Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Uploaded by
Rao GootleyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Uploaded by
Rao GootleyCopyright:
Available Formats
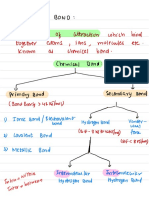
TYPES OF BONDS KOSSEL LEWIS APPROCH VALENCE BOND THEORY ( VBT)
THEORIES OF CO-VALENT BOND
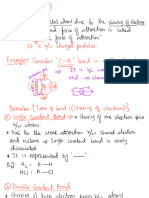
A covalent bond is formed by the overlapping of
CO-ORDINATE BONDING H H
two half filled atomic orbitals.
IONIC/ELECTROVALENT HYDROGEN BOND COVALENT Atoms can combine either by
BOND BOND . Bond formed by one sided transfer of e- or by sharing
. Bond formed when the -ve C : : C
sharing of electrons. of valence e- in order to have
end of one molecule . Bond formed by mutual ie: one atom donates a an Complete octet in their H H
. Strong electro static attracts the +ve end of sharing of e-. . Pair of e- while other valence shell. Type of overLapping
force of attraction H. . Low M.P. and B.P. accepts it.
between positive and 1. Intermolecular: H– Bonding . Bad conductor of . Bad conductors of
negative ions. occur within one single electricityv electricity.
molecule. Octet Rule
. Crystalline in nature . Insoluble in Polar Solvents . Sparingly soluble in polar
. High M.P and B.P 2. Intermolecular: H Bonding but soluble in non-polar solvents but readily soluble
. Soluble in Polar Solvents. between two different solvent. in non-polar solvents.
Eg: NaCl, MgCl2 etc. molecules of same or Ex: CH4, H2, Cl2.
LEWIS SYMBOLS Sigma(σ) Pi(π)
eg:- NH+4
different compounds. Valence e- are represented by Sidewise overlapping Sidewise overlapping
dots around the element.
: :
: :
H; Na; : Cl ; O , : N : . s-s overlapping
TYPE OF CO-VALENT
BOND + +
. Polar covalent bond
Eg: NH3, CHCl3 s s s-s overlap
. Non-polar covalent bond
Eg: Cl2, CO2. . s-p overlapping p p p-p overlap
+
CHEMICAL BONDING
FAJAN'S RULE AND s s s-p overlap
s+
MOLECULAR STRUCTURE HYBRIDISATION
No compounds is 100% ionic or 100% Concept of mixing
s-
covalent + atomic orbital to
. Covalent nature ∝ Charge on cation + form new hybrid
. Covalent nature ∝ 1 + p-p overlap
size of cation VSEPR THEORY p p
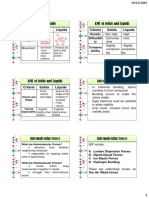
• Polarising Power ∝ Covalent C Cation Polarized anion The shape of a molecule depends upon the numbers of valence shell
e- (B.P or l.p) surrounding in the central atom.
Polarization of anion by cation
Decreasing order of repulsive interaction: lp - lp > lp - bp > bp - bp
B
FC = V − N − Type of No. of No. of Arrangement
2
BOND . Bond length: Molecule Bonding pair Lone Pair of e- pair
Shape Example
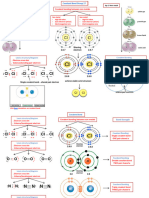
Formation of Molecular Orbitals
MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY
FORMAL distance between . MOT states that each atom tends to combine
PARAMETERS CHARGE the nuclei of two
bonded atom
AB2E 22 11 Bent SO2O3 together and form molecular orbitals
Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals No. of
boNd length ∝ 1 nodal plane . No. of molecular orbitals = no. of atomic orbital
bond order AB3E 33 11 Trigonal + combined.
