Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 Mathematics Number and Algebra Levels F-6
2 Mathematics Number and Algebra Levels F-6
Uploaded by
Govind Sharma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pages2 Mathematics Number and Algebra Levels F-6
2 Mathematics Number and Algebra Levels F-6
Uploaded by
Govind SharmaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
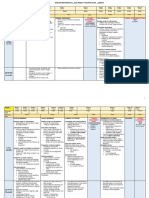
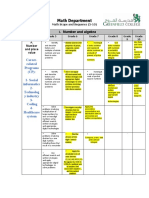
Mathematics – Number and Algebra: Foundation – Level 6
Foundation Level Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Level 6
Number and Algebra
Number and place value
Establish understanding of the language and Develop confidence with number sequences Investigate number sequences, initially those
Investigate the conditions required for a Identify and describe factors and multiples of
processes of counting by naming numbers in to and from 100 by ones from any starting increasing and decreasing by twos, threes, Investigate and use the properties of odd and Identify and describe properties of prime,
number to be odd or even and identify odd whole numbers and use them to solve
sequences, initially to and from 20, moving point. Skip count by twos, fives and tens fives and ten from any starting point, then even numbers composite, square and triangular numbers
and even numbers problems
from any starting point starting from zero moving to other sequences
Select and apply efficient mental and written
Connect number names, numerals and Recognise, model, read, write and order strategies and appropriate digital
Recognise, model, represent and order Recognise, model, represent and order Recognise, represent and order numbers to Use estimation and rounding to check the
quantities, including zero, initially up to 10 numbers to at least 100. Locate these technologies to solve problems involving all
numbers to at least 1000 numbers to at least 10 000 at least tens of thousands reasonableness of answers to calculations
and then beyond numbers on a number line four operations with whole numbers and
make estimates for these computations
Apply place value to partition, rearrange and Solve problems involving multiplication of
Group, partition and rearrange collections up Apply place value to partition, rearrange and Investigate everyday situations that use
Count collections to 100 by partitioning regroup numbers to at least tens of large numbers by one- or two-digit numbers
Subitise small collections of objects to 1000 in hundreds, tens and ones to regroup numbers to at least 10 000 to assist integers. Locate and represent these
numbers using place value thousands to assist calculations and solve using efficient mental, written strategies and
facilitate more efficient counting calculations and solve problems numbers on a number line
problems appropriate digital technologies
Represent and solve simple addition and
Compare, order and make correspondences Solve problems involving division by a one
subtraction problems using a range of Explore the connection between addition and Recognise and explain the connection Investigate number sequences involving
between collections, initially to 20, and digit number, including those that result in a
strategies including counting on, partitioning subtraction between addition and subtraction multiples of 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, and 9
explain reasoning remainder
and rearranging parts
Recall addition facts for single-digit numbers
Solve simple addition and subtraction Use efficient mental and written strategies
Represent practical situations to model Represent practical situations that model and related subtraction facts to develop Recall multiplication facts up to 10 × 10 and
problems using a range of efficient mental and apply appropriate digital technologies to
addition and subtraction sharing increasingly efficient mental strategies for related division facts
and written strategies solve problems
computation
Develop efficient mental and written
Represent practical situations to model Recognise and represent multiplication as Recall multiplication facts of two, three, five strategies and use appropriate digital Recognise, represent and order numbers to
sharing repeated addition, groups and arrays and ten and related division facts technologies for multiplication and for division at least hundreds of thousands
where there is no remainder
Represent and solve problems involving
Recognise and represent division as grouping
multiplication using efficient mental and
into equal sets and solve simple problems
