Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reding Material
Reding Material
Uploaded by
Absir MulugetaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- CatheterizationDocument46 pagesCatheterizationJam Maj60% (5)
- Pemasangan Kateter UrinDocument12 pagesPemasangan Kateter UrinYULI222100% (1)
- Female Urinary Cathterization PDFDocument8 pagesFemale Urinary Cathterization PDFmeseretNo ratings yet
- Catheterization:: Binal Joshi, Assistant Professor, MTINDocument58 pagesCatheterization:: Binal Joshi, Assistant Professor, MTINBinal JoshiNo ratings yet
- Fundam Nursing Skill Lab ManualDocument97 pagesFundam Nursing Skill Lab ManualBirhanu AyenewNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterizationDocument51 pagesUrinary CatheterizationRebira WorkinehNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterizationDocument35 pagesUrinary CatheterizationrnrmmanphdNo ratings yet
- Zela Cateter 2Document49 pagesZela Cateter 2Absir MulugetaNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterizationDocument37 pagesUrinary CatheterizationCharles100% (2)
- CatheterizationDocument23 pagesCatheterizationyuuki konnoNo ratings yet
- Insertion of TubesDocument29 pagesInsertion of Tubesqopcyrus10No ratings yet
- An Assi Gnment On Cat Het Eri Zat I OnDocument17 pagesAn Assi Gnment On Cat Het Eri Zat I OnGyanbhushan BhartiNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterisationDocument24 pagesUrinary CatheterisationmustaphaNo ratings yet
- Urinary EliminationDocument9 pagesUrinary EliminationTuTitNo ratings yet
- Tubes, Catheters, and DrainsDocument17 pagesTubes, Catheters, and DrainsInnocent BachiNo ratings yet
- Urinary CathDocument71 pagesUrinary Cathlouie roderosNo ratings yet
- Rle MidtermDocument77 pagesRle MidtermTrishaNo ratings yet
- Catheterization: NCM 107 LabDocument4 pagesCatheterization: NCM 107 LabCatherine PradoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Catheterization Nursing ProcedureDocument6 pagesUrinary Catheterization Nursing ProcedureDencel BarramedaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Interventions: By: Nursing Skills Laboratory GroupDocument57 pagesUrinary Interventions: By: Nursing Skills Laboratory GroupMelinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- CatheterizationDocument43 pagesCatheterizationJen Tirapan100% (2)
- Urology Case 10th March 2024Document35 pagesUrology Case 10th March 2024tamzidshafi78No ratings yet
- 7.urinary Cathetrization 2024Document19 pages7.urinary Cathetrization 2024Leul DawitNo ratings yet
- CatheterizationDocument2 pagesCatheterizationjannatul supti24No ratings yet
- UrologyDocument9 pagesUrologyDrmirfat AlkashifNo ratings yet
- 6 Urinary EliminationDocument5 pages6 Urinary EliminationkhautedameNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Urinary CatheterDocument28 pagesPresentation On Urinary Cathetersushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Osce Reviewer1Document17 pagesOsce Reviewer1Nicole TeoxonNo ratings yet
- Foley CatherterDocument18 pagesFoley CathertergwynNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterizationDocument5 pagesUrinary CatheterizationRita PokharelNo ratings yet
- Urinary Catheterization FemaleDocument13 pagesUrinary Catheterization Femaleroger100% (1)
- Catheterization & CystoclysisDocument6 pagesCatheterization & Cystoclysisclariceportin12No ratings yet
- Obpedia LabDocument8 pagesObpedia Labprincess.capa-anNo ratings yet
- Basic Invasive ProceduresDocument39 pagesBasic Invasive ProceduresLucas AresNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterizationDocument3 pagesUrinary CatheterizationElla LobenariaNo ratings yet
- Specimen CollectionDocument26 pagesSpecimen CollectionLulu MushiNo ratings yet
- Urinary Elimination and CatheterizationDocument41 pagesUrinary Elimination and CatheterizationMaria Margarita100% (1)
- CatheterizationDocument22 pagesCatheterizationravizbeea8No ratings yet
- Male CatheterizationDocument30 pagesMale CatheterizationJoeurielle CarteraNo ratings yet
- Retdem Week 8Document9 pagesRetdem Week 8Iris FrancheNo ratings yet
- How To Insert A CatheterDocument17 pagesHow To Insert A CatheterGreen ZeroNo ratings yet
- Performing Urinary CatheterizationDocument46 pagesPerforming Urinary CatheterizationAbelNo ratings yet
- Revised CATHETERIZATION 2Document43 pagesRevised CATHETERIZATION 2Insatiable CleeNo ratings yet
- CATHETERIZATIONDocument3 pagesCATHETERIZATIONanimesh pandaNo ratings yet
- Assisting in Catherization IDocument6 pagesAssisting in Catherization IGrezilmay MeninguitoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Catheterization PrintableDocument5 pagesUrinary Catheterization Printablemaricris atunNo ratings yet
- CATHETERIZATIONDocument5 pagesCATHETERIZATIONMonica JubaneNo ratings yet
- CatheterizationDocument32 pagesCatheterizationJohn Dave V. VillarmenteNo ratings yet
- CatheterizationDocument7 pagesCatheterizationMomee BarmanNo ratings yet
