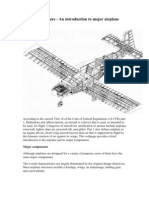
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Flaps and Slats
Flaps and Slats
Uploaded by
ASIM SHABANEHCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 737 Performance Reference Handbook - EASA EditionFrom Everand737 Performance Reference Handbook - EASA EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Matching PlotDocument15 pagesMatching PlotUmer CheemaNo ratings yet
- Airplane Flying Handbook: FAA-H-8083-3C (2024)From EverandAirplane Flying Handbook: FAA-H-8083-3C (2024)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (12)
- CFD AssignmentDocument19 pagesCFD Assignmentapi-231747194No ratings yet
- Aircraft Weight and Balance Handbook: FAA-H-8083-1AFrom EverandAircraft Weight and Balance Handbook: FAA-H-8083-1ARating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Helicopter Flying Handbook (2024): FAA-H-8083-21BFrom EverandHelicopter Flying Handbook (2024): FAA-H-8083-21BRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Principle of Flight Unit - 4Document22 pagesPrinciple of Flight Unit - 4Rajni VermaNo ratings yet
- Kapal TerbangDocument10 pagesKapal TerbangKhairul HaqeemNo ratings yet
- How Plane Flies: Presentation For Air Port Planning & DesignDocument61 pagesHow Plane Flies: Presentation For Air Port Planning & DesignJawad Amjad GhauriNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Design Project - 150 Seater Passenger AircraftDocument118 pagesAircraft Design Project - 150 Seater Passenger Aircraftsonusingh786775% (12)
- An Investigation of The Aerodynamic Efficiency of Tailess AircraftDocument9 pagesAn Investigation of The Aerodynamic Efficiency of Tailess AircraftPaul Pipi OkonkwoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Wing DesignDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Wing DesignJef LeNo ratings yet
- Airfoil SelectionDocument7 pagesAirfoil SelectionHui Wen Tan100% (3)
- Leading Edge Devices - IVAO Documentation LibraryDocument3 pagesLeading Edge Devices - IVAO Documentation LibrarySetayesh YmNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Design Lecture 4Document6 pagesAircraft Design Lecture 4IILSA STOWERNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PT 1 N 2-Theory of FLightDocument23 pagesChapter 3 PT 1 N 2-Theory of FLightzuliana_ismail8564100% (1)
- Leading Edge DevicesDocument2 pagesLeading Edge DevicesAllan Gabriel UmaliNo ratings yet
- Lift To Drag: AileronsDocument6 pagesLift To Drag: AileronsSyed Qasim ZaheerNo ratings yet
- AircraftDesign 8 HighLiftDocument21 pagesAircraftDesign 8 HighLiftSonu SamalaNo ratings yet
- A Study of High-Altitude Manned Research Aircraft Employing Strut-Braced Wings of High-Aspect-Ratio - NASA CR-159262 - Smith, DeYoung, Lovell, Price, WashburnDocument94 pagesA Study of High-Altitude Manned Research Aircraft Employing Strut-Braced Wings of High-Aspect-Ratio - NASA CR-159262 - Smith, DeYoung, Lovell, Price, WashburnodehNo ratings yet
- High Speed Flight Lesson 3 Design and Calculations-1Document21 pagesHigh Speed Flight Lesson 3 Design and Calculations-1MarvinNo ratings yet
- AeroMorph Technical Concept Report (Initial)Document23 pagesAeroMorph Technical Concept Report (Initial)mariojchrisNo ratings yet
- Aircraft High Lift DevicesDocument19 pagesAircraft High Lift DevicesJason Clark AlontoNo ratings yet
- Canards - Design With CareDocument3 pagesCanards - Design With CareMark Evan Salutin100% (1)
- Notes On 8 Phak Chapter 6 Flight Control WordDocument11 pagesNotes On 8 Phak Chapter 6 Flight Control WordYash JadhavNo ratings yet
- Flight Testing of Mission Adaptive Compliant WingDocument18 pagesFlight Testing of Mission Adaptive Compliant WingBlack ForestNo ratings yet
- Wing Box DesignDocument7 pagesWing Box DesignArpit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hermanto - OIC - MMIE 2022Document7 pagesHermanto - OIC - MMIE 2022Bung HaFiedNo ratings yet
