Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Reviewer
Science Reviewer
Uploaded by
gianne ongOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Reviewer
Science Reviewer
Uploaded by
gianne ongCopyright:
Available Formats
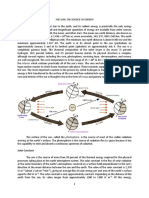
ELECTRICITY
Electricity-form of energy
Electric current- flow of energy
Electric charge-made up positive(protons)and negative(electorns
Electric circuit-made up electric components
1.open circuit-made up electric components
2.closed circuit energy flow
Components:
Cell- power supply
Lamp-source of light
Switch-make an electric
Wire-pathway electricity to flow
Conductor-flow easily
Copper
Aluminum
Steel
Metal
Insulator- Doesn’t let electricity flow
Wood
Plastic
Glass
Rubber
Temparature-material increase as temp
Diameter- of were
1.Thick-mahina
2.Thin-malakas
3 Types of electric:
1. Energy source
2. Wire
3. Load
Battery – soure of electricity
Switch – control the movement
Schematic diagram-symbol for components of circuit
- Single cell
- Battery
- Connecting wire
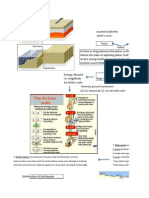
EARTHQUAKE
Earthquake – is an unpredictable disaster
2 types of crust
1.Continental crust – makes up earth’s landmass
2.Oceanic crust – makes up most of the ocean floor
3 types of fault
1.Normal fault – hanging wall
2. Reverse fault – hanging wall moves up . compression
3. Strike slip fault – horizontal movement
Stress – push- and-pull action
Fault – where the rocks break or tear apart
Trenches – are the deepest part of ocean
Mantle – 66%
Crust – 1%
Core – 33%
Cause of earthquake- faulting
Effect of earthquake – tsunami
Focus – source of earthquake
Epicenter – location on earth
3 types of seismic waves
1.Primary waves – can move through solid rocks and fluids
2.Secondary waves – perpendicular to the direction of the wave.can only move through solid rocks.can be
recorded
3.Surface waves – source of interaction . travels directly upward to the epicenter
Magnitude - a measure of the amount of energy released
Intensity- amount of damage
Seismograph – a instrument that detects and measures waves
Seismogram – a record
PAG-ASA – Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration.
PAR – Philippine Area of Responsibility
WMO – World Meteorological Organization
PHIVOLCS – Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology
RADAR – radio detection and ranging
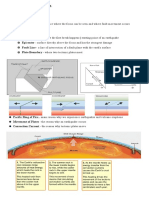
TYPHOONS
- Large storm system
Airmasses – weather changes are caused by the movements of bodies of air
2 types
1. Typhoons – northeast pacific ocean
2. Cyclones – Indian ocean.low pressure with rising warm air. Came from the latin word “kyklocin”
Coriolis effect - circulating air is deflected toward the right in the Northern Hemisphere and toward the left
in the Southern Hemisphere
Monsoon - the season of heavy rain, the wind that brings rain, or the heavy rain that falls during the
summer in hot Asian countries
Front – when two masses meet
2 types
1. Cold front
2. Warm front
Eye wall – strongest part
Spiral rainbods – katamtaman
Eye – calm center
You might also like
- ELSC Week 1-10Document66 pagesELSC Week 1-10Noel Andrei Delumen100% (1)
- CoreDocument4 pagesCorePatrick AmistadNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerrDocument10 pagesScience ReviewerrBJHSDomdomNo ratings yet
- Space WeatherDocument9 pagesSpace Weather靖康No ratings yet
- Solar StormsDocument6 pagesSolar StormsgoxtadNo ratings yet
