Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Key Points - Sci7-Q2
Key Points - Sci7-Q2
Uploaded by
Margaret GonzalesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Key Points - Sci7-Q2
Key Points - Sci7-Q2
Uploaded by
Margaret GonzalesCopyright:
Available Formats
KEY POINTS IN SCIENCE
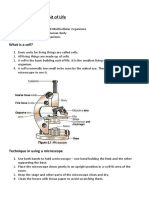
Microscope- An important investigative tool used for studying objects and organisms around us.
Compound Microscope- It is the most common type of microscope.
The three (3) groups of parts of microscope are Magnifying, Illuminating, and Mechanical.
Magnifying parts
1. Eyepiece- allows you to look through and observe the enlarge image of the object
2. Objective Lenses- magnify the image
Illuminating parts
1. Diaphragm – which controls the passing of light in the opening of the stage
2. Mirror – used to provide light on the object and help focuses it.
Mechanical parts
1. Coarse adjustment knob- which is used to move the tube and the objective lenses closer of
farther away from the stage to view the image of the object
2. Fine adjustment knob- moves the stage up and down and brings the image of the object into
fine focus producing a clearer and more detailed view of the object.
3. Stage- It supports the slide and stage clips.
4. Stage clip- It holds the slide plate in place.
5. Arm- supports the tube and connect it to the base
6. Revolving nosepiece- allows proper position of the objective lenses
7. Body tube- holds the eyepiece and the revolving nosepiece in place
8. Inclination joint- connects the arm to the base
9. Base- carry the body of microscope
Biological Organization- is the hierarchy of complex biological structures and systems that define life.
1. Cell- the smallest unit of life.
2. Organ- An organ is a structure which composed of two or more types of tissues that
work together.
3. Organ System- A group of organs working together to perform a specific function.
4. Organism- an individual living thing that may be made up of one or more organ systems
that carries out all basic life function.
5. Population- organisms of the same kind called species that live in the same area
6. Community- It consists of different populations of organism living in the same area.
7. Ecosystem- It consists of all the living things in a given area together with the non-living
things.
Deoxyribonucleic
acid (DNA) - exists in all living things and has the ability to make exact copies of itself.
Nucleus- It is the control center of the cell also labeled as “the brain” of the cell. This is where the
DNA is located.
Cytoplasm- It is a “jelly-like” substance that surrounds the organelles of the cell.
Mitochondrion / Mitochondria- The “powerhouse” of the cell
Chloroplasts- absorb light energy and convert it into chemical energy and allow plants to carry out the
process of photosynthesis.
Asexual Reproduction- -only involves one parent, there are no gametes (sex cells) produced and the
offspring are genetically identical to the parent.
Sexual Reproduction- involves two parents that produces gametes, the egg cell and sperm cell.
Abiotic factors – non-living parts of an organism’s environment
Biotic factors – living things
- It has obvious effects on living things.
Competition - is a powerful form of interaction in the organization of communities.
Mutualism - a symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit from each other.
Commensalism- a symbiotic relationship in which a member of one species benefit.
Predation is found in all ecosystems and includes organisms that eat plants and animals.
Extended lack of rainfall in the grassland can cause drought.
Different pollutions can harm the living and non-living things.
If the habitat of specific organism lost, the organisms will also lose their lives.
You might also like
- Gr.10 Remote Learning Workbook Term 2Document56 pagesGr.10 Remote Learning Workbook Term 2Sinethemba100% (2)
- Biofind and Bioscan WhitepapersDocument15 pagesBiofind and Bioscan WhitepapersCinthia Stephens100% (1)
- DNA StructureDocument4 pagesDNA StructureMaybella PruntyNo ratings yet
- On-Line Assignment DefinitionsDocument2 pagesOn-Line Assignment DefinitionsAbbey AdlerNo ratings yet
- SNAB T1 Teaching SchemeDocument16 pagesSNAB T1 Teaching SchemeJesuslover69noscope0% (2)
- An Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology MidwiferyDocument108 pagesAn Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology MidwiferyGayuh Kartika100% (4)
- Science Reviewer Quarter 2Document3 pagesScience Reviewer Quarter 2zeiah.marcellaNo ratings yet
- Pointers in Science 7-Q2Document3 pagesPointers in Science 7-Q2Margaret GonzalesNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument5 pagesScienceAngelita Pacia FelipeNo ratings yet
- Gen. ZoologyDocument13 pagesGen. ZoologyJulia ReignNo ratings yet