Pyramidal NH3 0
No. of Bond σ
BOND ORDER between the two
atoms AB3E2 22 22 MOT
& H2O +
Bent 1
σ∗
Angle between the
BOND ANGLE orbitals containing Bonding molecular Anti bonding atomic
bonding e- pair around orbitals orbitals
AB4E 44 11 +
central atom. See saw 1
SF4
π
BOND Amount of enrgy px px
ENTHALPY required to break
one mole of bonds. AB3E2
ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATION
33 22
T-Shape ClF5 -
2
Electron filling order upto 14 electrons
∗
σ1s < σ1s < σ2s < σ∗2s < π2p ≡ π2p < σ2p < π∗2p ≡ π∗2p < σ∗2p
px px π∗ x y z x y z
Product of the magnitude
of the charge and AB5E 55 11 Square XeF5 Electron filling order for more than 14 electrons
distance between Pyramid +
DIPOLE centres of positive and pz pz π
2
∗
MOMENT negative charge. σ1s < σ1s < σ2s < σ∗2s < σ2p < π2p ≡ π2p < π∗2p ≡ π∗2p
z x y x y
AB4E2 44 22 square XeF4 - 3
µ = charge × Distance Planner pz pz π∗
Between two atoms
anand_mani16 DR. Anand Mani https://www.anandmani.com/ https://discord.io/anandmani t.me/anandmani001
You might also like
- Kerboodle StuffDocument4 pagesKerboodle StuffRoshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Organic Chemistry Klein 3rd EditionDocument2 pagesChapter 2 Organic Chemistry Klein 3rd EditionJim Xie100% (1)
- Teraoka Article enDocument5 pagesTeraoka Article enCefeskyNo ratings yet
- 04 Chemical Bonding Formula SheetsDocument9 pages04 Chemical Bonding Formula SheetsRushil PahwaNo ratings yet
- Polar Covalent BondsDocument10 pagesPolar Covalent BondsParas ThakurNo ratings yet
- 2.ferrocene Mo DiagramDocument56 pages2.ferrocene Mo DiagramRuchika SoodNo ratings yet
- Transition Metals and Coordination ChemistryDocument80 pagesTransition Metals and Coordination ChemistryVincent Choo100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Lecture Notes - 0Document44 pagesChapter 2 Lecture Notes - 0KirilKocevskiNo ratings yet
- 5 半導體與光電材料 1112 2021Document131 pages5 半導體與光電材料 1112 2021谭晨晞No ratings yet
- Density of States - Derivation PDFDocument5 pagesDensity of States - Derivation PDFsarathsrnairNo ratings yet
- Formal Charge WorksheetDocument3 pagesFormal Charge WorksheethbjvghcgNo ratings yet
- Steady State Approximation: Supplementary Notes For The Course "Chemistry For Physicists"Document5 pagesSteady State Approximation: Supplementary Notes For The Course "Chemistry For Physicists"Rishav DugarNo ratings yet
- Padhle 10th - Periodic Classification of Elements + Integrated PYQsDocument40 pagesPadhle 10th - Periodic Classification of Elements + Integrated PYQsDhruv SariaNo ratings yet
- Padhle 10th - Excretion (Life Processes) Notes + Integrated PYQsDocument27 pagesPadhle 10th - Excretion (Life Processes) Notes + Integrated PYQsMadhu UrsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Test ReviewDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding Test ReviewAlakh Jagtap100% (1)
- Grade 10 Physical Science - Electric CircuitsDocument17 pagesGrade 10 Physical Science - Electric Circuitskanimoletsane3No ratings yet
- Structure and BondingDocument12 pagesStructure and BondingNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Atom and Its Structure Class 11 Notes NEET Chemistry (PDF)Document11 pagesAtom and Its Structure Class 11 Notes NEET Chemistry (PDF)Ankit KumarNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Class - 11 Physics Chapter 13 - Kinetic TheoryDocument23 pagesRevision Notes Class - 11 Physics Chapter 13 - Kinetic TheoryAngel KuttyNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Notes On States of MatterDocument8 pagesComprehensive Notes On States of Matterma100% (1)
- Isolobal AnalogyDocument4 pagesIsolobal Analogyindu priyaNo ratings yet
- A2 CHM Sol 05 Acid and Base WSDocument28 pagesA2 CHM Sol 05 Acid and Base WSnsNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction To Molecular Orbital Theory oDocument4 pagesA Brief Introduction To Molecular Orbital Theory oBheim LlonaNo ratings yet
- Resonance Structure WorksheetDocument3 pagesResonance Structure WorksheethbjvghcgNo ratings yet
- 3 Fajan's RuleDocument13 pages3 Fajan's RuleNazmi LatifNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: Crystal SymmetryDocument47 pagesLecture 2: Crystal SymmetryZul FadliNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument1 pageChemical Bonding and Molecular Structuresarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 AssessmentDocument19 pagesChapter 8 AssessmentLeinNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Ib Chemistry On VseprDocument14 pagesDokumen - Tips Ib Chemistry On VseprIwona Agata GórnickaNo ratings yet