- Space Weather: Dr. Piyush KuchhalDocument26 pagesSpace Weather: Dr. Piyush KuchhalAnurag RanaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 2Document6 pagesReviewer 2jazlynmaygalleposo417No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - The Lunar Environment and IssuesDocument35 pagesChapter 5 - The Lunar Environment and IssuesgovindaraoyNo ratings yet
- Disturbances of The SunDocument32 pagesDisturbances of The SunRuby AnnNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and Faults LectureDocument41 pagesEarthquakes and Faults Lectureervynsana100% (1)
- Solar Storm Threat Analysis James Marusek Impact 2007Document29 pagesSolar Storm Threat Analysis James Marusek Impact 2007Alex Bernal, CMTNo ratings yet
- Natural Disasters ReviewDocument9 pagesNatural Disasters ReviewKalaisan KalaichelvanNo ratings yet
- Space Weather Super-Storm Not IF But WHEN and Extreme Solar MinimumDocument30 pagesSpace Weather Super-Storm Not IF But WHEN and Extreme Solar Minimumbergindo7318No ratings yet
- ELSC 1atDocument43 pagesELSC 1atYsha Salonga100% (9)
- Geodynamo Stimulating ReportDocument10 pagesGeodynamo Stimulating ReportAn TranNo ratings yet
- Geophysics and Medical PhysicsDocument5 pagesGeophysics and Medical PhysicsjanetpriscillaNo ratings yet
- Two Kinds of Crust: Plate TectonicsDocument4 pagesTwo Kinds of Crust: Plate TectonicsPuki WukiNo ratings yet
- Science Dictionary: Imus Institute of Science and TechnologyDocument16 pagesScience Dictionary: Imus Institute of Science and Technologydenise blaireNo ratings yet
- Pointers in ScienceDocument4 pagesPointers in SciencenigeldavidmendanaNo ratings yet
- IEEE Dec 05 ArticleDocument6 pagesIEEE Dec 05 ArticleUivananNo ratings yet
- It Is A Record Made by The SeismographDocument3 pagesIt Is A Record Made by The SeismographCristy Villamor GestaNo ratings yet
- The Earth's Interior: SeismographsDocument3 pagesThe Earth's Interior: SeismographsHana ZaneNo ratings yet
- Science Dictionary: Imus Institute of Science and TechnologyDocument17 pagesScience Dictionary: Imus Institute of Science and Technologydenise blaireNo ratings yet
- ITCZ (Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone) : Hydrometeorogical HazardsDocument9 pagesITCZ (Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone) : Hydrometeorogical HazardsVjion BeloNo ratings yet
- Solar TsunamiDocument22 pagesSolar Tsunamipetrishia7_317164251No ratings yet
- Geomorphology Notes by PMFIAS PDFDocument302 pagesGeomorphology Notes by PMFIAS PDFAnkush RajNo ratings yet
- Observing The Earth Es 1000 Exam 2 Review QuestionsDocument4 pagesObserving The Earth Es 1000 Exam 2 Review QuestionsortijuanNo ratings yet
- Class Note 1 B - 2B - Radiation and Temperature-1Document23 pagesClass Note 1 B - 2B - Radiation and Temperature-1Mangal MurmuNo ratings yet
- Class Note 1 B - 2B - Radiation and Temperature-1Document23 pagesClass Note 1 B - 2B - Radiation and Temperature-1Mangal MurmuNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 Quarter 1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 10 Quarter 1 ReviewerLeslie IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Mind MapDocument6 pagesEarthquake Mind MapMalia DamitNo ratings yet
- Jose AaronDocument4 pagesJose AaronRady John Nacorda MarquillaNo ratings yet
- Badai MatahariDocument9 pagesBadai MatahariKhairun NisaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Pointers 1Document8 pagesEarth Science Pointers 1EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- Geography ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeography ReviewerAbet Barile100% (2)
