Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 viewsCC1 & CC2 Revision Notes
CC1 & CC2 Revision Notes
Uploaded by
tBLE806The document provides information on various states of matter and separation techniques. It discusses the key characteristics of solids, liquids, and gases. It also explains several separation methods including filtration, crystallization, chromatography, simple distillation, and fractional distillation. Each technique is described in terms of how it separates mixtures based on physical properties like solubility, boiling point, or molecular structure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Cambridge Primary Science Learner's Book Grade 6Document112 pagesCambridge Primary Science Learner's Book Grade 6Fatme Allawa69% (39)
- Grade 7 Science ReviewerDocument79 pagesGrade 7 Science ReviewerNini JimbuuNo ratings yet
- OSD 18-91-067 - Instruction Manual and Parts List - Ed. 806Document214 pagesOSD 18-91-067 - Instruction Manual and Parts List - Ed. 806Centrifugal Separator100% (2)
- Separation Techniques: How Do The Properties of Substances Aid in Their Classification and Separation?Document11 pagesSeparation Techniques: How Do The Properties of Substances Aid in Their Classification and Separation?D SNo ratings yet
- Mixtures and Separation TechniquesDocument60 pagesMixtures and Separation TechniquesAnuradha RamroopNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science 6Document2 pagesReviewer in Science 6MadisonNo ratings yet
- Notes - Separating and Purifying SubstancesDocument2 pagesNotes - Separating and Purifying SubstancesJayasutha Raman100% (1)
- 1stQ.1.4 Separating MixturesDocument22 pages1stQ.1.4 Separating MixturesRaiden Gabriel LontokNo ratings yet
- Separation of MixturesDocument25 pagesSeparation of MixturesYumie YamazukiNo ratings yet
- Separation Techniques 1Document8 pagesSeparation Techniques 1Kaylo KganyakoNo ratings yet
- Separation of MixturesDocument52 pagesSeparation of MixturesEdgarVincentCharlesSalazarNo ratings yet
- Separation Techniques: Separating A Mixture Solid by SolidDocument2 pagesSeparation Techniques: Separating A Mixture Solid by SolidGaurika BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Chemistry: Methods of PurificationDocument44 pagesExperimental Chemistry: Methods of PurificationAiman SanobarNo ratings yet
- Seperation TechniqueDocument6 pagesSeperation TechniquelindaoeghagharaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Summary TheDocument11 pagesChapter 2 Summary Thekrishna darjiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Double Awaed NotesDocument136 pagesChemistry Double Awaed NotesBame MakilindaNo ratings yet
- Chem 1.8 IGDocument3 pagesChem 1.8 IGKhantSithu HeinNo ratings yet
- IGCSE SME Chemistry Notes2 PDFDocument3 pagesIGCSE SME Chemistry Notes2 PDFEric TTLNo ratings yet
- Classifications of MatterDocument39 pagesClassifications of MatterKassandra Chellzy D. EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument7 pagesSeparation TechniquesPriyanka WadhwaniNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument27 pagesSeparation Techniquescarresha applewhaiteNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument47 pagesUntitledKaren OrlanskiNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument14 pagesSeparation TechniquesNathaniel WhyteNo ratings yet
- Mulima Chemistry New 4Document171 pagesMulima Chemistry New 4mphowalterthenguNo ratings yet
- Purity of A SubstanceDocument13 pagesPurity of A SubstanceAlly Bin AssadNo ratings yet
- S16 Class9ScienceNCERTSummaryPart IDocument93 pagesS16 Class9ScienceNCERTSummaryPart Isandeepkumarreddy2201No ratings yet
- Study Material - Separation MethodsDocument7 pagesStudy Material - Separation MethodsSahil NarkhedeNo ratings yet
- 2.5 (2.5) .Separating MixturesDocument24 pages2.5 (2.5) .Separating MixturesNicaliaNo ratings yet
- 2.5 (2.5) .Separating MixturesDocument24 pages2.5 (2.5) .Separating MixturesNicalia100% (1)
- Different Ways of Separating Mixtures: ChromatographyDocument2 pagesDifferent Ways of Separating Mixtures: ChromatographyClark Hailie Wayne EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument39 pagesOrganic Chemistryh2312416No ratings yet
- Chemistry 2 - Separating MixturesDocument7 pagesChemistry 2 - Separating MixturesNaseeb AliNo ratings yet
- Separation Methods: Ways To Separate Mixtures - Chapter 3: Matter & Its PropertiesDocument17 pagesSeparation Methods: Ways To Separate Mixtures - Chapter 3: Matter & Its PropertiesKateBarrionEspinosaNo ratings yet
- Separation Methods: Ways To Separate Mixtures - Chapter 3: Matter & Its PropertiesDocument17 pagesSeparation Methods: Ways To Separate Mixtures - Chapter 3: Matter & Its PropertiesNithy's AcademyNo ratings yet