- Science: Identify The Parts of The Microscope and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesScience: Identify The Parts of The Microscope and Their FunctionsKimverheart Dennisse NavalNo ratings yet
- Score A Programme Science - Form 1: Understanding CellsDocument21 pagesScore A Programme Science - Form 1: Understanding CellsAlya RoslanNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant Cell Unicellular and Multicellular Organisms Part of A Microscope and Their Function Cell OrganisationDocument21 pagesAnimal and Plant Cell Unicellular and Multicellular Organisms Part of A Microscope and Their Function Cell OrganisationNor Hafiza AhmadNo ratings yet
- Midterm ReviewerDocument15 pagesMidterm ReviewerlowdicakesNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument39 pagesBiologyRizzuya UrakuwaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer q2Document7 pagesScience Reviewer q2Kathleen Joy PasionNo ratings yet
- Science 6Document10 pagesScience 6Mary Stephanie AlbarracinNo ratings yet
- Reviewer q2Document7 pagesReviewer q2bonboncapuyanNo ratings yet
- 2nd Reviewer ScienceDocument9 pages2nd Reviewer ScienceTristeine MorattiNo ratings yet
- Ecz Grade 10 - 12 Biology Summarised Notes Pt.1 (Living Organisms)Document27 pagesEcz Grade 10 - 12 Biology Summarised Notes Pt.1 (Living Organisms)Leon Marko100% (1)
- Science - Form 1 Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument23 pagesScience - Form 1 Cell As A Unit of Lifejayanthi_rai24No ratings yet
- Cell As A Basic Unit of LifeDocument33 pagesCell As A Basic Unit of LifeadhamklNo ratings yet
- 7 Characteristics of Living Things: M R S G R E NDocument10 pages7 Characteristics of Living Things: M R S G R E Nmcda100% (1)
- Biology 2Document11 pagesBiology 2Mara MayoNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 Chapter 2Document9 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 2huisinNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument5 pagesScience Reviewerrinnxuxi12No ratings yet
- BiologyDocument7 pagesBiologyConrado Juisan CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unti of Life Cell Part 01Document4 pagesThe Fundamental Unti of Life Cell Part 01jeetjyoti787No ratings yet
- Science Chapter 1Document13 pagesScience Chapter 1Asia BibiNo ratings yet
- Levels of Biological OrganizationDocument7 pagesLevels of Biological Organizationflash newsNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes: Intro To BioDocument4 pagesBiology Notes: Intro To BioCorinne HooperNo ratings yet
- L 6 GP CX 5 U IFCf Wod DX 38 WDocument22 pagesL 6 GP CX 5 U IFCf Wod DX 38 WAradhana GuptaNo ratings yet
- Histo CompilationDocument217 pagesHisto CompilationNico LokoNo ratings yet
- 1.structure of A Generalized Cell The Basic Units of Structure For All Living Organisms Are CellsDocument5 pages1.structure of A Generalized Cell The Basic Units of Structure For All Living Organisms Are CellsDavidNo ratings yet
- s1 Biology NotesDocument87 pagess1 Biology NotesrichardwizleeNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 Chapter 2: Cell Is The Unit of LifeDocument25 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 2: Cell Is The Unit of LifeMuhammad Shazni Daud100% (1)
- Activity 1: General Physiology LaboratoryDocument29 pagesActivity 1: General Physiology LaboratoryDeasserei TatelNo ratings yet
- Bio For Olevel PDFDocument422 pagesBio For Olevel PDFNalweyiso JoyceNo ratings yet
- 02 BH - Stage 1 (Week 1)Document31 pages02 BH - Stage 1 (Week 1)AndreaArizpeNo ratings yet
- 1 - CytologyDocument58 pages1 - CytologySena JeevNo ratings yet
- Bio11 First LE ReviewerDocument9 pagesBio11 First LE ReviewerFREE ARTICLESNo ratings yet
- Biology Midterms ReviewerDocument11 pagesBiology Midterms ReviewerMarianne ManglicmotNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesbookletDocument115 pagesBiology Notesbookletm.umar.saiyedNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ReviewerAnn Fenelope AniscoNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument17 pagesCELLdina ahmedNo ratings yet
- Biology Full NotesDocument259 pagesBiology Full NotesthaseiphologoNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument15 pagesScience Noteslaramatraji45No ratings yet
- Eagle Quiz Biology ReviewerDocument3 pagesEagle Quiz Biology ReviewerYuan AcostaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Levels of Biological OrganizationDocument6 pagesLesson 3 - Levels of Biological Organizationhakuna matata100% (2)
- B1.1 Student GlossaryDocument4 pagesB1.1 Student GlossarymtauhidNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Science 7Document7 pagesReviewer Science 7Grace Anne C. MercadoNo ratings yet
- BIO121 Chapter 1 The Science of BiologyDocument45 pagesBIO121 Chapter 1 The Science of BiologyggttettanNo ratings yet
