Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 viewsLesson 2
Lesson 2
Uploaded by
JESSECA MARIE FERNANDEZThis document discusses key concepts related to entrepreneurship including the entrepreneurial process and opportunity identification.
The entrepreneurial process involves all functions, activities, and actions associated with identifying opportunities and bringing together necessary resources to start a new business. It includes innovation, triggering events, and opportunity identification.
Opportunity identification involves scanning the internal and external environment, identifying potential opportunities, developing and evaluating opportunities, and evaluating the entrepreneurial team. Factors like the product/service, market opportunity, costs/pricing, profitability, capital requirements, and risks are evaluated to determine if an identified opportunity is viable.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Crisis in The Red Zone The Story of The Deadliest Ebola Outbreak in History and of The Outbreaks To Come Richard PrestonDocument43 pagesCrisis in The Red Zone The Story of The Deadliest Ebola Outbreak in History and of The Outbreaks To Come Richard Prestonryan.salvo790100% (6)
- Entrepreneurship Full NotesDocument173 pagesEntrepreneurship Full Notesalokshri2587% (377)
- RIPMWC 2019-2021 SolutionsDocument15 pagesRIPMWC 2019-2021 SolutionsMarilyn CitadelNo ratings yet
- Ravengro Expanded CompleteDocument10 pagesRavengro Expanded Completeitsme5616No ratings yet
- What Customers Want: Using Outcome-Driven Innovation to Create Breakthrough Products and Services: Using Outcome-Driven Innovation to Create Breakthrough Products and ServicesFrom EverandWhat Customers Want: Using Outcome-Driven Innovation to Create Breakthrough Products and Services: Using Outcome-Driven Innovation to Create Breakthrough Products and ServicesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (23)
- Advanced Corporate Finance Quiz 2 SolutionsDocument3 pagesAdvanced Corporate Finance Quiz 2 SolutionslaurenNo ratings yet
- 3rd March 2022Document34 pages3rd March 2022simiyustevensNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document25 pagesCH 2amonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NewDocument33 pagesChapter 2 Newbesedegefub9131No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document32 pagesChapter 2AYNETU TEREFENo ratings yet
- Enter Ch-2 NewDocument26 pagesEnter Ch-2 NewTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Business Planning: Chapter ObjectivesDocument33 pagesBusiness Planning: Chapter ObjectivesyeabtsegaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 B PlanDocument83 pagesCH 2 B PlanEsayas NashaNo ratings yet
- R2: Rec Ogn Itio N, G Ene Rat Ing Eas, SP LA NN INGDocument91 pagesR2: Rec Ogn Itio N, G Ene Rat Ing Eas, SP LA NN INGAmirNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Feasibility of A New Venture 1.1 Assessment and Evaluation of Entrepreneurial OpportunitiesDocument13 pagesAssessing The Feasibility of A New Venture 1.1 Assessment and Evaluation of Entrepreneurial OpportunitiesBereket Desalegn100% (1)
- The Entrepreneurial & Intrapreneurial Mind-1Document25 pagesThe Entrepreneurial & Intrapreneurial Mind-1J BNo ratings yet
- A EnC9 PADocument31 pagesA EnC9 PAAnto DNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 Feasibility Studies and Business Plan LastDocument153 pagesChapter 04 Feasibility Studies and Business Plan Lastኢትኤል ኢትዮጵNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Business PlanningDocument39 pagesCHAPTER 2 Business PlanningFiromsa DineNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Business PlanDocument39 pagesCHAPTER 2 Business PlanSelam TenayeNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Development - An Introduction: Lecture Delivered by - Prof. Kumar Arijit (Asst. Prof. - Finance)Document21 pagesEntrepreneurship Development - An Introduction: Lecture Delivered by - Prof. Kumar Arijit (Asst. Prof. - Finance)Manasa P SNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Week 2 Opportunity+RecognitionDocument27 pagesEntrepreneurship Week 2 Opportunity+RecognitionCassandra AguiluchoNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Development - An Introduction: Lecture Delivered by - Prof. Kumar Arijit (Asst. Prof. - Finance)Document24 pagesEntrepreneurship Development - An Introduction: Lecture Delivered by - Prof. Kumar Arijit (Asst. Prof. - Finance)Shashi Bhushan100% (1)
- Lecture 3 - Feasibility AnalysisDocument20 pagesLecture 3 - Feasibility AnalysisWasay HanifNo ratings yet
- MBA-Marketing M-Developing Marketing StrategiesDocument12 pagesMBA-Marketing M-Developing Marketing StrategiesPavan AlluriNo ratings yet
