 pagesRecovering From An IP Address ChangesdfasdfaNo ratings yet
- Full Fix by Zafar HussainDocument13 pagesFull Fix by Zafar HussainZafar HussainNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document14 pagesLab 2umarNo ratings yet
- WiFi IssueDocument14 pagesWiFi Issuepardhasaradhi photosNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Basic TCP/IP Problems: Step 1: Check The ConfigurationDocument9 pagesTroubleshooting Basic TCP/IP Problems: Step 1: Check The ConfigurationIngwaar RosensonNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Network Connections KBDocument18 pagesTroubleshooting Network Connections KBAshu_SrivastavNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Win 8Document17 pagesTCP/IP Win 8Ahmed Said GhonimyNo ratings yet
- Basic Network TroubleshootingDocument2 pagesBasic Network TroubleshootingsundaresanmaniNo ratings yet
- Network Appliance How To Guide: PPTP ClientDocument13 pagesNetwork Appliance How To Guide: PPTP ClientAlam KabirNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer PracticalsDocument26 pagesPacket Tracer PracticalsAkanksha Dixit100% (1)
- Fix Unidentified Network and No Network Access Errors in Windows 7Document5 pagesFix Unidentified Network and No Network Access Errors in Windows 7zceljakNo ratings yet
- ETAP FAQ - Authrization From License Manager PDFDocument4 pagesETAP FAQ - Authrization From License Manager PDFAtabat AduduNo ratings yet
- ETAP FAQ Authrization From License ManagerDocument4 pagesETAP FAQ Authrization From License ManagersonsondosNo ratings yet
- Networking/Port Forwarding/DDNS Overview GuideDocument13 pagesNetworking/Port Forwarding/DDNS Overview GuideBeqir CubolliNo ratings yet
- DSL-G604T: Before You BeginDocument15 pagesDSL-G604T: Before You BeginDan WalshNo ratings yet
- Internet, Infinitum, Wifi, Thompson RouterDocument2 pagesInternet, Infinitum, Wifi, Thompson RouterAlejandro MorenoNo ratings yet
- Wi Tribe FixDocument2 pagesWi Tribe FixGemrose SantosNo ratings yet
- Airlink101 Access Point - Ap431wDocument42 pagesAirlink101 Access Point - Ap431wJim ParentNo ratings yet
- ENHWI-G2 BAYANTEL PPPoEDocument5 pagesENHWI-G2 BAYANTEL PPPoEohyeah08No ratings yet
- TD-W8101G: 54Mbps Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router User GuideDocument5 pagesTD-W8101G: 54Mbps Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router User GuideAnonymous DKv8vpNo ratings yet
- LTRXTS-Assigning An IP Address To A CoBos Product-020324-044738Document2 pagesLTRXTS-Assigning An IP Address To A CoBos Product-020324-044738vlarreal2No ratings yet
- Renew Your IP AddressDocument5 pagesRenew Your IP AddressKuya AlexNo ratings yet
- How To Configure Wired TCP - IP Properties of My Computer (Windows XP, Vista, 7,8, Mac) - Welcome To TP-LINK PDFDocument8 pagesHow To Configure Wired TCP - IP Properties of My Computer (Windows XP, Vista, 7,8, Mac) - Welcome To TP-LINK PDFFakhrur RaziNo ratings yet
- Lab 9.3.5 DHCP Client Setup: ObjectiveDocument8 pagesLab 9.3.5 DHCP Client Setup: Objectiveamna mukhtarNo ratings yet
- Creating A Split Tunnel VPN Connection in LinuxDocument11 pagesCreating A Split Tunnel VPN Connection in LinuxLORENA BOTERO BETANCURNo ratings yet
- Old Acn FileDocument38 pagesOld Acn FileAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Mobile Application DevelopmentDocument61 pagesMobile Application DevelopmentAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence MCADocument55 pagesArtificial Intelligence MCAAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: Instructions To CandidatesDocument2 pagesSoftware Engineering: Instructions To CandidatesAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligencreDocument38 pagesArtificial IntelligencreAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- AI & Soft ComputingDocument61 pagesAI & Soft ComputingAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: Instructions To CandidatesDocument2 pagesSoftware Engineering: Instructions To CandidatesAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: Instructions To CandidatesDocument2 pagesSoftware Engineering: Instructions To CandidatesAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- SQL