- Separating MixturesDocument1 pageSeparating MixturesAlvin Jan CampoNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument17 pagesSeparation TechniquesSamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- Experimental TechniquesDocument2 pagesExperimental TechniquesjrmonsefshNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 B Separation - TechniquesDocument64 pagesUnit 2 B Separation - TechniquesTravel UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Note On Separating TechniquesDocument8 pagesGrade 7 Note On Separating TechniquesBadass PolapainNo ratings yet
- HARAM SIDDIQUI - Exercise No. 1 - Demonstration Sessions For Various Purification Techniques Such As Filtration, Decantation, Crystallization, Distillation and Chromatography.Document7 pagesHARAM SIDDIQUI - Exercise No. 1 - Demonstration Sessions For Various Purification Techniques Such As Filtration, Decantation, Crystallization, Distillation and Chromatography.Arya SayedNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 First Quarter - Module 1 Properties of MatterDocument28 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 First Quarter - Module 1 Properties of MatterJRAVPNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument35 pagesSeparation Techniquesali AbbasNo ratings yet
- 8TH Grade Separating MixturesDocument12 pages8TH Grade Separating MixturesKolade Fatai OpeyemiNo ratings yet
- MixturesDocument25 pagesMixturesJoma Guerra ina moNo ratings yet
- 2 - Elements Compounds and MixturesDocument13 pages2 - Elements Compounds and MixturesKhin Yadanar KyawNo ratings yet
- Methods of Purification and Analysis TeachDocument20 pagesMethods of Purification and Analysis Teachhafizhapni91% (11)
- Separation Techniques: MagnetismDocument3 pagesSeparation Techniques: MagnetismJohnlloyd NageraNo ratings yet
- Purification MethodsDocument10 pagesPurification MethodsamyNo ratings yet
- Colloids Are Mixtures Whose Particles Are Larger Than The Size of ADocument2 pagesColloids Are Mixtures Whose Particles Are Larger Than The Size of AKyla Angela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Separating MixturesDocument13 pagesSeparating Mixturesver_at_workNo ratings yet
- Seperation of MixturesDocument24 pagesSeperation of MixturesShehbaaz SinghNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument1 pageChromatographyRey LarebilNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 1 WJEC (England) Chemistry GCSEDocument4 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 1 WJEC (England) Chemistry GCSErockingnilNo ratings yet
- Ways of Separating MixturesDocument5 pagesWays of Separating MixturesMay Anne AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Separating Mixtures PDFDocument4 pagesSeparating Mixtures PDFDenise Adriene ParanNo ratings yet
- Chem RevisionDocument5 pagesChem RevisionajeesharulkumaranNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument5 pagesChemJoelle SwaisNo ratings yet
- Ways of SeparatingmixturesDocument30 pagesWays of SeparatingmixturesGlena Bilda BarramedaNo ratings yet
- Science Year 09 CC2 Methods of Separating and Purifying SubstancesDocument3 pagesScience Year 09 CC2 Methods of Separating and Purifying Substancesheidi elleithyNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure Class 9th ScienceDocument15 pagesNotes of CH 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure Class 9th ScienceSingh JNo ratings yet
- Oil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandOil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- The Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Biology - CB1c-CB1d KeywordsDocument1 pageBiology - CB1c-CB1d KeywordstBLE806No ratings yet
- CB1 Revision NotesDocument2 pagesCB1 Revision NotestBLE806No ratings yet
- Edgcse Aap Cb2b Homework1Document1 pageEdgcse Aap Cb2b Homework1tBLE806No ratings yet
- Edgcse Aap Cb2c Homework1Document1 pageEdgcse Aap Cb2c Homework1tBLE806No ratings yet
- Edgcse Aap Cb2c Homework1-CombinedDocument2 pagesEdgcse Aap Cb2c Homework1-CombinedtBLE806No ratings yet
- Properties of Matter Test ReviewDocument9 pagesProperties of Matter Test ReviewAngel PeayNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Mallory Tanner - Practice Performance Task Limonene StudentDocument6 pagesKami Export - Mallory Tanner - Practice Performance Task Limonene Studentcupcake12345909No ratings yet
- Chemistry 11: Instructor: Raymond Gipson, PH.DDocument17 pagesChemistry 11: Instructor: Raymond Gipson, PH.DDemi ChangNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Coursework - Chapter 2.0 MethodologyDocument2 pagesChemistry Coursework - Chapter 2.0 MethodologyXuan Hua LaiNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Matter Properties and ChangeDocument103 pagesCH 3 Matter Properties and ChangeBryant BachelorNo ratings yet
