Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Evidence Based Practice
Evidence Based Practice
Uploaded by
Cassey Anne0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesEvidence-based practice aims to integrate the best available research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values to guide health care decisions. It began in the 1980s as evidence-based medicine and has since assumed priority over other sources of evidence in health care. The key aspects of evidence-based practice are asking clinically relevant questions, acquiring evidence from research and other sources, appraising the evidence, and applying the findings. The goals are to provide the most effective care possible and improve outcomes for patients. Common models for evidence-based practice include the John Hopkins Nursing Evidence-Based Practice model and the Iowa model.
Original Description:
Original Title
EVIDENCE BASED PRACTICE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEvidence-based practice aims to integrate the best available research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values to guide health care decisions. It began in the 1980s as evidence-based medicine and has since assumed priority over other sources of evidence in health care. The key aspects of evidence-based practice are asking clinically relevant questions, acquiring evidence from research and other sources, appraising the evidence, and applying the findings. The goals are to provide the most effective care possible and improve outcomes for patients. Common models for evidence-based practice include the John Hopkins Nursing Evidence-Based Practice model and the Iowa model.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesEvidence Based Practice
Evidence Based Practice
Uploaded by
Cassey AnneEvidence-based practice aims to integrate the best available research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values to guide health care decisions. It began in the 1980s as evidence-based medicine and has since assumed priority over other sources of evidence in health care. The key aspects of evidence-based practice are asking clinically relevant questions, acquiring evidence from research and other sources, appraising the evidence, and applying the findings. The goals are to provide the most effective care possible and improve outcomes for patients. Common models for evidence-based practice include the John Hopkins Nursing Evidence-Based Practice model and the Iowa model.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
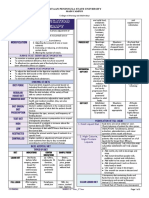
BATAAN PENINSULA STATE UNIVERSITY
MAIN CAMPUS
College of Nursing and Midwifery
APPLY disseminate findings review and local application
EVIDENCE BASED PRACTICE AUDIT/ASSESS
→ During 1980s the term “evidence-based medicine” emerged to
describe the approach that used scientific evidence to SOURCES OF EVIDENCE
determine the best the best practice. Evidence based practice RESEARCH has assumed priority over other sources of
movement started in England in early 1990s. EVIDENCE evidence in the delivery of evidence based
→ Evidence-Based Medicine (Ebm) Or Evidence Based Practice health care
(Ebp), is the judicious use of the best current evidence in FILTERED RESOURES clinical experts and subject specialist pose
making decisions about the care of the individual patient. a question and then synthesize evidence to
→ Evidence-based practice represents both an ideology and a state conclusion based on available
research. These sources are helpful
method. The ideology springs from ethical principle that the
because the literature has been searched
client deserve to be provided with most effective interventions
and results evaluated to provide an answer
possible. The Method Of Ebp is the way we go about finding to clinical question.
and then implementing those interventions.
UNFILTERED it provides most recent information. E.g.
DEFINITION RESOURCES medline, cinhal etc. provides primary and
it is something that furnishes proof or (PRIMARY secondary literature for medicine.
EVIDENCE testimony or something legally submitted
LITERATURE)
to ascertain in the truth of matter.
CLINICAL knowledge through professional practice
it is systemic inter connecting of
EXPERIENCES and life experiences makes up the second
scientifically generated evidence with the
part in the evidenced based, person-
tacit knowledge of the expert practitioner
EVIDENCE BASED centered care.
