Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grade 10 Wlas 4TH QTR Week 7
Grade 10 Wlas 4TH QTR Week 7
Uploaded by
MYLENE B. ZABALLEROOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Grade 10 Wlas 4TH QTR Week 7
Grade 10 Wlas 4TH QTR Week 7
Uploaded by
MYLENE B. ZABALLEROCopyright:
Available Formats
COPYRIGHT PAGE FOR UNIFIED LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEETS
Chemistry – Grade 10
Learning Activity Sheets
Quarter 4 – Week 7: The Factors Affecting Chemical Reaction
First Edition, 2021
Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the
Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or office
wherein the work is created shall be necessary for the exploitation of such work for a profit.
Such agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of royalties.
Borrowed materials (e.g., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names, trademarks,
etc.) included in the activity sheets are owned by their respective copyright holders. Every effort
has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use these materials from the respective
copyright owners. The authors do not represent nor claim ownership over them.
Development Team of Learner’s Activity Sheets
Writer Mylene B. Zaballero
Jane C. Basul
Editors: Delia P. Alcantara
Edgardo B. Tupas
Division Team Jesusa C. Olayon
Management Team Romeo O. Aprovechar, PhD, CESO IV, Schools Division Superintendent
Love Emma B. Sudario, Assistant Schools Division Superintendent
Rayfrocina Abao, CID Chief
Jane C. Basul, EPS - Science
Bernie Pamplona, LRMDS Manager - OIC
Junel M. Anino, Librarian II
Bernie Pamplona, PDO II
Printed in the Philippines by:
Department of Education – Bureau of Learning Resources (DepEd-BLR)
Office Address: Montilla Blvd., Butuan City, Agusan del Norte
Telephone Number: (085) 342 1804
E-mail Address: https://caraga.deped.gov.ph/
Author: MYLENE B. ZABALLERO
School/Station: Maningalao National High School
Division: Agusan del Norte
email address: mylene.zaballero001@deped.gov.ph
WEEKLY LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET
Grade 10, Quarter 4, Week – 7
Name: ___________________________________________ Grade/Sec: ____________________
Factors Affecting the Rate of Chemical Reaction
Most Essential Learning Competency (MELC)
Explain how the factors affecting rates of chemical reactions are applied in food
preservation, materials production, control of fire, pollution, and corrosion.
(S10MT – IVh-j-24)
Learning Objectives:
1. Describe effective collision resulting in the formation of products.
2. Determine the use of energy diagrams.
3. Describe the effect of the catalyst on the activation energy and reaction rate.
4. Determine the effect of temperature on the reaction rate.
Time Allotment: 2 hours
Key Concepts:
⮚ Chemical Reactions
In a chemical reaction, the rate of reaction refers to the speed at which reactants
break down and recombine to form new substances. Since a reaction involves the
breaking and forming of chemical bonds, contact between the species making up the
reactants is important. The species making up the reactants must come in contact
through collision theory. The Collision Theory explains that the chemical particles of
the reactants must collide with sufficient energy to break chemical bonds. In order for a
chemical reaction to proceed into completion, there must be an effective collisions
between reacting particles. The greater the rate of effective collision, the greater is
the reaction rate. There are two conditions for the collision to form a product. These are:
1. Collision between two reactant molecules must take place in the right orientation.
2. Collision must occur with enough energy to break the old bonds in the reactants so
that new bonds can form, thus forming the products.
To illustrate this theory, consider figure 1, the hypothetical chemical reaction involving
two hypothetical gases, A2 and B2.