- Weekly Learning Plan: Day & Time Learning Area Learning Competency Learning Task Mode of Delivery TuesdayDocument7 pagesWeekly Learning Plan: Day & Time Learning Area Learning Competency Learning Task Mode of Delivery TuesdayPABLITA CENTENONo ratings yet
- Supplementary Information: Revisiting The Classic Activity Coefficient ModelsDocument35 pagesSupplementary Information: Revisiting The Classic Activity Coefficient ModelsLeonardo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Chemistry 9th Edition Zumdahl Isbn 10 1133611095 Isbn 13 9781133611097Document17 pagesTest Bank For Chemistry 9th Edition Zumdahl Isbn 10 1133611095 Isbn 13 9781133611097Lynn Higgins100% (38)
- Chapter1 PDFDocument64 pagesChapter1 PDFsgw67No ratings yet
- Department of Education: Gamitin Ang Self Learning Modules Sa ESPDocument15 pagesDepartment of Education: Gamitin Ang Self Learning Modules Sa ESPSenen AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Science7 q1 Mod6 Solutions 1-19Document19 pagesScience7 q1 Mod6 Solutions 1-19api-114144039No ratings yet
- 1 2 2 5 2 PDFDocument16 pages1 2 2 5 2 PDFSrinivas VenkataramanNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Exam in ScienceDocument6 pages1st Quarter Exam in Sciencekathleenjane100% (2)
- g6 Science Text 03Document42 pagesg6 Science Text 03a.rodriguezmarcoNo ratings yet
- Tom Newby Grade 6 HomeworkDocument6 pagesTom Newby Grade 6 Homeworkafeuuljgm100% (1)
- First Quarterly Assessment Science 6Document7 pagesFirst Quarterly Assessment Science 6Jayral PradesNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Week 1Document41 pages1st Quarter Week 1Maria Irenea LynielleNo ratings yet
- Elementary Science Methods 1Document7 pagesElementary Science Methods 1api-279276416No ratings yet
- DLL Science 7 First QuarterDocument5 pagesDLL Science 7 First QuarterIVAN BARROGANo ratings yet
- Verbalreasoning: A. B. C. DDocument51 pagesVerbalreasoning: A. B. C. DAndresNo ratings yet
- Oceanography An Invitation To Marine Science 9th Edition Garrison Test BankDocument21 pagesOceanography An Invitation To Marine Science 9th Edition Garrison Test Bankrorybridgetewe100% (27)
- Lesson Plan in MixturesDocument10 pagesLesson Plan in MixturesRENA PRAQUELESNo ratings yet
- CH Unit2 Separation Lab Report WritingDocument6 pagesCH Unit2 Separation Lab Report WritingAbraham AguilarNo ratings yet
- Mock Test Gat - (28-3-22)Document8 pagesMock Test Gat - (28-3-22)Dhruva Chandra PandeyNo ratings yet
- I PUC Chem Chapterwise Q and AnswersDocument220 pagesI PUC Chem Chapterwise Q and AnswersPrakash ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chem's Studyguide IqDocument19 pagesChem's Studyguide IqYossuara PittiNo ratings yet
- Mixtures ReviewDocument3 pagesMixtures Reviewapi-301425989No ratings yet
CC1 & CC2 Revision Notes
CC1 & CC2 Revision Notes
Uploaded by
tBLE8060 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views2 pagesThe document provides information on various states of matter and separation techniques. It discusses the key characteristics of solids, liquids, and gases. It also explains several separation methods including filtration, crystallization, chromatography, simple distillation, and fractional distillation. Each technique is described in terms of how it separates mixtures based on physical properties like solubility, boiling point, or molecular structure.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides information on various states of matter and separation techniques. It discusses the key characteristics of solids, liquids, and gases. It also explains several separation methods including filtration, crystallization, chromatography, simple distillation, and fractional distillation. Each technique is described in terms of how it separates mixtures based on physical properties like solubility, boiling point, or molecular structure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views2 pagesCC1 & CC2 Revision Notes
CC1 & CC2 Revision Notes
Uploaded by
tBLE806The document provides information on various states of matter and separation techniques. It discusses the key characteristics of solids, liquids, and gases. It also explains several separation methods including filtration, crystallization, chromatography, simple distillation, and fractional distillation. Each technique is described in terms of how it separates mixtures based on physical properties like solubility, boiling point, or molecular structure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
CC1CC1
& CC2
& CC2Revision Notes
Revision Notes
CC1: States of Matter
● Solid
↳ The particles, or atoms and molecules, are tightly
packed together.