to achieve a change in a particular
PRACTICE KNOWLEDGE FROM evidence delivered from patients
practice for the benefit of a well-defined
PATIENT knowledge of themselves, their bodies and
client/ patient group (French 1999)
social lives
it is a process by which nurses make
KNOWLEDGE FROM → Audit and performance data
EVIDENCE BASED clinical decisions using the best available
LOCAL CONTEXT → Patients stories and narratives
research evidence, their clinical expertise
NURSING → Knowledge about the culture of the
and patient preferences (mulhall, 1998)
organization and individuals with in it
the conscientious, explicit and judicious
→ social and professional networks
EVIDENCE BASED use of current best evidence in making
→ Information from feedback
decision about the care of individual
MEDICINE/PRACTICE → Local and national policy
patient. (dr. david sackett, Rosenberg,
1996) HIERARCHY OF EVIDENCE
is a way of providing nursing care that is
guided by the integration of the best
available scientific knowledge with
nursing expertise. This approach requires
EBP IN NURSING nurses to critically assess relevant
scientific data or research evidence and
to implement high quality interventions for
their nursing practice. (NLM pubmed)
NEED FOR EBP
→ For making sure that each client get the best possible
services.
→ Update knowledge and is essential for lifelong learning
→ Provide clinical judgment
→ Improvement care provided and save lives
GOAL OF EBP
→ Provide practicing nurses the evidence based data to deliver MODELS OF EBP
effective care. JOHN-HOPKINS used as a framework to guide the
→ Resolve problem in clinical setting. synthesis and translation of evidence
NURSING EBP
→ Achieve excellence in care delivery. into practice.
MODEL
→ Reduces the variations in nursing care and assist with efficient
and effective decision making There are three phases to the jhnebp model
STEP IN EBP 1. The identification of an answerable question.
ASK frame focused questions to be answered by the
evidence review 2. A systematic review of the synthesis of both research and
ACQUIRE identify sources and collect potentially relevant non-research evidence
studies
create an evidence base by applying screening 3. Translation includes implementation of the practice change
APPRAISE
criteria related to topic, questions, practices, and as a pilot study, measurement of outcomes, and
outcomes
standardize, summarize and rate strength of body dissemination of findings.
ANALYZE
of evidence (study, characteristic, quality, effect
size, and consistency)
CSSYNNSRJ NUTRI LAB 2ND YEAR-1ST SEMESTER Page 1 of 2
BATAAN PENINSULA STATE UNIVERSITY
MAIN CAMPUS
College of Nursing and Midwifery
The Stetler model of evidence-based practice consists of five
phases (Stetler, 1994; Stetler, 2001; Stetler, 2010).
Each phase is designed to:
1. facilitate critical thinking about the practical application of
research findings;
2. result in the use of evidence in the context of daily practice; and
3. mitigate some of the human errors made in decision making.
focuses in organization and collaboration
IOWA MODEL incorporating conduct and uses of research,
along with other types of evidence. (titler et al,
2001). It was originated in 1994
The star point in the model can either be
1. A knowledge focus trigger (the emerges from awareness of
innovative research findings)
2. A problem- focus trigger (that has its root in a clinical
organizational problem) BARRIERS IN EBP
→ Lack of value for research in practice
→ Difficulty in bringing change
→ Lack of administrative support
→ Lack of knowledge mentors
→ Lack of time for research
→ Lack of knowledge about research
→ Research reports not easily available
→ Complexity of research reports
→ Lack of knowledge about ebp
ADVANTAGES OF EBP
→ Provide better information to practitioner
→ Enable consistency of care
→ Better patient outcome
→ Provide client focused care
→ Structured process
→ Increases confidence in decision-making
→ Generalize information
→ Contribute to science of nursing
→ Provide guidelines for further research
→ Helps nurses to provide high quality patient care
This model examines how to use evidence to DISADVANTAGES OF EBP
create formal change within organizations, as → Not enough evidence for ebp
STETLER MODEL well how individual practitioners can use → Time consuming
research on an informal basis as part of → Reduce client choice
critical thinking and reflective practice. → Reduced professional judgment/ autonomy
→ Suppress creativity
The settler model of evidence-based practice based on the → Influence legal proceedings
following: → Publication bias
CONCLUSION
1. Use may be instrumental, conceptual and/or
Evidence-based nursing care is a lifelong approach to clinical
symbolic/strategic.
decision making and excellence in practice. Evidence-based
2. Other types of evidence and/or non-research-related
nursing care is informed by research findings, clinical expertise,
information are likely to be combined with research findings to
and patient’s values and its use can improve patients outcome.
facilitate decision making or problem solving.