- Summary PDFDocument5 pagesSummary PDFStephen SianturiNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic CFD Analysis On High Lift MuDocument12 pagesAerodynamic CFD Analysis On High Lift MuBS GOURISARANNo ratings yet
- Flapping Wing MechanismDocument7 pagesFlapping Wing MechanismSiva BogaNo ratings yet
- FlapsDocument7 pagesFlapsamiino100% (1)
- Aircraft PerformanceDocument29 pagesAircraft PerformanceRajiv Vutukuri100% (1)
- Induce Drag Reduction of An Airplane WingDocument5 pagesInduce Drag Reduction of An Airplane WingAJER JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Structure - An Introduction To Major Airplane ComponentsDocument9 pagesAircraft Structure - An Introduction To Major Airplane ComponentsPj BaroesNo ratings yet
- Class 27Document54 pagesClass 27al98879No ratings yet
- Winglet Airfoil Maughmer Et AlDocument8 pagesWinglet Airfoil Maughmer Et Alzaid100% (1)
- Aerodynamics of A ParagliderDocument3 pagesAerodynamics of A Paraglider18th Attack SquadronNo ratings yet
- The Design and Testing of A Winglet Airfoil For Low-Speed AircraftDocument11 pagesThe Design and Testing of A Winglet Airfoil For Low-Speed AircraftJulio Herrera VenegasNo ratings yet
- Wing LetsDocument8 pagesWing LetsRuslan AganiNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Design Process: by G.Shivasam KumarDocument14 pagesAircraft Design Process: by G.Shivasam KumarShiva VickyNo ratings yet
- AIAA2003 6732 Blended Wing BodyDocument12 pagesAIAA2003 6732 Blended Wing BodyccoyureNo ratings yet
- 1358758693manuscript aeroIndia2013NagelDocument10 pages1358758693manuscript aeroIndia2013NagelMartin EliasNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Brake SystemDocument3 pagesAircraft Brake SystemYadana1No ratings yet
- The Aerodynamic Characteristics of High Lift Devices On Incompressible, Subsonic, andDocument8 pagesThe Aerodynamic Characteristics of High Lift Devices On Incompressible, Subsonic, andMj SantosNo ratings yet
- CFD Study of Annular Ducted FanDocument26 pagesCFD Study of Annular Ducted FanShravan Kumar YadamaniNo ratings yet
- Aircraft StructureDocument11 pagesAircraft StructureVagesh VagesNo ratings yet
- RC AirplaneDocument52 pagesRC AirplaneAvirup Sarkar50% (2)
- Design of A Biplane Wing For Small-Scale Aircraft: The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, 16802Document10 pagesDesign of A Biplane Wing For Small-Scale Aircraft: The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, 16802Anonymous qTKCWlxNo ratings yet
- Study Project (Ayyub Achilev)Document18 pagesStudy Project (Ayyub Achilev)Ayyub AchilevNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument4 pagesResearchmanvitha varmaNo ratings yet
- Eurofighter Typhoon Canard WingDocument1 pageEurofighter Typhoon Canard WingTinku BhargavNo ratings yet
- The Design of Winglets For Low-Speed AircraftDocument18 pagesThe Design of Winglets For Low-Speed Aircraftbarat3786100% (1)
- Design of The Modern Family of HeliDocument32 pagesDesign of The Modern Family of Heli邓帅No ratings yet
- AP4ATCO - Factors AffectingDocument12 pagesAP4ATCO - Factors Affectingsamirsamira928No ratings yet
- Lecture TA - 2: High Lift DevicesDocument9 pagesLecture TA - 2: High Lift DevicesSam LoveNo ratings yet
- Airplane Flying Handbook (2024): FAA-H-8083-3CFrom EverandAirplane Flying Handbook (2024): FAA-H-8083-3CRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Pilot's Encyclopedia of Aeronautical Knowledge: Federal Aviation AdministrationFrom EverandPilot's Encyclopedia of Aeronautical Knowledge: Federal Aviation AdministrationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- An Aviator's Field Guide to Middle-Altitude Flying: Practical skills and tips for flying between 10,000 and 25,000 feet MSLFrom EverandAn Aviator's Field Guide to Middle-Altitude Flying: Practical skills and tips for flying between 10,000 and 25,000 feet MSLRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- What Has Happened?: Issued A Warning To AirlinesDocument1 pageWhat Has Happened?: Issued A Warning To AirlinesASIM SHABANEHNo ratings yet