- The Cosmic Engine - Summary: Life Cycle of A Star of One Stellar/solar Mass, Which Is A Star Like Our SunDocument2 pagesThe Cosmic Engine - Summary: Life Cycle of A Star of One Stellar/solar Mass, Which Is A Star Like Our SunTon5698No ratings yet
- GD12 Gempa Bumi Dan TrsunamiDocument40 pagesGD12 Gempa Bumi Dan TrsunamiDea TantraNo ratings yet
- Vertical Structure of The Atmosphere: Introduction To Meteorology Leila CarvalhoDocument31 pagesVertical Structure of The Atmosphere: Introduction To Meteorology Leila CarvalhoAfsheen ZafarNo ratings yet
- Principles of StratigraphyDocument5 pagesPrinciples of StratigraphyMark Angelo Maylas DomingoNo ratings yet
- A Profile of Space WeatherDocument11 pagesA Profile of Space WeatherLisette SimonNo ratings yet
- Lec20 WEATHER ELEMENTS AND THEIR INFLUENCE ON DIFFERENT CROPSDocument31 pagesLec20 WEATHER ELEMENTS AND THEIR INFLUENCE ON DIFFERENT CROPSYashasvi ThakurNo ratings yet
- 6 - Earthquake Hazard and Risk ReductionmethodDocument4 pages6 - Earthquake Hazard and Risk ReductionmethodAnaliza Mg OriasNo ratings yet
- Physical Geography Ib Exam NotesDocument11 pagesPhysical Geography Ib Exam NotesvastovastareNo ratings yet
- Earth Science 2nd QuarterDocument11 pagesEarth Science 2nd QuarterJhoana paola SugayNo ratings yet
- Lecture Guide in Science 10Document5 pagesLecture Guide in Science 10reynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes: Class 9 - Total Geography Morning StarDocument7 pagesEarthquakes: Class 9 - Total Geography Morning StarLEKHRAJ YADAV K MNo ratings yet
- How Solar Flares Affect Communication - SciencingDocument2 pagesHow Solar Flares Affect Communication - SciencingchelseyNo ratings yet
- Life Giving Sun Written Report 1Document10 pagesLife Giving Sun Written Report 1Jeraldine ManipolNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Sci Q1 G10Document27 pagesPlate Tectonics Sci Q1 G10Charlotte Anne FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Science 2nd Periodical Test ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience 2nd Periodical Test ReviewerscribdpamoreNo ratings yet
- SunDocument18 pagesSunDheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- StarsDocument38 pagesStarsMunirah SaaidNo ratings yet
- Principles of StratigraphyDocument5 pagesPrinciples of StratigraphyMark Angelo Maylas DomingoNo ratings yet
- 9.3 Main Processes of The Earth: Exogenic Process - Endogenic ProcessDocument17 pages9.3 Main Processes of The Earth: Exogenic Process - Endogenic ProcessLim LenNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and FaultsDocument3 pagesEarthquakes and Faultsayeen miguelNo ratings yet
- Earth SciDocument9 pagesEarth SciChelsea AndreaNo ratings yet
- EarthDocument43 pagesEarthalutes2000No ratings yet
- Faults & Earthqaukes NotesDocument1 pageFaults & Earthqaukes NotesMARISTELA MACARANASNo ratings yet
- Mapeh Reviewer 2ndDocument3 pagesMapeh Reviewer 2ndgianne ongNo ratings yet
- CL ReviewerDocument2 pagesCL Reviewergianne ongNo ratings yet
- Esp ReviewerDocument2 pagesEsp Reviewergianne ongNo ratings yet
- English ReviewerDocument2 pagesEnglish Reviewergianne ongNo ratings yet
- Mapeh ReviewerDocument5 pagesMapeh Reviewergianne ongNo ratings yet
- Tle ReviewerDocument3 pagesTle Reviewergianne ongNo ratings yet
- 10 Science NcertSolutions Chapter 10 Intext Page 176Document4 pages10 Science NcertSolutions Chapter 10 Intext Page 176Anita GargNo ratings yet
- Vincent PDFDocument4 pagesVincent PDFSarinKorthawornwongNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion and Management: Daniel Chemisana, Joan Ignasi RosellDocument8 pagesEnergy Conversion and Management: Daniel Chemisana, Joan Ignasi RosellElie ZorbaNo ratings yet