- Catheterization DemoDocument48 pagesCatheterization Demojonna casumpangNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterDocument21 pagesUrinary CatheterGiFt Wimolratanachaisiri0% (1)
- Indwelling Urinary CatheterizationDocument5 pagesIndwelling Urinary CatheterizationNiña Jean Tormis AldabaNo ratings yet
- L12 Enema and Catheterization PDFDocument11 pagesL12 Enema and Catheterization PDFAilyn ValmoresNo ratings yet
- Compilation Except OxygenationDocument9 pagesCompilation Except OxygenationSharies ArgelNo ratings yet
- Kateterisasi: Departemen Urologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Padjadjaran Rumah Sakit Dr. Hasan Sadikin Bandung 2021Document18 pagesKateterisasi: Departemen Urologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Padjadjaran Rumah Sakit Dr. Hasan Sadikin Bandung 2021Efiran N S WandaNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterDocument28 pagesUrinary CatheterArie AngkiriwangNo ratings yet
- Rules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesFrom EverandRules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Vasectomy Reversal: All You Need To Know: Everything You Need To Know About Vasectomy Reversal But Never Knew To AskFrom EverandVasectomy Reversal: All You Need To Know: Everything You Need To Know About Vasectomy Reversal But Never Knew To AskNo ratings yet
- BioinformaticsDocument93 pagesBioinformaticsAbsir MulugetaNo ratings yet
- Zela Cateter 2Document49 pagesZela Cateter 2Absir MulugetaNo ratings yet
- PR Naval Ill, 2022 Microsoft PowerPoint Presentation Copy 21Document13 pagesPR Naval Ill, 2022 Microsoft PowerPoint Presentation Copy 21Absir MulugetaNo ratings yet
- PR GM Dis of Skin and Con New Icrosoft PowerPoint PresentationDocument76 pagesPR GM Dis of Skin and Con New Icrosoft PowerPoint PresentationAbsir MulugetaNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic HypertrophyDocument45 pagesBenign Prostatic Hypertrophyjitendra magarNo ratings yet
- Female Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesFemale Urinary SystemVikas SarkarNo ratings yet
- Prostate CancerDocument6 pagesProstate CancerfheisanzNo ratings yet
- Etiology: 1.urinary RetentionDocument38 pagesEtiology: 1.urinary RetentionAbdurre YNo ratings yet
- Concept of EliminationDocument42 pagesConcept of EliminationOpen UserNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract ObstructionDocument56 pagesUrinary Tract ObstructionMicky FantaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Catheterization: By: Michael John Z. Principio, RN, RM, MancDocument22 pagesUrinary Catheterization: By: Michael John Z. Principio, RN, RM, MancSarahlaine BrazasNo ratings yet
- CatheterizationDocument14 pagesCatheterizationV_RNNo ratings yet
- Pressure Flow Urodynamic Studies: The Gold Standard For Diagnosing Bladder Outlet ObstructionDocument8 pagesPressure Flow Urodynamic Studies: The Gold Standard For Diagnosing Bladder Outlet ObstructionmarcelloNo ratings yet
- L12 Enema and Catheterization PDFDocument11 pagesL12 Enema and Catheterization PDFAilyn ValmoresNo ratings yet
- Bladder Meridian - Guardian of PeaceDocument7 pagesBladder Meridian - Guardian of Peacemanket59No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument22 pagesNursing Care PlansAnonymous 0C4OZmR0% (1)
- Suprapubic CatheterizationDocument3 pagesSuprapubic CatheterizationHariniNo ratings yet
- Tubes, Catheters, and DrainsDocument17 pagesTubes, Catheters, and DrainsInnocent BachiNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)Document8 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)miftah ar rahmahNo ratings yet
- Prostate Infection: Acute Bacterial ProstatitisDocument3 pagesProstate Infection: Acute Bacterial ProstatitisZammira MutiaNo ratings yet
- Is Early Surgical Treatment For Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Preferable Medical Therapy - Pros and ConsDocument11 pagesIs Early Surgical Treatment For Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Preferable Medical Therapy - Pros and ConsClaudia FreyonaNo ratings yet
- Central Council of Indian Medicine New Delhi: Syllabus of Ayurvedacharya (Bams) CourseDocument29 pagesCentral Council of Indian Medicine New Delhi: Syllabus of Ayurvedacharya (Bams) CourseShubham Jain100% (1)
- Stoevelaar, Herman JohanDocument232 pagesStoevelaar, Herman JohanKamran AfzalNo ratings yet
- Urological Emergency CasesDocument6 pagesUrological Emergency CasesjamilNo ratings yet
- Student's Assessment Form PDFDocument4 pagesStudent's Assessment Form PDFpatriarch_fall100% (1)
- 1 - Inctruments KM RDocument33 pages1 - Inctruments KM RHelene AlawamiNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi Sistem PerkemihanDocument24 pagesPatofisiologi Sistem PerkemihanMasna Arisah NasutionNo ratings yet
- Cateter JurnalDocument10 pagesCateter JurnalLeli Khairani AdnanNo ratings yet
- BPH InternetDocument72 pagesBPH InternetDesty ArianiNo ratings yet
- Sas 30Document2 pagesSas 30Sistine Rose LabajoNo ratings yet
- Remedy Rate3Document16 pagesRemedy Rate3Divyajyoti DevaNo ratings yet