- CH Ers .Co .In Tea CH Ers .Co .In Tea CH Ers .Co .In Tea CH Ers .Co .InDocument3 pagesCH Ers .Co .In Tea CH Ers .Co .In Tea CH Ers .Co .In Tea CH Ers .Co .InMangesh WajeNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument20 pagesChemistryFatma SharifNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding One Day One Chapter Nitesh DevnaniDocument41 pagesChemical Bonding One Day One Chapter Nitesh Devnanivrinda11xxNo ratings yet
- Chemistry. Chemical BondingDocument31 pagesChemistry. Chemical BondingBatrisyia RozhanNo ratings yet
- C Chemical BondingDocument33 pagesC Chemical BondingMohitNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Vsepr: Standard Geometries (Part 1)Document12 pagesChemical Bonding: Vsepr: Standard Geometries (Part 1)Durgesh SINGHNo ratings yet
- @bohring - Bot 01. Chemical Bonding Syn (1-32)Document32 pages@bohring - Bot 01. Chemical Bonding Syn (1-32)PranavNo ratings yet
- General Organic ChemistryDocument3 pagesGeneral Organic ChemistrySamir DahalNo ratings yet
- 02 BondingDocument24 pages02 Bondingiron_trNo ratings yet
- Together: I of BindDocument15 pagesTogether: I of BindShreyas PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Bio 101Document157 pagesBio 101basharrebhi29No ratings yet
- Covalent BondingDocument26 pagesCovalent BondingNubar MammadovaNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding As AlphaDocument35 pagesCovalent Bonding As Alphahasnaindurrani45No ratings yet
- Forces of Attraction Notes and Practice QuestionsDocument10 pagesForces of Attraction Notes and Practice QuestionsDianna WattNo ratings yet
- KMT of Solids and Liquids KMT of Solids and LiquidsDocument6 pagesKMT of Solids and Liquids KMT of Solids and LiquidsBea Dacillo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 2Document13 pagesChemistry Chapter 2Symonette OcturaNo ratings yet
- 5 Alkenes Iedxcel779Document7 pages5 Alkenes Iedxcel779Best ProgressNo ratings yet
- 02.2 Chapter 2 - Polar Covalent Bonds Acids and BasesDocument12 pages02.2 Chapter 2 - Polar Covalent Bonds Acids and BaseselaineustNo ratings yet
- IB BondingDocument12 pagesIB BondingLetso JamesNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Chapter # 04Document2 pagesChemical Bonding: Chapter # 04AimanNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument27 pagesBiochemistryAasefa Shaikh100% (1)
- Aromatic CompoundsDocument18 pagesAromatic Compoundscoding727treeNo ratings yet
- Imaginary: AcquiringDocument20 pagesImaginary: AcquiringCat123No ratings yet
- CHM 171 Theme 3 Bonding and Molecular GeometryDocument91 pagesCHM 171 Theme 3 Bonding and Molecular Geometrycatman123123No ratings yet
- Adv Chem Compiled PDFDocument24 pagesAdv Chem Compiled PDFRaiza SarteNo ratings yet
- Molecular Orbitals and Hybridisation: Organic ChemistryDocument28 pagesMolecular Orbitals and Hybridisation: Organic ChemistryWinni TanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry BasicsDocument22 pagesBiochemistry Basicsjazlamba09No ratings yet
- 2 2 2 Bonding and StructureDocument7 pages2 2 2 Bonding and StructureAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- General Inorganic ChemistryDocument28 pagesGeneral Inorganic ChemistryGIDEON TEMIDAYO JUDENo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds Acids and BasesDocument13 pagesChapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds Acids and Bases黃向廷No ratings yet
- Mathematics 1st TermDocument4 pagesMathematics 1st TermRao GootleyNo ratings yet
- Important Scientists NameDocument10 pagesImportant Scientists NameRao GootleyNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 2022Document138 pagesPhysics Paper 2022Rao GootleyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 01Document151 pagesChemical Bonding 01Rao GootleyNo ratings yet
- Project WorkDocument2 pagesProject WorkRao GootleyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 1Document137 pagesChemical Bonding 1Rao GootleyNo ratings yet
- CH12 - GOC - Shobhit NirwanDocument61 pagesCH12 - GOC - Shobhit NirwanRao GootleyNo ratings yet