- Environment and MarketDocument39 pagesEnvironment and MarketJoni MurphyNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT OF ENTREPRENEURIAL OPPORTUNITIES GROUP 6 Saratao Achay LastimosoDocument31 pagesASSESSMENT OF ENTREPRENEURIAL OPPORTUNITIES GROUP 6 Saratao Achay LastimosoNyxz NightNo ratings yet
- Ch.8 New Ventr DevpDocument18 pagesCh.8 New Ventr DevpRitik MishraNo ratings yet
- EEB Cocludinging LectureDocument360 pagesEEB Cocludinging Lectureaepatil74No ratings yet
- Business SWOT Analysis Template PDF Download PDFDocument2 pagesBusiness SWOT Analysis Template PDF Download PDFSabhaya ChiragNo ratings yet
- ENVC Chapter 4 PDFDocument34 pagesENVC Chapter 4 PDFPotta SusmithaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Development Unit 2Document91 pagesEntrepreneurship Development Unit 2LAKSHMI MOUNICA MALLADINo ratings yet
- LO 2 Develop BusinssDocument44 pagesLO 2 Develop BusinssAb AbelNo ratings yet
- The Seven Domains Model - JabDocument27 pagesThe Seven Domains Model - JabpruthirajpNo ratings yet
- 1) Pitch Your Business IdeaDocument16 pages1) Pitch Your Business IdeaIvan Fong100% (1)
- Bird in Hand PrincipleDocument8 pagesBird in Hand Principlesripukrishna1711No ratings yet
- CH 4 Feasibility Study and Business PlanDocument79 pagesCH 4 Feasibility Study and Business PlanMihretab Bizuayehu (Mera)No ratings yet
- CH 4 Feasibility Study and Business PlanDocument87 pagesCH 4 Feasibility Study and Business PlanMihretab Bizuayehu (Mera)No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Chap 2 Note - 062528Document18 pagesEntrepreneurship Chap 2 Note - 062528tizazu bimrewNo ratings yet
- SOE 401 - Engineering Econs - Entre Lecture4 - Mr. Seini - DR Gazali - 2023Document80 pagesSOE 401 - Engineering Econs - Entre Lecture4 - Mr. Seini - DR Gazali - 2023safianuharunNo ratings yet
- Nature & Development of EntrepreneurshipDocument66 pagesNature & Development of EntrepreneurshiptrishikinNo ratings yet
- UNIT II - New IdeasDocument39 pagesUNIT II - New IdeasShivam GoelNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document12 pagesModule 3Christian Luis De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument39 pagesChapter TwoKalkidan NigatuNo ratings yet
- Environmental Analysis: Business Opportunity IdentificationDocument27 pagesEnvironmental Analysis: Business Opportunity IdentificationShane Barles100% (1)
- Chapter TwoDocument75 pagesChapter TwoGirma MogesNo ratings yet
- Business Planning Basics Amy ShapiroDocument35 pagesBusiness Planning Basics Amy ShapiroWAWAN SAHRONINo ratings yet
- Appreciation On Business Planning: AGEC 04 Introduction To Enterprise and EntrepreneurshipDocument56 pagesAppreciation On Business Planning: AGEC 04 Introduction To Enterprise and EntrepreneurshipAloi MendezNo ratings yet
- Group 6Document11 pagesGroup 6Marites Peñaranda LebigaNo ratings yet
- EntrepreneurshipDocument24 pagesEntrepreneurshipkanishka89No ratings yet
- Jagran Lakecity University: Jagran School of Commerce & EconomicsDocument11 pagesJagran Lakecity University: Jagran School of Commerce & EconomicsvibhuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Feasibility Study Vs Business PlanDocument31 pagesLecture 2 - Feasibility Study Vs Business PlanTiberiu CostinNo ratings yet
- Strategic Marketing: 2 Year Full Time PGDM Session 3Document35 pagesStrategic Marketing: 2 Year Full Time PGDM Session 3Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- CUL 407 WEEK 3 Feasibility StudiesDocument22 pagesCUL 407 WEEK 3 Feasibility Studieshasan coşkunNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management-1: Dr. Kamal Kishore SharmaDocument45 pagesStrategic Management-1: Dr. Kamal Kishore SharmaRadhakrishnan PadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- QB-CH 1-Entrepreneurial OpportunityDocument17 pagesQB-CH 1-Entrepreneurial OpportunityPariNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneur Process345Document35 pagesEntrepreneur Process345Abey ShimelisNo ratings yet
- Section 2 From Idea To Opportunity Section 2 From Idea To OpportunityDocument22 pagesSection 2 From Idea To Opportunity Section 2 From Idea To OpportunityJAYANT MAHAJANNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Knowing OneselfDocument46 pagesModule 1 Knowing OneselfjulietpamintuanNo ratings yet
- "Elevate Your Entrepreneurial Journey Unleashing the Power of Startup Success": BusinessFrom Everand"Elevate Your Entrepreneurial Journey Unleashing the Power of Startup Success": BusinessNo ratings yet
- How to Audit your Intellectual Property (IP)From EverandHow to Audit your Intellectual Property (IP)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Executing Innovation: Expert Solutions to Everyday ChallengesFrom EverandExecuting Innovation: Expert Solutions to Everyday ChallengesNo ratings yet