- Peran Dokter Keluarga Dalam Penatalaksanaan Komprehensif Keganasan Prostat 2018 DR Yusuf Alam R PDFDocument87 pagesPeran Dokter Keluarga Dalam Penatalaksanaan Komprehensif Keganasan Prostat 2018 DR Yusuf Alam R PDFBestariayuNo ratings yet
- Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) - DHT Stimulates Cell Growth in The Tissue That Lines The Prostate GlandDocument7 pagesDihydrotestosterone (DHT) - DHT Stimulates Cell Growth in The Tissue That Lines The Prostate GlandPeter Kenneth LampitocNo ratings yet
- Enlarged Prostate Booklet PDFDocument52 pagesEnlarged Prostate Booklet PDFnabin hamalNo ratings yet
Reding Material
Reding Material
Uploaded by
Absir MulugetaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reding Material
Reding Material
Uploaded by
Absir MulugetaCopyright:
Available Formats
Catheterization procedure GT COLLEGE
Objective: At the end of the chapter, the learner will be able to:-
1. Insert indwelling and plain urinary catheter for male and female clients
2. Perform bladder irrigation
3. Provide care for client with supra-pubic catheter
4. Identify types of enema solution with possible advantage and disadvantage
5. Re-demonstrate proper technique of enema administration
6. Provide care for colostomy appliance
7. Manage colostomy irrigation
Definition- act of voiding or expelling waste material from the bowels
1.1. Urinary elimination
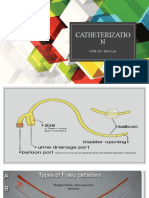
Categories of urethral catheters
1. Straight or Robinson catheter a single lumen tube
2. Retention or Foley catheter contains second lumen ( two and three way catheter)
3. Coude (elbowed):- used for elderly men who have BPH- which is curved tip
Types of Catheterization (routes)
Urinary catheterization
Suprapubic catheterizati
• onTypes of Catheters
1. External Catheters
• An external catheter is not inserted within the bladder; instead, it surrounds the
+urinary meatus.
Prepared by zeleke nora
Catheterization procedure GT COLLEGE
• Examples condom catheter It is more effective for male clients
2. Internal catheter
2.1 Straight Catheters(plain or robinson)
– A straight catheter is a urine drainage tube inserted but not left in
place. It drains urine temporarily or provides a sterile urine
specimen.
2.2 Retention Catheters(foley or indwelling)
– A retention catheter, also called an indwelling catheter, is left in
place for a period of time
• The.most.common.typeisa..Foleycatheter
Types of catheter- it has different variety of size, materials, and types.
• types of catheter are
– Straight (plain )
Prepared by zeleke nora
Catheterization procedure GT COLLEGE
– Retention (Foley, indwelling)
• Catheters can also differ in the number of lumens they have
– Straight catheter -has single lumen
– Double lumen catheter- has two lumens
• ----Triple lumen catheter – has three lumens.
• In double lumen catheter, one lumen is used to inflate balloon at the end of the catheter
and the other lumen is to drain urine.
The triple lumen catheter provides an additional lumen for the instillation of irrigating
solutions.
Indwelling catheter:-if it remain in place for continuous drainage of urine,
an indwelling urethral catheter is used.
– It is also called retention or Foley catheter.
– are used for gradual decompression of an over distended bladder, for
intermittent bladder drainage and for continuous bladder drainage.
– It has a balloon
Intermittent or straight catheter
is used to drain the bladder for shorter period of time (5-10min).clients
can be taught to insert and remove intermittent catheter themselves.
Alternatives for internal urethral catheterization
1 Suprapubic catheterization:-it is occasionally used for continuous drainage.
• This type of catheter is inserted through a small incision above the
pubic area directly into the urinary bladder.
2. Condom catheter: - when voluntary control of urination soft, pliable device
made of plastic or rubber material is applied externally to the penis.
•
. Selecting an appropriate catheter
May be made of
Plastic_ for one week
Latex_ 2-3weeks (rubber)
Silicon_ for 2-3 month
• Select the type of material in accordance with the estimated length of the catheterization
period.
2. Determine appropriate catheter size
Are determined by diameter of lumen.
Graded on French scale or number
Catheter size depends on the size of the urethral canal
• #8-10fr_ children
• #14-16fr_ female adults
• #18fr_ adult male
–
1.1.1. Urinary catheterization
Prepared by zeleke nora
Catheterization procedure GT COLLEGE
Learning objective: At the end of the lesson, the learner will be able to
1. Define urinary catheterization
2. List the purpose of urinary catheterization
3. Identify the necessary equipment for catheterization
4. Perform procedure of urinary catheterization
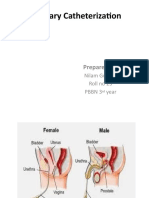
Definition: Urinary Catheterization- involves inserting a small tube/ catheter through the
urethra in to the bladder to allow urine to drain
Catheters: are tubes commonly made of rubber or plastics, although certain types are
made of woven silk or metal.
