Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L10. Cardiovascular System (CVS) Drugs
L10. Cardiovascular System (CVS) Drugs
Uploaded by
sabahOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
L10. Cardiovascular System (CVS) Drugs
L10. Cardiovascular System (CVS) Drugs
Uploaded by
sabahCopyright:
Available Formats
LECCTURE OF PHARMACOLOGY
MADE BY NURSING ZONE TEAM
L10. Cardiovascular system (CVS) drugs
THIRD YEAR
@Nursing_Zone39
New high blood pressure guidelines 14 Nov, 2017
Oral Rectal
/ Diastolic pressure (mmhg) SC
Hmmmm
Category Systolic
Easy
or Normal
< 120 / 80
or Verity Patient can
Bypasses liver
or Compact
Prehypertension 120 - 129 / 80 administer
Erratic absorption low
Convenient at
grade
compliance Complete
FirstStage
pass effect
1 130 - 139 / 80 - 89
absorption
Sometimes inefficient
Small does
Stage
difficultly 2
in swallowing ≥ 140 / 90
Pain full
Sublingual-Buccal IV IM
BP= CO (cardiac output) x PVR (peripheral vascular resistance)
TI Rapid absorption Rapid
I TI Large volume
E Stability of drug
GBBBEmMgm
Accurate
I K Sustained release
E Higher bioavailability
IX Can’t be retrieved possible
XI Inconvenient Antihypertensive
Expensive
agents
Trained personnel
Small doses only
EXRequires trained personnel Erratic absorption
Can’t be swallowed
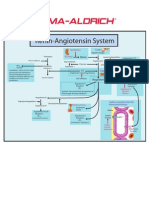
Angiotensinogen Kininogen
Renin
3 v
Increased
v
Aliskiren
Angiotensin I Bradykinin s prostaglandin
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (kininase II)
synthesis
Best of luck
Angiotensin II n Inactive metabolites
v ARBS v ACE inhibitors
i v
Vasoconstriction Aldosterone secretion v
Vasodilation e
Spironolactone, eplerenone
v v v
Increased peripheral Increased sodium Decreased peripheral
vascular resistance and water retention e
vascular resistance
s Increased blood pressure e Decreased blood pressure
Subclass M/A Effects Application Toxicities
Oral Rectal SC
Hmmmm
Easy
or converting
Angiotensin- - Chronic heart
- Cough
Inhibits
Arteriolar & - Hyperkalemia
or Verity
enzyme (ACE) inhibitors: failure
Patient can
- Angioneurotic
Captoprilor Compact
ACE Bypasses liver
venous dilation
- Hypertension
edema
administer
Erratic absorption low
Convenient
compliance Complete
Angiotensin receptor
First pass effect - Like ACEI
Blockers (ARBs):
Like ACEI absorption
Like ACEI
Sometimes inefficient
- Intolerant
Losartan
to ACEI Small does
difficultly in swallowing
Pain full
- Hyperkalemia
Reduces
Sublingual-Buccal Inhibits IV IM- Renal
Renin inhibitors enzyme angiotensin
Hypertension impairment
AliskirenRapid absorption activity I & Il and
TI - Potential
of renin I Rapid
Aldosterone
TI Large volume
Stability of drug teratogen
GBBBEmMgm
E
Higher bioavailability
I Accurate K Sustained release
E
Inconvenient
IX Can’t
Competiti be retrieved
- Slows heart
- Chronic heart
possible
XI
BETA BLOCKERS vely Expensive
rate Trained personnel
- Bronchospasm
Small doses only blocks B1 - Reduces blood failure
- Bradycardia
EXRequires trained personnel- Hypertension
Carvedilol Erratic absorption
Can’t be swallowed receptors pressure
- Reduces
cardiac rate
Venodilators:
Blocks - Hypertension
