Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SCI1
SCI1
Uploaded by
Sebastian Walay Tuon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesFaults are zones of crushed rock that can extend kilometers underground. There are three main types of faults: normal faults occur during stretching and form valleys, strike-slip faults involve horizontal sliding of rock, and reverse faults happen during collisions and form mountains. Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy stored in faults, as the sides are pushed together over time until slipping past each other.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFaults are zones of crushed rock that can extend kilometers underground. There are three main types of faults: normal faults occur during stretching and form valleys, strike-slip faults involve horizontal sliding of rock, and reverse faults happen during collisions and form mountains. Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy stored in faults, as the sides are pushed together over time until slipping past each other.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesSCI1
SCI1
Uploaded by
Sebastian Walay TuonFaults are zones of crushed rock that can extend kilometers underground. There are three main types of faults: normal faults occur during stretching and form valleys, strike-slip faults involve horizontal sliding of rock, and reverse faults happen during collisions and form mountains. Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy stored in faults, as the sides are pushed together over time until slipping past each other.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
SCIENCE Q2
Week 1
Earthquake & Faults
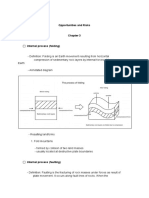
Fault - thin zones of crushed blocks of rocks. These are often in centimeters to thousands of
kilometers long. Their surfaces can be vertical or horizontal.
Earthquake - is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from the sudden release of
energy in the Earth’s lithosphere.
3 Types of Fault
Normal fault - two blocks of crust pull apart create space, stretching the crust into a valley.
- In a normal fault, the hanging wall drops down.
- valley
Strike-slip fault - rocks are sliding past each other horizontally.
Reverse fault - also known as thrust fault, sliding one block of crust on top of another.
- This fault is commonly found in collisions zones.
- mountain ranges
What causes Earthquakes
Stress in the outer layer of the Earth pushes the sides of the fault together. The grinding over the
surface of the fault holds the rocks together so they do not slip promptly when pushed sideways.
You might also like
- Earth Science 8 ReviewerDocument11 pagesEarth Science 8 ReviewerBraynell Owen ClaroNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 Q1W7 Dynamic of The EarthDocument25 pagesSCIENCE 10 Q1W7 Dynamic of The EarthtoshuaplayzminecraftNo ratings yet
- Movements of PlatesDocument29 pagesMovements of PlatesedceljanesolimanNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - 2nd Quarter EarthquakeDocument1 pageActivity 1 - 2nd Quarter Earthquakejay pascualNo ratings yet
- Stress and FaultsDocument36 pagesStress and FaultsG-9 BAÑADERA CHARCEL DNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Geological StructuresDocument50 pagesGroup 6 Geological StructuresAlexa Francoise Arao TanoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - ELSDocument50 pagesLesson 2 - ELSalshawy0909No ratings yet
- Research No.5Document11 pagesResearch No.5Ramona SmithNo ratings yet
- Earthquake and FaultsDocument1 pageEarthquake and FaultsTricia BautistaNo ratings yet
- NSTP Midterms Reviewer - 123446Document4 pagesNSTP Midterms Reviewer - 123446ShjajaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document23 pagesChapter 4Solomon DesalegnNo ratings yet
- 3 Kinds of Fault, Measuring Earthquake andDocument6 pages3 Kinds of Fault, Measuring Earthquake andMatthew TorrillaNo ratings yet
- M1-Topic 2. Plate Tectonics and Faults-1Document11 pagesM1-Topic 2. Plate Tectonics and Faults-1Mark Andykenn Liaga MaglinteNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes: Ive Polanco 14-1006Document17 pagesEarthquakes: Ive Polanco 14-1006LossyTNo ratings yet
- Sculpturing The Earth SurfaceDocument3 pagesSculpturing The Earth SurfaceBasco Martin JrNo ratings yet
- Folding and Faulting of RocksDocument1 pageFolding and Faulting of RocksSierra DrevouxNo ratings yet