written strategies and appropriate digital
using these representations
technologies
Money and financial mathematics
Count and order small collections of Represent money values in multiple ways and Solve problems involving purchases and the Investigate and calculate percentage
Represent simple, everyday financial Recognise, describe and order Australian
Australian coins and notes according to their count the change required for simple calculation of change to the nearest five cents Create simple financial plans discounts of 10%, 25% and 50% on sale
situations involving money coins according to their value
value transactions to the nearest five cents with and without digital technologies items, with and without digital technologies
Fractions and decimals
Recognise and interpret common uses of Model and represent unit fractions including Compare and order common unit fractions Compare fractions with related denominators
Recognise and describe one-half as one of Investigate equivalent fractions used in
halves, quarters and eighths of shapes and 1/2, 1/4, 1/3, 1/5 and their multiples to a and locate and represent them on a number and locate and represent them on a number
two equal parts of a whole contexts
collections complete whole line line
Count by quarters, halves and thirds, Investigate strategies to solve problems Solve problems involving addition and
including with mixed numerals. Locate and involving addition and subtraction of fractions subtraction of fractions with the same or
represent these fractions on a number line with the same denominator related denominators
Recognise that the place value system can
Find a simple fraction of a quantity where the
be extended to tenths and hundredths. Make Recognise that the place value system can
result is a whole number, with and without
connections between fractions and decimal be extended beyond hundredths
digital technologies
notation
Add and subtract decimals, with and without
digital technologies, and use estimation and
Compare, order and represent decimals
rounding to check the reasonableness of
answers
Multiply decimals by whole numbers and
perform divisions by non-zero whole numbers
where the results are terminating decimals,
with and without digital technologies
Multiply and divide decimals by powers of 10
Make connections between equivalent
fractions, decimals and percentages
© VCAA 24 February 2016
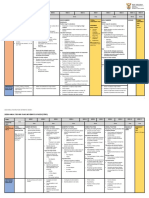
Mathematics – Number and Algebra: Foundation – Level 6
Foundation Level Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Level 6
Patterns and algebra
Sort and classify familiar objects and explain Continue and create sequences involving
Investigate and describe number patterns Describe, continue, and create number Describe, continue and create patterns with
the basis for these classifications, and copy, Describe patterns with numbers and identify Explore and describe number patterns whole numbers, fractions and decimals.
formed by skip counting and patterns with patterns resulting from performing addition or fractions, decimals and whole numbers
continue and create patterns with objects and missing elements resulting from performing multiplication Describe the rule used to create the
objects subtraction resulting from addition and subtraction
drawings sequence
Use a function machine and the inverse Solve word problems by using number Use equivalent number sentences involving
Recognise the importance of repetition of a Solve problems by using number sentences Explore the use of brackets and order of
Follow a short sequence of instructions machine as a model to apply mathematical sentences involving multiplication or division multiplication and division to find unknown
process in solving problems for addition or subtraction operations to write number sentences
rules to numbers or shapes where there is no remainder quantities
Apply repetition in arithmetic operations, Use equivalent number sentences involving Design algorithms involving branching and
Follow a mathematical algorithm involving
including multiplication as repeated addition addition and subtraction to find unknown iteration to solve specific classes of
branching and repetition (iteration)
and division as repeated subtraction quantities mathematical problems
Define a simple class of problems and use an
effective algorithm that involves a short
sequence of steps and decisions to solve
them
Achievement Standard
Students connect number names and Students count to and from 100 and locate Students count to and from, and order Students count and order numbers to and Students recall multiplication facts to 10 x 10 Students solve simple problems involving the Students recognise the properties of prime,