Use of research evidence in clinical practice is an expected
3. Internal or external factors can influence an individual's or
standard of practice for nurses and health care organizations, but
group's review and use of evidence.
numerous barriers exist that create a gap between new
4. Research and evaluation provide probabilistic information, not
knowledge and implementation of that knowledge to improve
absolutes.
patient care. Using the levels of evidence, nurses can determine
5. Lack of knowledge and skills pertaining to research use and
the strength of research studies, assess the findings, and evaluate
evidence-informed practice can inhibit appropriate and effective
the evidence for potential implementation into best practice.
use.
CSSYNNSRJ NUTRI LAB 2ND YEAR-1ST SEMESTER Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Evidence Based Practice in Nursing Healthcare A Guide To Best Practice 3rd Edition Ebook PDFDocument62 pagesEvidence Based Practice in Nursing Healthcare A Guide To Best Practice 3rd Edition Ebook PDFwilliam.tavares69198% (55)
- Evidence Based PracticeDocument18 pagesEvidence Based Practicemeghana100% (11)
- NMND 5103 Assignment 2Document49 pagesNMND 5103 Assignment 2Sithara JayatungaNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based PracticeDocument14 pagesEvidence Based PracticeKrini Tandel100% (2)
- 3 NCM119A Evidence Based Practice Sept. 3 2021Document5 pages3 NCM119A Evidence Based Practice Sept. 3 2021Ghianx Carlox PioquintoxNo ratings yet
- Jurnal EBP EmccDocument13 pagesJurnal EBP Emccrobert kelvin tudaiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nursing Research and EvidenceDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Nursing Research and Evidencestephaniecaronan15No ratings yet
- SJNHC 55 105-106 ewJDdEJDocument2 pagesSJNHC 55 105-106 ewJDdEJhassan mahmoodNo ratings yet
- Tugas Summary Artikel 2-DikonversiDocument10 pagesTugas Summary Artikel 2-DikonversiAyu WulansariNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Practice in Nursing ResearchDocument3 pagesEvidence Based Practice in Nursing ResearchLorenz Jude CańeteNo ratings yet
- Ebnp by DR Nandini MDocument75 pagesEbnp by DR Nandini MnandiniNo ratings yet
- A Review of Evidence-Based Practice, Nursing Research and Reflection: Levelling The HierarchyDocument10 pagesA Review of Evidence-Based Practice, Nursing Research and Reflection: Levelling The HierarchyLic. Enf. Irma Ithzury OrduñaNo ratings yet
- Choosing The Best Evidence To Guide Clinical Practice Application of AACN Levels of EvidenceDocument12 pagesChoosing The Best Evidence To Guide Clinical Practice Application of AACN Levels of EvidenceVernie Villarosa TuasonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nursing Research and Importance of The Course in NursingDocument1 pageIntroduction To Nursing Research and Importance of The Course in NursingAdiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- Artikel 1 Tugas Metopen Literatur ReviewDocument11 pagesArtikel 1 Tugas Metopen Literatur ReviewanindyaNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based Practice in Perioperative Nursing - Barriers and Facilitators To ComplianceDocument6 pagesEvidence-Based Practice in Perioperative Nursing - Barriers and Facilitators To ComplianceBong Yi LinNo ratings yet
- Definition of Evidence-Based PracticeDocument3 pagesDefinition of Evidence-Based Practiceaadomedia1No ratings yet
- Introductin To ResearchDocument7 pagesIntroductin To ResearchhalayehiahNo ratings yet