- Driven by The Internal Heat of The Earth, Which in Turn Results From The Radioactive Decay of Elements Deep Beneath The SurfaceDocument2 pagesDriven by The Internal Heat of The Earth, Which in Turn Results From The Radioactive Decay of Elements Deep Beneath The SurfaceSheryl BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Modules 5-8Document32 pagesEarth and Life Science Modules 5-8elise tanNo ratings yet
- 06 Geological Structures: FracturesDocument51 pages06 Geological Structures: FracturesParallag AlexNo ratings yet
- Earth Sci ReviewerDocument5 pagesEarth Sci Reviewerclarenceegliane204No ratings yet
- Proccesses and Landforms Along Plate BoundariesDocument87 pagesProccesses and Landforms Along Plate Boundariesayeshakelly268No ratings yet
- Movement of The Earths CrustDocument18 pagesMovement of The Earths CrustFinestzacky08No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Elements of SeismologyDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Elements of SeismologyJoshua John JulioNo ratings yet
- Earthquake FaultsDocument35 pagesEarthquake FaultsFauzea MadjadNo ratings yet
- Danes Kynel G Ricafort ScienceDocument3 pagesDanes Kynel G Ricafort ScienceJenny Ann Mariel ManaladNo ratings yet
- Types of Plate Boundaries: 1. Convergent Boundaries - Where Two Plates Are CollidingDocument2 pagesTypes of Plate Boundaries: 1. Convergent Boundaries - Where Two Plates Are CollidingstephNo ratings yet
- Week 7Document31 pagesWeek 7cathcathnarag07No ratings yet
- Movement of The Earths Crust 1234468842119210 2Document21 pagesMovement of The Earths Crust 1234468842119210 2Rhenn SongcoNo ratings yet
- Dynamic EarthDocument30 pagesDynamic EarthKathy Claire BallegaNo ratings yet
- NOTES - Earthquake and FaultsDocument1 pageNOTES - Earthquake and FaultsDesNo ratings yet
- Endogenic ProcessesDocument50 pagesEndogenic Processesedena delos santosNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Earthquake and FaultsDocument34 pagesUnit 6 Earthquake and FaultsCharmaine CanonoNo ratings yet
- Sci Fil TLE and AP REV 1st QTR-1Document4 pagesSci Fil TLE and AP REV 1st QTR-1Jan Franco FerrerNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes: by Emman ValleDocument17 pagesEarthquakes: by Emman ValleRaul Carl CapinpuyanNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Causes and EffectsDocument34 pagesEarthquake Causes and EffectsKC CampilanNo ratings yet
- Our Changing Earth: STD ViiDocument39 pagesOur Changing Earth: STD ViiAnnie AroraNo ratings yet
- Science 2ND Quarter NotesDocument12 pagesScience 2ND Quarter NotesPrecious ShemNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and FaultsDocument11 pagesEarthquakes and FaultsGregg LegaspiNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument59 pagesEarthquakemarites alcazarNo ratings yet
- Activity (Eathquake)Document3 pagesActivity (Eathquake)leonellevisaya2022No ratings yet
- Opportunities and RisksDocument15 pagesOpportunities and Risks葉凌曦No ratings yet
- Group 4 How Rocks Behave Under Different Types of StressDocument32 pagesGroup 4 How Rocks Behave Under Different Types of StressAlyssa Rico-PiedadNo ratings yet
- EscDocument1 pageEscSan Gabriel, Shannarah DewelflorNo ratings yet
- Elements of SeismologyDocument29 pagesElements of SeismologyJoshua John Julio100% (1)
- What Caused EarthquakesDocument2 pagesWhat Caused EarthquakesRECHELL ANN GULAYNo ratings yet
- CH3 Sec6Document10 pagesCH3 Sec6Yasmeena SayedNo ratings yet
- Structural Geology GroundwaterDocument109 pagesStructural Geology Groundwaterkiran_ran99No ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument34 pagesEarthquakeRahul ShahNo ratings yet
- Earth Science ReviewerDocument17 pagesEarth Science ReviewerMGKaozNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument6 pagesEarthquakeKrizhia MacayaonNo ratings yet
- Faults That The Earth HasDocument15 pagesFaults That The Earth HasHalliah Viv ฅ•ω•ฅNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Earthquake and FaultsDocument33 pagesUnit 6 Earthquake and FaultsJohn Mark LaurioNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument1 pageScienceClarice Ann SadsadNo ratings yet
- Geologic Processes Within The Earth's SurfaceDocument15 pagesGeologic Processes Within The Earth's SurfaceGee DragonNo ratings yet
- Internal Structure of EarthDocument15 pagesInternal Structure of EarthYasserMohsenNo ratings yet
- Cengr 4140-Eq ReviewerDocument19 pagesCengr 4140-Eq Reviewerdarwin18No ratings yet
- 5 - Folds, Faults & UnconformityDocument30 pages5 - Folds, Faults & Unconformitymoorpvr100% (1)
- Local Media4445242459237597223Document22 pagesLocal Media4445242459237597223John Rey DumaguinNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument2 pagesEarthquakecashieentan05No ratings yet