numerals with sets of up to 20 elements, these numbers on a number line. They numbers up to 1000. They perform simple from 10 000. They recognise the connection and related division facts. They choose four operations using a range of strategies composite, square and triangular numbers
estimate the size of these sets, and use partition numbers using place value and carry addition and subtraction calculations, using a between addition and subtraction, and solve appropriate strategies for calculations including digital technology. They estimate to and determine sets of these numbers. They
counting strategies to solve problems that out simple additions and subtractions, using range of strategies. They find the total value problems using efficient strategies for involving multiplication and division, with and check the reasonableness of answers and solve problems that involve all four operations
involve comparing, combining and separating counting strategies. Students recognise of simple collections of Australian notes and multiplication with and without the use of without the use of digital technology, and approximate answers by rounding. Students with whole numbers and describe the use of
these sets. They match individual objects with Australian coins according to their value. coins. Students represent multiplication and digital technology. Students recall addition estimate answers accurately enough for the identify and describe factors and multiples. integers in everyday contexts. Students
counting sequences up to and back from 20. They identify representations of one half. division by grouping into sets and divide and multiplication facts for single-digit context. Students solve simple purchasing They explain plans for simple budgets. locate fractions and integers on a number line
Students order the first 10 elements of a set. Students describe number sequences collections and shapes into halves, quarters numbers. They represent money values in problems with and without the use of digital Students order decimals and unit fractions and connect fractions, decimals and
They represent, continue and create simple resulting from skip counting by 2s, 5s and and eighths. They recognise increasing and various ways and correctly count out change technology. They locate familiar fractions on a and locate them on a number line. Students percentages as different representations of
patterns. 10s. They continue simple patterns involving decreasing number sequences involving 2s, from financial transactions. Students model number line, recognise common equivalent add and subtract fractions with the same the same number. They solve problems
numbers and objects with and without the use 3s, 5s and 10s, identify the missing element and represent unit fractions for halves, thirds, fractions in familiar contexts and make denominator. They find unknown quantities in involving the addition and subtraction of
of digital technology. in a number sequence, and use digital quarters, fifths and eighths, and multiples of connections between fractions and decimal number sentences and continue patterns by related fractions. Students calculate a simple
technology to produce sequences by constant these up to one. They classify numbers as notations up to two decimal places. Students adding or subtracting fractions and decimals. fraction of a quantity and calculate common
addition. either odd or even, continue number patterns identify unknown quantities in number percentage discounts on sale items, with and
involving addition or subtraction, and explore sentences. They use the properties of odd without the use of digital technology. They
simple number sequences based on and even numbers and describe number make connections between the powers of 10
multiples. patterns resulting from multiplication. and the multiplication and division of
Students continue number sequences decimals. Students add, subtract and multiply
involving multiples of single-digit numbers decimals and divide decimals where the
and unit fractions, and locate them on a result is rational. Students write number
number line. sentences using brackets and order of
operations, and specify rules used to
generate sequences involving whole
numbers, fractions and decimals. They use
ordered pairs of integers to represent
coordinates of points and locate a point in any
one of the four quadrants on the Cartesian
plane.
© VCAA Page 2
You might also like