- Ge 9 SimDocument83 pagesGe 9 SimJESSECA MARIE FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Acc225 Business Law and RegulationsDocument201 pagesAcc225 Business Law and RegulationsJESSECA MARIE FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Summary MMVDocument20 pagesSummary MMVJESSECA MARIE FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- ACC 212 Market Watch Weekly Scoring SheetDocument3 pagesACC 212 Market Watch Weekly Scoring SheetJESSECA MARIE FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Acc213 Week 4 5 MMV MyvDocument40 pagesAcc213 Week 4 5 MMV MyvJESSECA MARIE FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Famous Letters of Mahatma GandhiDocument146 pagesFamous Letters of Mahatma Gandhivishalnaidu2010No ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - AnswerDocument10 pagesChapter 03 - AnswerMinsky GoceNo ratings yet
- Postmodernism and Its Comparative Education ImplicationsDocument18 pagesPostmodernism and Its Comparative Education ImplicationsLetta ZaglaNo ratings yet
- Einhorn, E S & Logue, J - Modern Welfare States - Scandinavial Politics and Policy in The Global AgeDocument7 pagesEinhorn, E S & Logue, J - Modern Welfare States - Scandinavial Politics and Policy in The Global AgeclawthebandNo ratings yet
- Critical Essay in Reading in The Philippine HistoryDocument24 pagesCritical Essay in Reading in The Philippine HistoryCatherine EscabusaNo ratings yet
- If You Liked Selling The 740 Series You'll Love Selling The New 753/754Document8 pagesIf You Liked Selling The 740 Series You'll Love Selling The New 753/754HINANo ratings yet
- Case Study 6: Maternal and Child NursingDocument18 pagesCase Study 6: Maternal and Child NursingJayson Ray AbellarNo ratings yet
- (ACV-S01) Week 01 - Pre-Task - Quiz - Weekly Quiz (PA) - INGLES IV (37832)Document5 pages(ACV-S01) Week 01 - Pre-Task - Quiz - Weekly Quiz (PA) - INGLES IV (37832)Alicia PadillaNo ratings yet
- Canadian Business English Canadian 7th Edition Guffey Test Bank 1Document20 pagesCanadian Business English Canadian 7th Edition Guffey Test Bank 1tedNo ratings yet
- Python + OpenAI Powered Humanoid AI Desktop Assistant Robot Guided by - Dr. S. Malathi - Ashwin M - 2020PECAI130 - Rijo Benny - 2020PECAI152Document10 pagesPython + OpenAI Powered Humanoid AI Desktop Assistant Robot Guided by - Dr. S. Malathi - Ashwin M - 2020PECAI130 - Rijo Benny - 2020PECAI152Ashwin MNo ratings yet
- Hall Management - Rules, Procedures and GuidelinesDocument27 pagesHall Management - Rules, Procedures and GuidelinesNitish ShankarNo ratings yet
- Legal Metrology Act: Analysis: Dhruv Sharma, 01319103516 BBALLB 9Document4 pagesLegal Metrology Act: Analysis: Dhruv Sharma, 01319103516 BBALLB 9dhruv sharmaNo ratings yet
- Matabuena vs. CervantesDocument1 pageMatabuena vs. CervantesAndrew GallardoNo ratings yet
- Service Operation Management: Session 8Document59 pagesService Operation Management: Session 8mukul3087_305865623No ratings yet
- Julie Tozer Aldrich ResumeDocument2 pagesJulie Tozer Aldrich ResumeJulie Tozer AldrichNo ratings yet
- 2012-02-09 - Moneysaver - Lewis-Clark EditionDocument20 pages2012-02-09 - Moneysaver - Lewis-Clark EditionDavid ArndtNo ratings yet
- Bey A1plus GrEx Wsh3&4 PDFDocument1 pageBey A1plus GrEx Wsh3&4 PDFCeciBravoNo ratings yet
- ABO Blood Group DiscrepanciesDocument9 pagesABO Blood Group DiscrepanciesRichard SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Robin Hood Moral Hero or Immoral ThiefDocument2 pagesRobin Hood Moral Hero or Immoral Thiefanon-7131830% (1)
- Anatomy Physiology and Disease An Interactive Journey For Health Professions 2Nd Edition Colbert Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument8 pagesAnatomy Physiology and Disease An Interactive Journey For Health Professions 2Nd Edition Colbert Test Bank Full Chapter PDFcatherine.hanson719100% (15)
- Examiner Application FormDocument5 pagesExaminer Application FormKcaj WongNo ratings yet
- ChecklistDocument2 pagesChecklistLuisNo ratings yet
- ADR TopicsDocument14 pagesADR TopicsSathvik ReddyNo ratings yet
- Treasurer's+Report+ +AGA+February+2021Document12 pagesTreasurer's+Report+ +AGA+February+2021avesta HatamiNo ratings yet
- ESP32 Tutorial What Do You Have To Know About The ESP32 MicrocontrollerDocument10 pagesESP32 Tutorial What Do You Have To Know About The ESP32 MicrocontrollergessycaNo ratings yet
Lesson 2
Lesson 2
Uploaded by
JESSECA MARIE FERNANDEZ0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views18 pagesThis document discusses key concepts related to entrepreneurship including the entrepreneurial process and opportunity identification.