- Verapamil
Ca2+ and output - Angina
- Reduce
Best of luck
- Nifedipine
channel - Arrhythmias
vascular
resistance
Increases
Arteriolar dilators Reduces BP
- Tachycardia
NO Hypertension
Hydralazine & afterload - Fluid retention
synthesis
Subclass M/A Effects Application Toxicities
Oral Rectal SC
Hmmmm
or Easy
Releases - Acute cardiac - Excessive
NO & Reduces blood decompensat hypotension
or Verity
Combined arteriolar
activates Bypasses Patient can
and venodilator: pressure & liver ion - Thiocyanate
or Compact
Nitroprusside guanylyl
absorption low - Hypertensive administer
afterload
Erratic and cyanide
Convenient cyclase emergencies Completetoxicity
compliance
First pass effect
absorption
Sometimes inefficientSelectively Prevent
Blockers
SmallOrthostatic
does
difficultly in swallowingblock a1 sympathetic Hypertension
Prazosin
Adrenoceptors Painhypotension
full
vasoconstriction
Sublingual-Buccal
IV IM
DIURETICS - Hypertension,
- Block Na/CI - Reduce
mild heart
TI Rapid absorption
- Hydrochloro thiazide blood volume
I Rapid
transporter
Failure TI Large volume
Stability of drug
GBBBEmMgm
E
I Accurate - Severe Sustained release
- Frusemide K
E Higher bioavailability
hypertension,
Inconvenient
IX Can’t be retrieved
- Increase Na possible
XI heart Failure
- Spironolactone - Block
Expensive
and decrease K Trained personnel
Small doses only aldosterone excretion - Hypertension,
EXRequires trained personnelheart failure
receptor Erratic absorption
Can’t be swallowed
SYMPATHOPLEGICS,
Reduce central
Activate a2
CENTRALLY ACTING sympathetic Hypertension Sedation
adrenoceptors
Clonidine outflow
Best of luck
Heart Failure (HF)
Oral Rectal SC
Hmmmm
or Easy
• Heartor Verity
isn’t pumping as well (weaker than normal).
Patient can
Bypasses liver to body.
or Compact
• Heart can’t pump enough oxygen & nutrients
Erratic absorption administer
low to pump through
• Heart respond by stretching
Convenient to hold more blood the
body or by becoming stiff & compliance
thickened. Complete
First pass effect
• Heart muscle walls weaken & become unable to pump efficiently. absorption
Sometimes inefficient
• Kidneys respond by causing the body retain fluid (water) & salt. Small does
difficultly in swallowing
• Congestive HF: body becomes congested. Pain full
• Most common causes is coronary artery disease with
Sublingual-Buccal
hypertension. IV IM
• Cardinal symptoms: dyspnea, fatigue, fluid retention.
TI Rapid absorption
Stability of drug
I Rapid TI Large volume
GBBBEmMgm
E
Higher bioavailability
I Accurate K Sustained release
E
Inconvenient
IX Can’t be retrieved possible
XI Expensive Trained personnel
Small doses only
Subclass M/A
EX Requires trained
EffectspersonnelApplication
Erratic absorption
Toxicities
Can’t be swallowed
- Cough
Angiotensin- converting - Chronic heart
Inhibits Arteriolar & - Hyperkalemia
enzyme (ACE) inhibitors: failure
ACE venous dilation - Angioneurotic
Captopril - Hypertension
edema
Best of luck
Angiotensin receptor - Like ACEI
Blockers (ARBs):
Like ACEI - Intolerant Like ACEI
Losartan
to ACEI
Competiti - Slows heart
- Chronic heart - Bronchospasm
BETA BLOCKERS vely rate