↳ The particles are free to vibrate but cannot move.
↳ They can only change volume and shape when exposed
to an external force or cut into smaller pieces.
● Liquid
↳ They are incompressible liquid matter that is not
pressure dependent.
↳ If the pressure and temperature remain constant, they have a fixed volume.
↳ When exposed to temperatures above their specific melting points, solids have a tendency to
transform into liquids, subject to pressure properties.
● Gas
↳ Particles are randomly arranged and can move quickly in all directions and are far apart.
↳ A liquid can be converted to a gas by heating it to the boiling point while maintaining constant
pressure, or by decreasing pressure while maintaining constant boiling point.
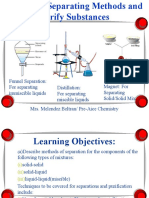
CC2: Separation Techniques
● Filtration
↳ A physical method of separating insoluble solids from liquids.
↳ Filtration is a physical separation process that uses a filter medium
with a complex structure through which only fluid can pass to
separate solid matter and fluid from a mixture.
↳ Filtration is a technique for separating an insoluble solid from a liquid.
It can be used to separate sand from a sand-water mixture or excess
reactant from a reaction mixture.
↳ Filtration is critical for keeping water and chemicals clean, pure, and
free of contaminants. We might not have safe drinking water if it weren't for filtration, which
plays an important role in removing sediment, sand, gravel, carbon, and other unwanted
particles.
↳ Filtration is the process of separating an insoluble solid from a pure liquid or solution. Filtration is
usually done by folding a circle of filter paper into a cone and placing it in a filter funnel. The
filtrate is the liquid that flows through the filter paper, while the residue is the solid that remains
on the filter paper.
● Crystallisation
↳ A physical method of separating soluble solids from liquids.
↳ Crystallisation is the process by which a solid forms in which the atoms
or molecules are highly organised into a structure known as a crystal.
↳ A soluble material is separated from a solvent by crystallisation. For
instance, salt can be extracted from a salt solution by crystallisation.
↳ Crystallisation is effectively used as a purification technique to separate
the product from impurities and the process solvent.
↳ In an open container, the solution is heated. The solvent molecules
begin to evaporate, leaving the solutes behind. As the solution cools, solute crystals begin to form
on the solution's surface. Crystals are collected and dried as needed for the product.
● Chromatography
↳ Paper chromatography is used to separate
dissolved chemical substances in a mixture.
↳ Chromatography is the separation of
components in a mixture. To begin the process,
the mixture is dissolved in a substance known as
the mobile phase, which carries it through a
second substance known as the stationary
phase.
↳ Chromatography can be used to separate coloured compound mixtures. Ink, dyes and food
colouring agents are examples of mixtures that can be separated using chromatography.
↳ Chromatography is useful as it is a purification tool, separating the components of a mixture for
use in other experiments or procedures.
↳ The separated mixture is dissolved in a fluid known as the mobile phase. This helps the mixture
move through the stationary phrase.
↳ Compounds are separated because they move at different speeds through the stationary phase.
● Simple Distillation
↳ Simple distillation is used to separate two liquids with
different boiling points.
↳ Simple distillation involves boiling the liquid mixture and
immediately condensing the resulting vapours.
↳ Simple distillation is a technique for removing a solvent
from a solution. Water, for example, can be separated
from salt solution using simple distillation. Because water
has a much lower boiling point than salt, this method
works. Water evaporates when the solution is heated.
