Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 1
Assignment 1
Uploaded by
weynOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 1
Assignment 1
Uploaded by
weynCopyright:
Available Formats
ASSIGNMENT-1
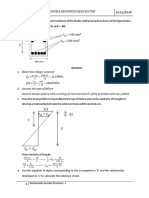
1. The stresses on a failure plane in a drained test form direct shear test on a cohesionless soil
are as shown below.
Normal stress 100 kPa
Shear stress 40 kPa
a) Draw the Mohr’s circle and determine the angle of shearing resistance and the angle
which the failure plane makes with the major principal plane.
b) Find the major and minor principal stresses.
c) The stresses on a plane oriented at 250 clockwise from the major principal stress plane.
2. The results shown in Table 1 were obtained at failure in a series of triaxial tests
on specimens of saturated clay initially 38 mm in diameter by 76 mm long. Determine the
values of the shear strength parameters with respect to (a) total stress and (b) effective
stress. The principal stress difference at failure in each test is obtained by dividing
the axial load by the cross-sectional area of the specimen at failure. The initial values
of length, area and volume for each specimen are:
Table-1:
Type of test Axial Volume
Cell Pressure Axial Load
Deformation change
(kN/m2) (N)
(mm) (ml)
200 222 9.83 -
Undraind (UU) 400 215 10.06 -
600 226 10.28 -
200 403 10.81 6.6
Draind (CD) 400 848 12.26 8.2
600 1265 14.17 9.5
3. The results shown in Table-2 were obtained for peak failure in a series of consolidated
undrained triaxial tests, with pore water pressure measurement, on specimens of saturated
clay. Plot the strength envelope in terms of total stress and effective stresses and determine
the strength parameters.
Table-2:
Cell-Pressure Deviatoric stress Pore-water pressure
Sample-No
(kN/m2) (kN/m2) (kN/m2)
1 250 152 120
2 500 300 250
3 750 455 350
You might also like
- Lab Report On Waren GirderDocument12 pagesLab Report On Waren GirderSamuel Ogeda Otieno100% (2)
- Gantry CraneDocument18 pagesGantry Craneamirthraj7494% (16)
- ANSYS NeoHook UsermatDocument15 pagesANSYS NeoHook UsermatRohan Nair100% (2)
- Tutorial 1 (7 Aug 2008)Document2 pagesTutorial 1 (7 Aug 2008)Rashma JomoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01Document3 pagesAssignment 01sahilbarbade.ee101No ratings yet
- C1 Shear StrengthDocument62 pagesC1 Shear StrengthSara LaiNo ratings yet
- Shear Resistance With SolutionsDocument6 pagesShear Resistance With Solutionscharlottekiel12No ratings yet
- Open Book: Department of Civil EngineeringDocument4 pagesOpen Book: Department of Civil EngineeringIlse FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Concrete Gravity Dam Using LusasDocument10 pagesAnalysis of Concrete Gravity Dam Using LusasTonderai RusereNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 3 Shear Strength of SoilDocument1 pageASSIGNMENT 3 Shear Strength of SoilKartik PandyaNo ratings yet
- M.E. 3300 Lab Memo: Table 1. Data TableDocument4 pagesM.E. 3300 Lab Memo: Table 1. Data TableJan YsNo ratings yet
- Assignment QUESTIONDocument6 pagesAssignment QUESTIONTaran Tatleender Kaur A/P Salinder SinghNo ratings yet
- CVEN 330 - Assignment #2 - Fall - 2021Document1 pageCVEN 330 - Assignment #2 - Fall - 2021abodqu2001No ratings yet
- Multi-Stage Pseudo-Static Analysis PDFDocument5 pagesMulti-Stage Pseudo-Static Analysis PDFRelu MititeluNo ratings yet
- CHP 1-ROCK TESTING-Part1Document49 pagesCHP 1-ROCK TESTING-Part1Koh Jia JieNo ratings yet
- MODULE 12 Mechanical Testing of WeldsDocument66 pagesMODULE 12 Mechanical Testing of WeldsIkeNo ratings yet
