Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Are Faults Formed
How Are Faults Formed
Uploaded by
Melodina Acain0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views2 pagesEarthquakes are caused by sudden movements along faults, which are fractures between blocks of rock. There are four main types of faults - normal, reverse, strike-slip, and oblique - that can cause earthquakes. The effects of earthquakes include ground shaking, surface ruptures, ground failures, and sometimes tsunamis. Damage occurs when the ground shaking from earthquakes causes structures like buildings and bridges to collapse and can disrupt services.
Original Description:
faults formation....
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEarthquakes are caused by sudden movements along faults, which are fractures between blocks of rock. There are four main types of faults - normal, reverse, strike-slip, and oblique - that can cause earthquakes. The effects of earthquakes include ground shaking, surface ruptures, ground failures, and sometimes tsunamis. Damage occurs when the ground shaking from earthquakes causes structures like buildings and bridges to collapse and can disrupt services.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views2 pagesHow Are Faults Formed
How Are Faults Formed
Uploaded by
Melodina AcainEarthquakes are caused by sudden movements along faults, which are fractures between blocks of rock. There are four main types of faults - normal, reverse, strike-slip, and oblique - that can cause earthquakes. The effects of earthquakes include ground shaking, surface ruptures, ground failures, and sometimes tsunamis. Damage occurs when the ground shaking from earthquakes causes structures like buildings and bridges to collapse and can disrupt services.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
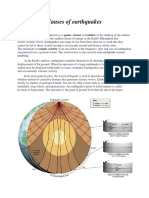
How are faults formed?
It forms when rock above an inclined fracture plane moves downward, sliding
along the rock on the other side of the fracture. Normal faults are often found along
divergent plate boundaries, such as under the ocean where new crust is forming. Long,
deep valleys can also be the result of normal faulting.
What is the relationship of faults and earthquake?
A fault is a fracture or zone of fractures between two blocks of rock. Faults allow the
blocks to move relative to each other. This movement may occur rapidly, in the
form of an earthquake - or may occur slowly, in the form of creep. Faults may
range in length from a few millimeters to thousands of kilometers.
What are the 4 types of earthquake faults?
There are four types of faulting -- normal, reverse, strike-slip, and oblique. A normal
fault is one in which the rocks above the fault plane, or hanging wall, move down
relative to the rocks below the fault plane, or footwall.
What causes earthquakes?
Earthquakes are usually caused when underground rock suddenly breaks and there
is rapid motion along a fault. This sudden release of energy causes the seismic
waves that make the ground shake.
What are three effects of earthquakes?
The effects from earthquakes include ground shaking, surface faulting, ground
failure, and less commonly, tsunamis.
What is the difference earthquake and fault?
An earthquake is ground shaking caused by a sudden movement on a fault, by a
volcanic disturbance, a landslide, or a explosion (natural or man made). A fault is a
fracture or crack along which two blocks of rock slide past one another.
How does earthquake cause damage?
Ground shaking from earthquakes can cause buildings and bridges to collapse; disrupt
gas, electricity, and telephone services; and sometimes trigger landslides, avalanches,
flash floods, fires, and tsunami.