↳ Distillation is useful as it separates from salt solution using simple distillation.
● Fractional Distillation
↳ Fractional distillation is used to separate two liquids with similar
boiling points.
↳ The difference between simple distillation and fractional distillation is
fractional distillation separates liquids with similar boiling points and
not different ones like simple distillation.
↳ Process
- Evaporation. Crude oil is heated until it evaporates. Crude oil
vapour is put into a fractionating column at the bottom and
rises upwards.
- Condensation. The temperature is highest at the bottom of the
column.
- Collection. The fractions are collected.
↳ Fractional distillation is a method for separating a liquid from a mixture of two or more liquids.
↳ Fractional distillation is very useful when separating more than two types of liquids from a
homogeneous mixture.
You might also like
- Cambridge Primary Science Learner's Book Grade 6Document112 pagesCambridge Primary Science Learner's Book Grade 6Fatme Allawa69% (39)
- Grade 7 Science ReviewerDocument79 pagesGrade 7 Science ReviewerNini JimbuuNo ratings yet
- OSD 18-91-067 - Instruction Manual and Parts List - Ed. 806Document214 pagesOSD 18-91-067 - Instruction Manual and Parts List - Ed. 806Centrifugal Separator100% (2)
- Separation Techniques: How Do The Properties of Substances Aid in Their Classification and Separation?Document11 pagesSeparation Techniques: How Do The Properties of Substances Aid in Their Classification and Separation?D SNo ratings yet
- Mixtures and Separation TechniquesDocument60 pagesMixtures and Separation TechniquesAnuradha RamroopNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science 6Document2 pagesReviewer in Science 6MadisonNo ratings yet
- Notes - Separating and Purifying SubstancesDocument2 pagesNotes - Separating and Purifying SubstancesJayasutha Raman100% (1)
- 1stQ.1.4 Separating MixturesDocument22 pages1stQ.1.4 Separating MixturesRaiden Gabriel LontokNo ratings yet
- Separation of MixturesDocument25 pagesSeparation of MixturesYumie YamazukiNo ratings yet
- Separation Techniques 1Document8 pagesSeparation Techniques 1Kaylo KganyakoNo ratings yet
- Separation of MixturesDocument52 pagesSeparation of MixturesEdgarVincentCharlesSalazarNo ratings yet
- Separation Techniques: Separating A Mixture Solid by SolidDocument2 pagesSeparation Techniques: Separating A Mixture Solid by SolidGaurika BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Chemistry: Methods of PurificationDocument44 pagesExperimental Chemistry: Methods of PurificationAiman SanobarNo ratings yet
- Seperation TechniqueDocument6 pagesSeperation TechniquelindaoeghagharaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Summary TheDocument11 pagesChapter 2 Summary Thekrishna darjiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Double Awaed NotesDocument136 pagesChemistry Double Awaed NotesBame MakilindaNo ratings yet
- Chem 1.8 IGDocument3 pagesChem 1.8 IGKhantSithu HeinNo ratings yet
- IGCSE SME Chemistry Notes2 PDFDocument3 pagesIGCSE SME Chemistry Notes2 PDFEric TTLNo ratings yet
- Classifications of MatterDocument39 pagesClassifications of MatterKassandra Chellzy D. EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument7 pagesSeparation TechniquesPriyanka WadhwaniNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument27 pagesSeparation Techniquescarresha applewhaiteNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument47 pagesUntitledKaren OrlanskiNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument14 pagesSeparation TechniquesNathaniel WhyteNo ratings yet
- Mulima Chemistry New 4Document171 pagesMulima Chemistry New 4mphowalterthenguNo ratings yet
- Purity of A SubstanceDocument13 pagesPurity of A SubstanceAlly Bin AssadNo ratings yet
- S16 Class9ScienceNCERTSummaryPart IDocument93 pagesS16 Class9ScienceNCERTSummaryPart Isandeepkumarreddy2201No ratings yet
- Study Material - Separation MethodsDocument7 pagesStudy Material - Separation MethodsSahil NarkhedeNo ratings yet
- 2.5 (2.5) .Separating MixturesDocument24 pages2.5 (2.5) .Separating MixturesNicaliaNo ratings yet
- 2.5 (2.5) .Separating MixturesDocument24 pages2.5 (2.5) .Separating MixturesNicalia100% (1)