- DronesDocument1 pageDronesASIM SHABANEHNo ratings yet
- Vision enDocument124 pagesVision enASIM SHABANEHNo ratings yet
- 02 Duty Manager ToolDocument5 pages02 Duty Manager ToolASIM SHABANEHNo ratings yet
- SSIM Review Final2Document17 pagesSSIM Review Final2ASIM SHABANEHNo ratings yet
- 5G and Aviation SafetyDocument9 pages5G and Aviation SafetyASIM SHABANEHNo ratings yet
- Aviation Dispatch Oral QuestionsDocument49 pagesAviation Dispatch Oral QuestionsASIM SHABANEHNo ratings yet
- CasestudyThe Crash of ValuJet Flight 592Document2 pagesCasestudyThe Crash of ValuJet Flight 592Inventive MinecraftNo ratings yet
- Airport Thesis PresentationDocument6 pagesAirport Thesis Presentationcrystalwilliamscleveland100% (2)
- AviationDocument27 pagesAviationAmar NathNo ratings yet
- Airlincolndata Sas7bdatDocument2 pagesAirlincolndata Sas7bdatAnis BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Airport Activities VocabularyDocument4 pagesAirport Activities VocabularyMariana TomsonNo ratings yet
- Amt 1101 Learning Module 6 (Guided Questions) 1. What Is An Airport Wind Direction Indicator and Its Function?Document4 pagesAmt 1101 Learning Module 6 (Guided Questions) 1. What Is An Airport Wind Direction Indicator and Its Function?ligaya delgadoNo ratings yet
- Basic Aircraft StructureDocument5 pagesBasic Aircraft StructureAndrie Vonn NerpiolNo ratings yet
- Your Electronic Ticket-EMD Receipt - 27 Agustus 2023Document2 pagesYour Electronic Ticket-EMD Receipt - 27 Agustus 2023SYAIFULLAH NURNo ratings yet
- Makgantai - Journal of Xi'an University of Architecture & Technology - 2021Document18 pagesMakgantai - Journal of Xi'an University of Architecture & Technology - 2021Adi SetiyawanNo ratings yet
- Pretest Section 5Document10 pagesPretest Section 5Sri Setio NingrumNo ratings yet
- Notes On 8 Phak Chapter 6 Flight Control WordDocument11 pagesNotes On 8 Phak Chapter 6 Flight Control WordYash JadhavNo ratings yet
- Easa Ad Us-2020-11-04 1Document7 pagesEasa Ad Us-2020-11-04 1Talha stajNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Acts Rules UpdatedDocument11 pagesAircraft Acts Rules UpdatedReena Bansal100% (1)
- Lumbia Airfield Type: Civil Aviation Authority of The Philippines (Document2 pagesLumbia Airfield Type: Civil Aviation Authority of The Philippines (Kristian Alexander ColocarNo ratings yet
- Mu1y335c General Personnel Authorization List For Avh Operators (Roster Avianca) 05may2023Document74 pagesMu1y335c General Personnel Authorization List For Avh Operators (Roster Avianca) 05may2023Camilo GiraldoNo ratings yet
- NTSB Accident Preliminary Report: Lamoni, IowaDocument2 pagesNTSB Accident Preliminary Report: Lamoni, IowaLocal 5 News (WOI-TV)No ratings yet
- ACL 01-08-2018 (Part A, B, C, D, E) + - 2-GARUDADocument106 pagesACL 01-08-2018 (Part A, B, C, D, E) + - 2-GARUDAilyas jamainNo ratings yet
- NAT OPS Bulletin 2017 - 002rev04Document9 pagesNAT OPS Bulletin 2017 - 002rev04FrançoisNo ratings yet
- Theory of FlightDocument9 pagesTheory of FlightBibek DubeyNo ratings yet
- Fuel Management 1666325772Document9 pagesFuel Management 1666325772wittyspiritNo ratings yet
- Aviation Study - Regulation Miscellaneous Que. Paper - 3Document4 pagesAviation Study - Regulation Miscellaneous Que. Paper - 3parul sharmaNo ratings yet
- CAD359Document61 pagesCAD359Tashbaev RuslanNo ratings yet
- Air Asia ThreatsDocument3 pagesAir Asia ThreatsIrwan NizarNo ratings yet
- Hürkuş, THY, Nuri DemirağDocument3 pagesHürkuş, THY, Nuri DemirağSinan AydemirNo ratings yet
- About Stapleford Flight Centre: Jetway Integrated TrainingDocument2 pagesAbout Stapleford Flight Centre: Jetway Integrated TrainingData Really CoolNo ratings yet