The reaction follows: A2 (g) + B2 (g) 2 AB(g)
Author: MYLENE B. ZABALLERO
School/Station: Maningalao National High School
Division: Agusan del Norte
email address: mylene.zaballero001@deped.gov.ph
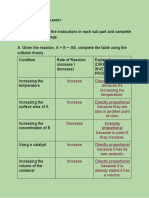
Conditions Before Collision Collision After Collision
Sufficient
energy and A B
A B A B
Proper
orientation:
Reaction A B A B
A B
Occur
Products are
formed They collide with sufficient
Reactant particles approaches each
energy and correct
other Products formed
orientation
Insufficient
energy and A B B
A B A
proper
orientation:
A B A B A B
No reaction
occur
Reactant particles approaches each
They collide with Reactant particles
other
insufficient energy and separate
correct orientation
Wrong
orientation of A A B B A A B B A A B B
reactants : No
reaction
occur
B B
B
A A A A
B B A A B
Reactant particles approaches each
other They collide with incorrect Reactant particles
orientation separate
Figure 1 The reaction of a hypothetical gases A2 and B2
⮚ Activation Energy
The minimum amountof energy that reactant particles must possess in order to
react is called activation energy. For example, if hydrogen and oxygen are mixed
together at room temperature, they do not react, no reaction takes place. But if a burning
splinter or spark is introduced into the mixture, an explosive “popping sound” occurs
immediately. If properly colliding molecules have kinetic energy equal to or greater than
the activation energy, a reaction will take place; if not, they move away from each other
unchanged. This is again illustrated in figure 1 by the two hypothetical diatomic
elements A2 and B2, as they move to a collision with the proper orientation that has
enough energy for reaction, and finally to the formation of products.
The energy level of reactants is always at the left – hand end of the energy diagram,
and the energy level of products is always at the right – hand end . A potential energy
diagram shows the change in potential energy of a system as reactants are converted
into products.
Author: MYLENE B. ZABALLERO
School/Station: Maningalao National High School
Division: Agusan del Norte
email address: mylene.zaballero001@deped.gov.ph
Figure 2. Activation energy is the potential energy difference between the activated complex and the
reactants.
Chemistry for the New Millenium
⮚ The Effect of a Catalyst
A catalyst is a substance that increases or decrceases the rate of a chemical
reaction without being used up in the reaction. It change the mechanism of a chemical
reaction by increasing its rate significantly. In the presence of a catalyst, the chemical
reaction requires a smaller amount of energy to form the products. Catalyst have the
following characteristics:
● Provides an alternate reaction pathway.
● Accelerates a reaction (Increases the rate)
● Unchanged at the end
● Lowers the Activation Energy (Ea)
Figure 3. Energy profiles of catalyzed and uncatalyzed pathways
Exploring Life through Science Chemistry
⮚ The Effect of Temperature
At any temperature, the particles of reacting substances possess characteristics
average velocity and energy. As the temperature increases, the energy of the particles also
increases, resulting in greater movements of the particles. This will result in the increase
in the number of collisions between particles, thus increasing the rate of reaction.
Author: MYLENE B. ZABALLERO
School/Station: Maningalao National High School
Division: Agusan del Norte
email address: mylene.zaballero001@deped.gov.ph
Figure 4. Temperature and Reaction Rate
https://opentextbc.ca/introductorychemistry/chapter/factors-that-affect-the-rate-of-reactions-2/
Activity 1. How Effective Am I?
Learning Objective:
Describe effective collision resulting in the formation of products.
What you need:
Activity sheets, Answer sheets, and pen
What to do: Write in the three circles below the word that best describe an effective collision.
Write your answer in a separate sheet of paper.
EFFECTIVE
COLLISION
Author: MYLENE B. ZABALLERO
School/Station: Maningalao National High School
Division: Agusan del Norte
email address: mylene.zaballero001@deped.gov.ph
Activity 2. Am I Activated?
Learning Objective:
Determine the use of energy diagrams.
What you need: Activity sheets, Answer sheets, and pen,
What to do: From the word list to the right, select the term that describe the energy represented
by each letter (A, B, C, D) in the energy diagram. Write that term in the box beside the letter.
Letter A is done for you. Write your answer in a separate sheet of paper.
Word List
B PE of
Products
PE of
Reactants
PE of Reactants Activation
Energy
C
Heat of
http://www.bing.com/images/search?q=Activation+energy
Guide Questions:
1. What are the components of an Energy Diagram?
___________________________________________________________
2. Why is energy diagram important in studying chemical reaction?
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Rubric for scoring:
Points Description
3 Practical application is scientifically explained consistent to the concept, and
has no misconception.