failure - Bradycardia
Carvedilol blocks B1 - Reduces blood
- Hypertension
receptors pressure
Subclass M/A Effects Application Toxicities
Oral Rectal SC
Hmmmm
Increases
Arteriolaror Easy
dilators
NO
Reduces BP - Tachycardia
Hypertension
or Verity
Hydralazine & afterload
synthesis Bypasses liver
- Fluid retention
Patient can
or Compact
Erratic absorption low administer
Convenient Releases - Acute cardiac - Excessive
compliance
Reduces blood Complete
Combined First pass effect NO &
arteriolar decompensat hypotension
and venodilator: activates pressure & ion absorption
- Thiocyanate
Sometimes inefficient
Nitroprusside guanylyl afterload and cyanide
- HypertensiveSmall does
difficultly in swallowingcyclase emergencies Pain toxicity
full
Sublingual-BuccalReduced IV IM - Nausea
Ca2+
Increases Chronic - Vomiting
TI Rapid
CARDIAC absorption expulsion &
GLYCOSIDE
cardiac
Rapid symptomatic
Large volume
- Diarrhea
Digoxin increased I contractility TI
E Stability of drug Ca2+
GBBBEmMgm
heart failure
Accurate
I K Sustained release
- Arrhythmias
E Higher bioavailability stored
IX Can’t be retrieved possible
XI Inconvenient - Release Expensive Trained personnel
Small doses only - Acute and
EXRequires preload
nitric trained personnel
& chronic Erratic
heart absorption
- Postural
Can’t be swallowed oxide reduces
Venodilators: failure hypotension
Isosorbide dinitrate (NO) ventricular - Angina - Tachycardia
- Activate Stretch - Headache
guanylyl
cyclase
Best of luck
- Blselective Increases Acute heart
BETA- ADRENOCEPTOR agonist cardiac failure Arrhythmias
- Increases contractility,
AGONISTS: decompensated
CAMP
Dobutamine output
synthesis
اﻟﻠﻲ ﺑﺎﻟﻠﻮن دا ﻛﻠﻬﺎ اﻧﺬﻛﺮت ﻓﻮق
Signs & Symptoms of
Oral digoxin toxicityRectal SC
Hmmmm
or Easy
or Verity Patient can
• May causes due to narrow TI. Bypasses liver
or Compact
• Early indication of toxicity are usually
Erratic GI low
absorption related administer
Convenient
• GI: compliance Complete
First pass
- Abdominal paineffect - Anorexia - Diarrhea
absorption
Sometimes
- Nausea inefficient - Vomiting
Small does
•difficultly in swallowing
Neurologic:
Pain full
- Blue-yellow color blindness - Blurred vision
Sublingual-Buccal
- Colored dots in vision -IVComa IM
- Confusion - Depression
TI-Rapid
Seizuresabsorption
Stability of drug
I Rapid TI Large volume
GBBBEmMgm
E
Higher bioavailability
I Accurate K Sustained release
E
Inconvenient
IX Can’t be retrieved possible
XI Expensive Trained personnel
Small doses only Arrhythmia
EXRequires trained personnel Erratic absorption
Can’t be swallowed
• Irregular heartbeat (dysrhythmia)
• HR can be irregular or normal (50-100b/min)
- Bradyarrhythmias (<50b/min) = arrhythmias + normal / slow HR
- Tachyarrhythmias (>100b/min) = arrhythmias + rapi d HR
Best of luck
• Symptoms:
- Palpitation (feeling skipped heart beats / fluttering / “flip-flops” /
heart is “running away”)
- Pounding in chest - Dizziness / feeling light-headed
- Fainting - SOB
- Chest discomfort - Weakness / Fatigue (very tired)
Tess
Antiarrhythmic drugs
Oral Rectal SC
Hmmmm
or Easy
or Verity Patient can
Bypasses liver
• Treat disturbances of heart rhythm.