The entrepreneurial process involves all functions, activities, and actions associated with identifying opportunities and bringing together necessary resources to start a new business. It includes innovation, triggering events, and opportunity identification.
Opportunity identification involves scanning the internal and external environment, identifying potential opportunities, developing and evaluating opportunities, and evaluating the entrepreneurial team. Factors like the product/service, market opportunity, costs/pricing, profitability, capital requirements, and risks are evaluated to determine if an identified opportunity is viable.
Original Description:
Original Title
LESSON-2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses key concepts related to entrepreneurship including the entrepreneurial process and opportunity identification.
The entrepreneurial process involves all functions, activities, and actions associated with identifying opportunities and bringing together necessary resources to start a new business. It includes innovation, triggering events, and opportunity identification.
Opportunity identification involves scanning the internal and external environment, identifying potential opportunities, developing and evaluating opportunities, and evaluating the entrepreneurial team. Factors like the product/service, market opportunity, costs/pricing, profitability, capital requirements, and risks are evaluated to determine if an identified opportunity is viable.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views18 pagesLesson 2
Lesson 2
Uploaded by
JESSECA MARIE FERNANDEZThis document discusses key concepts related to entrepreneurship including the entrepreneurial process and opportunity identification.
The entrepreneurial process involves all functions, activities, and actions associated with identifying opportunities and bringing together necessary resources to start a new business. It includes innovation, triggering events, and opportunity identification.
Opportunity identification involves scanning the internal and external environment, identifying potential opportunities, developing and evaluating opportunities, and evaluating the entrepreneurial team. Factors like the product/service, market opportunity, costs/pricing, profitability, capital requirements, and risks are evaluated to determine if an identified opportunity is viable.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 18
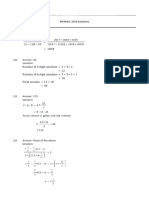
Lesson 2 1
Metalanguage
1. Marketing. "The process of planning and executing
conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of
ideas, goods, and services to create exchanges that
satisfy individual and organizational objectives" (AMA,
2013).
2. Networking. "The activity of meeting people who
might be useful to know, especially in your job."
(Source:
https://dictionary.cambridge.org/dictionary/english/net
working)
Entrepreneurial Process
- A course of action that involves all functions, activities and
actions associated with identifying and evaluating perceived
opportunities and the bringing together of resources necessary
for the successful formation of a new firm to pursue and seize
the said opportunities (Bygrave, 1997:2; Cornwall & Naughton,
2003:62).”
1. Innovation, which includes generating the idea, innovation,
identifying a market opportunity, information search, conception,
screening ideas for feasibility, identifying where to extract value
and the development of the product or service.
Stages Activities Skills
Entrepreneurial 1. Getting the idea 1. Technical skills
Process - Stage 1 2. Opportunity identification (idea/scanning
the environment, identifying the opportunity,
developing the opportunity, evaluating the
opportunity and evaluating the team) 2. Communication
3. Opportunity development 3. Problem solving
4. Opportunity evaluation 4. Motivation (need for
achievement)
5. Assessment of the entrepreneurial team 5. Adaptability to change
6. Time management skills
7. Financial management
8. Human resources
9. Marketing
10. Networking
The Opportunity Identification
The opportunity identification in the stage 1 of the entrepreneurial process
includes opportunity identification.
1. Idea/scanning the environment. This involves macro scanning and
micro scanning.
• Micro scanning is done when one is studying the micro environment
which involves the environment that has a direct impact on the business
being planned. These environments could influence the daily undertakings
of your business but the effects are usually not long-lasting.
• The micro environment includes customers, suppliers, intermediaries,
competitors and the general public.
• On the other hand, the macro-environment is composed of environments
that the company can't control but can be really easily affected by it.
Business establishments are usually encouraged to track these
environments for patterns and updates.
• The macro-environment of the firm includes demographic forces,
economic factors, technological factors, legal factors, political
factors, geographic factors, cultural factors etc.
The Opportunity Identification
2. Identifying the opportunity. The entrepreneur is encouraged to
understand the difference between challenges and opportunities.
Opportunities can come from personal experiences or from observations
gathered as a result of research. The goal here is to seek better ways of
surviving the existing competition.
3 . Developing the opportunity. The timely adaption of opportunities fit for
the target market can be a good ticket to succeed. Kodithuwakhu & Rosa
(2002:434) defined this stage as the process of combining resources in order
to pursue the identified market opportunities. A systematic research in order to
refine the ideas of an entrepreneur is necessary in this stage.
4. Evaluating the opportunity. This screening and evaluation part is critical.
A professionally evaluated product or service is essential before taking the
risk. Several authors suggested ways in order to evaluate a business idea.
The table below is suggested by several authors ((Timmons, 1999:109;
Rwigema & Venter, 2004:171; Gartner et al, 1999:223; Carter et al, 1996:157).
It is encouraged that an entrepreneurs must answer each questions.
Evaluating the opportunity
Business factor Questions for evaluation
Product or service
• Description of the product or service, its differentiator, purpose and
the need it fills
• What competitive advantage / benefits does the product have?