2 Practical application is scientifically explained consistent to the concepts,
but with minimal misconception.
1 Practical application is explained consistent to the concepts, but with
misconception.
Author: MYLENE B. ZABALLERO
School/Station: Maningalao National High School
Division: Agusan del Norte
email address: mylene.zaballero001@deped.gov.ph
Activity 3. Catalyst vs. Activation Energy and Reaction Rate
Learning Objective:
Describe the effect of the catalyst on the activation energy and reaction rate.
What you need: Activity sheets, Answer sheets, pen
Part I. Catalyst on the Activation Energy
What to do: Analyze the diagram below, and label the activation energy as to
with catalyst or with no catalyst. Write your answer in a separate sheet of paper.
High
1.
2.
Low
https://www.google.com/search?q=catalyst+in+the+activation+energy
Guide Question:
What does the graph show about the effect of a catalyst on the activation energy?
_______________________________________________________________________________.
Part II. Catalyst on Reaction Rate
What to do: Study the graph below and answer the question that follow. Write your answer in
a separate sheet of paper.
5s 10s 15s 20s 25s 30s
Reaction rate
https://www.google.com/search?q=catalyst+in+the+activation+energy
Guide Question:
What does the graph show about the effect of a catalyst on the rate of reaction?
__________________________________________________________________________.
Author: MYLENE B. ZABALLERO
School/Station: Maningalao National High School
Division: Agusan del Norte
email address: mylene.zaballero001@deped.gov.ph
Activity 4. Reaction rate Vs. Temperature
Learning Objective:
Determine the effect of temperature on the reaction rate.
What you need: Activity sheets, Answer sheets, pen
What to do: Study the graph below showing the temperature and the reaction rate in mole per
second of a particular substance and answer the following questions on a separate sheet of
paper.
https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Southeast_Missouri_State_University/Ragain_CH185%3A_General_Chemistry
Guide Questions:
1. At what temperature does a substance reach to the rate of 4.0 mole per second?
_____________
2. What is the rate of the substance at 200 K? _____________
3. Which temperature is needed to raise the rate of reaction to 2.1 mole per second?
___________________
4. How is the effect of temperature on the reaction rate?
________________________________________________________________________________.
Reflection:
Why does milk take a longer time to become sour when placed in a refrigerator?
_______________________________________________________________________________.
Rubric for scoring:
Points Description
3 Practical application is scientifically explained consistent to the concept, and
has no misconception.
2 Practical application is scientifically explained consistent to the concepts,
but with minimal misconception.
1 Practical application is explained consistent to the concepts, but with
misconception.
Author: MYLENE B. ZABALLERO
School/Station: Maningalao National High School
Division: Agusan del Norte
email address: mylene.zaballero001@deped.gov.ph
References for Learners:
Bayquen, A.V. (2007) Chemistry. Phoenix Publishing House, Inc. 927 Quezon City Avenue,
Quezon City pp.177 – 182
Mapa, Amelia P., et.al (2001) Chemistry. SD Publications, Inc. G. Araneta Avenue , Quezon City
pp. 204 – 209.
Soriano, Emil F., et.al (2000) Chemistry for the New Millenium. Adriana Printing Co.,Inc.776
Aurora Blvd, Cubao, Quezon City
Accessed from Unknown Author. Microsoft World,
https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Southeast_Missouri_State_University/
Ragain_CH185%3A_General_Chemistry Accessed on April 5, 2021
Accessed from Unknown Author. Microsoft World,
https://www.google.com/search?q=catalyst+in+the+activation+energy
Accessed on March 29, 2021
Accessed from Unknown Author. Microsoft World,
https://opentextbc.ca/introductorychemistry/chapter/factors-that-affect-the-rate-
ofreactions-2/ Accessed on
Answer Key
Activity 4: Reaction rate
Activity 1: How Vs. Temperature
Effective Am I?
350K
Sufficient
0.4 mole per
energy
second
Right
300K
orientation
The higher the
Reactant
temperature, the
Activity 2: Am I Activated? higher the rate of
PE of Reactants reaction.