- EC2 Bending With or Without Axial ForceDocument11 pagesEC2 Bending With or Without Axial ForceselinaNo ratings yet
- 10 Chapter5Document18 pages10 Chapter5Mulukallavinay ReddyNo ratings yet
- Residual Static Strength of Tubular T-Joints With Fatigue Surface CracksDocument6 pagesResidual Static Strength of Tubular T-Joints With Fatigue Surface CracksVignesh Chellappan NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Tensile Test ReportDocument12 pagesTensile Test ReportNURUL AINA BINTI MOHAMAD FUAD STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Qu1 Qu2 Qu3 Qu4 (Question)Document8 pagesQu1 Qu2 Qu3 Qu4 (Question)Khairil MukminNo ratings yet
- PLO Attainment Assignmet-Shear Strength (2019-Civ-39) PLO-2Document2 pagesPLO Attainment Assignmet-Shear Strength (2019-Civ-39) PLO-2Asif HameedNo ratings yet
- Direct Shear Test Soil ReportDocument12 pagesDirect Shear Test Soil ReportNAJA MOHAMEDNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 2Document2 pagesTutorial 5 2Maajith MarzookNo ratings yet
- Tuesday-2 Tensile Arko Basak 210184Document6 pagesTuesday-2 Tensile Arko Basak 210184Dewanshu JaiswalNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Failure Pressure Estimates of Unflawed Pressure Vessels Without Residual StressDocument16 pages9.1 Failure Pressure Estimates of Unflawed Pressure Vessels Without Residual StressFaturahman FNo ratings yet
- Fernandez 09 CDocument4 pagesFernandez 09 CPhạm Tiến ĐạtNo ratings yet
- University of Nairobi Department of Civil and Construction EngineeringDocument9 pagesUniversity of Nairobi Department of Civil and Construction EngineeringLovian MagandaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1EYU Eyuel Abrham ArbaNo ratings yet
- VrubfirbDocument8 pagesVrubfirb9245126694No ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics PP 2013Document4 pagesSoil Mechanics PP 2013Zack FengNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Shear Force in A Beam: Dam 11203 Solid MechanicsDocument13 pagesExperiment 2 Shear Force in A Beam: Dam 11203 Solid MechanicsHafiz NordinNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Hardness On The Transition of The Abrasive Wear Mechanism of SteelsDocument11 pagesThe Effect of Hardness On The Transition of The Abrasive Wear Mechanism of SteelsMatheus SoranzzoNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument1 pageEngineering MechanicsmafiapumbaNo ratings yet
- Substructure DesignADocument53 pagesSubstructure DesignACharisse Ann Arado BadoriaNo ratings yet
- Shear Strength of Concrete Deep BeamDocument11 pagesShear Strength of Concrete Deep BeamAyad GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Restoration Design For Capacity Performance Assessment of RC Slab BridgesDocument8 pagesRestoration Design For Capacity Performance Assessment of RC Slab BridgesbadmaNo ratings yet
- Effective Punching Shear and Moment Capacity of FL PDFDocument12 pagesEffective Punching Shear and Moment Capacity of FL PDFju_jbsNo ratings yet
- Mass Property Material Property Mass Strength Material StrengthDocument9 pagesMass Property Material Property Mass Strength Material StrengthVikneswaran VigayakumarNo ratings yet
- 7 Gutachten Pasternak EnglDocument8 pages7 Gutachten Pasternak EnglShervin2010No ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Confined Masonry Squat Walls: M. SekiDocument7 pagesExperimental Study On Confined Masonry Squat Walls: M. SekiMihai PurcaruNo ratings yet
- Unbound MaterialsDocument3 pagesUnbound Materialsmadhav choudharyNo ratings yet