or Compact
• Capable of worsening / causing Erratic the very low
absorption administer
Convenient
arrhythmias. compliance Complete
First pass effect
• Categorized absorption
Sometimes
- Class I (Na+inefficient
channel blockers)
Small does
difficultly
- Class II in swallowing
(Beta adrenoceptor blockers)
Pain full
- Class III (K+ channel blockers)
Sublingual-Buccal
- Class IV (Ca+ channel blockers) IV IM
TI Rapid absorption Rapid
I TI Large volume
E Stability of drug
GBBBEmMgm
Accurate
I K Sustained release
E Higher bioavailability
IX Can’t be retrieved possible
XI Inconvenient
Subclass M/A Effects
Expensive
Application Toxicities
Trained personnel
Small doses only
EXRequires trained personnel
Sodium Erratic absorption
Can’t be swallowed Slows conduction Most atrial and
CLASS 1A : channel
velocity and ventricular Hypotension
- Procainamide (INa)
pacemaker rate arrhythmias
blockade
Terminate
Does not
Best of luck
Sodium ventricular
CLASS 1B :
prolong and
channel tachycardias and Neurologic
- Lidocaine
may shorten symptoms
(INa) prevent ventricular
action potential
blockade fibrillation after
cardioversion
Sodium Supraventricular
Proarrhythmic
CLASS 1C :
channel arrhythmias in
[precipitate
- Flecainide
(INa) patients with
pre-existing
blockade normal heart
arrhythmia]
Subclass M/A Effects Application Toxicities
Oral Rectal SC
Hmmmm
CLASS 2 :
or Easy
or Verity
- Propranolol
Nonselective
competitive
Decreased
heart rate,
cardiac output,
antagonist at Bypasses liver
- Prophylaxis of - Asthma
angina
- Atrial
- Atrioventricular
Block
Patient can
or Compact B-adrenoceptors
and blood
- Acute heart
arrhythmia administer
Erratic absorption low failure
Convenient pressure
compliance Complete
- Sedation
First pass effect
Serious absorption
Sometimes inefficientBlocks IKr, Prolongs action
ventricular Small does
Bradycardia and
difficultly
CLASS 3: in swallowingINa, ICa-L potential
heart
- Amiodarone channels, duration and
arrhythmias andPain full block in
supraventricular diseased heart
Sublingual-Buccal QT interval
B-adrenoceptors
IV arrhythmias IM
TI Rapid absorption - Reduces
Rapid
Stability of drug
I cardiac rate TI Large volume
GBBBEmMgm
Class E
- Hypertension
4:
Higher
bioavailability
Blocks
I Accurate
and output K Sustained release
- Angina
- Verapamil
E Ca2+
Inconvenient
IX Can’t
channel
be retrieved - Arrhythmiaspossible
- Reduce
XI
Expensive
vascular Trained personnel
Small doses only resistance
EXRequires trained personnel Erratic absorption
Can’t be swallowed
اﻟﻠﻲ ﺑﺎﻟﻠﻮن دا ﻛﻠﻬﺎ اﻧﺬﻛﺮت ﻓﻮق
Antianginal drugs
Best of luck
• Angina: occurs when the coronary arteries supply insufficient
O2 to the myocardium.
• n Heart’s workload by n HR, preload, afterload & force of
myocardial contractility.
• Myocardial O2 demand
• Supply of O2 to the heart
Subclass M/A Effects Application Toxicities
Oral Rectal SC
Hmmmm
or Easy - Release
Verity nitric - Acute and - Postural
NITRATES:or
oxide Bypasses liver
Smooth muscle Patient
chronic heart can
hypotension
or Compact
- Isosorbide dinitrate
(NO) Erratic
relaxation
absorption low failure administer
- Tachycardia
- Nitroglycerin
Convenient - Activate failure
compliance - Angina Complete
- Headache
First pass effect guanylyl
absorption
Sometimes inefficient cyclase
Small does
difficultly in swallowing
Nonselective Decreased - Prophylaxis of
Pain full
- Asthma
BETA BLOCKERS
competitive heart rate, - Atrioventricular
Sublingual-Buccalantagonist at cardiac
- Propranolol
IV output, angina
IM Block
B-adrenoceptors - Atrial - Acute heart
and blood
arrhythmia
TI Rapid absorption pressure
Rapid
failure
Stability of drug
I TI Large volume
- Sedation
GBBBEmMgm
E
Accurate
I K Sustained release
E Higher bioavailability
IX Can’t be retrieved
- Reduces possible
XI Inconvenient
Venodilators: Blocks Expensive
cardiac rate Trained personnel
- Hypertension
Small doses only Ca2+ and output - Angina
- Verapamil EXRequires trained personnel Erratic absorption
Can’t
- Nifedipine be swallowed channel - Reduce - Arrhythmias
vascular
resistance
اﻟﻠﻲ ﺑﺎﻟﻠﻮن دا ﻛﻠﻬﺎ اﻧﺬﻛﺮت ﻓﻮق
Best of luck
MADE BY NURSING ZONE TEAM
Pharma references
A- Basic and Clinical Pharmacology 13 E Paperback
Bertram Katzung (Author), Anthony Trevor (Author) Publisher: McGraw-Hill Medical; 13 edition
(December 23, 2014)
Language: English
ISBN13:97 0071825054
ISBN 10:0071825053
B. Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Pharmacology 6th edition (Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Series)
Paperback
Karen Whalen PharmD BCPS (Author) Edition: Sixth, North American.