Activation Energy
Heat of reaction
Reflection:
PE of Products
Milk take a longer time to
Guide Questions: become sour when place in
a refrigerator because the
PE of Products, PE of average kinetic energy of
Reactants, Activation Energy, Heat the molecules slows down
of Reaction due to the decrease in
The energy diagrams shows temperature.
the change in potential energy of a
Author: MYLENE B. ZABALLERO
Activity Maningalao
School/Station: 3: Catalyst Vs. School
National High Activation energy and
Division: Agusan del
Reaction Norte
Rate
email address: mylene.zaballero001@deped.gov.ph
Part 1: Catalyst on the Activation Energy
Without catalyst
Author: MYLENE B. ZABALLERO
School/Station: Maningalao National High School
Division: Agusan del Norte
email address: mylene.zaballero001@deped.gov.ph
You might also like
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Chemical Reactionsgorio98% (58)
- Scope of WorkDocument7 pagesScope of WorkKriengsak Ruangdech100% (3)
- Exercise 1 - Rates of Chemical ReactionsDocument25 pagesExercise 1 - Rates of Chemical ReactionsMark Ryan Rosal TripoleNo ratings yet
- Gen. Chemistry 2Document5 pagesGen. Chemistry 2pinedaisleNo ratings yet
- Angelica Aragon - CHEMICAL KINETICSDocument7 pagesAngelica Aragon - CHEMICAL KINETICSSTEM 1207- Angelica AragonNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1661500425931 6968837882484963749Document31 pagesOrca Share Media1661500425931 6968837882484963749Justin Rain GregorioNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - KineticsDocument20 pagesChemistry - Kineticssgw67No ratings yet
- Gr.11, Unit 3, Mod 15, L1, Reaction RatesDocument35 pagesGr.11, Unit 3, Mod 15, L1, Reaction Ratesaminbigman15No ratings yet
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : What Are Irreversible and Reversible Reactions?Document16 pagesSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : What Are Irreversible and Reversible Reactions?Thea GeraldeNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument2 pagesGen BioAngelica AycochoNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document24 pagesModule 4MARIE ANN DIAMANo ratings yet
- DLP Science-10 Chem - RXNDocument9 pagesDLP Science-10 Chem - RXNImelda BayonaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Act. 20Document13 pagesInorganic Chemistry Act. 20blake dreiNo ratings yet
- 1 Kinetics From Chemistry Atoms First 3e 2018 Burdge-Overby PDFDocument64 pages1 Kinetics From Chemistry Atoms First 3e 2018 Burdge-Overby PDFMiemma Puenya Leo100% (1)
- Summative Test 4 Q 3 Gen - Chem 2 SY 2022 2023 Copy - Edited Copy - Edited.edited Copy - Edited Copy - EditedDocument11 pagesSummative Test 4 Q 3 Gen - Chem 2 SY 2022 2023 Copy - Edited Copy - Edited.edited Copy - Edited Copy - EditedJV Subang PatindolNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: Quarter 3 - WEEK 4Document13 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Quarter 3 - WEEK 4RODEL AZARESNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: 2 Semester - Module 7Document16 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: 2 Semester - Module 7Juan JohnNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Module 3 L3 &4Document10 pagesGen Chem Module 3 L3 &4Hazel Cosep RicoNo ratings yet
- Collision Theory States That For A Reaction To OccurDocument9 pagesCollision Theory States That For A Reaction To OccurSupia NazmaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: Quarter 3 - Module 4Document16 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Quarter 3 - Module 4Rose Ann Carlos100% (3)
- Physical Science Quarter 3 Week 5: Not For SaleDocument7 pagesPhysical Science Quarter 3 Week 5: Not For SaleMurs H. AsbiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Study Guide ANSWER KEYDocument6 pagesChapter 17 Study Guide ANSWER KEYMohammed AlhalabiNo ratings yet