You might also like
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10 For Demo TeachingFINALDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 10 For Demo TeachingFINALMelodina Acain100% (3)
- Activity (Eathquake)Document3 pagesActivity (Eathquake)leonellevisaya2022No ratings yet
- Danes Kynel G Ricafort ScienceDocument3 pagesDanes Kynel G Ricafort ScienceJenny Ann Mariel ManaladNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes: Ive Polanco 14-1006Document17 pagesEarthquakes: Ive Polanco 14-1006LossyTNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Architecture: Presented by Naveen Minj 19122035 P.B.V. Laxman 19122043Document15 pagesEarthquake Resistant Architecture: Presented by Naveen Minj 19122035 P.B.V. Laxman 19122043Ar Shubham JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes Powerpoint 2Document20 pagesEarthquakes Powerpoint 2Gian HipolitoNo ratings yet
- Endogenic ProcessesDocument50 pagesEndogenic Processesedena delos santosNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 Earthquakes and FaultsDocument56 pagesWEEK 1 Earthquakes and FaultsMarissa FontanilNo ratings yet
- Earthquake: Naturally Occurring EarthquakesDocument5 pagesEarthquake: Naturally Occurring EarthquakesShree VidhyaNo ratings yet
- Types of Fault and Its Effect On Earthquake: Prepared byDocument10 pagesTypes of Fault and Its Effect On Earthquake: Prepared bynirmalNo ratings yet
- Tensional Tectonic PlatesDocument6 pagesTensional Tectonic PlatesRODJHEN ANNE P. BARQUILLANo ratings yet
- Earth Lithosphere Seismic Waves Seismicity Non-Earthquake Seismic RumblingDocument4 pagesEarth Lithosphere Seismic Waves Seismicity Non-Earthquake Seismic RumblingGray GonzalezNo ratings yet
- AssignmenttGeography 3Document3 pagesAssignmenttGeography 3Muhammad Shahzaib AzharNo ratings yet
- AssignmenttGeography 2Document3 pagesAssignmenttGeography 2Muhammad Shahzaib AzharNo ratings yet
- Research No.5Document11 pagesResearch No.5Ramona SmithNo ratings yet
- DRRR Module 4 Earthquake HazardDocument28 pagesDRRR Module 4 Earthquake HazardAbia Annieson A. LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and FaultsDocument16 pagesEarthquakes and FaultsJoeseph CoNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and Faults ModuleDocument8 pagesEarthquakes and Faults ModuleJoeseph CoNo ratings yet
- Causes of EarthquakesDocument8 pagesCauses of Earthquakesdumea paulNo ratings yet
- Fault, In: Geology Fracture Earth'sDocument4 pagesFault, In: Geology Fracture Earth'sMandeep Man-eNo ratings yet
- What Causes EarthquakesDocument5 pagesWhat Causes EarthquakesNatesa IndrasenanNo ratings yet
- Earthquke PresentationDocument34 pagesEarthquke PresentationKenny CantilaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake PPT Week 1Document25 pagesEarthquake PPT Week 1Helen DV. ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Seismos, "To Shake") - Scientists Who Study Earthquakes AreDocument28 pagesSeismos, "To Shake") - Scientists Who Study Earthquakes AreMuhammad Asad FaroquiNo ratings yet
- Earthquake HazardsDocument2 pagesEarthquake HazardsDexter Jimenez ResullarNo ratings yet
- What Caused EarthquakesDocument2 pagesWhat Caused EarthquakesRECHELL ANN GULAYNo ratings yet
- Earth Quakes and Dams-3Document16 pagesEarth Quakes and Dams-3Vitalis KinyuaNo ratings yet
- Fault TypesDocument16 pagesFault TypesNathanNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument41 pagesEarthquakeASNINo ratings yet
- Trisha SciencesDocument6 pagesTrisha SciencesTrisha FranciscoNo ratings yet
- G8 Science Q2 - Week1 - EarthquakeDocument61 pagesG8 Science Q2 - Week1 - EarthquakeIemmee Jane DinglasanNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of EarthquakesDocument1 pageCharacteristics of EarthquakesVinay ChandwaniNo ratings yet
- G8 Science Q2 - Week1 - EarthquakeDocument55 pagesG8 Science Q2 - Week1 - Earthquakewinincepido29No ratings yet
- What Is An EarthquakeDocument1 pageWhat Is An EarthquakeKevs TolentinoNo ratings yet