- EVALUATION OF MECHANICAL ANCHORAGE OF Beam Column JointDocument9 pagesEVALUATION OF MECHANICAL ANCHORAGE OF Beam Column JointDr Ahmed Al-RubaieNo ratings yet
- 9-Jointed Rock ModelDocument4 pages9-Jointed Rock ModelKTMONo ratings yet
- Bolton - 1999 - A Non-Linear Elasticperfectly Plastic Analysis For Plane Strain Undrained Expansion TestsDocument9 pagesBolton - 1999 - A Non-Linear Elasticperfectly Plastic Analysis For Plane Strain Undrained Expansion TestsHUGINo ratings yet
- Atzori 2004Document10 pagesAtzori 2004Majed NesrineNo ratings yet
- Pbee Toolbox - Examples of ApplicationDocument54 pagesPbee Toolbox - Examples of ApplicationCem Demir100% (1)
- Bolt Capacity Is 800 2007Document1 pageBolt Capacity Is 800 2007JaineshNo ratings yet
- School of Civil Engineering: (Assignment/Project Received Without This Declaration Form Will Not Be Graded)Document12 pagesSchool of Civil Engineering: (Assignment/Project Received Without This Declaration Form Will Not Be Graded)NasrulNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Shear Wall Analysis Design CSA A23!3!14Document21 pagesReinforced Concrete Shear Wall Analysis Design CSA A23!3!14ahmedhatemlabibNo ratings yet
- FWD BallastDocument8 pagesFWD BallastYusuf CatiNo ratings yet
- Soils 2 Exam 2012-2013Document5 pagesSoils 2 Exam 2012-2013Sarah SmithNo ratings yet
- Advanced Structural Analysis Lab Exercise 1 Aim: To Understand Modelling, Support Conditions and Material PropertiesDocument5 pagesAdvanced Structural Analysis Lab Exercise 1 Aim: To Understand Modelling, Support Conditions and Material Propertiesmayank kapriNo ratings yet
- Week 4 (Prob 6.30)Document3 pagesWeek 4 (Prob 6.30)Daniel CedeñoNo ratings yet
- ECS 238 - Chapter 2b (Bending and Shear Stresses and in Symmetrical Beams)Document53 pagesECS 238 - Chapter 2b (Bending and Shear Stresses and in Symmetrical Beams)Izzat JalilNo ratings yet
- Solids Lab 2 - 201110737.AL AQEEB FAIQ BIN ROZAIDEDocument14 pagesSolids Lab 2 - 201110737.AL AQEEB FAIQ BIN ROZAIDEpicul 08No ratings yet
- Kanazawa, Miller, Brown - Cyclic Deformation of 1% Cr-Mo-V Steel Under Out-Of-Phase LoadsDocument12 pagesKanazawa, Miller, Brown - Cyclic Deformation of 1% Cr-Mo-V Steel Under Out-Of-Phase LoadsDavid C HouserNo ratings yet
- Behavior of SFRC Walls Without Conventional Shear ReinforcementDocument6 pagesBehavior of SFRC Walls Without Conventional Shear ReinforcementEden De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- FoM - LCF QuestionsDocument5 pagesFoM - LCF Questionsbharath kumarNo ratings yet
- The University of Dar Es SalaamDocument6 pagesThe University of Dar Es SalaamChris AdaminovicNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of The Shear Transfer Actions in RC Short Span Beams Using Crack Kinematics Recorded Via DicDocument8 pagesAn Analysis of The Shear Transfer Actions in RC Short Span Beams Using Crack Kinematics Recorded Via DicmarcuspasNo ratings yet
- Energy DissipatorDocument41 pagesEnergy DissipatorweynNo ratings yet
- Example On Design of Biaxial Column With Design EccecntricitiessDocument10 pagesExample On Design of Biaxial Column With Design EccecntricitiessweynNo ratings yet
- Example of Analysis of DRB SectionDocument2 pagesExample of Analysis of DRB SectionweynNo ratings yet
- Vertical CurveDocument24 pagesVertical CurveweynNo ratings yet
- Design Aids-2015Document106 pagesDesign Aids-2015weynNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Introduction To Aircraft StructuresDocument4 pagesAssignment 1: Introduction To Aircraft StructuresLv NanhengNo ratings yet