Query (5th Semester)Document28 pagesSQL Query (5th Semester)Ajit KumarNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Master of Computer Applications Common Entrance Test (NIMCET) 2020Document16 pagesNational Institute of Technology Master of Computer Applications Common Entrance Test (NIMCET) 2020Ajit KumarNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: Roll No. Total No. of Pages: 02 Total No. of Questions:07Document2 pagesSoftware Engineering: Roll No. Total No. of Pages: 02 Total No. of Questions:07Ajit KumarNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: Instructions To CandidatesDocument2 pagesSoftware Engineering: Instructions To CandidatesAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Guidelines To Giving A Proper Introduction:-: Greeting:-Opening LineDocument1 pageGuidelines To Giving A Proper Introduction:-: Greeting:-Opening LineAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- C++ Pointer To Object - InfoBrother114519Document7 pagesC++ Pointer To Object - InfoBrother114519Ajit KumarNo ratings yet
- Study Scheme & Syllabus of Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) Batch 2018 OnwardsDocument49 pagesStudy Scheme & Syllabus of Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) Batch 2018 OnwardsAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- BCA Syllabus 2019 OnwardsDocument68 pagesBCA Syllabus 2019 OnwardsAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- C++ Practical File: Session TopicDocument3 pagesC++ Practical File: Session TopicAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- SUV300Document18 pagesSUV300MayankNo ratings yet
- Iub Transport Engineering GuideUMT IRC APP 007149 V06.02Document198 pagesIub Transport Engineering GuideUMT IRC APP 007149 V06.02Moh diakNo ratings yet
- Unit III SPMDocument65 pagesUnit III SPMMukesh KatoleNo ratings yet
- Scrap SalesDocument3 pagesScrap SalesSankariKommiNo ratings yet
- M4 - PseudocodeDocument38 pagesM4 - PseudocodeVemas SatriaNo ratings yet
- Are You A 21st Century TeacherDocument3 pagesAre You A 21st Century TeacherChristianTorresNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Execution in Combination With Autonomous Agents Based On SAP and OPC UADocument40 pagesManufacturing Execution in Combination With Autonomous Agents Based On SAP and OPC UASonyAcerNo ratings yet
- The Increased Strength of The Gear in The Main Hydraulic Pump Improves DurabilityDocument6 pagesThe Increased Strength of The Gear in The Main Hydraulic Pump Improves DurabilityjfarcoNo ratings yet
- History: 2006-2007: Creation and Initial ReactionDocument3 pagesHistory: 2006-2007: Creation and Initial ReactionCorina Cristiana C.No ratings yet
- Netwrok Setup Manual v1.40Document5 pagesNetwrok Setup Manual v1.40Jose ElenilsonNo ratings yet
- New Product Development Examining Its Evolution AnDocument13 pagesNew Product Development Examining Its Evolution AnRahul GargNo ratings yet
- B2BM Project Report - Business To Business MarketingDocument18 pagesB2BM Project Report - Business To Business MarketingPradeep SethiaNo ratings yet
- Optimize CAD/CAM Processes With Tebis SoftwareDocument45 pagesOptimize CAD/CAM Processes With Tebis Softwareturago0% (1)
- Electrical & Electronics Engg.: University of CalicutDocument20 pagesElectrical & Electronics Engg.: University of Calicutjohnpeter1989No ratings yet
- ICCAE 2021: Proceedings ofDocument139 pagesICCAE 2021: Proceedings ofAbigailNo ratings yet
- AlienVault Correlation CustomizationDocument12 pagesAlienVault Correlation Customizationmario_kglNo ratings yet
- ABB Turbo Systems LTD - Activity Report 2010Document12 pagesABB Turbo Systems LTD - Activity Report 2010Zaal DgebuadzeNo ratings yet
- Dlscrib Com PDF Rendezvous 2012xlsx DL PDFDocument783 pagesDlscrib Com PDF Rendezvous 2012xlsx DL PDFAryan TyagiNo ratings yet
- Back To Basics - Car Audio 101 - Battery and AltenatorDocument4 pagesBack To Basics - Car Audio 101 - Battery and AltenatorMax BeeksNo ratings yet
- (C) En-Ppg-Pulsed-Power-Supplies-White-PaperDocument15 pages(C) En-Ppg-Pulsed-Power-Supplies-White-PaperPrashant SinghNo ratings yet