- M1-Topic 2. Plate Tectonics and Faults-1Document11 pagesM1-Topic 2. Plate Tectonics and Faults-1Mark Andykenn Liaga MaglinteNo ratings yet
- Earthquake and FaultsDocument3 pagesEarthquake and FaultsCirille AgpaoaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake EngineeringDocument7 pagesEarthquake Engineeringelainesiapno82No ratings yet
- Seismology: Earthquake Kinematics and DynamicsDocument29 pagesSeismology: Earthquake Kinematics and DynamicsJam Allana QuismundoNo ratings yet
- 3 Kinds of Fault, Measuring Earthquake andDocument6 pages3 Kinds of Fault, Measuring Earthquake andMatthew TorrillaNo ratings yet
- Cengr 4140-Eq ReviewerDocument19 pagesCengr 4140-Eq Reviewerdarwin18No ratings yet
- 5 - Folds, Faults & UnconformityDocument30 pages5 - Folds, Faults & Unconformitymoorpvr100% (1)
- Unit 6 Earthquake and FaultsDocument34 pagesUnit 6 Earthquake and FaultsCharmaine CanonoNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and FaultsDocument19 pagesEarthquakes and FaultsMasTer CrafT (MasTerCrafT89)No ratings yet
- Earthquake and FaultsDocument9 pagesEarthquake and FaultsCharm VergaraNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and FaultsDocument14 pagesEarthquakes and FaultsBEALYN OLANNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Earthquake and FaultsDocument33 pagesUnit 6 Earthquake and FaultsJohn Mark LaurioNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Type & FaultsDocument11 pagesEarthquake Type & FaultsibrahimNo ratings yet
- Earthquake: 1. Volcanic ActivitiesDocument2 pagesEarthquake: 1. Volcanic ActivitiesNoellhaJeanetteGabeLiwagonNo ratings yet
- Reading Material For Disaster Risk Readiness and ReductionDocument14 pagesReading Material For Disaster Risk Readiness and ReductionTommy PascuaNo ratings yet
- FAULTDocument2 pagesFAULTJoyce De Guzman100% (1)
- Endogenic Processes ReportDocument50 pagesEndogenic Processes ReportRosemarie LigutanNo ratings yet
- Grade Eight EarthquakeDocument55 pagesGrade Eight EarthquakeCirille AgpaoaNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 SeismologyDocument101 pagesChapter1 SeismologyJulyNo ratings yet
- Faults and EarthquakesDocument7 pagesFaults and EarthquakesAngela AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Proccesses and Landforms Along Plate BoundariesDocument87 pagesProccesses and Landforms Along Plate Boundariesayeshakelly268No ratings yet
- Earthquakes, Causes and EffectsDocument3 pagesEarthquakes, Causes and EffectsEdwin KaranjqNo ratings yet
- Earth Science 8 ReviewerDocument11 pagesEarth Science 8 ReviewerBraynell Owen ClaroNo ratings yet
- Earthquake LessonDocument46 pagesEarthquake LessonAvis pittNo ratings yet
- AyokonatamanaDocument2 pagesAyokonatamanaPaolo MalabananNo ratings yet
- Engineering Geology Assignment No. 2: How Disasters Are Caused by Earthquake?Document2 pagesEngineering Geology Assignment No. 2: How Disasters Are Caused by Earthquake?Sheikh MuneebNo ratings yet
- Day 4Document4 pagesDay 4Melodina AcainNo ratings yet
- Day 2Document5 pagesDay 2Melodina AcainNo ratings yet
- Day 1Document4 pagesDay 1Melodina AcainNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument29 pagesEarthquakeMelodina AcainNo ratings yet
- Second Periodical Test ScienceDocument2 pagesSecond Periodical Test ScienceMelodina AcainNo ratings yet
- Body FInalDocument41 pagesBody FInalMelodina AcainNo ratings yet
- FILIPINODocument2 pagesFILIPINOMelodina AcainNo ratings yet
- Digestion Worksheet AnswersDocument2 pagesDigestion Worksheet AnswersMelodina AcainNo ratings yet
- Activity On Science 8Document2 pagesActivity On Science 8Melodina AcainNo ratings yet
- Stratified Random SamplingDocument19 pagesStratified Random SamplingMelodina AcainNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Aims, Goals and Educational Objectives: Learning CompetenciesDocument11 pagesCurriculum Aims, Goals and Educational Objectives: Learning CompetenciesMelodina AcainNo ratings yet
- Classifying Organisms Using The HEIRARCHIAL Taxonomy ClassificationDocument63 pagesClassifying Organisms Using The HEIRARCHIAL Taxonomy ClassificationMelodina AcainNo ratings yet