• What is the required customer care support for this product/service?
• Is the company able to produce product and supply required aftercare
support?
Market opportunity
• Where is the market demand? What is the target market? Is it generic
or a niche?
• Industry characteristics (growth rates, change, entry barriers).
• What market share can the product reasonably expect today? In 2, 5 or
10 years?
• Timing and length of the window of opportunity?
• What competition exists in this market? Substitutes? How big is their
turnover?
• How accessible are the desired distribution channels?
Evaluating the opportunity
Business factor Questions for evaluation
Costing and pricing
• How much will it cost to develop the product and
commercialize it?
• Where will the funds come from?
• How do the pricing, costs and economies of scale
compare with competitors?
• How easy is it to acquire equipment, skills and other
inputs required?
Profitability
• Where is the money to be made in this activity? What are
the gross margins?
• Would the return on investment be acceptable? What is
the payback period?
• What are the cash flow patterns and the source of working
capital?
Evaluating the opportunity
Business factor Questions for evaluation
Capital requirements • How much capital (people, operating expense and assets)
is required to start?
• What are the long-term capital needs?
• How much of the required capital is secured and where
will the rest come from?
• What securities are available to guarantee the required
funds?
• Is there a list of potential funders? In case the funders
withdraw their capital?
Issues and risks
• What risks (real and perceived) are inherent with the
product/service?
• Industry based risks e.g. is the market on a decline?
• Are there plans for surviving the death of the lead
entrepreneur?
• Unreliable forecasts? Inadequate cash flow?
• Inability to grow with the demand or cope with shrinking
sales?
• Supplier and value chain management?
The Opportunity Identification
5. Evaluating the team. A team with strong skills can pursue
opportunities better. After evaluating an opportunity, it is
essential to check on the people who will make the idea into a
reality. Bygrave (1997) and Gartner et al (1999) suggested to
evaluate the team using the questions below.
Business
Questions for evaluation
factor
Focus • Is the founder really an entrepreneur, bent on
building a company?
• Does the entrepreneur (or his team) have some
experience (work or industry)?
• Do they really like this product/sector? Do they
really want this?
• Can the team create products to suit that market
need?
• How stressful is the opportunity for the team?
• Does the team have the necessary selling and
Selling closing skills?
Business
Questions for evaluation
factor
Management
• Who will work full time? Do your managers represent
competitive advantage?
• Does the team have the necessary management and technical
skills?
• If the required skills are not available, can they be acquired at
competitive rates?
• How is their relationship with the entrepreneur, commitment and
motivation?
Ownership • Have the critical decisions about ownership and equity splits
been resolved?
• Are the members committed to these?
• Does the owners have enough financial capital for required own
contributions?
2. Triggering event, which includes gestation, the motivation to start a
business, the decision to proceed, the business planning, identifying the
different resources required, risk assessment, resource acquisition and
assembling.
Entrepreneurial Process 1. Motivation to become an
- Stage 2 entrepreneur 1. Technical skills (T/S)
2. Planning 2. Problem solving
3. Gathering resources 3. Numeracy and literacy
4. Communication skills
5. Motivation (need for achievement)
6. Adaptability to change
7. Learning abilities
8. Decision-making skills
9. Negotiating skill
10. Financial management
11. Human resources
12. Legal
13. Marketing
14. Networking
15. Planning
16. Role model interpretation
17. Ability to gather and control
resources
18. Calculated risk taking
3. Implementation, which includes infancy, incorporation, setting up and launching
the new venture, business strategy, implementing the business plan, running the
business, deploying of resources, building success and managing the venture.
Skills required for success in 1. improving organizational capabilities 1. Technical skills (T/S)
stage 3 2. implementing a management style in order to grow 2. Problem solving
managerial competencies
3. setting up production processes 3. Decision making skills
4. setting up structures and systems
4. Motivation (need for achievement)
5. ensuring quality control 5. Time management
6. waste elimination and cost effectiveness activities 6. Negotiating skills
7. dealing with distributors and suppliers 7. Communication skills
8. selling to customers 8. Adaptability to change
9. collecting the finance 9. Learning abilities
10. resolving operational problems 10. Business systems management
11. fending off competitors 11. General management
12. steering the organization towards its goals and 12. Financial management
determining the key variables for success
13. Human resources management skills
14. ICT skills
15. Marketing
16. Networking
17. Operational
18. Planning
19. Value chain management
20. Creativity
21. Innovation
22. Opportunity recognition
23. Role model interpretation
24. Ability to gather and control resources
25. Calculated risk taking
4. Growth which includes adolescence, maximizing profits, harvesting the rewards
and continually growing the venture to include other opportunities.