Edition Language: English. ISBN-13: 978-1451191776 ISBN-10: 1451191774
2. List Essential References Materials (Journals, Reports, etc.) British National Formulary (BNF)
You might also like
- Hypertension Concept MapDocument1 pageHypertension Concept Mapashleydean100% (7)
- P2 Top 200 Part 1Document10 pagesP2 Top 200 Part 1Drashtibahen PatelNo ratings yet
- Adult Cardiac Arrest Algorithm: VF/PVT Asystole/PEADocument8 pagesAdult Cardiac Arrest Algorithm: VF/PVT Asystole/PEAVitor Hugo100% (3)
- Algo ArrestDocument2 pagesAlgo ArrestLocomotorica FK UkiNo ratings yet
- Antidote Chart: N-Acetylcysteine, NAC (Mucomyst) PO: Loading Dose: 140mg/kg PO: NauseaDocument11 pagesAntidote Chart: N-Acetylcysteine, NAC (Mucomyst) PO: Loading Dose: 140mg/kg PO: NauseaTapioca PearlNo ratings yet
- Jane Detailed Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesJane Detailed Lesson PlanYe ShuaNo ratings yet
- L7. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) IIDocument8 pagesL7. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) IIsabahNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document5 pagesWeek 5Joanna BakNo ratings yet
- Renin-Angiotensin SystemDocument1 pageRenin-Angiotensin SystemSigma-Aldrich100% (2)
- L11. GIT - Respiratory Tract DrugsDocument14 pagesL11. GIT - Respiratory Tract DrugssabahNo ratings yet
- Ecg ReadingsDocument11 pagesEcg ReadingsAnton Laurenciana100% (5)
- UrologyDocument5 pagesUrologyJoshua AtienzaNo ratings yet
- ACLS 2015 Algorithm and Anesthesia ACLS PDFDocument14 pagesACLS 2015 Algorithm and Anesthesia ACLS PDFTaufiqurrahman RizkiNo ratings yet
- Antidote Toxic Exposure Indication Dose Lab Monitoring Adverse Rxns CommentsDocument5 pagesAntidote Toxic Exposure Indication Dose Lab Monitoring Adverse Rxns CommentsAjie FloridaNo ratings yet
- (BatMC MedSurg) Palma - NCPDocument4 pages(BatMC MedSurg) Palma - NCPJann Reinna PALMANo ratings yet
- Drug-Study ErgonDocument2 pagesDrug-Study ErgonPaolo UyNo ratings yet
- Bored Lang AqDocument2 pagesBored Lang AqKIANA LOUISE ROMANONo ratings yet
- LOSARTAN (ARBs) Drug Study (GERIATRICS)Document5 pagesLOSARTAN (ARBs) Drug Study (GERIATRICS)CHRISTIE MONTANONo ratings yet
- AutacoidsDocument12 pagesAutacoidsRamiz IsrafNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Drug Reference SheetDocument12 pagesCritical Care Drug Reference SheetYanina CoxNo ratings yet
- NCP AnemiaDocument1 pageNCP AnemiaJennah JozelleNo ratings yet
- Effects: PharmacokineticsDocument7 pagesEffects: PharmacokineticsShiraz SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Pals TachycardiaDocument1 pagePals TachycardiadarlingcarvajalduqueNo ratings yet
- ACLS AritmiaDocument18 pagesACLS AritmiaZega AgustianNo ratings yet
- Anti HistaminesDocument5 pagesAnti HistaminesAnkit PandeyNo ratings yet
- BP Regulation Medications ChartDocument6 pagesBP Regulation Medications ChartsydNo ratings yet
- Stress Eco and Eco ReportDocument4 pagesStress Eco and Eco ReportguptarichaandassociatesNo ratings yet
- 1.inhibit Synergistic EffectDocument8 pages1.inhibit Synergistic EffectSITTIE JOBAISAH TOMINAMAN ALINo ratings yet
- HPN Drug StudyDocument4 pagesHPN Drug StudyJohn Haider Colorado GamolNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument4 pagesDiazepamElyhna Mara U. GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studychinchin ramosNo ratings yet