- Atp - (Chap. 07) Emergencies, Hazards, and Flight PhysiologyDocument9 pagesAtp - (Chap. 07) Emergencies, Hazards, and Flight Physiologycorina vargas cocaNo ratings yet
- Delta Airlines Case StudyDocument4 pagesDelta Airlines Case Studynrmpz9b54dNo ratings yet
- Explanatory Note Tcds Easa.a.064 Airbus A318 A319 A320 A321 Annex I Iss 21-20230602Document295 pagesExplanatory Note Tcds Easa.a.064 Airbus A318 A319 A320 A321 Annex I Iss 21-20230602HENIGUEDRINo ratings yet
- Sin Oktober 2022Document1 pageSin Oktober 2022Faisal AzharNo ratings yet
- 4 Forces of FlightDocument2 pages4 Forces of FlightSenan ShahverdiyevNo ratings yet
Flaps and Slats
Flaps and Slats
Uploaded by
ASIM SHABANEHOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Flaps and Slats
Flaps and Slats
Uploaded by
ASIM SHABANEHCopyright:
Available Formats
Abstract
With advent of latest manufacturing processes in aviation industry, ways to improve the
aerodynamic performance of aircraft wings have been researched by several companies in
aviation and defence industry. These new design and manufacturing techniques help to
enhance the aerodynamic behaviour of aircraft wings at high or very high Reynolds
number which typically conform to the cruising altitudes of aircrafts as well as during
landing and take-off stages. The slat and flap devices usually serve as extensions to main
aerofoil element of an aircraft wing and intended to divert the turbulent flow along the
chord length and improve the maximum lift coefficient by 40-60%. More so than before,
these methods have also aimed to achieve improved fuel efficiency by up to 10-13% by
drag reduction. With a net change of 24% in fuel prices in aviation turbine fuel seen over
the last decade, the future of commercial aviation will continue to look for advanced
technologies in design of aircraft wings that are promised to provide safe and reliable air
transportation.
Keywords: slat, flap, aerofoil, lift coefficient, drag coefficient
Introduction
Slats and flaps are high lift devices, intended to produce maximum lift coefficients on
aerodynamically designed wings of aircraft. The use of aerodynamic extensions are done in
order to increase the effective plan form area of wing thereby generating extra lift force
required for an aircraft wing. A typical passenger aircraft has three stages in a flight during
which the high lift devices are deployed and retracted when required. From Figure 1A,
there are seven types of extensions. The first one known as plain flap is attached to trailing
edge; second one is slotted flap and has cove in the aft region of main element. A split flap is
integrated into the main element and activated by means of a lever near the trailing edge.
A zap flap is similar to a split flap but operates using a hinged kinematic mechanism
present at the main element along with a crank and lever actuator to retract and deploy
when required. The most frequently used flap in aircraft is Fowler flap which forms a
unique combination with main element, since it operates using a servo mechanism with a
transverse beam support along the wing span. Hence to increase the lift coefficient, the no
of slots can be added in order two or three and arranged in tandem at the trailing edge of
aerofoil. This is done to augment maximum lift coefficient at a given angle of attack and to
enable the lateral stability of aircraft during rolling manoeuvre. 1
You might also like
- 737 Performance Reference Handbook - EASA EditionFrom Everand737 Performance Reference Handbook - EASA EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Matching PlotDocument15 pagesMatching PlotUmer CheemaNo ratings yet
- Airplane Flying Handbook: FAA-H-8083-3C (2024)From EverandAirplane Flying Handbook: FAA-H-8083-3C (2024)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (12)
- CFD AssignmentDocument19 pagesCFD Assignmentapi-231747194No ratings yet