Entrepreneurial 1. Market expansion 1. Technical Skills (T/S)
Process - Stage 4 2. Technological change 2. Problem solving
3. Garnering resources 3. Adaptability to change
4. Operations 4. Learning abilities
5. Organizational development 5. Numeracy and literacy
6. Motivation (need for achievement)
7. Time management
8. Communication skills
9. Negotiating skills
10. Decision making skills
11. Business systems management
12. General management
13. Financial management
14. ICT skills
15. Marketing
16. Networking
17. Operational
18. Research and development
19. Creativity
20. Innovation
21. Opportunity recognition
22. Ability to gather and control
resources
23. Calculated risk taking
• From the above table, it can be noticed that only
the motivation as a skill is considered important
in all of the stages in the entrepreneurship
process. Moreover, marketing is deemed
important in all stage except in stage 2.
• The gathering of resources started to become an
important skill from stage 2 until stage 4.
• Opportunity identification is considered important
in stage 1 and 4.
• Furthermore, human resources management,
financial management and technical skills are
deemed necessary in stage 3 and 4.
• Creativity can be seen as an important skill for
stage 1 and 3
• Lastly, communication, operations and
innovation skills are considered key skills in
stage 3.
Thank you....
Any Questions......
You might also like
- Crisis in The Red Zone The Story of The Deadliest Ebola Outbreak in History and of The Outbreaks To Come Richard PrestonDocument43 pagesCrisis in The Red Zone The Story of The Deadliest Ebola Outbreak in History and of The Outbreaks To Come Richard Prestonryan.salvo790100% (6)
- Entrepreneurship Full NotesDocument173 pagesEntrepreneurship Full Notesalokshri2587% (377)
- RIPMWC 2019-2021 SolutionsDocument15 pagesRIPMWC 2019-2021 SolutionsMarilyn CitadelNo ratings yet
- Ravengro Expanded CompleteDocument10 pagesRavengro Expanded Completeitsme5616No ratings yet
- What Customers Want: Using Outcome-Driven Innovation to Create Breakthrough Products and Services: Using Outcome-Driven Innovation to Create Breakthrough Products and ServicesFrom EverandWhat Customers Want: Using Outcome-Driven Innovation to Create Breakthrough Products and Services: Using Outcome-Driven Innovation to Create Breakthrough Products and ServicesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (23)
- Advanced Corporate Finance Quiz 2 SolutionsDocument3 pagesAdvanced Corporate Finance Quiz 2 SolutionslaurenNo ratings yet
- 3rd March 2022Document34 pages3rd March 2022simiyustevensNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document25 pagesCH 2amonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NewDocument33 pagesChapter 2 Newbesedegefub9131No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document32 pagesChapter 2AYNETU TEREFENo ratings yet
- Enter Ch-2 NewDocument26 pagesEnter Ch-2 NewTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Business Planning: Chapter ObjectivesDocument33 pagesBusiness Planning: Chapter ObjectivesyeabtsegaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 B PlanDocument83 pagesCH 2 B PlanEsayas NashaNo ratings yet
- R2: Rec Ogn Itio N, G Ene Rat Ing Eas, SP LA NN INGDocument91 pagesR2: Rec Ogn Itio N, G Ene Rat Ing Eas, SP LA NN INGAmirNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Feasibility of A New Venture 1.1 Assessment and Evaluation of Entrepreneurial OpportunitiesDocument13 pagesAssessing The Feasibility of A New Venture 1.1 Assessment and Evaluation of Entrepreneurial OpportunitiesBereket Desalegn100% (1)
- The Entrepreneurial & Intrapreneurial Mind-1Document25 pagesThe Entrepreneurial & Intrapreneurial Mind-1J BNo ratings yet
- A EnC9 PADocument31 pagesA EnC9 PAAnto DNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 Feasibility Studies and Business Plan LastDocument153 pagesChapter 04 Feasibility Studies and Business Plan Lastኢትኤል ኢትዮጵNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Business PlanningDocument39 pagesCHAPTER 2 Business PlanningFiromsa DineNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Business PlanDocument39 pagesCHAPTER 2 Business PlanSelam TenayeNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Development - An Introduction: Lecture Delivered by - Prof. Kumar Arijit (Asst. Prof. - Finance)Document21 pagesEntrepreneurship Development - An Introduction: Lecture Delivered by - Prof. Kumar Arijit (Asst. Prof. - Finance)Manasa P SNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Week 2 Opportunity+RecognitionDocument27 pagesEntrepreneurship Week 2 Opportunity+RecognitionCassandra AguiluchoNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Development - An Introduction: Lecture Delivered by - Prof. Kumar Arijit (Asst. Prof. - Finance)Document24 pagesEntrepreneurship Development - An Introduction: Lecture Delivered by - Prof. Kumar Arijit (Asst. Prof. - Finance)Shashi Bhushan100% (1)