- Integral Bridge Midas SeminarDocument36 pagesIntegral Bridge Midas SeminarSony JsdNo ratings yet
- (Eng) Steel Code Check 2011.0 v1Document123 pages(Eng) Steel Code Check 2011.0 v1chhouch100% (1)
- Control of Natural FrequencyDocument11 pagesControl of Natural FrequencyMoHammadNashatSabbahNo ratings yet
- Technical Supplement 14R Design and Use of Sheet Pile Walls in Stream Restoration and Stabilization ProjectsDocument36 pagesTechnical Supplement 14R Design and Use of Sheet Pile Walls in Stream Restoration and Stabilization ProjectsThaung Myint OoNo ratings yet
- (Solid Mechanics and Its Applications 190) Joshua Pelleg (Auth.) - Mechanical Properties of Materials-Springer Netherlands (2013)Document644 pages(Solid Mechanics and Its Applications 190) Joshua Pelleg (Auth.) - Mechanical Properties of Materials-Springer Netherlands (2013)Bryan TrackNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering - I PDFDocument3 pagesGeotechnical Engineering - I PDFSunny PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Beam LoadingDocument5 pagesBeam LoadingBudi SimatupangNo ratings yet
- Spread Footing Design ExampleDocument8 pagesSpread Footing Design Examplemorphie_blackNo ratings yet
- Contact PressureDocument2 pagesContact PressurerpkodamNo ratings yet
- FRP Tensile Strength PPT-3Document15 pagesFRP Tensile Strength PPT-3laurenjiaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Dents in PipelinesDocument9 pagesEffect of Dents in PipelinesAnonymous avGU1iNo ratings yet
- 20-Seismic Ground Improvement of Soft Soil Sites With Compacted Soil Cement Panels and Deep Soil Mixing PanelsDocument109 pages20-Seismic Ground Improvement of Soft Soil Sites With Compacted Soil Cement Panels and Deep Soil Mixing PanelsAbdelmoez ElgarfNo ratings yet
- Reg - No:: Ii) Design A Rectangular Key For The Following Application: A ShaftDocument3 pagesReg - No:: Ii) Design A Rectangular Key For The Following Application: A ShaftManivannanNo ratings yet
- 10) What Are The Types of Earthquakes?: 4) Seismic GapDocument3 pages10) What Are The Types of Earthquakes?: 4) Seismic GapkiranNo ratings yet
- 1 Pile FoundationsDocument68 pages1 Pile FoundationsJeremy100% (1)
- Column Interaction DiagramDocument4 pagesColumn Interaction DiagramAhmedNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design and Performance Criteria PDFDocument16 pagesSeismic Design and Performance Criteria PDFmeldi suhatrilNo ratings yet
- Effect of Lead Rubber Bearing CharacteristicsDocument11 pagesEffect of Lead Rubber Bearing Characteristicsümit özkanNo ratings yet
- Checks For CompactnessDocument15 pagesChecks For CompactnessjologscresenciaNo ratings yet
- Bracing Back To Back (Version 1)Document118 pagesBracing Back To Back (Version 1)Tameem AnsariNo ratings yet
- Elastic Stability of ColumnsDocument11 pagesElastic Stability of ColumnsSayantan GhosalNo ratings yet
- SchmertmannDocument4 pagesSchmertmannWaqas SadiqNo ratings yet
- Solution-ME F314Document3 pagesSolution-ME F314sai ramNo ratings yet
- IACS M53 - Calculation of Crankshafts For I.C EnginesDocument28 pagesIACS M53 - Calculation of Crankshafts For I.C EnginesbogodavidNo ratings yet
- Element Technology: Chapter TwoDocument100 pagesElement Technology: Chapter TwoAyush ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Development of Material Model Subroutines For Linear and Nonlinea PDFDocument83 pagesDevelopment of Material Model Subroutines For Linear and Nonlinea PDFPablo Peña TorresNo ratings yet