- Hikvision Ds-2cd63c2f - I (V) (S)Document5 pagesHikvision Ds-2cd63c2f - I (V) (S)Oscar HerreraNo ratings yet
- Web Technology Lab ManualDocument69 pagesWeb Technology Lab Manual505-CSE-A Afrah KhatoonNo ratings yet
- Soilmec T 108 Drill RigDocument8 pagesSoilmec T 108 Drill RigEduardo ServínNo ratings yet
- AGFA Drystar - 5302Document222 pagesAGFA Drystar - 5302ClaudiaNo ratings yet
- VGB PDFDocument16 pagesVGB PDFbajrangNo ratings yet
Suraj 2111933
Suraj 2111933
Uploaded by
Ajit Kumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views11 pagesThe document provides steps to troubleshoot network connectivity issues between PCs connected to the same network. It involves checking the IP address settings, releasing and renewing the IP address if it is invalid, using ping and tracert commands to test connectivity to the router and internet, and determining if the issue is local to the network or farther in the connection.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides steps to troubleshoot network connectivity issues between PCs connected to the same network. It involves checking the IP address settings, releasing and renewing the IP address if it is invalid, using ping and tracert commands to test connectivity to the router and internet, and determining if the issue is local to the network or farther in the connection.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views11 pagesSuraj 2111933
Suraj 2111933
Uploaded by
Ajit KumarThe document provides steps to troubleshoot network connectivity issues between PCs connected to the same network. It involves checking the IP address settings, releasing and renewing the IP address if it is invalid, using ping and tracert commands to test connectivity to the router and internet, and determining if the issue is local to the network or farther in the connection.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 11
Advanced Computer Networking
Lab (PGCA 1928)
ASSIGNMENT-1
Submitted By:- Submitted To:-
Name:- Ajit Kumar Mrs. Harjot Kaur
Course:- MCA - 3
Roll No.:- 2111914
Experiment-1
AIM :- To demonstrate the connectivity of PC’s with
TCP/IP Protocols in windows and show how to assign
IP addresses to your computer.
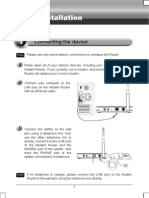
Step 1:- Click on Network Settings as shown in fig.
Step 2:- Now click on Ethernet settings, then choose
“change adapter settings”.
Now you will see this these type of option as shown in
fig,
Step 3:- Now simply click on Properties, choose
“Internet Protocol Version 4”
Step 4:- Now click on properties you will see a page as
shown in fig:-
Step 5:- Change the IP address and click OK
Step 6:- Open command Prompt and write ipconfig
with IP Address
Experiment-3
AIM :- Demonstrate how the network troubleshooting
problem can be resolved with the help of ping and
IPconfig. Take the screenshot of each step to show the
communication of one Pc with other Pc.
Confirm That You Have a Valid IP Address
At this point, you've verified that the problem is not
temporary and that all your hardware works. Since
Windows can't fix the problem on its own, you need to
pinpoint the spot along the connection where the
network problem is occurring.
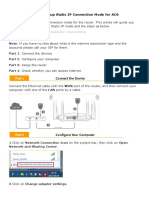
It's a good idea to make sure that you don't have any
strange IP settings selected. To check this,
open Settings and go to Network & Internet > Status.
Below the Advanced network settings header,
choose Change adapter options. In the resulting
window, double-click the name of your network.
Next, you'll see a status window. Click
the Properties button here.
Inside the next dialog, double-click the Internet
Protocol Version 4 entry.
Unless you've set up a static IP address (if you don't
know what this is, you probably don't use one), make
sure you have both Obtain an IP address
automatically and Obtain DNS server address
automatically checked.
Repeat this process for Internet Protocol Version 6, if
it's enabled, to ensure everything is automatic there as
well.
Reviewing Your IP Address Validity
Once you've done the above, you should check to
confirm if the router is giving you a valid IP address.