- Lecture 3 - Feasibility AnalysisDocument20 pagesLecture 3 - Feasibility AnalysisWasay HanifNo ratings yet
- MBA-Marketing M-Developing Marketing StrategiesDocument12 pagesMBA-Marketing M-Developing Marketing StrategiesPavan AlluriNo ratings yet
- Environment and MarketDocument39 pagesEnvironment and MarketJoni MurphyNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT OF ENTREPRENEURIAL OPPORTUNITIES GROUP 6 Saratao Achay LastimosoDocument31 pagesASSESSMENT OF ENTREPRENEURIAL OPPORTUNITIES GROUP 6 Saratao Achay LastimosoNyxz NightNo ratings yet
- Ch.8 New Ventr DevpDocument18 pagesCh.8 New Ventr DevpRitik MishraNo ratings yet
- EEB Cocludinging LectureDocument360 pagesEEB Cocludinging Lectureaepatil74No ratings yet
- Business SWOT Analysis Template PDF Download PDFDocument2 pagesBusiness SWOT Analysis Template PDF Download PDFSabhaya ChiragNo ratings yet
- ENVC Chapter 4 PDFDocument34 pagesENVC Chapter 4 PDFPotta SusmithaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Development Unit 2Document91 pagesEntrepreneurship Development Unit 2LAKSHMI MOUNICA MALLADINo ratings yet
- LO 2 Develop BusinssDocument44 pagesLO 2 Develop BusinssAb AbelNo ratings yet
- The Seven Domains Model - JabDocument27 pagesThe Seven Domains Model - JabpruthirajpNo ratings yet
- 1) Pitch Your Business IdeaDocument16 pages1) Pitch Your Business IdeaIvan Fong100% (1)
- Bird in Hand PrincipleDocument8 pagesBird in Hand Principlesripukrishna1711No ratings yet
- CH 4 Feasibility Study and Business PlanDocument79 pagesCH 4 Feasibility Study and Business PlanMihretab Bizuayehu (Mera)No ratings yet
- CH 4 Feasibility Study and Business PlanDocument87 pagesCH 4 Feasibility Study and Business PlanMihretab Bizuayehu (Mera)No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Chap 2 Note - 062528Document18 pagesEntrepreneurship Chap 2 Note - 062528tizazu bimrewNo ratings yet
- SOE 401 - Engineering Econs - Entre Lecture4 - Mr. Seini - DR Gazali - 2023Document80 pagesSOE 401 - Engineering Econs - Entre Lecture4 - Mr. Seini - DR Gazali - 2023safianuharunNo ratings yet
- Nature & Development of EntrepreneurshipDocument66 pagesNature & Development of EntrepreneurshiptrishikinNo ratings yet
- UNIT II - New IdeasDocument39 pagesUNIT II - New IdeasShivam GoelNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document12 pagesModule 3Christian Luis De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument39 pagesChapter TwoKalkidan NigatuNo ratings yet
- Environmental Analysis: Business Opportunity IdentificationDocument27 pagesEnvironmental Analysis: Business Opportunity IdentificationShane Barles100% (1)
- Chapter TwoDocument75 pagesChapter TwoGirma MogesNo ratings yet
- Business Planning Basics Amy ShapiroDocument35 pagesBusiness Planning Basics Amy ShapiroWAWAN SAHRONINo ratings yet
- Appreciation On Business Planning: AGEC 04 Introduction To Enterprise and EntrepreneurshipDocument56 pagesAppreciation On Business Planning: AGEC 04 Introduction To Enterprise and EntrepreneurshipAloi MendezNo ratings yet
- Group 6Document11 pagesGroup 6Marites Peñaranda LebigaNo ratings yet
- EntrepreneurshipDocument24 pagesEntrepreneurshipkanishka89No ratings yet
- Jagran Lakecity University: Jagran School of Commerce & EconomicsDocument11 pagesJagran Lakecity University: Jagran School of Commerce & EconomicsvibhuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Feasibility Study Vs Business PlanDocument31 pagesLecture 2 - Feasibility Study Vs Business PlanTiberiu CostinNo ratings yet
- Strategic Marketing: 2 Year Full Time PGDM Session 3Document35 pagesStrategic Marketing: 2 Year Full Time PGDM Session 3Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- CUL 407 WEEK 3 Feasibility StudiesDocument22 pagesCUL 407 WEEK 3 Feasibility Studieshasan coşkunNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management-1: Dr. Kamal Kishore SharmaDocument45 pagesStrategic Management-1: Dr. Kamal Kishore SharmaRadhakrishnan PadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- QB-CH 1-Entrepreneurial OpportunityDocument17 pagesQB-CH 1-Entrepreneurial OpportunityPariNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneur Process345Document35 pagesEntrepreneur Process345Abey ShimelisNo ratings yet
- Section 2 From Idea To Opportunity Section 2 From Idea To OpportunityDocument22 pagesSection 2 From Idea To Opportunity Section 2 From Idea To OpportunityJAYANT MAHAJANNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Knowing OneselfDocument46 pagesModule 1 Knowing OneselfjulietpamintuanNo ratings yet