Purpose
To empty the bladder in case of retention of urine, occurring as a post operative
complication
In case of retention due to injury or tumor of the spinal cord
In case of obstruction due to the blockage of the urethra causing stricture
To obtain sterile specimen of urine
To ensure that the bladder is empty before an abdominal or pelvic operation or
Paracentesis
To keep incontinent patient dry
To avoid contamination after operation of vagina or perineum
To empty bladder irrigation or instillation of the bladder
To determine if residual urine is present in the bladder
For an accurate measurement of urinary out put
To facilitate healing of urethra
1.1.1.1. Straight or plain catheterization
1.1.1.1.1. Catheterization using a straight or plain catheter for female
Definition: introducing plain or straight catheter through the female urethra to the urinary
bladder
Prepared by zeleke nora
Catheterization procedure GT COLLEGE
Purpose
To relieve discomfort due to bladder distention
To obtain a sterile urine specimen
To empty the bladder prior to surgery
Equipment
Sterile
1. Sterile plain catheter rubber or plastic
2. A bowl for antiseptic 5. forceps 10.13
3. Gauze 6. Sterile receiver
4. Sterile towel(3#) 7. Kidney dish
8. Sterile urine specimen container if needed
Clean
1. Rubber and draw sheet 8. Vital sign equipment
2. Antiseptic solution 9. PPE
3. Receiver 10. Syringe 5ml
4. Measuring jug 11. lubricant
5. Urinary bag 12. Flash light
6. Fenestrated towel 13. Screen
7. Glove clean & surgical 14. Specimen form
Procedure
1. Explain procedure to the patient
2. Screen the bed
3. Wash hands
4. Turn blanket and bedspread down to foot of bed
5. Turn top linen up wards to the patient’s chest to protect form complete exposure.
6. Place patient in dorsal recumbent position with the knees flexed and thigh apart then
7. Put rubber and draw sheet under buttocks, cover patient with the linen(if patient soaked use
examination glove)
8. Apply disposable glove
Prepared by zeleke nora
Catheterization procedure GT COLLEGE
9. Clean starting from mid thigh with clean warm water and soap and dry the area
10. Open sterile filed
11. Done sterile gloving
12. Create a sterile field and Drape the client with a sterile drape (bottom far side nearside
pubic area)
13. Prepare the equipment and Put receiver for urine near the genital area
14. Place sterile equipment on drape between patient tight
15. Prepare the equipment and Put receiver for urine near the vulva.
16. Use non dominant hand to separate labia until the catheter is inserted
17. Wash the outer skin folds then inner labia and urethral meatus with antiseptic solution from
front to back. (Starting from outer proceeding to inside)
18. Put forceps in the receiver kidney dish
19. Wash and Rinse the area well from outer skin folds then inner labia and urethral meatus
finally with distil water from front to back.
20. Put forceps in the receiver kidney dish
21. Dry the dry gauze the outer skin folds then inner labia and urethral meatus from front to back
22. Put forceps in the receiver kidney dish
23. Lubricate the insertion tip of the catheter (5-7 cm in)
24. Expose the urinary meatus adequately by retracting the tissue or the labia minora in an
upward direction
25. Gently insert the catheter into meatus until urine is noted. Continue inserting for 2.5 to 5cm
additional.
26. Remove catheter after desired duration or all expected urine expelled
27. Measure urine, dry area with dry gauze, remove bed protection
28. Position patient comfortable and cover
29. Remove and clean equipment
30. Send specimen to the laboratory
1.1.1.1.2. Male plain or straight urinary catheterization
Definition: Introducing plain or straight catheter through the male urethra to the urinary bladder
Equipment
Prepared by zeleke nora
Catheterization procedure GT COLLEGE
Sterile
1. Sterile plain catheter rubber or plastic
2. A bowl for antiseptic 7. forceps ( 3 )
3. Cotton swab 8. Sterile receiver
4. Gauze 9. Kidney dish
5. Large sterile fenestrated towel 10. Lubricant
6. Sterile towel
11. Sterile urine specimen container if needed
Clean
1. Rubber and draw sheet 5. Flash light
2. Antiseptic solution 6. Screen
3. Receiver 7. Specimen forms
4. Measuring jug
Procedure
1. Explain procedure to the patient
2. Screen the bed
3. Wash hands
4. Turn top linen up wards to the patient’s Umbilicus and blanket and bed spread up to
mid-thigh.
5. Place patient in dorsal recumbent position with the knees flexed and thigh apart then put
rubber and draw sheet under buttocks, cover patient with the linen
6. Wash the perennial area with warm water and soap
7. Wash hands
8. Open sterile field
9. Put on sterile gloves
10. Place sterile towel under the patient and fenestrated towel over the patient thigh
11. Prepare antiseptic swabs and Pick up penis with non-dominate hand protract foreskin if
not circumcised, grasp directly behind glans and spread meatus between forefingers and
thumbs.
Prepared by zeleke nora
Catheterization procedure GT COLLEGE
12. Cleanse penis using circular motion, starting over meatus and working down wards
glans, repeat procedure twice using new swabs always by the help of forceps.