Open up a Command Prompt window by
typing cmd into the Start Menu. Enter ipconfig and
hit Enter, then look for the text under Ethernet
adapter (for wired connections) or Wireless LAN
Adapter (for wireless connections).
If IPv4 Address looks like 169.x.x.x, your computer is
not receiving a valid IP address from your router.
Typing the following two commands, one at a time, will
release your computer's current IP address and request a
new one, which may resolve this:
ipconfig /release \nipconfig /renew
Should you still have a 169.x.x.x address after typing
the above commands and entering ipconfig again, your
machine still isn't receiving an IP from the router. Try
plugging your PC directly into the modem with an
Ethernet cable and see if you can get online.
If the connection works this way, your router is the
problem. You may need to factory reset your router, or
consider replacing it.
5. Try a Ping and Trace Its Route
If your IP address starts with anything other
than 169 when you run ipconfig, you have a valid IP
address from your router. At this point, you've
confirmed the problem is somewhere between your
router and the internet.
Type the below command to ping Google's DNS servers
to see if you can reach a website online (you can
replace 8.8.8.8 with anything you like, such
as www.msn.com):
ping 8.8.8.8
This will send four packets to Google's DNS server. If
they fail to send, you'll see some basic info about the
failure. In case you want to continue pinging
indefinitely so you can monitor it while
troubleshooting, just add a -t to the end, like so:
ping 8.8.8.8 -t
You can press Ctrl + C to stop pinging at any time. For
more information, type this command to trace the route
between your computer and Google's DNS servers:
tracert 8.8.8.8
The above command gives you a step-by-step
breakdown of the path the information takes to reach
the destination you specify. Watch it, and if it fails,
check to see where the problem occurs.
If an error pops up early in the route, the issue is likely
with your local network.
You might also like
- Huawei HCIA-IoT v. 2.5 Evaluation QuestionsDocument77 pagesHuawei HCIA-IoT v. 2.5 Evaluation Questionstest oneNo ratings yet
- Diy Microcontroller Projects For Hobbyists The Ultimate Project Based Guide To Building Real World Embedded Applications in C and C Programming 1nbsped 9781800564138 - CompressDocument320 pagesDiy Microcontroller Projects For Hobbyists The Ultimate Project Based Guide To Building Real World Embedded Applications in C and C Programming 1nbsped 9781800564138 - Compressbeck67% (3)
- ASSEMBLY AND PARTS ALBUM - Kipor Power Systems - KDE16STA PDFDocument1 pageASSEMBLY AND PARTS ALBUM - Kipor Power Systems - KDE16STA PDFracso0% (1)
- Ansys User Programmable Features (UPFs) .Document167 pagesAnsys User Programmable Features (UPFs) .kiran_wakchaure100% (1)
- How To Configure Peer To Peer Workgroup Network Step by Step GuideDocument62 pagesHow To Configure Peer To Peer Workgroup Network Step by Step GuiderezhabloNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Principles and Practices of Maintenance Planning KVNDocument23 pagesUnit 1 Principles and Practices of Maintenance Planning KVNVenkadeshwaran KuthalingamNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Doesn't Have A Valid IP Configuration: Try To Restart Your Machine First Thing FirstDocument4 pagesEthernet Doesn't Have A Valid IP Configuration: Try To Restart Your Machine First Thing FirstMuntaha ZyanNo ratings yet
- Postupak Kada IP Adresa Nije ValidnaDocument47 pagesPostupak Kada IP Adresa Nije ValidnajovanicmarijaNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Dynamic Ip ArticleDocument4 pagesEthernet Dynamic Ip ArticleMuntaha ZyanNo ratings yet
- Questions CeragonDocument3 pagesQuestions CeragonAndrei ZebreniucNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Troubleshooting ToolsDocument10 pagesTCP/IP Troubleshooting ToolsLoredel Doria LueteNo ratings yet
