Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.5 The Periodic Table Contd.
2.5 The Periodic Table Contd.
Uploaded by
NodicaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.5 The Periodic Table Contd.
2.5 The Periodic Table Contd.
Uploaded by
NodicaCopyright:
Available Formats
Alloy Nodica
CICT-125
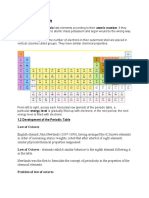
2.5 The Periodic Table contd.
The elements can be further categorized by subcategory: in the first group, called lanthanides, is
top group is defined by having elements 3–18 in it; the transition metals in the bottom group are made
up of elements in columns 3–12; and inner transition metals are in the last two rows of the table, also
defined by having elements 3–12. The elements can be further divided into finer categories by their
compounding. For instance, group 1 elements have single atoms of the element and a hydrogen atom
together to form a compound. In addition to hydrogen, the alkali metals have the same chemical
properties, and are called that because they all belong to the same group of elements. Group 2
elements have compounds that consist of a single atom and two atoms of hydrogen: the elements in the
second column of the periodic table. In this class of elements, the metals exhibit similar traits. Some of
the individual elements include the chalcogens (group 16), the halogens (group 17), and the noble gases
(group 18). (group 18, also known as inert gases). These names can refer to each group via the first part
of each group: For instance, the chalcogens, which are also known as the oxygen group or oxygen family,
are included in the oxygen family. Hydrogen, a unique nonmetallic element with characteristics similar
to Group 1A and Group 7A elements, has properties similar to Group 1A and Group 7A elements.
Because of this, hydrogen could appear alone at the top of both groups, or appear at the top of both
groups together.
You might have discovered some things about certain atomic masses when you were looking at
the periodic table. The atomic mass of many elements with atomic numbers of 84 and higher (such as
polonium) is given in square brackets. In order to track unstable radioactive isotopes, we need a starting
point, and that's why we began here (you will learn more about radioactivity in the nuclear chemistry
chapter). Radioisotopes may vary significantly in relative abundance from one sample to the next, which
can lead to wildly divergent atomic weights that are not comparable. The atomic mass number (and
approximate atomic mass) of the most stable isotope of that element are in square brackets.
You might also like
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Periodic Table of Elements (Chemistry)Document24 pagesPeriodic Table of Elements (Chemistry)christian jay pilarNo ratings yet
- GC1 Lesson 3 Atoms Molecules and Ions 3 The Periodic TableDocument31 pagesGC1 Lesson 3 Atoms Molecules and Ions 3 The Periodic TableYeri KimNo ratings yet
- CHEM 2 - Module 2 Periodic Table of ElementsDocument4 pagesCHEM 2 - Module 2 Periodic Table of ElementsMicah BlazaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table IDocument12 pagesPeriodic Table IDavid PhilemonNo ratings yet
- P-Block ElementsDocument10 pagesP-Block ElementsSubramanian Gk100% (1)
- Chemistry f5Document22 pagesChemistry f5ALshafiq ShuaiNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Elements: Chemistry Lec 3Document11 pagesThe Periodic Table of Elements: Chemistry Lec 3المونتاج الاخيرNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Periodic TableDocument0 pagesIntroduction To The Periodic TableAdnan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Modern Periodic TableDocument8 pagesModern Periodic Tablemixing hubNo ratings yet
- Development of The Periodic TableDocument8 pagesDevelopment of The Periodic TableAbigael Jhem Soriano ArtuzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - The Periodic Table of ElementsDocument3 pagesChapter 6 - The Periodic Table of ElementsIftikhar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Priodic TableDocument11 pagesChemistry Priodic TableGada HadaNo ratings yet
- Modern Periodic TableDocument4 pagesModern Periodic TableNabil Abdullah0% (1)
- Priodic TableDocument12 pagesPriodic TableHitesh MoreNo ratings yet
- Modern Periodic TableDocument8 pagesModern Periodic TableSabbir HossainNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Assignment 1Document10 pagesBiochemistry Assignment 1THE LIGHT AND NIGHTNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument5 pagesPeriodic Table of Elementsmichael tenajerosNo ratings yet
- Classification of ElementsDocument26 pagesClassification of ElementsSyeda Farzana Sadia BithiNo ratings yet
- Elements As Building BlocksDocument4 pagesElements As Building BlocksLUVAI KIOKONo ratings yet
- Jay Report Chem LabDocument10 pagesJay Report Chem LabJAYNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter Atom-Periodic TableDocument34 pagesProperties of Matter Atom-Periodic Tableleojohn2No ratings yet
- Diploma Science Faculty of Science and Mathematics Department of Chemistry Universiti Pendidikan Sultan IdrisDocument3 pagesDiploma Science Faculty of Science and Mathematics Department of Chemistry Universiti Pendidikan Sultan IdrisAZRIN NAJUA BINTI MD NORNo ratings yet
- The Periodic TableDocument39 pagesThe Periodic TableNihatNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table: Periods or SeriesDocument23 pagesThe Periodic Table: Periods or SeriesStephNo ratings yet
