Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 2 Tropical Cyclone
Module 2 Tropical Cyclone
Uploaded by
Santhea AmbrocioOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 2 Tropical Cyclone
Module 2 Tropical Cyclone
Uploaded by
Santhea AmbrocioCopyright:
Available Formats
MODULE 2 : UNDERSTANDING TYPHOONS
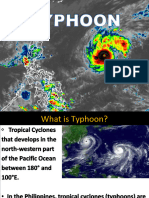
TROPICAL CYCLONE
- Is a system of thunderstorm that move around a center. As the winds intensify or weaken, the category
is upgraded or downgraded accordingly.
Tropical Cyclone Categories
CATEGORY Maximum Wind Speed Kilometers per hour
(kph)
Tropical Depression 64
Tropical Storm 118
Typhoon 200
Super Typhoon Greater than 200
REMEMBER :
The term typhoon is used only in the northwestern part of the Pacific Ocean. The word typhoon was
derived from the Chinese word tai fung which means “great winds”
In the northeastern part of the Pacific Ocean and northern part of the Atlantic Ocean, the equivalent term
is hurricane.
Note :
• In the Philippines, we use the same word “BAGYO” for all categories of tropical cyclones.
• Tropical cyclones have been given name male and female name. These names are from the lists
contributed by all the nations and territories that are members of WMO.
How tropical cyclone develops?
Most tropical cyclones from over vast ocean areas covered by very warm moist air masses. Such areas are found
near the equator where the Northeast trade winds and the Southeast trade winds met, forming the Intertropical
Convergence Zone (ITZC). The temperature of water should be at least 26.5 C.
The twisting forces of the earth’s rotation cause the spinning of the winds of the cyclone, starting from the twirling
of the opposing trade winds around each other.
The spinning wind of the cyclone creates a rotating low-pressure area that pushes air towards the center and hot
moist air to rise and cool off. This cooling of the air causes its moisture to condense, which causes heat to escape. This
heat that is thrown off during condensation further warms the air, which becomes lighter and rises fast. As more moist air
replaces the rising air, more condensation takes place, so air at the center rises faster and faster.
The violence of tropical cyclone is due to the tremendous energy released as condensation occurs continuously.
Three conditions where Tropical Cyclone continue to develop:
a. There must be a continuous supply of rising warm moist air.
b. The air at the center must rise high enough to cool and bring about condensation.
c. The exit of the air above is continuous, thus permitting a continuous flow of warm moist air from below.
These conditions will prevent the spiraling wind to weaken and low pressure area will not dissipate.
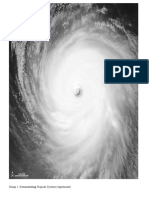
EYE OF THE TYPHOON
- The calm area in the center of tropical cyclone and bordered by the spinning winds.
- It’s like a hole, one distinct feature of typhoon
REMEMBER :
The lowest air pressure is at the eye of tropical cyclone.
COMPARISON BETWEEN THE WIND SPEED WITHIN THE EYE AND AT THE EYEWALL
When the eye of the tropical cyclone passes over certain place, it is the winds at the eyewall that create a lot of
damage. As it approaches, one side of the eyewall brings strong winds flowing in one direction. Then comes the eye with
somewhat calm weather. As it leaves, the other side of the eyewall brings strong winds again, but this time in the opposite
direction.
Effects of tropical cyclone
1. Strong winds that very dangerous.
2. Many people have been hurt or killed by flying objects blown by powerful winds.
3. Can cause a lot of agricultural damage, destroying plants, trees and crops that cost up to hundreds of millions of
pesos.
Definition of Terms :
a. PHILIPPINE AREA OF RESPONSIBILITY ( PAR) – refers to a designated area in the Northwestern Pacific to monitor
tropical cyclone occurrences.
b. Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ ) – is the region where the northern and southern hemisphere trade winds
come together.
c. PHILIPPINE ATMOSPHERIC, GEOPHYSICAL AND ASTRONOMICAL SERVICES ADMINISTRATION ( PAGASA ) – is a
government agency for flood control, astronomical observations, time service and weather forecasting that
predicts weather phenomena and changes caused by atmospheric conditions.
d. Public Storm Warning Signal (PSWS) – helps people prepare for an approaching weather disturbance
e. World Meteorological Organization (WMO) – is a specialized agency of the United Nations, that serves as the
authority on the behavior and state of the atmosphere and its interaction with the oceans and the type of climate
it brings.