- Aircraft Weight and Balance Handbook: FAA-H-8083-1AFrom EverandAircraft Weight and Balance Handbook: FAA-H-8083-1ARating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Helicopter Flying Handbook (2024): FAA-H-8083-21BFrom EverandHelicopter Flying Handbook (2024): FAA-H-8083-21BRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Principle of Flight Unit - 4Document22 pagesPrinciple of Flight Unit - 4Rajni VermaNo ratings yet
- Kapal TerbangDocument10 pagesKapal TerbangKhairul HaqeemNo ratings yet
- How Plane Flies: Presentation For Air Port Planning & DesignDocument61 pagesHow Plane Flies: Presentation For Air Port Planning & DesignJawad Amjad GhauriNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Design Project - 150 Seater Passenger AircraftDocument118 pagesAircraft Design Project - 150 Seater Passenger Aircraftsonusingh786775% (12)
- An Investigation of The Aerodynamic Efficiency of Tailess AircraftDocument9 pagesAn Investigation of The Aerodynamic Efficiency of Tailess AircraftPaul Pipi OkonkwoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Wing DesignDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Wing DesignJef LeNo ratings yet
- Airfoil SelectionDocument7 pagesAirfoil SelectionHui Wen Tan100% (3)
- Leading Edge Devices - IVAO Documentation LibraryDocument3 pagesLeading Edge Devices - IVAO Documentation LibrarySetayesh YmNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Design Lecture 4Document6 pagesAircraft Design Lecture 4IILSA STOWERNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PT 1 N 2-Theory of FLightDocument23 pagesChapter 3 PT 1 N 2-Theory of FLightzuliana_ismail8564100% (1)
- Leading Edge DevicesDocument2 pagesLeading Edge DevicesAllan Gabriel UmaliNo ratings yet
- Lift To Drag: AileronsDocument6 pagesLift To Drag: AileronsSyed Qasim ZaheerNo ratings yet
- AircraftDesign 8 HighLiftDocument21 pagesAircraftDesign 8 HighLiftSonu SamalaNo ratings yet
- A Study of High-Altitude Manned Research Aircraft Employing Strut-Braced Wings of High-Aspect-Ratio - NASA CR-159262 - Smith, DeYoung, Lovell, Price, WashburnDocument94 pagesA Study of High-Altitude Manned Research Aircraft Employing Strut-Braced Wings of High-Aspect-Ratio - NASA CR-159262 - Smith, DeYoung, Lovell, Price, WashburnodehNo ratings yet
- High Speed Flight Lesson 3 Design and Calculations-1Document21 pagesHigh Speed Flight Lesson 3 Design and Calculations-1MarvinNo ratings yet
- AeroMorph Technical Concept Report (Initial)Document23 pagesAeroMorph Technical Concept Report (Initial)mariojchrisNo ratings yet
- Aircraft High Lift DevicesDocument19 pagesAircraft High Lift DevicesJason Clark AlontoNo ratings yet
- Canards - Design With CareDocument3 pagesCanards - Design With CareMark Evan Salutin100% (1)
- Notes On 8 Phak Chapter 6 Flight Control WordDocument11 pagesNotes On 8 Phak Chapter 6 Flight Control WordYash JadhavNo ratings yet
- Flight Testing of Mission Adaptive Compliant WingDocument18 pagesFlight Testing of Mission Adaptive Compliant WingBlack ForestNo ratings yet
- Wing Box DesignDocument7 pagesWing Box DesignArpit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hermanto - OIC - MMIE 2022Document7 pagesHermanto - OIC - MMIE 2022Bung HaFiedNo ratings yet
- Summary PDFDocument5 pagesSummary PDFStephen SianturiNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic CFD Analysis On High Lift MuDocument12 pagesAerodynamic CFD Analysis On High Lift MuBS GOURISARANNo ratings yet
- Flapping Wing MechanismDocument7 pagesFlapping Wing MechanismSiva BogaNo ratings yet
- FlapsDocument7 pagesFlapsamiino100% (1)
- Aircraft PerformanceDocument29 pagesAircraft PerformanceRajiv Vutukuri100% (1)
- Induce Drag Reduction of An Airplane WingDocument5 pagesInduce Drag Reduction of An Airplane WingAJER JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Structure - An Introduction To Major Airplane ComponentsDocument9 pagesAircraft Structure - An Introduction To Major Airplane ComponentsPj BaroesNo ratings yet