- Different Ways of Separating Mixtures: ChromatographyDocument2 pagesDifferent Ways of Separating Mixtures: ChromatographyClark Hailie Wayne EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument39 pagesOrganic Chemistryh2312416No ratings yet
- Chemistry 2 - Separating MixturesDocument7 pagesChemistry 2 - Separating MixturesNaseeb AliNo ratings yet
- Separation Methods: Ways To Separate Mixtures - Chapter 3: Matter & Its PropertiesDocument17 pagesSeparation Methods: Ways To Separate Mixtures - Chapter 3: Matter & Its PropertiesKateBarrionEspinosaNo ratings yet
- Separation Methods: Ways To Separate Mixtures - Chapter 3: Matter & Its PropertiesDocument17 pagesSeparation Methods: Ways To Separate Mixtures - Chapter 3: Matter & Its PropertiesNithy's AcademyNo ratings yet
- Separating MixturesDocument1 pageSeparating MixturesAlvin Jan CampoNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument17 pagesSeparation TechniquesSamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- Experimental TechniquesDocument2 pagesExperimental TechniquesjrmonsefshNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 B Separation - TechniquesDocument64 pagesUnit 2 B Separation - TechniquesTravel UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Note On Separating TechniquesDocument8 pagesGrade 7 Note On Separating TechniquesBadass PolapainNo ratings yet
- HARAM SIDDIQUI - Exercise No. 1 - Demonstration Sessions For Various Purification Techniques Such As Filtration, Decantation, Crystallization, Distillation and Chromatography.Document7 pagesHARAM SIDDIQUI - Exercise No. 1 - Demonstration Sessions For Various Purification Techniques Such As Filtration, Decantation, Crystallization, Distillation and Chromatography.Arya SayedNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 First Quarter - Module 1 Properties of MatterDocument28 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 First Quarter - Module 1 Properties of MatterJRAVPNo ratings yet
- Separation TechniquesDocument35 pagesSeparation Techniquesali AbbasNo ratings yet
- 8TH Grade Separating MixturesDocument12 pages8TH Grade Separating MixturesKolade Fatai OpeyemiNo ratings yet
- MixturesDocument25 pagesMixturesJoma Guerra ina moNo ratings yet
- 2 - Elements Compounds and MixturesDocument13 pages2 - Elements Compounds and MixturesKhin Yadanar KyawNo ratings yet
- Methods of Purification and Analysis TeachDocument20 pagesMethods of Purification and Analysis Teachhafizhapni91% (11)
- Separation Techniques: MagnetismDocument3 pagesSeparation Techniques: MagnetismJohnlloyd NageraNo ratings yet
- Purification MethodsDocument10 pagesPurification MethodsamyNo ratings yet
- Colloids Are Mixtures Whose Particles Are Larger Than The Size of ADocument2 pagesColloids Are Mixtures Whose Particles Are Larger Than The Size of AKyla Angela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Separating MixturesDocument13 pagesSeparating Mixturesver_at_workNo ratings yet
- Seperation of MixturesDocument24 pagesSeperation of MixturesShehbaaz SinghNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument1 pageChromatographyRey LarebilNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 1 WJEC (England) Chemistry GCSEDocument4 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 1 WJEC (England) Chemistry GCSErockingnilNo ratings yet
- Ways of Separating MixturesDocument5 pagesWays of Separating MixturesMay Anne AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Separating Mixtures PDFDocument4 pagesSeparating Mixtures PDFDenise Adriene ParanNo ratings yet
- Chem RevisionDocument5 pagesChem RevisionajeesharulkumaranNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument5 pagesChemJoelle SwaisNo ratings yet
- Ways of SeparatingmixturesDocument30 pagesWays of SeparatingmixturesGlena Bilda BarramedaNo ratings yet
- Science Year 09 CC2 Methods of Separating and Purifying SubstancesDocument3 pagesScience Year 09 CC2 Methods of Separating and Purifying Substancesheidi elleithyNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure Class 9th ScienceDocument15 pagesNotes of CH 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure Class 9th ScienceSingh JNo ratings yet