- WR-854 - B - Manual-01202004Document45 pagesWR-854 - B - Manual-01202004Alexis MedinaNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Fundamentals of Troubleshooting The NetworkDocument9 pages2.0 Fundamentals of Troubleshooting The NetworkAmsalu SeteyNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Computer Network System: By: Alyssa Joi Viloria Tracy Mae Quizon Jerico RayoDocument30 pagesTroubleshooting Computer Network System: By: Alyssa Joi Viloria Tracy Mae Quizon Jerico RayoDanilo AggabaoNo ratings yet
- EXPARIMENT # 9 and 10 DCNDocument20 pagesEXPARIMENT # 9 and 10 DCNSaad AliNo ratings yet
- Network DebugDocument5 pagesNetwork DebugFERNANDONo ratings yet
- TLE-Presentation 9-BAUTISTADocument7 pagesTLE-Presentation 9-BAUTISTAruzzel cedrick g zaballeroNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2-LAB 2-Understanding Network CommandsDocument10 pagesWEEK 2-LAB 2-Understanding Network CommandsAbu SufyanNo ratings yet
- HOWTO ResetWin7NetworkConnections NewDocument7 pagesHOWTO ResetWin7NetworkConnections NewAlexandro MarquesNo ratings yet
- Internet IssuuesDocument7 pagesInternet IssuuesMilind MehtaNo ratings yet
- TD-8840T QigDocument18 pagesTD-8840T QigChu Văn Nam100% (1)
- W6-Network Checking Procedures and TechniquesDocument6 pagesW6-Network Checking Procedures and TechniquesEchelle OgatisNo ratings yet
- Airlink Wireless Router Rt210wDocument4 pagesAirlink Wireless Router Rt210wdonsterthemonsterNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 1.6Document11 pagesLab Activity 1.6amna mukhtarNo ratings yet
- For VistaDocument2 pagesFor VistaSyafiqah ZahariNo ratings yet
- TD w8151n QigDocument18 pagesTD w8151n Qigtotos20100% (1)
- Computer N LabbbbbDocument13 pagesComputer N LabbbbbNoman saddiqueNo ratings yet
- AC6-How To Setup Static IP ModeDocument9 pagesAC6-How To Setup Static IP ModeawakkoNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing and Troubleshooting Wireless NetworkDocument5 pagesDiagnosing and Troubleshooting Wireless NetworkJudy Ann T. UchiNo ratings yet
- User'S Guide Speedtouch 511EDocument7 pagesUser'S Guide Speedtouch 511EsohailsamarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document26 pagesExperiment 4kumarjigar4727No ratings yet
- Lab No # 03 Network Basic Commands Objective:: Computer System Command PromptDocument10 pagesLab No # 03 Network Basic Commands Objective:: Computer System Command Promptaftab_sweet3024No ratings yet
- CCN Lab Manual # 1: Networking Basic CommandsDocument10 pagesCCN Lab Manual # 1: Networking Basic CommandsTanveer KhadimNo ratings yet
- Resnet: Resetting Network Connections For Windows 7: Basic TroubleshootingDocument7 pagesResnet: Resetting Network Connections For Windows 7: Basic TroubleshootingperoslawNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5Document2 pagesExperiment 5mk9995236No ratings yet
- RouterDocument18 pagesRoutersaipratapbecNo ratings yet
- IPCONFIG Command PDFDocument3 pagesIPCONFIG Command PDFCharles CaadanNo ratings yet
- Setup Peer To Peer NetworkDocument3 pagesSetup Peer To Peer NetworkDan AvergonzadoNo ratings yet
- LAB 3 DEC30023 NewDocument14 pagesLAB 3 DEC30023 NewFirdausNo ratings yet
- Recovering From An IP Address ChangeDocument4 pagesRecovering From An IP Address ChangesdfasdfaNo ratings yet
- Full Fix by Zafar HussainDocument13 pagesFull Fix by Zafar HussainZafar HussainNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document14 pagesLab 2umarNo ratings yet
- WiFi IssueDocument14 pagesWiFi Issuepardhasaradhi photosNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Basic TCP/IP Problems: Step 1: Check The ConfigurationDocument9 pagesTroubleshooting Basic TCP/IP Problems: Step 1: Check The ConfigurationIngwaar RosensonNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Network Connections KBDocument18 pagesTroubleshooting Network Connections KBAshu_SrivastavNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Win 8Document17 pagesTCP/IP Win 8Ahmed Said GhonimyNo ratings yet