- Medsurg Lecture Evidence-Based Practice: Evidence Can Be A Policy or A Standard Used by A Certain PopulationDocument5 pagesMedsurg Lecture Evidence-Based Practice: Evidence Can Be A Policy or A Standard Used by A Certain PopulationDada Tin GoTanNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Nursing in Clinical PractDocument5 pagesEvidence Based Nursing in Clinical PractVivi DisNo ratings yet
- Vpe 006Document4 pagesVpe 006Jailouise PerezNo ratings yet
- Handout EbpDocument1 pageHandout EbpjatheeshNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Nursing ResearchDocument101 pagesUnit 1: Nursing ResearchHardeep Kaur100% (1)
- Evidence Based Report Mam KathDocument3 pagesEvidence Based Report Mam KathLorenz Jude CańeteNo ratings yet
- DR Hadeel Tayeb: Insert Your ImageDocument42 pagesDR Hadeel Tayeb: Insert Your ImageWani GhootenNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based NursingDocument2 pagesEvidence Based NursingMiina EkkaNo ratings yet
- Clase1 - 2009 - Melnyk - Ebp and InquiryDocument4 pagesClase1 - 2009 - Melnyk - Ebp and InquiryHelga Francesconi BütikoferNo ratings yet
- What Is "Evidence-Based" Strength and Conditioning?Document7 pagesWhat Is "Evidence-Based" Strength and Conditioning?ok okNo ratings yet
- Ten Essential Papers For The Practice of Evidencebased MedicineDocument4 pagesTen Essential Papers For The Practice of Evidencebased MedicineAndrieli TodescatoNo ratings yet
- Aus Occup Therapy J - 2001 - Bennett - The Process of Evidenceâ - Based Practice in Occupational Therapy Informing ClinicalDocument10 pagesAus Occup Therapy J - 2001 - Bennett - The Process of Evidenceâ - Based Practice in Occupational Therapy Informing ClinicalFelipe Gonzalez AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Medicine:: The Know What, How and Where!Document68 pagesEvidence Based Medicine:: The Know What, How and Where!Dima MasadehNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based PracticeDocument11 pagesEvidence Based Practicedana-samer100% (2)
- h7d) KCD, 5bc$9zm-5Document29 pagesh7d) KCD, 5bc$9zm-5Kristel AnneNo ratings yet
- Konsep EBNPDocument16 pagesKonsep EBNPMoch Ridwan Pujiar PamungkasNo ratings yet
- 2 Building An Evidenced-Based Nursing PracticeDocument24 pages2 Building An Evidenced-Based Nursing Practicefordsantiago01No ratings yet
- NCM 114 Core Elements of Evidenced Based Gerontological Practice and Violence and Elder Mistreatment Mrs. OrprezaDocument5 pagesNCM 114 Core Elements of Evidenced Based Gerontological Practice and Violence and Elder Mistreatment Mrs. OrprezaRoyce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Decision MakingDocument78 pagesEvidence Based Decision MakingSaherish FarhanNo ratings yet
- Research Notes 2: (Deliberately Planned)Document4 pagesResearch Notes 2: (Deliberately Planned)Myangel Loise100% (1)
- Evidencebasedpractice 190912083548Document33 pagesEvidencebasedpractice 190912083548Tamanna Verma100% (1)
- Evaluating The Use of Casuistry During Moral Case Deliber - 2024 - Social SciencDocument9 pagesEvaluating The Use of Casuistry During Moral Case Deliber - 2024 - Social SciencMateoNo ratings yet
- McCurtin - 2012 - Evidence Based Practice in Speech Language TherapyDocument16 pagesMcCurtin - 2012 - Evidence Based Practice in Speech Language TherapymaximilianogaeteNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Practices: CORE ConceptsDocument154 pagesEvidence Based Practices: CORE ConceptsJasthen Audrey StamboughNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based NSG Pratice Shilpi Maam FinalDocument5 pagesEvidence Based NSG Pratice Shilpi Maam FinalNisha FatmaNo ratings yet