- Maths IGCSE Scheme of Work 0580 - 2010Document6 pagesMaths IGCSE Scheme of Work 0580 - 2010Yenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Presentation DifferentiationDocument193 pagesPresentation DifferentiationPulsmade MalawiNo ratings yet
- Number Theory Problems and SolutionsDocument9 pagesNumber Theory Problems and Solutionsobelix20% (1)
- 2021 Mathematics Atp Grade 5Document5 pages2021 Mathematics Atp Grade 5Koketso SekwenyaneNo ratings yet
- SPII - Grade 7 Curriculum Mathematics Curriculum REVISEDDocument26 pagesSPII - Grade 7 Curriculum Mathematics Curriculum REVISEDtrudyNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Atp 2023-24 Mathematics With DatesDocument4 pagesGrade 4 Atp 2023-24 Mathematics With DatesnareNo ratings yet
- TNTET Maths DetailsDocument35 pagesTNTET Maths DetailsSaranya SNo ratings yet
- Maths - End of Year 5 Expectations New National Curriculum ObjectivesDocument2 pagesMaths - End of Year 5 Expectations New National Curriculum ObjectivesShaminaNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 5 Mathematics SyllabusDocument15 pagesICSE Class 5 Mathematics SyllabusRakshitha ManjunathNo ratings yet
- End of Year 4 ExpectationsDocument2 pagesEnd of Year 4 ExpectationsAhmed100% (1)
- RPT MT Yr 1aDocument13 pagesRPT MT Yr 1aTAMIL VAANI A/P M.DIVAGARAN PILLAI KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- 4th Grade Goals Ccss 1Document5 pages4th Grade Goals Ccss 1api-287945109No ratings yet
- RPT Math DLP Year 1Document13 pagesRPT Math DLP Year 1Teck Bing LukNo ratings yet
- RPT Math DLP Year 1 2022-2023Document12 pagesRPT Math DLP Year 1 2022-2023NOORMEZANA BINTI MD NOOR KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- RPT Math DLP Year 2 2023-2024Document16 pagesRPT Math DLP Year 2 2023-2024MOHD ZULKIFLI BIN ZAKARIA KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- RPT Mathematics Year 1 DLP 2021 by Rozayus AcademyDocument13 pagesRPT Mathematics Year 1 DLP 2021 by Rozayus AcademyRacheleNo ratings yet
- RPT Math DLP Year 1 2023-2024Document13 pagesRPT Math DLP Year 1 2023-2024TAMIL VAANI A/P M.DIVAGARAN PILLAI KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- English Mathematics - 2022 Weekly Teaching Plan - Grade 9: Formal Assessment Task Revision and Formal Assessment TaskDocument6 pagesEnglish Mathematics - 2022 Weekly Teaching Plan - Grade 9: Formal Assessment Task Revision and Formal Assessment TaskThemba NyoniNo ratings yet
- Math Workbook Unit 01Document48 pagesMath Workbook Unit 01spcwtiNo ratings yet
- Week 3-Lesson-Plan-Math-Grade 5Document2 pagesWeek 3-Lesson-Plan-Math-Grade 5Bright Life Montessori Academy Inc.No ratings yet
- D2022+563029++Watermarked Mathematics+K-6+continuum+of+key+ideas (2022)Document6 pagesD2022+563029++Watermarked Mathematics+K-6+continuum+of+key+ideas (2022)cindy06nguyenNo ratings yet
- RPT Math DLP Year 1 2022-2023 by Rozayus AcademyDocument12 pagesRPT Math DLP Year 1 2022-2023 by Rozayus Academyrphsekolahrendah100% (1)
- RPT Math DLP Y1 EditedDocument11 pagesRPT Math DLP Y1 EditedNURSAKINAH BINTI RAMLI KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Math-Scope and Sequence-New Form - Career ProgramsDocument18 pagesMath-Scope and Sequence-New Form - Career ProgramsAmal MokalledNo ratings yet
- Animal Legs LessonDocument7 pagesAnimal Legs Lessonapi-374359720100% (1)
- Erong, Debriel P.Document7 pagesErong, Debriel P.Rod JoaquinoNo ratings yet
- RPT Matematik DLP Tahun2Document15 pagesRPT Matematik DLP Tahun2KALAIVANI A/P GOTHANDAPANI MoeNo ratings yet
- RPT MATH DLP YEAR 4 (SK) 2024-2025 by Rozayus AcademyDocument22 pagesRPT MATH DLP YEAR 4 (SK) 2024-2025 by Rozayus Academyosin98 jack sparowNo ratings yet
- RPT Maths DLP T4Document22 pagesRPT Maths DLP T4wannabetcherNo ratings yet
- ICSEClass 2 Maths SyllabusDocument8 pagesICSEClass 2 Maths Syllabussailasree potayNo ratings yet
- Class 2 Maths SyllabusDocument7 pagesClass 2 Maths Syllabuskids duniyaNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Autumn Term Unit 1 Algebra 1 6 Hours: Objective NNS Resources Support Plenary Homework Lesson 1Document36 pagesYear 7 Autumn Term Unit 1 Algebra 1 6 Hours: Objective NNS Resources Support Plenary Homework Lesson 1SimraNo ratings yet
- RPT Mathematics Year 5Document24 pagesRPT Mathematics Year 5Anonymous wirViz1tyoNo ratings yet
- RPT Math DLP Year 1 2023-2024Document13 pagesRPT Math DLP Year 1 2023-2024KANG CHIN LEONG MoeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 456 - q1w6 - DlpsDocument33 pagesMathematics 456 - q1w6 - DlpsLie ZhelNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 4 Mathematics SyllabusDocument11 pagesICSE Class 4 Mathematics SyllabusAnanya Ray0% (1)