- Class 27Document54 pagesClass 27al98879No ratings yet
- Winglet Airfoil Maughmer Et AlDocument8 pagesWinglet Airfoil Maughmer Et Alzaid100% (1)
- Aerodynamics of A ParagliderDocument3 pagesAerodynamics of A Paraglider18th Attack SquadronNo ratings yet
- The Design and Testing of A Winglet Airfoil For Low-Speed AircraftDocument11 pagesThe Design and Testing of A Winglet Airfoil For Low-Speed AircraftJulio Herrera VenegasNo ratings yet
- Wing LetsDocument8 pagesWing LetsRuslan AganiNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Design Process: by G.Shivasam KumarDocument14 pagesAircraft Design Process: by G.Shivasam KumarShiva VickyNo ratings yet
- AIAA2003 6732 Blended Wing BodyDocument12 pagesAIAA2003 6732 Blended Wing BodyccoyureNo ratings yet
- 1358758693manuscript aeroIndia2013NagelDocument10 pages1358758693manuscript aeroIndia2013NagelMartin EliasNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Brake SystemDocument3 pagesAircraft Brake SystemYadana1No ratings yet
- The Aerodynamic Characteristics of High Lift Devices On Incompressible, Subsonic, andDocument8 pagesThe Aerodynamic Characteristics of High Lift Devices On Incompressible, Subsonic, andMj SantosNo ratings yet
- CFD Study of Annular Ducted FanDocument26 pagesCFD Study of Annular Ducted FanShravan Kumar YadamaniNo ratings yet
- Aircraft StructureDocument11 pagesAircraft StructureVagesh VagesNo ratings yet
- RC AirplaneDocument52 pagesRC AirplaneAvirup Sarkar50% (2)
- Design of A Biplane Wing For Small-Scale Aircraft: The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, 16802Document10 pagesDesign of A Biplane Wing For Small-Scale Aircraft: The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, 16802Anonymous qTKCWlxNo ratings yet
- Study Project (Ayyub Achilev)Document18 pagesStudy Project (Ayyub Achilev)Ayyub AchilevNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument4 pagesResearchmanvitha varmaNo ratings yet
- Eurofighter Typhoon Canard WingDocument1 pageEurofighter Typhoon Canard WingTinku BhargavNo ratings yet
- The Design of Winglets For Low-Speed AircraftDocument18 pagesThe Design of Winglets For Low-Speed Aircraftbarat3786100% (1)
- Design of The Modern Family of HeliDocument32 pagesDesign of The Modern Family of Heli邓帅No ratings yet
- AP4ATCO - Factors AffectingDocument12 pagesAP4ATCO - Factors Affectingsamirsamira928No ratings yet
- Lecture TA - 2: High Lift DevicesDocument9 pagesLecture TA - 2: High Lift DevicesSam LoveNo ratings yet
- Airplane Flying Handbook (2024): FAA-H-8083-3CFrom EverandAirplane Flying Handbook (2024): FAA-H-8083-3CRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Pilot's Encyclopedia of Aeronautical Knowledge: Federal Aviation AdministrationFrom EverandPilot's Encyclopedia of Aeronautical Knowledge: Federal Aviation AdministrationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- An Aviator's Field Guide to Middle-Altitude Flying: Practical skills and tips for flying between 10,000 and 25,000 feet MSLFrom EverandAn Aviator's Field Guide to Middle-Altitude Flying: Practical skills and tips for flying between 10,000 and 25,000 feet MSLRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- What Has Happened?: Issued A Warning To AirlinesDocument1 pageWhat Has Happened?: Issued A Warning To AirlinesASIM SHABANEHNo ratings yet
- DronesDocument1 pageDronesASIM SHABANEHNo ratings yet
- Vision enDocument124 pagesVision enASIM SHABANEHNo ratings yet
- 02 Duty Manager ToolDocument5 pages02 Duty Manager ToolASIM SHABANEHNo ratings yet
- SSIM Review Final2Document17 pagesSSIM Review Final2ASIM SHABANEHNo ratings yet
- 5G and Aviation SafetyDocument9 pages5G and Aviation SafetyASIM SHABANEHNo ratings yet