PSWS NO. 1 - wind of 30-60kph may be expected in at least 36 hours
PSWS NO. 2 - winds of greater than 60kph up to 100kph ma be expected in at least 24 hours
PSWS NO. 3 -100kph to 185kph in at least 18 hours
PSWS NO. 4 -more than 185kph in at least 12 hours
Csg
You might also like
- Carteret County FAA ReportDocument16 pagesCarteret County FAA ReportWITNNo ratings yet
- 73 SP-JSA-Mandrel Test in Ductbank Inside ManholeDocument7 pages73 SP-JSA-Mandrel Test in Ductbank Inside Manholeabrahmanjazbi100% (2)
- Kharadkar Wada PresentationDocument15 pagesKharadkar Wada Presentation19SA103. Ali100% (2)
- English File: Grammar, Vocabulary, and PronunciationDocument3 pagesEnglish File: Grammar, Vocabulary, and PronunciationБабина Мария100% (1)
- DisreadiDocument2 pagesDisreadiPaul MacasaetNo ratings yet
- TyphoonDocument1 pageTyphoonJean Rose IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Cyclones 170306080858Document47 pagesCyclones 170306080858Arciete Dyr100% (1)
- Week 8 Topic 2 Tropical CyclonesDocument34 pagesWeek 8 Topic 2 Tropical CyclonessugarraysheepNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document15 pagesUnit 4Imran Ul haq (Ammar choudhary)No ratings yet
- Tropical Cyclone 101Document66 pagesTropical Cyclone 101Maricon R. RollanNo ratings yet
- Weather DisturbancesDocument2 pagesWeather DisturbancesEmman Revilla86% (37)
- Hydrometeorological HazardsDocument12 pagesHydrometeorological HazardsMARGARITA MARIANONo ratings yet
- Met o 218 Midterm HatulanDocument12 pagesMet o 218 Midterm HatulanNick HatulanNo ratings yet
- Tropical CycloneDocument17 pagesTropical CycloneclarissejanealegreNo ratings yet
- Typhoon Formation PPT IntroDocument14 pagesTyphoon Formation PPT IntroSkaya 11No ratings yet
- Causes, Impacts & Associated Secondary HazardsDocument32 pagesCauses, Impacts & Associated Secondary HazardsSajid Mahmood FarooqiNo ratings yet
- Understanding The TyphoonsDocument27 pagesUnderstanding The TyphoonsDICES MNK Wesley L. ArconNo ratings yet
- DRRRDocument4 pagesDRRRWinsleth ManguladNo ratings yet
- Tropical CycloneDocument12 pagesTropical CycloneDe GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Hydrometeorological Hazard ReviewerDocument3 pagesHydrometeorological Hazard ReviewerAxl FoxNo ratings yet
- Presentation in Science Quarter 2: Prensent By: Prince Leynard P. PradoDocument5 pagesPresentation in Science Quarter 2: Prensent By: Prince Leynard P. PradoPrince PradoNo ratings yet
- Defination: CyclonesDocument31 pagesDefination: CyclonesprachiNo ratings yet
- Weather DisturbancesDocument5 pagesWeather DisturbancescyriaaNo ratings yet
- Esci344 Lesson02 TC DefinitionsDocument6 pagesEsci344 Lesson02 TC DefinitionsSajjad Husham SalihNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 TyphoonDocument53 pagesLesson 2 TyphoonAlvin TaburadaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Hydrometeorological HazardsDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Hydrometeorological HazardsEthanYTNo ratings yet
- Concept of CycloneDocument9 pagesConcept of CycloneBlessie FernandezNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of Tropical Cyclones - The Dynamics of Disaster, Disease, and DevelopmentDocument118 pagesEpidemiology of Tropical Cyclones - The Dynamics of Disaster, Disease, and Developmentsonewel975No ratings yet
- Cot 2Document36 pagesCot 2MICHELLE SUIZONo ratings yet
- 00.16 Trs and Relevant Storm TerminologiesDocument130 pages00.16 Trs and Relevant Storm TerminologiesuyawakokoNo ratings yet