- Prática Baseada em Evidências em ForçaDocument5 pagesPrática Baseada em Evidências em ForçaRenata SouzaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Clinical Nursing - 2020 - Halberg - Understandings of and Experiences With Evidence Based Practice in PracticeDocument11 pagesJournal of Clinical Nursing - 2020 - Halberg - Understandings of and Experiences With Evidence Based Practice in Practicexisici5890No ratings yet
- Evidence Based PracticeDocument18 pagesEvidence Based PracticeAmanda Scarlet100% (2)
- Ebp FTDocument64 pagesEbp FTAfifah NurNo ratings yet
- NCMB 315 - Research ReviewerDocument17 pagesNCMB 315 - Research ReviewerMARIA STEPHANY DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Generating Evidence For Clinical Nursing Practice PDFDocument39 pagesGenerating Evidence For Clinical Nursing Practice PDFTamanna VermaNo ratings yet
- EVIDENCE BASED PRACTICE Tools and TechniDocument16 pagesEVIDENCE BASED PRACTICE Tools and Technihassan mahmoodNo ratings yet
- Pone 0256600Document12 pagesPone 0256600wispa handayaniNo ratings yet
- NCM 111Document6 pagesNCM 111Erika Mae Sta. MariaNo ratings yet
- Analisa Jurnal Kelompok 9 (The History of Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing Education and Practice)Document9 pagesAnalisa Jurnal Kelompok 9 (The History of Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing Education and Practice)Viola AlvionitaNo ratings yet
- NCMB 311 LecDocument4 pagesNCMB 311 LecGian Carlo BenitoNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Dentistry: An Overview: Dr. R MadhumalaDocument3 pagesEvidence Based Dentistry: An Overview: Dr. R MadhumalaSitta Dea ViastiyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Evidence-Based Practice: Learning ObjectivesDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Evidence-Based Practice: Learning ObjectivesNicolas VallesNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Dentistry - A Review: January 2014Document5 pagesEvidence Based Dentistry - A Review: January 2014Sitta Dea ViastiyaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Practice and Leadership in Radiology NursingFrom EverandAdvanced Practice and Leadership in Radiology NursingKathleen A. GrossNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based Nursing Care for Stroke and Neurovascular ConditionsFrom EverandEvidence-Based Nursing Care for Stroke and Neurovascular ConditionsSheila A. AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Evidence-based Decisions and Economics: Health Care, Social Welfare, Education and Criminal JusticeFrom EverandEvidence-based Decisions and Economics: Health Care, Social Welfare, Education and Criminal JusticeIan ShemiltNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Across LifespanDocument4 pagesNutrition Across LifespanCassey AnneNo ratings yet
- Nutri Lab-Diet Modification & Diet TherapyDocument5 pagesNutri Lab-Diet Modification & Diet TherapyCassey AnneNo ratings yet
- Nutri Lab - Filipino Food Culture and TraditionsDocument3 pagesNutri Lab - Filipino Food Culture and TraditionsCassey AnneNo ratings yet
- Computation in NutritionDocument2 pagesComputation in NutritionCassey AnneNo ratings yet
- Doh - Mental Health Gap Action ProgramDocument4 pagesDoh - Mental Health Gap Action ProgramCassey AnneNo ratings yet
- CHN1 LEC-non Communicable DiseasesDocument4 pagesCHN1 LEC-non Communicable DiseasesCassey AnneNo ratings yet
- CHN1 LEC - DOH Nutritional ProgramDocument3 pagesCHN1 LEC - DOH Nutritional ProgramCassey Anne100% (1)
- Philippine Family Planning ProgramDocument6 pagesPhilippine Family Planning ProgramCassey AnneNo ratings yet
- CHN 1 - Health Care Delivery System 3Document3 pagesCHN 1 - Health Care Delivery System 3Cassey AnneNo ratings yet
- CHN1 Lec-Health Care Delivery SystemDocument2 pagesCHN1 Lec-Health Care Delivery SystemCassey AnneNo ratings yet