- Adult Asystole or PeaDocument1 pageAdult Asystole or PeamayNo ratings yet
- 14 1pm EPODocument1 page14 1pm EPOReal TetisoraNo ratings yet
- AclsDocument1 pageAclsJoice DasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 3Document5 pagesDrug Study 3jasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest Algorithm: Give OxygenDocument2 pagesCardiac Arrest Algorithm: Give OxygenJunius SimarmataNo ratings yet
- Adenosine: Scheduling BLS (CPR/First Aid) Acls PalsDocument4 pagesAdenosine: Scheduling BLS (CPR/First Aid) Acls PalsPhilippe Ceasar C. BascoNo ratings yet
- Oxytocin Drug StudyDocument1 pageOxytocin Drug Studysweetpixie1887% (15)
- BP Regulation Medications ChartDocument5 pagesBP Regulation Medications ChartLovely CervantesNo ratings yet
- Management of Normal Labour ChartDocument1 pageManagement of Normal Labour ChartwedishaNo ratings yet
- With A Pulse and Poor Perfusion: Pediatric TachycardiaDocument1 pageWith A Pulse and Poor Perfusion: Pediatric TachycardiaIin-Ignasia Diahayujulindah Mujiman0% (1)
- Electrolyte - Water BalanceDocument5 pagesElectrolyte - Water BalancechrisibinuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For Paracetamol, Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexDocument3 pagesDrug Study For Paracetamol, Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexMichelle Manibale R.N100% (4)
- Wa0000.Document7 pagesWa0000.benitez1228No ratings yet
- Optimizing Clinical Benefit of Anticoagulant in Acute Coronary Syndrome and Venous ThrombosisDocument46 pagesOptimizing Clinical Benefit of Anticoagulant in Acute Coronary Syndrome and Venous ThrombosisCresti Chandra PradeltaNo ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithm Pulse No Yes: Stable Patient Unstable Patient Stable PatientDocument1 pageACLS Algorithm Pulse No Yes: Stable Patient Unstable Patient Stable PatientAhmed AlkhaqaniNo ratings yet
- Pcol 2Document9 pagesPcol 2cyk7xcdsj4No ratings yet
- Surgery PancreasDocument15 pagesSurgery PancreasAnnie HadassahNo ratings yet
- Note 2 Dec 2022Document3 pagesNote 2 Dec 2022Queen ShNo ratings yet
- Figure 4 AlgorithmACLS CACOVID 220101Document1 pageFigure 4 AlgorithmACLS CACOVID 220101AndhikaNo ratings yet
- L8. Central Nervous System (CNS) IDocument11 pagesL8. Central Nervous System (CNS) IsabahNo ratings yet
- L7. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) IIDocument8 pagesL7. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) IIsabahNo ratings yet
- L12. Endocrine System DrugsDocument12 pagesL12. Endocrine System DrugssabahNo ratings yet
- L11. GIT - Respiratory Tract DrugsDocument14 pagesL11. GIT - Respiratory Tract DrugssabahNo ratings yet
- B.pharmacy Time Table June 2010Document7 pagesB.pharmacy Time Table June 2010jntuforumNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0921448819302093 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0921448819302093 MainHenry Daniel Ruiz AlbaNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminlogy Body Planes SectionsDocument75 pagesMedical Terminlogy Body Planes SectionsSTEM-G.04 Kiarrah Katrina BotinNo ratings yet
- Polycythemia PaedsDocument12 pagesPolycythemia PaedscesczatNo ratings yet
- Four Abdominal Quadrants and Nine Abdominal Regions - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesFour Abdominal Quadrants and Nine Abdominal Regions - Anatomy and PhysiologySpoiled BratNo ratings yet