- Oil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandOil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- The Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Biology - CB1c-CB1d KeywordsDocument1 pageBiology - CB1c-CB1d KeywordstBLE806No ratings yet
- CB1 Revision NotesDocument2 pagesCB1 Revision NotestBLE806No ratings yet
- Edgcse Aap Cb2b Homework1Document1 pageEdgcse Aap Cb2b Homework1tBLE806No ratings yet
- Edgcse Aap Cb2c Homework1Document1 pageEdgcse Aap Cb2c Homework1tBLE806No ratings yet
- Edgcse Aap Cb2c Homework1-CombinedDocument2 pagesEdgcse Aap Cb2c Homework1-CombinedtBLE806No ratings yet
- Properties of Matter Test ReviewDocument9 pagesProperties of Matter Test ReviewAngel PeayNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Mallory Tanner - Practice Performance Task Limonene StudentDocument6 pagesKami Export - Mallory Tanner - Practice Performance Task Limonene Studentcupcake12345909No ratings yet
- Chemistry 11: Instructor: Raymond Gipson, PH.DDocument17 pagesChemistry 11: Instructor: Raymond Gipson, PH.DDemi ChangNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Coursework - Chapter 2.0 MethodologyDocument2 pagesChemistry Coursework - Chapter 2.0 MethodologyXuan Hua LaiNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Matter Properties and ChangeDocument103 pagesCH 3 Matter Properties and ChangeBryant BachelorNo ratings yet
- Weekly Learning Plan: Day & Time Learning Area Learning Competency Learning Task Mode of Delivery TuesdayDocument7 pagesWeekly Learning Plan: Day & Time Learning Area Learning Competency Learning Task Mode of Delivery TuesdayPABLITA CENTENONo ratings yet
- Supplementary Information: Revisiting The Classic Activity Coefficient ModelsDocument35 pagesSupplementary Information: Revisiting The Classic Activity Coefficient ModelsLeonardo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Chemistry 9th Edition Zumdahl Isbn 10 1133611095 Isbn 13 9781133611097Document17 pagesTest Bank For Chemistry 9th Edition Zumdahl Isbn 10 1133611095 Isbn 13 9781133611097Lynn Higgins100% (38)
- Chapter1 PDFDocument64 pagesChapter1 PDFsgw67No ratings yet
- Department of Education: Gamitin Ang Self Learning Modules Sa ESPDocument15 pagesDepartment of Education: Gamitin Ang Self Learning Modules Sa ESPSenen AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Science7 q1 Mod6 Solutions 1-19Document19 pagesScience7 q1 Mod6 Solutions 1-19api-114144039No ratings yet
- 1 2 2 5 2 PDFDocument16 pages1 2 2 5 2 PDFSrinivas VenkataramanNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Exam in ScienceDocument6 pages1st Quarter Exam in Sciencekathleenjane100% (2)
- g6 Science Text 03Document42 pagesg6 Science Text 03a.rodriguezmarcoNo ratings yet
- Tom Newby Grade 6 HomeworkDocument6 pagesTom Newby Grade 6 Homeworkafeuuljgm100% (1)
- First Quarterly Assessment Science 6Document7 pagesFirst Quarterly Assessment Science 6Jayral PradesNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Week 1Document41 pages1st Quarter Week 1Maria Irenea LynielleNo ratings yet
- Elementary Science Methods 1Document7 pagesElementary Science Methods 1api-279276416No ratings yet
- DLL Science 7 First QuarterDocument5 pagesDLL Science 7 First QuarterIVAN BARROGANo ratings yet
- Verbalreasoning: A. B. C. DDocument51 pagesVerbalreasoning: A. B. C. DAndresNo ratings yet
- Oceanography An Invitation To Marine Science 9th Edition Garrison Test BankDocument21 pagesOceanography An Invitation To Marine Science 9th Edition Garrison Test Bankrorybridgetewe100% (27)
- Lesson Plan in MixturesDocument10 pagesLesson Plan in MixturesRENA PRAQUELESNo ratings yet
- CH Unit2 Separation Lab Report WritingDocument6 pagesCH Unit2 Separation Lab Report WritingAbraham AguilarNo ratings yet
- Mock Test Gat - (28-3-22)Document8 pagesMock Test Gat - (28-3-22)Dhruva Chandra PandeyNo ratings yet
- I PUC Chem Chapterwise Q and AnswersDocument220 pagesI PUC Chem Chapterwise Q and AnswersPrakash ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chem's Studyguide IqDocument19 pagesChem's Studyguide IqYossuara PittiNo ratings yet
- Mixtures ReviewDocument3 pagesMixtures Reviewapi-301425989No ratings yet