13. Pick up catheter, lubricated at least 7.5cm from distal end. Draw penis upwards and
forwards at 900 angle to the leg insert the catheter, lower penis when feeling resistance at
an angle of 60 degree
14. Insert catheter about 18-20cm till urine flow
15. Remove catheter, replace foreskin to avoid complication
16. Remove catheter measure urine, dry area with dry cotton swab, remove bed protection
position patient comfortable and cover
17. Remove and clean equipment
18. Send specimen to the laboratory
1.1.1.2. Insertions of indwelling Urinary catheter
1.1.1.2.1. Insertions of indwelling catheter for male patient
Learning Objective: At the end of the lesson, the learner will be able to
1. Define insertions of indwelling catheter
2. Identify the no cessary equipment for insertions of indwelling catheter
3. Demonstrating the procedure of indwelling catheter
Definition: introductions of indwelling catheter through the male urethra in to the bladder
Purpose
To prevent retention by use of an indwelling catheter
To prevent frequent catheterization in case where pt is unable to pass urine
To prevent bed sore in case of urine incontinence
Prepared by zeleke nora
Catheterization procedure GT COLLEGE
To prevent infection in cases of perineal operation
Equipment
1. Indwelling catheter rubber or plastic
2. A bowl for antiseptic 7. Forceps ( 3 )
3. Cotton swab 8. Sterile receiver
4. Gauze 9. Kidney dish
5. Large sterile fenestrated 10. Syringe
towel 11. Sterile water
6. Sterile towel 12. Lubricant
13. Sterile urine specimen container if needed
Clean
1. Rubber and draw sheet 4. Urinary drainage bag
2. Antiseptic solution 5. Screen
3. Receiver 6. Adhesive plaster
Procedure
1. Explain procedure to the patient
2. Screen the bed
3. Wash hands
4. Turn top linen up wards to the patient’s chest to protect from complete exposure.
5. Place patient in dorsal recumbent position with the knees flexed and thigh apart then put
rubber and draw sheet under buttocks, cover patient with the linen
6. Wash the perennial area with warm water and soap
7. Wash hands
8. Prepare sterile trolley
9. Uncover patient,
10. Put on sterile gloves, place sterile towel under the patient and fenestrated towel over
the pt thigh
11. Test balloon before insertion on sterile filed with recommended amount of sterile water
Prepared by zeleke nora
Catheterization procedure GT COLLEGE
12. Prepare antiseptic swabs and Pick up penis with non-dominate hand retract foreskin if
not circumcised, grasp directly behind glans and spread meatus between forefingers and
thumbs.
13. Cleanse penis using circular motion, starting over meatus and working down wards
glans, repeat procedure twice using new swabs always by the help of forceps.
14. Pick up catheter, lubricated at least 7.5cm from distal end. Draw penis upwards and
forwards at 900 angle to the leg insert the catheter, lower penis when feeling resistance at
an angle of 60 degree
15. When catheter is inserted, inflate the balloon with 5-15ml as indicated on catheter
16. Pull gently on the end of the catheter to be sure it will not leave the bladder then push
back 2cm to relieve pressure from sphincter
17. Attach drainage tube to catheter and drainage bag
18. Tie tube and drainage bag to the bed ,put the bottle below the patient level
19. Cover and comfort the patient
20. Return the equipment
21. Wash hands and document the procedure
1.1.1.2.2. Insertions of indwelling catheter for Female patient
Leaning objective: At the end of the lesson, the learner will be able to
1. Define indwelling catheter for female pt
2. Identify equipments for insertions of indwelling catheter
3. Demonstrate insertions of indwelling catheter
Definition: Introduction of the indwelling catheter through the female urethra in the bladder
Purpose
To prevent retention by use of an indwelling catheter
To prevent frequent catheterization in case where pt is unable to pass urine
To prevent bed sore in case of urine incontinence
To prevent infection in cases of perineal operation
Equipment
Sterile
1. Indwelling catheter rubber or plastic
Prepared by zeleke nora
Catheterization procedure GT COLLEGE
2. A bowl for antiseptic 7. Forceps ( 3)
3. Cotton swab 8. Sterile receiver
4. Gauze 9. Kidney dish
5. Large sterile fenestrated 10. Syringe
towel 11. Sterile water
6. Sterile towel 12. Lubricant
Clean
1. Rubber and draw sheet 4. Urinary drainage bag
2. Antiseptic solution 5. Screen
3. Receiver 6. Adhesive plaster
Procedure
1. Explain procedure to client and Provide for privacy
2. Set the bed to a comfortable height to work, and raise the side rail on the side opposite
you.
3. -Assist the client to a supine position with legs spread and feet together or to a side-lying
position with upper leg flexed.
4. Drape client’s abdomen and thighs.
5. Ensure adequate lighting of the perineum.
6. Wash hands, don disposable gloves, and wash perineal area from the mid thigh.
7. Remove gloves and wash hands.
8. bring urine collection bag ready for attaching near to side of bed
9. Done sterile gloving
10. Create a sterile field and Drape the client with a sterile drape (bottom far side
nearside pubic area)
11. Prepare the equipment and Put receiver for urine near the genital area
12. Place sterile equipment on drape between patient tight
13. Prepare the equipment and Put receiver for urine near the vulva.
14. Use non dominant hand to separate labia until the catheter is inserted
15. Wash the outer skin folds then inner labia and urethral meatus with antiseptic solution
from front to back. (Starting from outer proceeding to inside)
Prepared by zeleke nora
Catheterization procedure GT COLLEGE
16. Put forceps in the receiver kidney dish
17. Wash and Rinse the area well from outer skin folds then inner labia and urethral meatus
finally with distil water from front to back.
18. Put forceps in the receiver kidney dish
19. Dry the dry gauze the outer skin folds then inner labia and urethral meatus from front to
back
20. Put forceps in the receiver kidney dish
21. Lubricate the insertion tip of the catheter (5-7 cm in)
22. Expose the urinary meatus adequately by retracting the tissue or the labia minora in an
upward direction
23. Gently insert the catheter into meatus until urine is noted. Continue inserting for 2.5 to
5cm additional.
24. After catheter insertion, the balloon is inflated to hold the catheter in place within the
bladder.