- Elements Having The Same Number of Electrons in Their Outermost Shell Are Placed inDocument26 pagesElements Having The Same Number of Electrons in Their Outermost Shell Are Placed inMai AbdelgelilNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document6 pagesWeek 4Prima LebananNo ratings yet
- ATOMSDocument6 pagesATOMSSarah HantonNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument47 pagesPeriodic Table of Elementsbrent tobiasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Periodic TableDocument11 pagesChemistry Periodic Tablesubhadeepdey85No ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of Elements PDFDocument8 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements PDFDeepak GH100% (1)
- C3 - The Periodic TableDocument7 pagesC3 - The Periodic TableEdward HarveyNo ratings yet
- Structure of An AtomDocument16 pagesStructure of An Atomkatrina freoNo ratings yet
- Zafeer Aaryan Reza PTDocument13 pagesZafeer Aaryan Reza PTZafeer Aaryan RezaNo ratings yet
- SSS 2 E-Note 1st Term ChemistryDocument23 pagesSSS 2 E-Note 1st Term ChemistryDave Blessed90% (10)
- The Periodic TableDocument6 pagesThe Periodic Tabledarshika artistoNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of The Organization of The Periodic TableDocument3 pagesA Brief History of The Organization of The Periodic TableLucila QuinquilleriaNo ratings yet
- Classification of The ElementsDocument17 pagesClassification of The ElementsNoor Mohammad NofaerNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table Groups Periods Atomic Number Explained 7b24244bDocument14 pagesThe Periodic Table Groups Periods Atomic Number Explained 7b24244bmithiraiNo ratings yet
- Periodicclassificationofelements Notes&QuestionsDocument5 pagesPeriodicclassificationofelements Notes&QuestionsAngelic ShineNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of The ElementDocument4 pagesPeriodic Table of The ElementHoangTuan LyNo ratings yet
- 4.0 The Periodic TableDocument2 pages4.0 The Periodic TablejimmyhongruNo ratings yet
- What Are The Features of The Periodic Table?: Research On The Follwing QuestionsDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Features of The Periodic Table?: Research On The Follwing QuestionsNoaj PalonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument10 pagesChemistry ProjectShakina FyffeNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Chemistry Form 4Document60 pagesPeriodic Table Chemistry Form 4Siti Fairus MohammadNo ratings yet
- Lectures Part 1Document87 pagesLectures Part 1anomaniNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument11 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsMozibor RahmanNo ratings yet
- Complete Chpter#4 (The Periodic Table)Document8 pagesComplete Chpter#4 (The Periodic Table)shahshujaat75% (4)
- CH 2 Atoms, Elements and Compounds Igcse NotesDocument4 pagesCH 2 Atoms, Elements and Compounds Igcse NotesKim BoraNo ratings yet
- 41GATE Material For Chemistry - OptDocument70 pages41GATE Material For Chemistry - OptSanthi SriNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument58 pagesPeriodic Table of ElementsMichelle Casayuran - RegalaNo ratings yet
- By Pri Nce Sir: ChemistryDocument37 pagesBy Pri Nce Sir: ChemistryShantam AnandNo ratings yet
- Textbook Chemistry Without The Useless InformationDocument5 pagesTextbook Chemistry Without The Useless Informationfathead4269No ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument12 pagesPeriodic TableFysal JanjowaNo ratings yet
- Farfan Morales Jessicagpe M14S2AI4Document10 pagesFarfan Morales Jessicagpe M14S2AI4Yess MoralesNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5-Periodic-Classification-Of-Elements/: Dobereiner's TriadsDocument6 pagesChapter-5-Periodic-Classification-Of-Elements/: Dobereiner's TriadsAhmed shakilNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5-Periodic-Classification-Of-Elements/: Dobereiner's TriadsDocument6 pagesChapter-5-Periodic-Classification-Of-Elements/: Dobereiner's TriadsAhmed shakilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Periodic TableDocument23 pagesChapter 1 Periodic TablevsyoiNo ratings yet
- 2478 - UN IT III Lanthanides and ActinidesDocument70 pages2478 - UN IT III Lanthanides and ActinidesAmr AdelNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- 2.6 Molecular and Ionic CompoundsDocument1 page2.6 Molecular and Ionic CompoundsNodicaNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Chemical FormulasDocument1 page2.4 Chemical FormulasNodicaNo ratings yet
- 2.6 Molecular and Ionic Compounds Contd.Document1 page2.6 Molecular and Ionic Compounds Contd.NodicaNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Chemical Formulas Contd.Document1 page2.4 Chemical Formulas Contd.NodicaNo ratings yet
- 2.5 The Periodic TableDocument1 page2.5 The Periodic TableNodicaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Physical and Chemical PropertiesDocument1 page1.3 Physical and Chemical PropertiesNodicaNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Atomic Structure and SymbolismDocument1 page2.3 Atomic Structure and SymbolismNodicaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Physical and Chemical Properties ContdDocument2 pages1.3 Physical and Chemical Properties ContdNodicaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Evolution of Atomic TheoryDocument1 page2.2 Evolution of Atomic TheoryNodicaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Phases and Classification of Matter Contd.Document2 pages1.2 Phases and Classification of Matter Contd.NodicaNo ratings yet
- 1.4 MeasurementsDocument2 pages1.4 MeasurementsNodicaNo ratings yet