- Number System NotesDocument6 pagesNumber System NotesRao GootleyNo ratings yet
- Xi Iit Chemistry-Chemical Bonding (Bond Parameters & Dipolemoment) CW - 6 Bond Length and Bond Angle ComparisionDocument8 pagesXi Iit Chemistry-Chemical Bonding (Bond Parameters & Dipolemoment) CW - 6 Bond Length and Bond Angle ComparisionVVK XI B SIVABALAKUMARAN SNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry: HintsDocument258 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry: HintsSwayam PagareNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes & Haloarenes (QP)Document2 pagesHaloalkanes & Haloarenes (QP)riorocksNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Units and MeasurementsDocument12 pagesChapter 7. Units and Measurementsnguyen anNo ratings yet
- Identifying Effects! Directions:: Learning Task 2Document4 pagesIdentifying Effects! Directions:: Learning Task 2Aeveil PalejaroNo ratings yet
- Bond Fission, Types of Reagents-TtDocument23 pagesBond Fission, Types of Reagents-TtdhanushNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry (Second Edition)Document6 pagesEncyclopedia of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry (Second Edition)Sabela González GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Richard Johnston - Evolution - Fact or Fable (2002)Document94 pagesRichard Johnston - Evolution - Fact or Fable (2002)hfjsdhfNo ratings yet
- NCHE 221-Lewis StructuresDocument17 pagesNCHE 221-Lewis StructuresNOMKHULEKO ALICENo ratings yet
- November 2020 MS - Paper 2 OCR (B) Physics A-LevelDocument17 pagesNovember 2020 MS - Paper 2 OCR (B) Physics A-LevelTendai MatomaNo ratings yet
- Mpharm 1 Sem Modern Pharmaceutical Analytical Techniques Mpa101t 2020Document1 pageMpharm 1 Sem Modern Pharmaceutical Analytical Techniques Mpa101t 2020anujsharma02011999No ratings yet
- Questions - For - NOVA - Elegant - Universe (Part 2)Document3 pagesQuestions - For - NOVA - Elegant - Universe (Part 2)Michael J HulsteinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Electrophilic Additions To AlkenesDocument30 pagesChapter 10 - Electrophilic Additions To AlkenesBianca-Rebeca PetreNo ratings yet
- Rayleigh Scattering Cross Section Redward of Lyα by Atomic HydrogenDocument7 pagesRayleigh Scattering Cross Section Redward of Lyα by Atomic HydrogenRodrigo BarrosNo ratings yet
- M1-1B - Atomic Theory - Part 1Document26 pagesM1-1B - Atomic Theory - Part 1samNo ratings yet
- No Mor Ato M Nama Unsur Kimia Lamb Ang Unsur Kimia No Mor Ato M Nama Unsur Kimia Lamb Ang Unsur KimiaDocument4 pagesNo Mor Ato M Nama Unsur Kimia Lamb Ang Unsur Kimia No Mor Ato M Nama Unsur Kimia Lamb Ang Unsur KimiaNight MareNo ratings yet
- MagnetismAndMatter CWDocument5 pagesMagnetismAndMatter CWAyesha AnjumNo ratings yet
- Just Six Numbers (Excerpt) by Martin Rees (Basic Books, 1999)Document2 pagesJust Six Numbers (Excerpt) by Martin Rees (Basic Books, 1999)dsrdjanNo ratings yet
- GRADE 10 - SCIENCE Notes 1 (2nd Quarter)Document4 pagesGRADE 10 - SCIENCE Notes 1 (2nd Quarter)gwenn enaje100% (1)
- DPP 1 ThermoDocument1 pageDPP 1 ThermoBhushanNo ratings yet
- Physics: Pearson Edexcel International Advanced LevelDocument32 pagesPhysics: Pearson Edexcel International Advanced LevelIftekhar AkhandNo ratings yet
- Ib Chem PrepDocument26 pagesIb Chem PrepSaketh VuppalapatiNo ratings yet
- Assignment Solution Engg Phys RelativityDocument26 pagesAssignment Solution Engg Phys RelativitySaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42afyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Chemical FoundationDocument50 pagesChapter 1 - Chemical Foundation杨致远No ratings yet
- FLOURIMETRYDocument88 pagesFLOURIMETRYchannanjappamcNo ratings yet
- The Investigated Material: Calcium Fluoride: 2.1. Structure of The Caf CrystalDocument14 pagesThe Investigated Material: Calcium Fluoride: 2.1. Structure of The Caf CrystalChemophilicNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Plus Two Physics Chapter 11 SeemaDocument14 pagesHsslive Plus Two Physics Chapter 11 SeemastudyhardworksuccessNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table 1 QPDocument8 pagesAtomic Structure & The Periodic Table 1 QPAisha Jakhro100% (1)
- All India Test Series: JEE (Advanced) - 2022 Open Test - IDocument29 pagesAll India Test Series: JEE (Advanced) - 2022 Open Test - IHarshit SharmaNo ratings yet