- Aviation Dispatch Oral QuestionsDocument49 pagesAviation Dispatch Oral QuestionsASIM SHABANEHNo ratings yet
- CasestudyThe Crash of ValuJet Flight 592Document2 pagesCasestudyThe Crash of ValuJet Flight 592Inventive MinecraftNo ratings yet
- Airport Thesis PresentationDocument6 pagesAirport Thesis Presentationcrystalwilliamscleveland100% (2)
- AviationDocument27 pagesAviationAmar NathNo ratings yet
- Airlincolndata Sas7bdatDocument2 pagesAirlincolndata Sas7bdatAnis BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Airport Activities VocabularyDocument4 pagesAirport Activities VocabularyMariana TomsonNo ratings yet
- Amt 1101 Learning Module 6 (Guided Questions) 1. What Is An Airport Wind Direction Indicator and Its Function?Document4 pagesAmt 1101 Learning Module 6 (Guided Questions) 1. What Is An Airport Wind Direction Indicator and Its Function?ligaya delgadoNo ratings yet
- Basic Aircraft StructureDocument5 pagesBasic Aircraft StructureAndrie Vonn NerpiolNo ratings yet
- Your Electronic Ticket-EMD Receipt - 27 Agustus 2023Document2 pagesYour Electronic Ticket-EMD Receipt - 27 Agustus 2023SYAIFULLAH NURNo ratings yet
- Makgantai - Journal of Xi'an University of Architecture & Technology - 2021Document18 pagesMakgantai - Journal of Xi'an University of Architecture & Technology - 2021Adi SetiyawanNo ratings yet
- Pretest Section 5Document10 pagesPretest Section 5Sri Setio NingrumNo ratings yet
- Notes On 8 Phak Chapter 6 Flight Control WordDocument11 pagesNotes On 8 Phak Chapter 6 Flight Control WordYash JadhavNo ratings yet
- Easa Ad Us-2020-11-04 1Document7 pagesEasa Ad Us-2020-11-04 1Talha stajNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Acts Rules UpdatedDocument11 pagesAircraft Acts Rules UpdatedReena Bansal100% (1)
- Lumbia Airfield Type: Civil Aviation Authority of The Philippines (Document2 pagesLumbia Airfield Type: Civil Aviation Authority of The Philippines (Kristian Alexander ColocarNo ratings yet
- Mu1y335c General Personnel Authorization List For Avh Operators (Roster Avianca) 05may2023Document74 pagesMu1y335c General Personnel Authorization List For Avh Operators (Roster Avianca) 05may2023Camilo GiraldoNo ratings yet
- NTSB Accident Preliminary Report: Lamoni, IowaDocument2 pagesNTSB Accident Preliminary Report: Lamoni, IowaLocal 5 News (WOI-TV)No ratings yet
- ACL 01-08-2018 (Part A, B, C, D, E) + - 2-GARUDADocument106 pagesACL 01-08-2018 (Part A, B, C, D, E) + - 2-GARUDAilyas jamainNo ratings yet
- NAT OPS Bulletin 2017 - 002rev04Document9 pagesNAT OPS Bulletin 2017 - 002rev04FrançoisNo ratings yet
- Theory of FlightDocument9 pagesTheory of FlightBibek DubeyNo ratings yet
- Fuel Management 1666325772Document9 pagesFuel Management 1666325772wittyspiritNo ratings yet
- Aviation Study - Regulation Miscellaneous Que. Paper - 3Document4 pagesAviation Study - Regulation Miscellaneous Que. Paper - 3parul sharmaNo ratings yet
- CAD359Document61 pagesCAD359Tashbaev RuslanNo ratings yet
- Air Asia ThreatsDocument3 pagesAir Asia ThreatsIrwan NizarNo ratings yet
- Hürkuş, THY, Nuri DemirağDocument3 pagesHürkuş, THY, Nuri DemirağSinan AydemirNo ratings yet
- About Stapleford Flight Centre: Jetway Integrated TrainingDocument2 pagesAbout Stapleford Flight Centre: Jetway Integrated TrainingData Really CoolNo ratings yet
- Atp - (Chap. 07) Emergencies, Hazards, and Flight PhysiologyDocument9 pagesAtp - (Chap. 07) Emergencies, Hazards, and Flight Physiologycorina vargas cocaNo ratings yet
- Delta Airlines Case StudyDocument4 pagesDelta Airlines Case Studynrmpz9b54dNo ratings yet
- Explanatory Note Tcds Easa.a.064 Airbus A318 A319 A320 A321 Annex I Iss 21-20230602Document295 pagesExplanatory Note Tcds Easa.a.064 Airbus A318 A319 A320 A321 Annex I Iss 21-20230602HENIGUEDRINo ratings yet
- Sin Oktober 2022Document1 pageSin Oktober 2022Faisal AzharNo ratings yet
- 4 Forces of FlightDocument2 pages4 Forces of FlightSenan ShahverdiyevNo ratings yet