- Gr.11, Unit 3, Mod 15, L1, Reaction Rates 3Document32 pagesGr.11, Unit 3, Mod 15, L1, Reaction Rates 3aminbigman15No ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 Q2 Module 19Document14 pagesGen Chem 2 Q2 Module 19Beverly JoyNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter Exam PS 2019 2020Document2 pages4th Quarter Exam PS 2019 2020Franklin AdremesinNo ratings yet
- 4 5 Energy ChangesDocument3 pages4 5 Energy ChangesAmmaarNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q4 Module 7 8Document19 pagesScience 10 Q4 Module 7 8Dennis Douglas Alo Jr.No ratings yet
- Physical Science: Quarter 3module 8/week 5 Collision Theory and Chemical Reaction RateDocument16 pagesPhysical Science: Quarter 3module 8/week 5 Collision Theory and Chemical Reaction RateJennie KimNo ratings yet
- 5 2024 245 CH 5 ReactionsAlkenesAlkynes Lecture V3 STUDENTDocument38 pages5 2024 245 CH 5 ReactionsAlkenesAlkynes Lecture V3 STUDENTdingdong19690No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Part2Document48 pagesUnit 5 Part2Gem khyle VelascoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelRoseNo ratings yet
- STEM General Chemistry 1 Q1 M2Document19 pagesSTEM General Chemistry 1 Q1 M2GINA BAYTA100% (1)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Chemical ReactionsHIRAL SOLANKINo ratings yet
- CollisionDocument30 pagesCollisionKutoo BayNo ratings yet
- Notes and Questions: Aqa GcseDocument12 pagesNotes and Questions: Aqa Gcseapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Scan 17 Jan 2022Document3 pagesScan 17 Jan 2022Sam KumarNo ratings yet
- SIM Chemistry 1Document13 pagesSIM Chemistry 1Bernadeth DaracanNo ratings yet
- CK 04 (Arrhenius Equation)Document17 pagesCK 04 (Arrhenius Equation)snehaa92906No ratings yet
- Chemistry: Distance Learning Plan Week 6Document12 pagesChemistry: Distance Learning Plan Week 6Travel UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 11th ABM HUMSS - NOKEYDocument3 pagesPhysical Science 11th ABM HUMSS - NOKEYOliver VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry in Modern TimesDocument26 pagesChemistry in Modern Timespmjoygarciaandal09No ratings yet
- Oct.4 8 Chem 1 WorksheetDocument3 pagesOct.4 8 Chem 1 WorksheetXander Christian RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Energy and Chem EquilibriumDocument39 pagesEnergy and Chem EquilibriumPotato SquadNo ratings yet
- "Connecting Chemistry To Life": Grade 12 Learning Module First Quarter - First Semester 2020-2021Document28 pages"Connecting Chemistry To Life": Grade 12 Learning Module First Quarter - First Semester 2020-2021RJ AcepcionNo ratings yet
- Post-Lab Report: de Luna Doronila Mendoza Villarosa Group 6Document27 pagesPost-Lab Report: de Luna Doronila Mendoza Villarosa Group 6CloudetteMendozaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 EdittedDocument22 pagesModule 4 EdittedMARIE ANN DIAMANo ratings yet
- Lesson 28Document5 pagesLesson 28MarcTnnNo ratings yet
- Unit Start Grand Challenges Essential Questions Concepts Skills LO Code Learning Outcomes Textbook & Resource Materials Evidence of LearningDocument2 pagesUnit Start Grand Challenges Essential Questions Concepts Skills LO Code Learning Outcomes Textbook & Resource Materials Evidence of LearninghenryNo ratings yet
- Module 1.2 Chem Eng-Converted (1Document9 pagesModule 1.2 Chem Eng-Converted (1Nuclear PotatoesNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium - The Equilibrium Constant KC Part 1Document20 pagesChemical Equilibrium - The Equilibrium Constant KC Part 1Sophia HussainNo ratings yet
- Kinetics WebDocument11 pagesKinetics Webعوض أمحمدNo ratings yet