- CHN 2Document3 pagesCHN 2Cassey AnneNo ratings yet
- CHN 1 Lec - Health Care Delivery System 2Document3 pagesCHN 1 Lec - Health Care Delivery System 2Cassey AnneNo ratings yet
- Effective Methodology For Security RiskDocument7 pagesEffective Methodology For Security RiskEsa FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of MusicDocument57 pagesPhilosophy of MusicSilvestreBoulez100% (2)
- EARTH SCIENCE. Lesson 1 - Universe & Solar SystemDocument65 pagesEARTH SCIENCE. Lesson 1 - Universe & Solar SystemJeydibi MharjomNo ratings yet
- The Vibrant Nature of The CosmosDocument91 pagesThe Vibrant Nature of The CosmosDr. Peter Fritz Walter100% (3)
- Analysing Competitive IntelligenceDocument9 pagesAnalysing Competitive IntelligenceAnonymous fZqz9Z2No ratings yet
- InterferometryDocument5 pagesInterferometryasdg asdgNo ratings yet
- Physical Science DLL q2 (Week 2)Document2 pagesPhysical Science DLL q2 (Week 2)Esmale RyaNo ratings yet
- 1BauconItaly (Aldrovandi & Leonardo)Document16 pages1BauconItaly (Aldrovandi & Leonardo)Muerto DmNo ratings yet
- Velocity Lab-Danika StreckoDocument5 pagesVelocity Lab-Danika Streckoapi-292000448No ratings yet
- DISSDocument4 pagesDISSAngeli Benan Degan100% (2)
- Death, Hope, and Sex LifeHistory Theory and The Development of ReproductiveDocument25 pagesDeath, Hope, and Sex LifeHistory Theory and The Development of ReproductiveRoberta LimaNo ratings yet
- RationalismDocument5 pagesRationalismankit boxerNo ratings yet
- UCPSDocument27 pagesUCPSMikhaellaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document32 pagesLecture 1Shruti DhariyaNo ratings yet
- Report WritingDocument3 pagesReport WritingRabea ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Zombies On The Web - David ChalmersDocument10 pagesZombies On The Web - David Chalmersbengisu çatalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 STSDocument3 pagesUnit 1 STSHannah Alvarado BandolaNo ratings yet
- Psikoedukasi Strategi Coping Stres Pada Mahasiswa Yang Bekerja Di Universitas Negeri MalangDocument11 pagesPsikoedukasi Strategi Coping Stres Pada Mahasiswa Yang Bekerja Di Universitas Negeri MalangneufcatsNo ratings yet
- Forces Motion Phet SimulationDocument4 pagesForces Motion Phet Simulationapi-542317996No ratings yet
- Strand & Funtowicz Springer2017Document14 pagesStrand & Funtowicz Springer2017Roger StrandNo ratings yet
- Kuhn 1970Document14 pagesKuhn 1970sulley119No ratings yet
- Experiment - Newton's CradleDocument3 pagesExperiment - Newton's CradleSNEHAL 8118-11No ratings yet
- Management Principle and Application Unit 1 IntroDocument54 pagesManagement Principle and Application Unit 1 IntroAiwiwNo ratings yet
- International Journal On Bioinformatics & Biosciences (IJBB)Document1 pageInternational Journal On Bioinformatics & Biosciences (IJBB)Anonymous pKuPK3zUNo ratings yet
- IberianjournalofclinicalforensicneurosciencevolDocument111 pagesIberianjournalofclinicalforensicneurosciencevolDaniel MartinsNo ratings yet
- Weekly Learning Plan: Describe The Components of A Scientific Investigation (S7MT-Ia-1)Document5 pagesWeekly Learning Plan: Describe The Components of A Scientific Investigation (S7MT-Ia-1)Leslie QuingcoNo ratings yet
- Churchland - The Rediscovery of LightDocument19 pagesChurchland - The Rediscovery of LightMaríaMaríaNo ratings yet
- The Social and Value Dimensions of TechnologyDocument34 pagesThe Social and Value Dimensions of TechnologyJennifer ZaraNo ratings yet
- Painting On Stones Purs 2020Document27 pagesPainting On Stones Purs 2020Ivo PursNo ratings yet
- Historical Research: Unit IIIDocument18 pagesHistorical Research: Unit IIIDr. Nisanth.P.MNo ratings yet