- Basic Network TroubleshootingDocument2 pagesBasic Network TroubleshootingsundaresanmaniNo ratings yet
- Network Appliance How To Guide: PPTP ClientDocument13 pagesNetwork Appliance How To Guide: PPTP ClientAlam KabirNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer PracticalsDocument26 pagesPacket Tracer PracticalsAkanksha Dixit100% (1)
- Fix Unidentified Network and No Network Access Errors in Windows 7Document5 pagesFix Unidentified Network and No Network Access Errors in Windows 7zceljakNo ratings yet
- ETAP FAQ - Authrization From License Manager PDFDocument4 pagesETAP FAQ - Authrization From License Manager PDFAtabat AduduNo ratings yet
- ETAP FAQ Authrization From License ManagerDocument4 pagesETAP FAQ Authrization From License ManagersonsondosNo ratings yet
- Networking/Port Forwarding/DDNS Overview GuideDocument13 pagesNetworking/Port Forwarding/DDNS Overview GuideBeqir CubolliNo ratings yet
- DSL-G604T: Before You BeginDocument15 pagesDSL-G604T: Before You BeginDan WalshNo ratings yet
- Internet, Infinitum, Wifi, Thompson RouterDocument2 pagesInternet, Infinitum, Wifi, Thompson RouterAlejandro MorenoNo ratings yet
- Wi Tribe FixDocument2 pagesWi Tribe FixGemrose SantosNo ratings yet
- Airlink101 Access Point - Ap431wDocument42 pagesAirlink101 Access Point - Ap431wJim ParentNo ratings yet
- ENHWI-G2 BAYANTEL PPPoEDocument5 pagesENHWI-G2 BAYANTEL PPPoEohyeah08No ratings yet
- TD-W8101G: 54Mbps Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router User GuideDocument5 pagesTD-W8101G: 54Mbps Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router User GuideAnonymous DKv8vpNo ratings yet
- LTRXTS-Assigning An IP Address To A CoBos Product-020324-044738Document2 pagesLTRXTS-Assigning An IP Address To A CoBos Product-020324-044738vlarreal2No ratings yet
- Renew Your IP AddressDocument5 pagesRenew Your IP AddressKuya AlexNo ratings yet
- How To Configure Wired TCP - IP Properties of My Computer (Windows XP, Vista, 7,8, Mac) - Welcome To TP-LINK PDFDocument8 pagesHow To Configure Wired TCP - IP Properties of My Computer (Windows XP, Vista, 7,8, Mac) - Welcome To TP-LINK PDFFakhrur RaziNo ratings yet
- Lab 9.3.5 DHCP Client Setup: ObjectiveDocument8 pagesLab 9.3.5 DHCP Client Setup: Objectiveamna mukhtarNo ratings yet
- Creating A Split Tunnel VPN Connection in LinuxDocument11 pagesCreating A Split Tunnel VPN Connection in LinuxLORENA BOTERO BETANCURNo ratings yet
- Old Acn FileDocument38 pagesOld Acn FileAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Mobile Application DevelopmentDocument61 pagesMobile Application DevelopmentAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence MCADocument55 pagesArtificial Intelligence MCAAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: Instructions To CandidatesDocument2 pagesSoftware Engineering: Instructions To CandidatesAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligencreDocument38 pagesArtificial IntelligencreAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- AI & Soft ComputingDocument61 pagesAI & Soft ComputingAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: Instructions To CandidatesDocument2 pagesSoftware Engineering: Instructions To CandidatesAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: Instructions To CandidatesDocument2 pagesSoftware Engineering: Instructions To CandidatesAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- SQL Query (5th Semester)Document28 pagesSQL Query (5th Semester)Ajit KumarNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Master of Computer Applications Common Entrance Test (NIMCET) 2020Document16 pagesNational Institute of Technology Master of Computer Applications Common Entrance Test (NIMCET) 2020Ajit KumarNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: Roll No. Total No. of Pages: 02 Total No. of Questions:07Document2 pagesSoftware Engineering: Roll No. Total No. of Pages: 02 Total No. of Questions:07Ajit KumarNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: Instructions To CandidatesDocument2 pagesSoftware Engineering: Instructions To CandidatesAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Guidelines To Giving A Proper Introduction:-: Greeting:-Opening LineDocument1 pageGuidelines To Giving A Proper Introduction:-: Greeting:-Opening LineAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- C++ Pointer To Object - InfoBrother114519Document7 pagesC++ Pointer To Object - InfoBrother114519Ajit KumarNo ratings yet