- Types of ReactionsDocument2 pagesTypes of ReactionsDina NassarNo ratings yet
- Module 5&6 Chemistry Notes (Created by Etho - X - BOS)Document25 pagesModule 5&6 Chemistry Notes (Created by Etho - X - BOS)noorNo ratings yet
- Ite The LC Code For Each: Tarlac National High School - Main Joan A. Riparip Physical ScienceDocument3 pagesIte The LC Code For Each: Tarlac National High School - Main Joan A. Riparip Physical ScienceJoan RiparipNo ratings yet
- 11.2 Collision Theory and Transition State TheoryDocument15 pages11.2 Collision Theory and Transition State TheoryAvicenna Ibnu Bahrin100% (9)
- Matriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 4Document13 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 4ridwan100% (1)
- What Is The Difference Between A Physical Change and A Chemical Reaction?Document49 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between A Physical Change and A Chemical Reaction?nkznghidsnidvNo ratings yet
- CMC Chapter 16 (1) - 1Document84 pagesCMC Chapter 16 (1) - 1Raghad AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Reaction Rate NotesDocument6 pagesReaction Rate Notes2nqdq9crs2No ratings yet
- The Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsFrom EverandThe Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsJohn ApSimonNo ratings yet
- TQ - Q3 - Science 8Document5 pagesTQ - Q3 - Science 8MYLENE B. ZABALLERONo ratings yet
- Fourth Quarter Examination in Science 8Document3 pagesFourth Quarter Examination in Science 8MYLENE B. ZABALLERONo ratings yet
- Fourth Quarter Examination in TleDocument2 pagesFourth Quarter Examination in TleMYLENE B. ZABALLERONo ratings yet
- Fourth Quarter Examin Ation in TL eDocument2 pagesFourth Quarter Examin Ation in TL eMYLENE B. ZABALLERONo ratings yet
- Q3 Summative Test #4 Science 7Document3 pagesQ3 Summative Test #4 Science 7MYLENE B. ZABALLERONo ratings yet
- Q3 Summative Test #4 Science 8Document2 pagesQ3 Summative Test #4 Science 8MYLENE B. ZABALLERONo ratings yet
- Science 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 3 ValidatedDocument10 pagesScience 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 3 ValidatedMYLENE B. ZABALLERONo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument39 pagesUntitledMYLENE B. ZABALLERONo ratings yet
- Science 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 1 Validated 1Document7 pagesScience 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 1 Validated 1MYLENE B. ZABALLERONo ratings yet
- Chess: Indoor Recreational GameDocument39 pagesChess: Indoor Recreational GameMYLENE B. ZABALLERONo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Wlas 4TH QTR Week 8Document8 pagesGrade 10 Wlas 4TH QTR Week 8MYLENE B. ZABALLERONo ratings yet
- DLP Science 7 Q1W1Document6 pagesDLP Science 7 Q1W1MYLENE B. ZABALLERONo ratings yet
- DLP SCIENCE 8 4th QTR Week 2Document7 pagesDLP SCIENCE 8 4th QTR Week 2MYLENE B. ZABALLERONo ratings yet
- Science 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 1 Validated 1Document7 pagesScience 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 1 Validated 1MYLENE B. ZABALLERONo ratings yet
- Science 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 2 ValidatedDocument10 pagesScience 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 2 ValidatedMYLENE B. ZABALLERONo ratings yet
- DLP Science 8 Q1 W1Document12 pagesDLP Science 8 Q1 W1MYLENE B. ZABALLERONo ratings yet
- MSOCHA3 - Tutorial 3 - LU 2 - Gas Absorption & Liquid StrippingDocument4 pagesMSOCHA3 - Tutorial 3 - LU 2 - Gas Absorption & Liquid StrippingTshwarelo MahlakoaneNo ratings yet
- Task 34 Booklet (Biomass Pyrolysis)Document20 pagesTask 34 Booklet (Biomass Pyrolysis)suputamadreNo ratings yet