- Typhoon: Typhoon (Disambiguation) Tropical Cyclone Basins TyphooDocument10 pagesTyphoon: Typhoon (Disambiguation) Tropical Cyclone Basins TyphooVanellope VonschweettzNo ratings yet
- Typhoon: Atmospheric ConditionDocument14 pagesTyphoon: Atmospheric ConditionCleofe SobiacoNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions On Tropical CyclonesDocument53 pagesFrequently Asked Questions On Tropical CyclonesNabarun BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Hydrometeorological Hazards: DRRR ReviewerDocument16 pagesHydrometeorological Hazards: DRRR ReviewerMarcelo BaldonNo ratings yet
- Module 2 4 - Lecture - Understanding TyphoonDocument25 pagesModule 2 4 - Lecture - Understanding Typhoonredox francisco100% (1)
- Understanding The TyphoonsDocument25 pagesUnderstanding The TyphoonsDICES MNK Wesley L. ArconNo ratings yet
- Different Weather DisturbancesDocument20 pagesDifferent Weather DisturbancesArchie AwasNo ratings yet
- Unit IV - Earth and Space FinalDocument107 pagesUnit IV - Earth and Space FinalRonel BuhayNo ratings yet
- Notes DRRR 6.1Document5 pagesNotes DRRR 6.1Noella may de MesaNo ratings yet
- Typhoon g4Document31 pagesTyphoon g4Laiza RemasogNo ratings yet
- Science8 q2 Mod4 Understanding TyphoonsDocument6 pagesScience8 q2 Mod4 Understanding TyphoonsArgyll PaguibitanNo ratings yet
- Science 8-Quarter 2-Lesson 5Document28 pagesScience 8-Quarter 2-Lesson 5Ms. Rhonabelle Llerin PagudNo ratings yet
- Storm: By: Group 2Document35 pagesStorm: By: Group 2Earl Lynus Susada CabasagNo ratings yet
- G8 Science Q2 - Week 4 - TyphoonDocument25 pagesG8 Science Q2 - Week 4 - TyphoonAlvin RudioNo ratings yet
- Understanding Typhoon NotesDocument1 pageUnderstanding Typhoon NotesMARISTELA MACARANASNo ratings yet
- Report in Science 'Finalistststs'Document24 pagesReport in Science 'Finalistststs'queen baguinaonNo ratings yet
- Report in Science 'Finalistststs'Document24 pagesReport in Science 'Finalistststs'queen baguinaonNo ratings yet
- Pingol, Jessica - LAS Q2 W6 Understanding TyphoonsDocument6 pagesPingol, Jessica - LAS Q2 W6 Understanding TyphoonsjhzcartNo ratings yet
- IN Earth Science (Cyclone)Document9 pagesIN Earth Science (Cyclone)Otsenre Cari Otiralab100% (1)
- Typhoon 5Document1 pageTyphoon 5CJay ArnauNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions On Tropical Cyclones and Marine Weather ServicesDocument87 pagesFrequently Asked Questions On Tropical Cyclones and Marine Weather ServicesSANJITAVA BISWASNo ratings yet
- TyphoonDocument2 pagesTyphoonaradillaicielveniaNo ratings yet
- Typhoon: A Severe Weather DisturbanceDocument23 pagesTyphoon: A Severe Weather DisturbanceJonathan Blanca JulitoNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document11 pagesGroup 1Neb Louies Vallescas LaguaNo ratings yet
- Typhoon WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesTyphoon WPS OfficeNoo NameeNo ratings yet
- Typhoon 2022 2023Document46 pagesTyphoon 2022 2023vhdemaala.tshsNo ratings yet
- Meteorology CYCLONES BSCDocument57 pagesMeteorology CYCLONES BSCjaysonNo ratings yet
- Tropical Cyclones - Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesTropical Cyclones - Lecture NotesLeandro Remojo JrNo ratings yet
- TyphoonsDocument46 pagesTyphoonsCirille AgpaoaNo ratings yet
- Yojna Daily Current Affairs Eng Med 24 August 2023Document7 pagesYojna Daily Current Affairs Eng Med 24 August 2023Aman kumar MahatoNo ratings yet
- Disaster Risk ReductionDocument16 pagesDisaster Risk ReductionBeatriz Helaena RasonableNo ratings yet