- New CRSDocument15 pagesNew CRSohdonna1No ratings yet
- KSSR Mathematics Year 4Document22 pagesKSSR Mathematics Year 4Suganthi SupaiahNo ratings yet
- 1.160 ATP 2023-24 GR 4 Maths FinalDocument4 pages1.160 ATP 2023-24 GR 4 Maths FinalPiccadilly TivaneNo ratings yet
- English Mathematics - 2023 Weekly Teaching Plan - Grade 5Document5 pagesEnglish Mathematics - 2023 Weekly Teaching Plan - Grade 5cindyNo ratings yet
- RPT Math DLP Year 1 2023-2024Document13 pagesRPT Math DLP Year 1 2023-2024Nurbaizura JuaNo ratings yet
- RPT Maths DLP Year 1Document12 pagesRPT Maths DLP Year 1Karthiga MohanNo ratings yet
- Year 5 Objectives: Place Value Addition and SubtractionDocument2 pagesYear 5 Objectives: Place Value Addition and SubtractionApp BountyNo ratings yet
- 1.180 ATP 2023-24 GR 6 Maths FinalDocument5 pages1.180 ATP 2023-24 GR 6 Maths FinalnareNo ratings yet
- 1. Progression in Mathematics WM1 Number (Incomplete)Document31 pages1. Progression in Mathematics WM1 Number (Incomplete)Jyothi SinghNo ratings yet
- Math Scope and SequenceDocument3 pagesMath Scope and SequenceF. O.No ratings yet
- 2021 Mathematics Atp Grade 8Document7 pages2021 Mathematics Atp Grade 8siyabonga mpofuNo ratings yet
- Grade-8-ATP-2022 MATHEMATICSDocument7 pagesGrade-8-ATP-2022 MATHEMATICSBuhle SibandaNo ratings yet
- P.5 Primary Five MTC Notes - Teacher - AcDocument102 pagesP.5 Primary Five MTC Notes - Teacher - AcDongo DanielNo ratings yet
- RPT MATH DLP YEAR 2 2023-2024 by Rozayus AcademyDocument16 pagesRPT MATH DLP YEAR 2 2023-2024 by Rozayus AcademySaravanaJothiNo ratings yet
- RPT MATH DLP YEAR 4 2022-2023Document21 pagesRPT MATH DLP YEAR 4 2022-2023nurulfatihahzidNo ratings yet
- RPT Math DLP Year 4 2022-2023 by Rozayus AcademyDocument20 pagesRPT Math DLP Year 4 2022-2023 by Rozayus AcademyrphsekolahrendahNo ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate Understanding Of: The Learners Should Be Able To: The LearnersDocument7 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate Understanding Of: The Learners Should Be Able To: The LearnersMaravillas Gargar FarjayNo ratings yet
- Class 3 Maths SyllabusDocument8 pagesClass 3 Maths SyllabusKamal VermaNo ratings yet
- Year 2 Maths Assessment Targets Colouring Sheet: Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesYear 2 Maths Assessment Targets Colouring Sheet: Page 1 of 2TaylorNo ratings yet
- Comparing Math Curriculum of Philippines and South KoreaDocument4 pagesComparing Math Curriculum of Philippines and South KoreaMarco Dumlao MataNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 1ST Quarter First ModuleDocument10 pagesGrade 7 1ST Quarter First ModuleFaith Marie QuintoNo ratings yet
- RPT Mathematics Year 2 (DLP) 2021 by Rozayus AcademyDocument16 pagesRPT Mathematics Year 2 (DLP) 2021 by Rozayus AcademyAzrin MohayaddinNo ratings yet
- RPT Math DLP Year 2 2022-2023Document15 pagesRPT Math DLP Year 2 2022-2023puva nesNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Melcs ObjectivesDocument16 pagesMath 7 Melcs ObjectivesNor Ali EbrahimNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Scheme of Work For Year 1-5Document11 pagesMathematics Scheme of Work For Year 1-5Femi ThomasNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Adding Decimals 3 Digit FDocument1 pageGrade 5 Adding Decimals 3 Digit FGovind SharmaNo ratings yet
- Complete 1Document1 pageComplete 1Govind SharmaNo ratings yet
- EE330A: Power Systems: Fault AnalysisDocument7 pagesEE330A: Power Systems: Fault AnalysisGovind SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module7lecturenotes 19981Document12 pagesModule7lecturenotes 19981Govind SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2018 - 19 Semester I: EE330A: Tutorial 6Document4 pages2018 - 19 Semester I: EE330A: Tutorial 6Govind SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2018 - 19 Semester I: EE330A: Tutorial 5Document3 pages2018 - 19 Semester I: EE330A: Tutorial 5Govind SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2017 - 18 Semester I: EE330A: Tutorial 2Document3 pages2017 - 18 Semester I: EE330A: Tutorial 2Govind SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module4lecturenotes 19253Document7 pagesModule4lecturenotes 19253Govind SharmaNo ratings yet
- EE330A: Tutorial 1 Solution: 2018 - 19 Semester IDocument3 pagesEE330A: Tutorial 1 Solution: 2018 - 19 Semester IGovind SharmaNo ratings yet
- EE330A: Power Systems: Synchronous GeneratorsDocument20 pagesEE330A: Power Systems: Synchronous GeneratorsGovind SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture4,5 18223Document7 pagesLecture4,5 18223Govind SharmaNo ratings yet