- "Elevate Your Entrepreneurial Journey Unleashing the Power of Startup Success": BusinessFrom Everand"Elevate Your Entrepreneurial Journey Unleashing the Power of Startup Success": BusinessNo ratings yet
- How to Audit your Intellectual Property (IP)From EverandHow to Audit your Intellectual Property (IP)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Executing Innovation: Expert Solutions to Everyday ChallengesFrom EverandExecuting Innovation: Expert Solutions to Everyday ChallengesNo ratings yet
- Ge 9 SimDocument83 pagesGe 9 SimJESSECA MARIE FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Acc225 Business Law and RegulationsDocument201 pagesAcc225 Business Law and RegulationsJESSECA MARIE FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Summary MMVDocument20 pagesSummary MMVJESSECA MARIE FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- ACC 212 Market Watch Weekly Scoring SheetDocument3 pagesACC 212 Market Watch Weekly Scoring SheetJESSECA MARIE FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Acc213 Week 4 5 MMV MyvDocument40 pagesAcc213 Week 4 5 MMV MyvJESSECA MARIE FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Famous Letters of Mahatma GandhiDocument146 pagesFamous Letters of Mahatma Gandhivishalnaidu2010No ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - AnswerDocument10 pagesChapter 03 - AnswerMinsky GoceNo ratings yet
- Postmodernism and Its Comparative Education ImplicationsDocument18 pagesPostmodernism and Its Comparative Education ImplicationsLetta ZaglaNo ratings yet
- Einhorn, E S & Logue, J - Modern Welfare States - Scandinavial Politics and Policy in The Global AgeDocument7 pagesEinhorn, E S & Logue, J - Modern Welfare States - Scandinavial Politics and Policy in The Global AgeclawthebandNo ratings yet
- Critical Essay in Reading in The Philippine HistoryDocument24 pagesCritical Essay in Reading in The Philippine HistoryCatherine EscabusaNo ratings yet
- If You Liked Selling The 740 Series You'll Love Selling The New 753/754Document8 pagesIf You Liked Selling The 740 Series You'll Love Selling The New 753/754HINANo ratings yet
- Case Study 6: Maternal and Child NursingDocument18 pagesCase Study 6: Maternal and Child NursingJayson Ray AbellarNo ratings yet
- (ACV-S01) Week 01 - Pre-Task - Quiz - Weekly Quiz (PA) - INGLES IV (37832)Document5 pages(ACV-S01) Week 01 - Pre-Task - Quiz - Weekly Quiz (PA) - INGLES IV (37832)Alicia PadillaNo ratings yet
- Canadian Business English Canadian 7th Edition Guffey Test Bank 1Document20 pagesCanadian Business English Canadian 7th Edition Guffey Test Bank 1tedNo ratings yet
- Python + OpenAI Powered Humanoid AI Desktop Assistant Robot Guided by - Dr. S. Malathi - Ashwin M - 2020PECAI130 - Rijo Benny - 2020PECAI152Document10 pagesPython + OpenAI Powered Humanoid AI Desktop Assistant Robot Guided by - Dr. S. Malathi - Ashwin M - 2020PECAI130 - Rijo Benny - 2020PECAI152Ashwin MNo ratings yet
- Hall Management - Rules, Procedures and GuidelinesDocument27 pagesHall Management - Rules, Procedures and GuidelinesNitish ShankarNo ratings yet
- Legal Metrology Act: Analysis: Dhruv Sharma, 01319103516 BBALLB 9Document4 pagesLegal Metrology Act: Analysis: Dhruv Sharma, 01319103516 BBALLB 9dhruv sharmaNo ratings yet
- Matabuena vs. CervantesDocument1 pageMatabuena vs. CervantesAndrew GallardoNo ratings yet
- Service Operation Management: Session 8Document59 pagesService Operation Management: Session 8mukul3087_305865623No ratings yet
- Julie Tozer Aldrich ResumeDocument2 pagesJulie Tozer Aldrich ResumeJulie Tozer AldrichNo ratings yet
- 2012-02-09 - Moneysaver - Lewis-Clark EditionDocument20 pages2012-02-09 - Moneysaver - Lewis-Clark EditionDavid ArndtNo ratings yet
- Bey A1plus GrEx Wsh3&4 PDFDocument1 pageBey A1plus GrEx Wsh3&4 PDFCeciBravoNo ratings yet
- ABO Blood Group DiscrepanciesDocument9 pagesABO Blood Group DiscrepanciesRichard SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Robin Hood Moral Hero or Immoral ThiefDocument2 pagesRobin Hood Moral Hero or Immoral Thiefanon-7131830% (1)
- Anatomy Physiology and Disease An Interactive Journey For Health Professions 2Nd Edition Colbert Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument8 pagesAnatomy Physiology and Disease An Interactive Journey For Health Professions 2Nd Edition Colbert Test Bank Full Chapter PDFcatherine.hanson719100% (15)
- Examiner Application FormDocument5 pagesExaminer Application FormKcaj WongNo ratings yet
- ChecklistDocument2 pagesChecklistLuisNo ratings yet
- ADR TopicsDocument14 pagesADR TopicsSathvik ReddyNo ratings yet
- Treasurer's+Report+ +AGA+February+2021Document12 pagesTreasurer's+Report+ +AGA+February+2021avesta HatamiNo ratings yet
- ESP32 Tutorial What Do You Have To Know About The ESP32 MicrocontrollerDocument10 pagesESP32 Tutorial What Do You Have To Know About The ESP32 MicrocontrollergessycaNo ratings yet