25. Instruct the client to immediately report discomfort or pressure during balloon inflation;
if pain occurs, discontinue the procedure, deflate the balloon, and insert the catheter
further into the bladder.
26. Gently pull the catheter until the retention balloon is snuggled against the bladder neck
(resistance will be met) re-push back 2cm after the test
27. If laboratory test is prescribed, collect some amount of urine in the sterile specimen
bottle straight from the catheter
28. Secure the catheter to the abdomen or thigh and connect to drainage tube
29. Place the drainage bag below the level of the bladder.
30. Remove gloves, dispose of equipment, and wash hands.
31. Help client adjust position.
32. Assess and document
1.1.1.3. Applying a Condom Catheter
Objective- at the end of this lesson, the learner will be able to
1. define condom catheter
Prepared by zeleke nora
Catheterization procedure GT COLLEGE
2. describe the purposes of condom catheter
3. apply condom catheter by following the steps
Definition- The condom catheter is an external drainage system to collect urine from male
clients who have incontinence
Purpose
Provide a means of collecting urine and controlling incontinence without the risk of
infection that an indwelling urinary catheter imposes
Equipment
Condom catheter kit with adhesive strip
• Urinary drainage bag/bed pan
• Clean gloves
• Basin with warm water and soap
Towel and washcloth
Procedure
1. Wash hands and apply gloves.
2. Select an appropriate condom catheter.
3. Cleanse the penile shaft.
4. Inspect the penile shaft for excessive hair.
5. Inspect the penis for altered skin integrity.
6. Stretch the shaft of the penis and unroll the condom to the base of the penis.
7. Follow product directions for the application of the sealant
8. Attach the condom to the drainage apparatus,
9. either a leg bag or bedside drainage bag.
10. Remove gloves and wash hands.
11. Remove and reapply the condom catheter every 24 to 48 hours, or when leakage occurs.
1.1.2. Bladder Irrigation (open and closed method)
Objective: at the end of this lesson, the learner will able to :
1. Define bladder irrigation
2. Demonstrate bladder irrigation
Prepared by zeleke nora
Catheterization procedure GT COLLEGE
Definition: it is the washing out of the bladder to clear the catheter and/or the bladder.
Purpose
To clean the bladder before operation depending on the surgeons order
To arrest bleeding from the bladder
To clean the catheter from mucous or blood clots
To clean bladder form pus
Precaution
Care should be taken not air into the balder as it may cause spasm
Not more than 100-300ml must be instilled at a time after bladder operation capacity may
be limited.
If the catheter is blocked by blood clots, a suction of the catheter must be proceed the
irrigation
Equipment
a complete set to catheterization pail
A sterile bladder syringe for open glove
method
Irrigation solution e.g. normal saline or
cold solution to stop bleeding
Irrigation solution in a beg, infusion set,
Y-piece, urine drainage tube and bag
clamp for closed method
Receiver with plaster to put the catheter
end (open method)
Rubber and draw sheet
clamp
Prepared by zeleke nora
Catheterization procedure GT COLLEGE
Procedure for open method
1. Insert catheter as in catheterization
2. If catheter is already in the bladder
3. Put bed protection
4. Draw solution in the syringe
5. Clamp catheter, attach syringe in the catheter, place drainage tube on a swab
6. Decamp instill the solution gently into the bladder
7. With draw syringe, put end of catheter on the receiver which is placed on the bed
protection
8. Repeat this procedure 2-3 times or more until the return solution is clear
9. Clean catheter and drainage tubing with a swab and connect it again
Closed method
1. Prepare solution bag with IV set
2. Connect Y-place to the catheter and IV set to one end of the “Y” and drainage tube to
the other end
3. Intermittent irrigation clamp the drainage tube and let irrigation solution run in the
bladder (100-200ml) then close the set and open the drainage tube empty the bladder.
4. Repeat this procedure as soften as necessary
5. Empty the collection bag frequently
6. Subtract the irrigation solution form the total urinary output if balance
1.1.3. Suprapubic catheter care
Objective: at the end of this lesson, the learner will able to define Supra-pubic catheter and
demonstrate care of catheter.
Definition: A Suprapubic catheter is inserted through the abdominal wall above the symphysis
pubis into the urinary bladder.
Purpose
Prepared by zeleke nora
Catheterization procedure GT COLLEGE
o to prevent bladder infection
o To keep skin integrity
Care of clients with Suprapubic catheter include
Regular assessment of the client’s urine, fluid drainage system.
Skin care around the insertion site involves sterile technique.
Periodic clamping of the catheter preparatory to removing it and measurement of
residual urine.
Leaving the catheter open to drainage for 48to 72 hours then clamping the catheter for
3 to 4 hour periods during the day the client can void satisfactory amounts.
Dressing should be changed whenever they are soiled.
A small amount of iodine is used.