- What Is Inside A Tropical CycloneDocument16 pagesWhat Is Inside A Tropical CycloneJohn Lariu C. LabininayNo ratings yet
- What Is ClimateDocument12 pagesWhat Is ClimateDannielyn BuayaNo ratings yet
- RRV GeographyDocument48 pagesRRV GeographyPublic IDNo ratings yet
- 7S - Water - Lesson Plan Version 1.1Document4 pages7S - Water - Lesson Plan Version 1.1Pushpa Kumari100% (2)
- Principles of Passive SystemsDocument32 pagesPrinciples of Passive SystemsMuhamad RizkyNo ratings yet
- Depy Conference2015Document23 pagesDepy Conference2015Diego MorenoNo ratings yet
- Fate Hollow Academy Term 1 by LyraDocument375 pagesFate Hollow Academy Term 1 by Lyrads6hn8j4pgNo ratings yet
- Report On Hvac Design of A BuildingDocument66 pagesReport On Hvac Design of A BuildingHemani SinghNo ratings yet
- Toefl 试题: Section One: Listening ComprehensionDocument13 pagesToefl 试题: Section One: Listening Comprehension张雨婷No ratings yet
- In The Sea-Language - Sailing Terms in Britannica's First Edition - BritannicaDocument13 pagesIn The Sea-Language - Sailing Terms in Britannica's First Edition - BritannicaA.G. AshishNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Drishan Saksham Siyaram: Submitted To: Ar. Neeti KhannaDocument14 pagesSubmitted By: Drishan Saksham Siyaram: Submitted To: Ar. Neeti KhannaVidhisha BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Apparent Temperature As A Modelling Substitute ForDocument11 pagesApparent Temperature As A Modelling Substitute ForPrabavathyNo ratings yet
- Penecrete Mortar Data SheetDocument2 pagesPenecrete Mortar Data SheetMajdi ShannibNo ratings yet
- Chapter V: Run Off: Phases of Hydrologic CycleDocument49 pagesChapter V: Run Off: Phases of Hydrologic Cyclejefferson v. sabadoNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Form 4 - With SameecoDocument84 pagesEnglish Grammar Form 4 - With SameecoOmer WarsamehNo ratings yet
- Stand by MeDocument1 pageStand by MeDaniel Esteban Hormazábal LópezNo ratings yet
- General Science1-6Document78 pagesGeneral Science1-6poshannoNo ratings yet
- Đề Luyện Thi Hsg Năm Học 2019 -2020 Môn thi:ANH 8: (Thời gian làm bài 90 phút)Document5 pagesĐề Luyện Thi Hsg Năm Học 2019 -2020 Môn thi:ANH 8: (Thời gian làm bài 90 phút)KinokarinoNo ratings yet
- A1 - Clothing and MaterialsDocument15 pagesA1 - Clothing and Materialsapi-527274757No ratings yet
- Annual Planning 4TH GradeDocument10 pagesAnnual Planning 4TH Grademabel yapuraNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 12 - Temperature of Different Cities Around The WorldDocument1 pageActivity No. 12 - Temperature of Different Cities Around The WorldCristina Aguinaldo100% (1)
- Control Application Diagram For Four Boilers Linear-Temp Installation HW-300 THRU HW-670 DURA-MAX 720 THRU 1810Document1 pageControl Application Diagram For Four Boilers Linear-Temp Installation HW-300 THRU HW-670 DURA-MAX 720 THRU 1810ErmiasNo ratings yet
- HDW UpperInt Grammar 5.1 EditedDocument8 pagesHDW UpperInt Grammar 5.1 EditedNevena BajicNo ratings yet
- Activity 3. Tracking A Tropical Cyclone - MAMURIDocument4 pagesActivity 3. Tracking A Tropical Cyclone - MAMURIEirik Nathan MamuriNo ratings yet
- Group7 ReportDocument10 pagesGroup7 ReportBattagiri Sai JyothiNo ratings yet
- Summer Vacation Home Work: English: Question 1: Write Paragraph On Topics That Are Given BelowDocument5 pagesSummer Vacation Home Work: English: Question 1: Write Paragraph On Topics That Are Given BelowALI RAZANo ratings yet
- G6 Đề Cương Giữa Kỳ Ii 22 23Document3 pagesG6 Đề Cương Giữa Kỳ Ii 22 23Quỳnh Anh HàNo ratings yet