- EE330A: Power SystemsDocument10 pagesEE330A: Power SystemsGovind SharmaNo ratings yet
- EE330A: Power Systems: TransformersDocument28 pagesEE330A: Power Systems: TransformersGovind SharmaNo ratings yet
- EE330A: Power Systems: Dr. Abheejeet MohapatraDocument16 pagesEE330A: Power Systems: Dr. Abheejeet MohapatraGovind SharmaNo ratings yet
- EE330A: Power Systems: Basic PrinciplesDocument21 pagesEE330A: Power Systems: Basic PrinciplesGovind SharmaNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur EE 210 Home Assignment #5 Assigned: 6/2/18Document1 pageDepartment of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur EE 210 Home Assignment #5 Assigned: 6/2/18Govind SharmaNo ratings yet
- A 3 SolnDocument2 pagesA 3 SolnGovind SharmaNo ratings yet
- Information About The Transistor and Its Bias State. AlsoDocument1 pageInformation About The Transistor and Its Bias State. AlsoGovind SharmaNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur EE 210 Home Assignment #2 Assigned: 16/1/18Document1 pageDepartment of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur EE 210 Home Assignment #2 Assigned: 16/1/18Govind SharmaNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur EE 210 Home Assignment #3 Assigned: 23/1/18Document1 pageDepartment of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur EE 210 Home Assignment #3 Assigned: 23/1/18Govind SharmaNo ratings yet
- BYJU ShortcutsDocument10 pagesBYJU ShortcutsSiddharth JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 FunctionsDocument4 pagesChapter 1 FunctionsRaymondNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Maths Exam June 2022Document9 pagesGrade 7 Maths Exam June 2022mithraseeryNo ratings yet
- Tarea de Conversión de NúmerosDocument10 pagesTarea de Conversión de Númerosbloddy MarkNo ratings yet
- PDT 1 Revision Worksheet Cls 10Document2 pagesPDT 1 Revision Worksheet Cls 10Midas PatNo ratings yet
- Let A, A, A ,......, A Be A Set of Numbers, Average (A + A + A ,+...... + A) /NDocument2 pagesLet A, A, A ,......, A Be A Set of Numbers, Average (A + A + A ,+...... + A) /NmgrfanNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Module 2 Integers WSDocument7 pagesGrade 9 Module 2 Integers WSfrankdebruin261No ratings yet
- Form 1 Chapter 11Document2 pagesForm 1 Chapter 11Emma NourNo ratings yet
- Least Common MultipleDocument2 pagesLeast Common MultiplelullabytaNo ratings yet
- A Library of Functions: Constant FunctionDocument4 pagesA Library of Functions: Constant FunctionDoom RefugeNo ratings yet
- Practice Differentiation Math 120 Calculus IDocument6 pagesPractice Differentiation Math 120 Calculus IArdvarkNo ratings yet
- Algebra Esp 2Document185 pagesAlgebra Esp 2carmenvasquezcmNo ratings yet
- DLD - Ch.1 Notes PDFDocument35 pagesDLD - Ch.1 Notes PDFAlradi Malak FadiNo ratings yet
- Searchable Content ListsDocument8 pagesSearchable Content ListsVincents Genesius EvansNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document13 pagesChapter 3haileNo ratings yet
- M01 Aircraft Engineering Principles 2013 PDFDocument70 pagesM01 Aircraft Engineering Principles 2013 PDFTactical Ivan TacticalNo ratings yet
- Logarithms and Exponential Functions: Skills CheckDocument7 pagesLogarithms and Exponential Functions: Skills CheckAyesha MaryamNo ratings yet
- Multiplying Rational NumbersDocument4 pagesMultiplying Rational NumbersSanjith Jothi BalaNo ratings yet
- MTH002 D Course OutlineDocument7 pagesMTH002 D Course OutlineRodane Immaculate MontannaNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma Solution Jan2021 Class 7 Chapter 3Document32 pagesRD Sharma Solution Jan2021 Class 7 Chapter 3Meghana LakshmiNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarterly Assessment in Math 4Document7 pages2nd Quarterly Assessment in Math 4Vener Menciano BuriasNo ratings yet
- Lab 08 C++ OperatorsDocument3 pagesLab 08 C++ OperatorsMUHAMMAD HAMZANo ratings yet
- TG - Math 7 - Q3 PDFDocument37 pagesTG - Math 7 - Q3 PDFDoris Rosario Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper 04 Chapter 1 Real NumbersDocument9 pagesCBSE Test Paper 04 Chapter 1 Real NumbersNamita VarmaNo ratings yet
- Fractions 120213071428 Phpapp01Document40 pagesFractions 120213071428 Phpapp01Christian RiveraNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Geometric ProgressionDocument10 pagesChapter Two Geometric ProgressionFongoh Bobga RemiNo ratings yet
- RPHDocument2 pagesRPHFaizal ZaInNo ratings yet
- Quiz #1Document3 pagesQuiz #1Joanna Marie CalibaraNo ratings yet