- Sodium Potassium Pump and Action PotentialDocument4 pagesSodium Potassium Pump and Action PotentialPiyush BhallaNo ratings yet
- Questions G 1Document8 pagesQuestions G 1Nader Smadi80% (5)
- Lesson 1 - The Human Body - 1.2. - Anatomical PositionsDocument5 pagesLesson 1 - The Human Body - 1.2. - Anatomical PositionsAlphine DalgoNo ratings yet
- DR Stuart Crisp DR Per Grinsted: Written byDocument8 pagesDR Stuart Crisp DR Per Grinsted: Written byRizky MarethaNo ratings yet
- EXAM BipolarDocument14 pagesEXAM BipolarTiong NeeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Hazard in BiomedicalDocument14 pagesElectrical Hazard in BiomedicalDhurai Onely100% (1)
- Fitness Program GuideDocument24 pagesFitness Program Guideandreea gheorgheNo ratings yet
- Biliary Enteric BypassDocument25 pagesBiliary Enteric BypassAlexandru Ferdohleb100% (1)
- Yatas Bedding Catalogue 1 ComDocument97 pagesYatas Bedding Catalogue 1 ComMirza Ibrar razaNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System: © 2011 The Mcgraw Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument67 pagesThe Muscular System: © 2011 The Mcgraw Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights ReservedJoanna PoshnjaNo ratings yet
- Snake Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesSnake Anatomy and Physiologybrpnaidu2157No ratings yet
- Treatment of Anxiety Disorders: Cherryrich M. Cheng, MD, DSBPPDocument43 pagesTreatment of Anxiety Disorders: Cherryrich M. Cheng, MD, DSBPPDexter FloresNo ratings yet
- Review of Evidence Suggesting That The Fascia Network Could Be The Anatomical Basis For Acupoints and Meridians in The Human BodyDocument7 pagesReview of Evidence Suggesting That The Fascia Network Could Be The Anatomical Basis For Acupoints and Meridians in The Human BodyscribalbNo ratings yet
- Circadian RhythmsDocument2 pagesCircadian RhythmsOmar Saleh100% (1)
- All Gone: A Memoir of My Mother's Dementia With Refreshments by Alex WitchelDocument4 pagesAll Gone: A Memoir of My Mother's Dementia With Refreshments by Alex WitchelSouthern California Public RadioNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and Coordination - Shobhit NirwanDocument14 pagesNeural Control and Coordination - Shobhit NirwanSWASTIKA MALONo ratings yet
- IDC 4U2 - Unit 3 Task 5 - SSDocument4 pagesIDC 4U2 - Unit 3 Task 5 - SSsavannah.e.stonehouseNo ratings yet
- Proteinas RecombinantesDocument16 pagesProteinas Recombinanteskike1790No ratings yet
- Week 2 Learning Objectives - Structure and Function of CarbohydratesDocument2 pagesWeek 2 Learning Objectives - Structure and Function of Carbohydratessteve457No ratings yet
- Anesthesiology PDFDocument40 pagesAnesthesiology PDFBiswajyoti SahuNo ratings yet
- Serology Part1Document18 pagesSerology Part1Alina Mihaela MarianNo ratings yet
- Tamil Nadu Board Class 12 BioBotany Study Material Guide in EnglishDocument55 pagesTamil Nadu Board Class 12 BioBotany Study Material Guide in Englishx a m xNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Riantika Nur Utami 30101407303Document40 pagesCase Presentation: Riantika Nur Utami 30101407303RiantikaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of HemoglobinDocument6 pagesPhysiology of HemoglobinAldi DenandaNo ratings yet