- BKI Rules For Machinery Sec 11Document80 pagesBKI Rules For Machinery Sec 11Hendri FathurNo ratings yet
- Thermal Analysis of Extruded Aluminum Fin Heat Sink For LED Cooling ApplicationDocument4 pagesThermal Analysis of Extruded Aluminum Fin Heat Sink For LED Cooling ApplicationDilip SwamiNo ratings yet
- Issue No 20 - Cantilever Beams - Part 1 Beam StiffnessDocument2 pagesIssue No 20 - Cantilever Beams - Part 1 Beam Stiffnessdox4useNo ratings yet
- Wigner PDFDocument4 pagesWigner PDFShweta SridharNo ratings yet
- 5 6075848336798123065Document6 pages5 6075848336798123065Ajay JayanNo ratings yet
- Ebook Chemistry and Chemical Reactivity 9Th Edition Kotz Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument44 pagesEbook Chemistry and Chemical Reactivity 9Th Edition Kotz Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFMrNicolasGuerraJrnsadz100% (14)
- SuspensionDocument56 pagesSuspensionHarnil SoniNo ratings yet
- Egyptian FRP CodeDocument166 pagesEgyptian FRP CodeBaher M. El-GendyNo ratings yet
- Soal Soal Kimia Kelas 10Document4 pagesSoal Soal Kimia Kelas 10rohmatul aziziNo ratings yet
- 3 Module III Basic Concept of HazardDocument96 pages3 Module III Basic Concept of HazardJohn Robert AbinaNo ratings yet
- Ex1 SolutionDocument6 pagesEx1 SolutionArifiantoNo ratings yet
- The Profoto Ad PDFDocument128 pagesThe Profoto Ad PDFGeorge Palacios100% (2)
- Emulsions: - Part 1 Preparation Methods (Some) PropertiesDocument52 pagesEmulsions: - Part 1 Preparation Methods (Some) PropertieschandramohanNo ratings yet
- Sharifullah Kamran Pile Load Testing ReportDocument12 pagesSharifullah Kamran Pile Load Testing Reportstromek2006No ratings yet
- Data Sheet - Ozone Generator Water SystemDocument3 pagesData Sheet - Ozone Generator Water SystemleeNo ratings yet
- 35-TCV-005 & 35-TCV-006 Control Valve Sizing Project - Pembangunan 2 Tangki Black Product Control Valve - Gas, Steam or Vapor FlowDocument1 page35-TCV-005 & 35-TCV-006 Control Valve Sizing Project - Pembangunan 2 Tangki Black Product Control Valve - Gas, Steam or Vapor FlowFIRMANSYAHNo ratings yet
- Photochemistry 1Document364 pagesPhotochemistry 1praveen t m0% (1)
- 2 Combustion and ThermochemistryDocument111 pages2 Combustion and ThermochemistryAjin SajeevanNo ratings yet
- S8 - Language Worksheets - Unit 3Document4 pagesS8 - Language Worksheets - Unit 3Nazima MunirNo ratings yet
- Three-Point Bend Testing of HVOF AMDRY 9954 Coating On Ti-6Al-4V AlloyDocument7 pagesThree-Point Bend Testing of HVOF AMDRY 9954 Coating On Ti-6Al-4V AlloyNikhilNo ratings yet
- FWDS 0245 ADocument4 pagesFWDS 0245 AAlanka PrasadNo ratings yet
- Examples For Equation of StateDocument5 pagesExamples For Equation of StateAntarim Dutta100% (1)
- Chapter 9: Fluid Dynamics: A. The Equation of Continuity - Conservation of MassDocument12 pagesChapter 9: Fluid Dynamics: A. The Equation of Continuity - Conservation of MassLorenzo Miguel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 1.5.1 Memerhati Interferens Gelombang AirDocument3 pages1.5.1 Memerhati Interferens Gelombang AirNOR ZAWANI BINTI ABD.HALIM MoeNo ratings yet
- 2013 Yan Synthesis of Fiber Crosslinking Cationic Latex and Its Effect On Surface Properties ofDocument6 pages2013 Yan Synthesis of Fiber Crosslinking Cationic Latex and Its Effect On Surface Properties ofMohammed JamaliNo ratings yet
- FCI FlowmeterDocument4 pagesFCI FlowmeterMahesh KumbharNo ratings yet
- Evaporation (Lab Report)Document5 pagesEvaporation (Lab Report)Ynno0% (1)