Prepared by zeleke nora
You might also like
- CatheterizationDocument46 pagesCatheterizationJam Maj60% (5)
- Pemasangan Kateter UrinDocument12 pagesPemasangan Kateter UrinYULI222100% (1)
- Female Urinary Cathterization PDFDocument8 pagesFemale Urinary Cathterization PDFmeseretNo ratings yet
- Catheterization:: Binal Joshi, Assistant Professor, MTINDocument58 pagesCatheterization:: Binal Joshi, Assistant Professor, MTINBinal JoshiNo ratings yet
- Fundam Nursing Skill Lab ManualDocument97 pagesFundam Nursing Skill Lab ManualBirhanu AyenewNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterizationDocument51 pagesUrinary CatheterizationRebira WorkinehNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterizationDocument35 pagesUrinary CatheterizationrnrmmanphdNo ratings yet
- Zela Cateter 2Document49 pagesZela Cateter 2Absir MulugetaNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterizationDocument37 pagesUrinary CatheterizationCharles100% (2)
- CatheterizationDocument23 pagesCatheterizationyuuki konnoNo ratings yet
- Insertion of TubesDocument29 pagesInsertion of Tubesqopcyrus10No ratings yet
- An Assi Gnment On Cat Het Eri Zat I OnDocument17 pagesAn Assi Gnment On Cat Het Eri Zat I OnGyanbhushan BhartiNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterisationDocument24 pagesUrinary CatheterisationmustaphaNo ratings yet
- Urinary EliminationDocument9 pagesUrinary EliminationTuTitNo ratings yet
- Tubes, Catheters, and DrainsDocument17 pagesTubes, Catheters, and DrainsInnocent BachiNo ratings yet
- Urinary CathDocument71 pagesUrinary Cathlouie roderosNo ratings yet
- Rle MidtermDocument77 pagesRle MidtermTrishaNo ratings yet
- Catheterization: NCM 107 LabDocument4 pagesCatheterization: NCM 107 LabCatherine PradoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Catheterization Nursing ProcedureDocument6 pagesUrinary Catheterization Nursing ProcedureDencel BarramedaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Interventions: By: Nursing Skills Laboratory GroupDocument57 pagesUrinary Interventions: By: Nursing Skills Laboratory GroupMelinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- CatheterizationDocument43 pagesCatheterizationJen Tirapan100% (2)
- Urology Case 10th March 2024Document35 pagesUrology Case 10th March 2024tamzidshafi78No ratings yet
- 7.urinary Cathetrization 2024Document19 pages7.urinary Cathetrization 2024Leul DawitNo ratings yet
- CatheterizationDocument2 pagesCatheterizationjannatul supti24No ratings yet
- UrologyDocument9 pagesUrologyDrmirfat AlkashifNo ratings yet
- 6 Urinary EliminationDocument5 pages6 Urinary EliminationkhautedameNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Urinary CatheterDocument28 pagesPresentation On Urinary Cathetersushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Osce Reviewer1Document17 pagesOsce Reviewer1Nicole TeoxonNo ratings yet
- Foley CatherterDocument18 pagesFoley CathertergwynNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterizationDocument5 pagesUrinary CatheterizationRita PokharelNo ratings yet
- Urinary Catheterization FemaleDocument13 pagesUrinary Catheterization Femaleroger100% (1)
- Catheterization & CystoclysisDocument6 pagesCatheterization & Cystoclysisclariceportin12No ratings yet
- Obpedia LabDocument8 pagesObpedia Labprincess.capa-anNo ratings yet
- Basic Invasive ProceduresDocument39 pagesBasic Invasive ProceduresLucas AresNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterizationDocument3 pagesUrinary CatheterizationElla LobenariaNo ratings yet
- Specimen CollectionDocument26 pagesSpecimen CollectionLulu MushiNo ratings yet
- Urinary Elimination and CatheterizationDocument41 pagesUrinary Elimination and CatheterizationMaria Margarita100% (1)
- CatheterizationDocument22 pagesCatheterizationravizbeea8No ratings yet
- Male CatheterizationDocument30 pagesMale CatheterizationJoeurielle CarteraNo ratings yet
- Retdem Week 8Document9 pagesRetdem Week 8Iris FrancheNo ratings yet
- How To Insert A CatheterDocument17 pagesHow To Insert A CatheterGreen ZeroNo ratings yet
- Performing Urinary CatheterizationDocument46 pagesPerforming Urinary CatheterizationAbelNo ratings yet
- Revised CATHETERIZATION 2Document43 pagesRevised CATHETERIZATION 2Insatiable CleeNo ratings yet
- CATHETERIZATIONDocument3 pagesCATHETERIZATIONanimesh pandaNo ratings yet
- Assisting in Catherization IDocument6 pagesAssisting in Catherization IGrezilmay MeninguitoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Catheterization PrintableDocument5 pagesUrinary Catheterization Printablemaricris atunNo ratings yet
- CATHETERIZATIONDocument5 pagesCATHETERIZATIONMonica JubaneNo ratings yet
- CatheterizationDocument32 pagesCatheterizationJohn Dave V. VillarmenteNo ratings yet
- CatheterizationDocument7 pagesCatheterizationMomee BarmanNo ratings yet
- Catheterization DemoDocument48 pagesCatheterization Demojonna casumpangNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterDocument21 pagesUrinary CatheterGiFt Wimolratanachaisiri0% (1)
- Indwelling Urinary CatheterizationDocument5 pagesIndwelling Urinary CatheterizationNiña Jean Tormis AldabaNo ratings yet
- L12 Enema and Catheterization PDFDocument11 pagesL12 Enema and Catheterization PDFAilyn ValmoresNo ratings yet