- Cells 1444056007Document36 pagesCells 1444056007Clausel MilordNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec Final ReviewerDocument87 pagesAnaphy Lec Final ReviewerDaniela Nicole Manibog ValentinoNo ratings yet
- Botany Notes Part 1Document22 pagesBotany Notes Part 1Rochenick MagoNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument159 pagesBiology NotesbasheerqawlaqNo ratings yet
- Life Chap 1 Part1Document16 pagesLife Chap 1 Part1Elhade ElbakushNo ratings yet
- Sci7 Q2 Wk3 Module3Document11 pagesSci7 Q2 Wk3 Module3Lester Noel RosalesNo ratings yet
- How To Focus A MicroscopeDocument31 pagesHow To Focus A Microscopekimsioco02No ratings yet
- Genbio 1Document10 pagesGenbio 1Marxinne PajarinNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Activity in Chapter 2. Exploring The CellDocument4 pagesAssessment and Activity in Chapter 2. Exploring The CellArmie Rose FaldasNo ratings yet
- Biology Lesson Note SS1 First TermDocument76 pagesBiology Lesson Note SS1 First Termemmysun38No ratings yet
- BIOLOGY 0610iDocument17 pagesBIOLOGY 0610imimoakal24No ratings yet
- Hapter: Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument29 pagesHapter: Cell As A Unit of LifeShu85No ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Pointers in Tle 7 - Q2Document3 pagesPointers in Tle 7 - Q2Margaret GonzalesNo ratings yet
- LQ Sci7 W3 4Document2 pagesLQ Sci7 W3 4Margaret GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz in TLE 7 Quarter 2 (Week 3-4)Document2 pagesLong Quiz in TLE 7 Quarter 2 (Week 3-4)Margaret GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Pointers in Science 7-Q2Document3 pagesPointers in Science 7-Q2Margaret GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Cell Communication NotesDocument3 pagesCell Communication NoteselyssaNo ratings yet
- Evo101 - 03 - Mechanisms - The Process of Evolution - UEDocument34 pagesEvo101 - 03 - Mechanisms - The Process of Evolution - UEJanice LerioratoNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Revision - BacteriaDocument5 pagesIGCSE Biology Revision - BacteriaNikhil YadavNo ratings yet
- (Updated) SECOND QUARTER EXAM in Earth and Life ScienceDocument8 pages(Updated) SECOND QUARTER EXAM in Earth and Life ScienceMELECIA, Dhenielle Mae T.100% (1)
- Study of Cancer Investigatory ProjectDocument15 pagesStudy of Cancer Investigatory ProjectRavi KNo ratings yet
- SPM Biology Form 4 NotesDocument3 pagesSPM Biology Form 4 NotesDelima Adan86% (7)
- Human Genome Project EssayDocument6 pagesHuman Genome Project EssayAndrea BonillaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Module 1 Week 1Document8 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Module 1 Week 1Melanie OrayNo ratings yet
- Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun Terengganu Tingkatan 4 - Paper 2Document11 pagesPeperiksaan Akhir Tahun Terengganu Tingkatan 4 - Paper 2Alaister Bernard Jampong75% (4)
- Cells IntroDocument26 pagesCells Introapi-324822024No ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellAlexa MacailoNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme For June 2010: BiologyDocument22 pagesMark Scheme For June 2010: Biologyamar_12345No ratings yet
- CELL CITY PROJECT - You Are The Architect: Manuel S. Enverga University Foundation Candelaria, IncDocument3 pagesCELL CITY PROJECT - You Are The Architect: Manuel S. Enverga University Foundation Candelaria, IncDEL ROSARIO GWEN ASHLEY R.No ratings yet
- Science Answer KeyDocument6 pagesScience Answer KeyAngel MarieNo ratings yet
- Biology - November 2017Document1 pageBiology - November 2017Rahique ShuaibNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Cell Structure and Function Chapters 6-7Document4 pagesUnit 2: Cell Structure and Function Chapters 6-7api-542216138No ratings yet
- Lesson Title:: Self-Learning Activity Sheet Grade 12 - Day 13Document11 pagesLesson Title:: Self-Learning Activity Sheet Grade 12 - Day 13Feedback Or BawiNo ratings yet
- The Bioreactor A Powerful Tool For Large-Scale Culture of Animal CellsDocument8 pagesThe Bioreactor A Powerful Tool For Large-Scale Culture of Animal CellsADITI AWASTHINo ratings yet
- Colegio Campestre Sabana de Lourdes: Malla CurricularDocument3 pagesColegio Campestre Sabana de Lourdes: Malla Curricularjennifer nogueraNo ratings yet
- Biological Science 5Th Edition Freeman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument37 pagesBiological Science 5Th Edition Freeman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFElizabethRuizrxka100% (15)
- Sci F1 FY (E)Document9 pagesSci F1 FY (E)Shakilla HamzahNo ratings yet
- The Making of The Fittest: Evolving Switches, Evolving BodiesDocument13 pagesThe Making of The Fittest: Evolving Switches, Evolving BodiesZ. Miller07No ratings yet
- Grade 7 ExamDocument3 pagesGrade 7 Examzylene100% (1)
- Antibacterial Agents in Textile Industry PDFDocument20 pagesAntibacterial Agents in Textile Industry PDFimran24No ratings yet