- Study Scheme & Syllabus of Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) Batch 2018 OnwardsDocument49 pagesStudy Scheme & Syllabus of Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) Batch 2018 OnwardsAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- BCA Syllabus 2019 OnwardsDocument68 pagesBCA Syllabus 2019 OnwardsAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- C++ Practical File: Session TopicDocument3 pagesC++ Practical File: Session TopicAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- SUV300Document18 pagesSUV300MayankNo ratings yet
- Iub Transport Engineering GuideUMT IRC APP 007149 V06.02Document198 pagesIub Transport Engineering GuideUMT IRC APP 007149 V06.02Moh diakNo ratings yet
- Unit III SPMDocument65 pagesUnit III SPMMukesh KatoleNo ratings yet
- Scrap SalesDocument3 pagesScrap SalesSankariKommiNo ratings yet
- M4 - PseudocodeDocument38 pagesM4 - PseudocodeVemas SatriaNo ratings yet
- Are You A 21st Century TeacherDocument3 pagesAre You A 21st Century TeacherChristianTorresNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Execution in Combination With Autonomous Agents Based On SAP and OPC UADocument40 pagesManufacturing Execution in Combination With Autonomous Agents Based On SAP and OPC UASonyAcerNo ratings yet
- The Increased Strength of The Gear in The Main Hydraulic Pump Improves DurabilityDocument6 pagesThe Increased Strength of The Gear in The Main Hydraulic Pump Improves DurabilityjfarcoNo ratings yet
- History: 2006-2007: Creation and Initial ReactionDocument3 pagesHistory: 2006-2007: Creation and Initial ReactionCorina Cristiana C.No ratings yet
- Netwrok Setup Manual v1.40Document5 pagesNetwrok Setup Manual v1.40Jose ElenilsonNo ratings yet
- New Product Development Examining Its Evolution AnDocument13 pagesNew Product Development Examining Its Evolution AnRahul GargNo ratings yet
- B2BM Project Report - Business To Business MarketingDocument18 pagesB2BM Project Report - Business To Business MarketingPradeep SethiaNo ratings yet
- Optimize CAD/CAM Processes With Tebis SoftwareDocument45 pagesOptimize CAD/CAM Processes With Tebis Softwareturago0% (1)
- Electrical & Electronics Engg.: University of CalicutDocument20 pagesElectrical & Electronics Engg.: University of Calicutjohnpeter1989No ratings yet
- ICCAE 2021: Proceedings ofDocument139 pagesICCAE 2021: Proceedings ofAbigailNo ratings yet
- AlienVault Correlation CustomizationDocument12 pagesAlienVault Correlation Customizationmario_kglNo ratings yet
- ABB Turbo Systems LTD - Activity Report 2010Document12 pagesABB Turbo Systems LTD - Activity Report 2010Zaal DgebuadzeNo ratings yet
- Dlscrib Com PDF Rendezvous 2012xlsx DL PDFDocument783 pagesDlscrib Com PDF Rendezvous 2012xlsx DL PDFAryan TyagiNo ratings yet
- Back To Basics - Car Audio 101 - Battery and AltenatorDocument4 pagesBack To Basics - Car Audio 101 - Battery and AltenatorMax BeeksNo ratings yet
- (C) En-Ppg-Pulsed-Power-Supplies-White-PaperDocument15 pages(C) En-Ppg-Pulsed-Power-Supplies-White-PaperPrashant SinghNo ratings yet
- Hikvision Ds-2cd63c2f - I (V) (S)Document5 pagesHikvision Ds-2cd63c2f - I (V) (S)Oscar HerreraNo ratings yet
- Web Technology Lab ManualDocument69 pagesWeb Technology Lab Manual505-CSE-A Afrah KhatoonNo ratings yet
- Soilmec T 108 Drill RigDocument8 pagesSoilmec T 108 Drill RigEduardo ServínNo ratings yet
- AGFA Drystar - 5302Document222 pagesAGFA Drystar - 5302ClaudiaNo ratings yet
- VGB PDFDocument16 pagesVGB PDFbajrangNo ratings yet