- Compilation Except OxygenationDocument9 pagesCompilation Except OxygenationSharies ArgelNo ratings yet
- Kateterisasi: Departemen Urologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Padjadjaran Rumah Sakit Dr. Hasan Sadikin Bandung 2021Document18 pagesKateterisasi: Departemen Urologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Padjadjaran Rumah Sakit Dr. Hasan Sadikin Bandung 2021Efiran N S WandaNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterDocument28 pagesUrinary CatheterArie AngkiriwangNo ratings yet
- Rules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesFrom EverandRules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Vasectomy Reversal: All You Need To Know: Everything You Need To Know About Vasectomy Reversal But Never Knew To AskFrom EverandVasectomy Reversal: All You Need To Know: Everything You Need To Know About Vasectomy Reversal But Never Knew To AskNo ratings yet
- BioinformaticsDocument93 pagesBioinformaticsAbsir MulugetaNo ratings yet
- Zela Cateter 2Document49 pagesZela Cateter 2Absir MulugetaNo ratings yet
- PR Naval Ill, 2022 Microsoft PowerPoint Presentation Copy 21Document13 pagesPR Naval Ill, 2022 Microsoft PowerPoint Presentation Copy 21Absir MulugetaNo ratings yet
- PR GM Dis of Skin and Con New Icrosoft PowerPoint PresentationDocument76 pagesPR GM Dis of Skin and Con New Icrosoft PowerPoint PresentationAbsir MulugetaNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic HypertrophyDocument45 pagesBenign Prostatic Hypertrophyjitendra magarNo ratings yet
- Female Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesFemale Urinary SystemVikas SarkarNo ratings yet
- Prostate CancerDocument6 pagesProstate CancerfheisanzNo ratings yet
- Etiology: 1.urinary RetentionDocument38 pagesEtiology: 1.urinary RetentionAbdurre YNo ratings yet
- Concept of EliminationDocument42 pagesConcept of EliminationOpen UserNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract ObstructionDocument56 pagesUrinary Tract ObstructionMicky FantaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Catheterization: By: Michael John Z. Principio, RN, RM, MancDocument22 pagesUrinary Catheterization: By: Michael John Z. Principio, RN, RM, MancSarahlaine BrazasNo ratings yet
- CatheterizationDocument14 pagesCatheterizationV_RNNo ratings yet
- Pressure Flow Urodynamic Studies: The Gold Standard For Diagnosing Bladder Outlet ObstructionDocument8 pagesPressure Flow Urodynamic Studies: The Gold Standard For Diagnosing Bladder Outlet ObstructionmarcelloNo ratings yet
- L12 Enema and Catheterization PDFDocument11 pagesL12 Enema and Catheterization PDFAilyn ValmoresNo ratings yet
- Bladder Meridian - Guardian of PeaceDocument7 pagesBladder Meridian - Guardian of Peacemanket59No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument22 pagesNursing Care PlansAnonymous 0C4OZmR0% (1)
- Suprapubic CatheterizationDocument3 pagesSuprapubic CatheterizationHariniNo ratings yet
- Tubes, Catheters, and DrainsDocument17 pagesTubes, Catheters, and DrainsInnocent BachiNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)Document8 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)miftah ar rahmahNo ratings yet
- Prostate Infection: Acute Bacterial ProstatitisDocument3 pagesProstate Infection: Acute Bacterial ProstatitisZammira MutiaNo ratings yet
- Is Early Surgical Treatment For Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Preferable Medical Therapy - Pros and ConsDocument11 pagesIs Early Surgical Treatment For Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Preferable Medical Therapy - Pros and ConsClaudia FreyonaNo ratings yet
- Central Council of Indian Medicine New Delhi: Syllabus of Ayurvedacharya (Bams) CourseDocument29 pagesCentral Council of Indian Medicine New Delhi: Syllabus of Ayurvedacharya (Bams) CourseShubham Jain100% (1)
- Stoevelaar, Herman JohanDocument232 pagesStoevelaar, Herman JohanKamran AfzalNo ratings yet
- Urological Emergency CasesDocument6 pagesUrological Emergency CasesjamilNo ratings yet
- Student's Assessment Form PDFDocument4 pagesStudent's Assessment Form PDFpatriarch_fall100% (1)
- 1 - Inctruments KM RDocument33 pages1 - Inctruments KM RHelene AlawamiNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi Sistem PerkemihanDocument24 pagesPatofisiologi Sistem PerkemihanMasna Arisah NasutionNo ratings yet
- Cateter JurnalDocument10 pagesCateter JurnalLeli Khairani AdnanNo ratings yet
- BPH InternetDocument72 pagesBPH InternetDesty ArianiNo ratings yet
- Sas 30Document2 pagesSas 30Sistine Rose LabajoNo ratings yet
- Remedy Rate3Document16 pagesRemedy Rate3Divyajyoti DevaNo ratings yet
- Peran Dokter Keluarga Dalam Penatalaksanaan Komprehensif Keganasan Prostat 2018 DR Yusuf Alam R PDFDocument87 pagesPeran Dokter Keluarga Dalam Penatalaksanaan Komprehensif Keganasan Prostat 2018 DR Yusuf Alam R PDFBestariayuNo ratings yet
- Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) - DHT Stimulates Cell Growth in The Tissue That Lines The Prostate GlandDocument7 pagesDihydrotestosterone (DHT) - DHT Stimulates Cell Growth in The Tissue That Lines The Prostate GlandPeter Kenneth LampitocNo ratings yet
- Enlarged Prostate Booklet PDFDocument52 pagesEnlarged Prostate Booklet PDFnabin hamalNo ratings yet