- Enzyme KineticsDocument22 pagesEnzyme Kineticsmercy koNo ratings yet
- RANGKAIAN PNEUMATIK - BakDocument1 pageRANGKAIAN PNEUMATIK - BakDzulatip As ShodikNo ratings yet
- 1982 - Aibi - Heat Transfer Around Tubes in In-Line Tube Banks 2Document8 pages1982 - Aibi - Heat Transfer Around Tubes in In-Line Tube Banks 2arif aktaşNo ratings yet
- Issued For Construction: Sandy Sabkha STA. 2+065 STA. 2+310Document1 pageIssued For Construction: Sandy Sabkha STA. 2+065 STA. 2+310Mohamed HaleemNo ratings yet
- 15-501-EP-RP-001 Rev.1 (Process Description Report)Document9 pages15-501-EP-RP-001 Rev.1 (Process Description Report)Umair A. KhanNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Parametric Study Separation Using Membrane ProcessesDocument6 pagesModeling and Parametric Study Separation Using Membrane ProcessesTpegteam TrainingNo ratings yet
- FFEDocument8 pagesFFEsarthak vyavhareNo ratings yet
- Circulation Pump - CP-4 - Pressure Head Loss CalculationDocument19 pagesCirculation Pump - CP-4 - Pressure Head Loss CalculationKalai MNo ratings yet
- Power Plant ChemistryDocument5 pagesPower Plant ChemistrysoumitrabanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Question Bank - Part 2 1634501492967Document32 pagesHeat Transfer Question Bank - Part 2 1634501492967Inventory gammaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Performance and Life Cycle Cost of Sequencing Batch Reactor A-Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Performance and Life Cycle Cost of Sequencing Batch Reactor A-Literature ReviewAbdul rahmanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2: Ce123 - HydraulicsDocument2 pagesProblem Set 2: Ce123 - HydraulicsZENRIRNo ratings yet
- FM GPSCDocument13 pagesFM GPSCVishal DhandhukiyaNo ratings yet
- PSA Operation ManualDocument83 pagesPSA Operation ManualAbassyacoubouNo ratings yet
- Annex E Severity Levels For Copper Alloy Castings: (Normative)Document2 pagesAnnex E Severity Levels For Copper Alloy Castings: (Normative)bhavin178No ratings yet
- Poster PresentationDocument1 pagePoster PresentationKarli KingNo ratings yet
- PRV PTFE PlastomaticDocument4 pagesPRV PTFE PlastomaticMuhammadThoriqAzmiNo ratings yet
- Wind Tunnel AnalysisDocument24 pagesWind Tunnel AnalysisVenkitaraj K PNo ratings yet
- 1) Introduction To VCM Process: 1.1vinyl Chloride From AcetyleneDocument12 pages1) Introduction To VCM Process: 1.1vinyl Chloride From AcetyleneSaleamlak ZerihunNo ratings yet
- 4.1.1 HAZOP Worksheet-Ammonia Unit-Raw - India ProjectDocument116 pages4.1.1 HAZOP Worksheet-Ammonia Unit-Raw - India Projectsafety pt pcsNo ratings yet
- PEDWPRTS771025A1 - Main Compressor B Train 1 - 5Document1 pagePEDWPRTS771025A1 - Main Compressor B Train 1 - 5macielNo ratings yet
- Process Design Characteristics of Syngas (CO/H) Separation Using Composite MembraneDocument12 pagesProcess Design Characteristics of Syngas (CO/H) Separation Using Composite MembraneNadia S. HafifaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Polyethylene PolymerisationDocument49 pagesChapter 3 - Polyethylene PolymerisationEss NatashaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Plastics Engineering CalculationsDocument12 pagesUnderstanding Plastics Engineering CalculationsKursatNo ratings yet
- PEE321 Lecture Note 1Document24 pagesPEE321 Lecture Note 1nazeertasiu999No ratings yet
- MLVSS / MLSS Ratio's Standard Value Obtained From Different Aeration Tank Samples of Different Capacity Sewage Treatment Plant - A Case StudyDocument5 pagesMLVSS / MLSS Ratio's Standard Value Obtained From Different Aeration Tank Samples of Different Capacity Sewage Treatment Plant - A Case StudyRanadive AnanthNo ratings yet
- Teori-Response Surface MethodologyDocument3 pagesTeori-Response Surface MethodologynanniehNo ratings yet