Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 viewsHaisham ICP
Haisham ICP
Uploaded by
Jijo JosephThis document outlines Mohammed Haisham's grade 8 outcomes, indicators, and assessment criteria for several math topics. The topics covered include money, length, mass, capacity, perimeter, area, 3D shapes, and 2D shapes. For each topic, 1-7 indicators are provided to demonstrate competency, as well as the assessment method which includes formative assessments, integrated learning, and self/peer assessments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- G9 U1 Math MYP Unit Planner 20182019Document6 pagesG9 U1 Math MYP Unit Planner 20182019Ayuu Nur AfifahNo ratings yet
- Tro Chapter E - Study GuideDocument6 pagesTro Chapter E - Study GuideRyan Diaz0% (1)
- Olympiad Sample Paper 4: Useful for Olympiad conducted at School, National & International levelsFrom EverandOlympiad Sample Paper 4: Useful for Olympiad conducted at School, National & International levelsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- To Calculate A Quick Budget Price For A Stainless Steel Tank That Includes The FollowingDocument18 pagesTo Calculate A Quick Budget Price For A Stainless Steel Tank That Includes The Followingjayvijay009No ratings yet
- General Formula For Hydroponic Nutrient Stock SolutionDocument3 pagesGeneral Formula For Hydroponic Nutrient Stock Solutionalvaro100% (1)
- 10 Fao 1-6 ManualsDocument1,164 pages10 Fao 1-6 Manualsshahid ali100% (1)
- Grade 3 Unit 5 Scope and SequenceDocument9 pagesGrade 3 Unit 5 Scope and SequencereemaNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Mathematics CurriculumDocument2 pagesYear 10 Mathematics CurriculumJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Target Sheet For Term 1Document2 pagesGrade 6 Target Sheet For Term 1manilaNo ratings yet
- Common Core Math Standards Jigsaw 3rd GradeDocument2 pagesCommon Core Math Standards Jigsaw 3rd Gradeapi-28847298No ratings yet
- Math Distribution Plan Syllabus 4 2022-2023Document5 pagesMath Distribution Plan Syllabus 4 2022-2023katyaNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument31 pagesMathematicskgotsoncengaNo ratings yet
- Intro Geo 4 - Surface Area NetsDocument8 pagesIntro Geo 4 - Surface Area NetsTariq ZuhlufNo ratings yet
- Subject - Mathematics Level A2 Class - V Lesson - 1 (The Fish Tale) Worksheet - 1Document40 pagesSubject - Mathematics Level A2 Class - V Lesson - 1 (The Fish Tale) Worksheet - 1Mayur ChhagNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Term 2 Mathematics SchemesDocument21 pagesGrade 6 Term 2 Mathematics SchemescyberkaplongNo ratings yet
- 2 Grade (US) or Year 3 (UK) : A Full Month of Real Life Problem Solving!Document32 pages2 Grade (US) or Year 3 (UK) : A Full Month of Real Life Problem Solving!Jwan DelawiNo ratings yet
- Beaa 3 CFB 5 e 957 DCDocument12 pagesBeaa 3 CFB 5 e 957 DCapi-296345301No ratings yet
- 2016NJSLS-M Grade4Document17 pages2016NJSLS-M Grade4Gene HermanNo ratings yet
- Shapes and Symmetry LessonplanDocument5 pagesShapes and Symmetry LessonplananilbajnathNo ratings yet
- Math High School Algebra IDocument3 pagesMath High School Algebra IAzwa NadhiraNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Unit 2 Scope and SequenceDocument11 pagesGrade 4 Unit 2 Scope and SequencereemaNo ratings yet
- Gr34measurement 1Document5 pagesGr34measurement 1api-334498218No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Introductory Geomet Ry: Identify Geometric Attributes & VolumeDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Introductory Geomet Ry: Identify Geometric Attributes & VolumeTariq ZuhlufNo ratings yet
- PLN 6 U3Document1 pagePLN 6 U3Dylan wiazmuNo ratings yet
- Class 8Document130 pagesClass 8Ajmal NayabNo ratings yet
- Unit PlannerDocument5 pagesUnit Plannerapi-523656984No ratings yet
- Intro Geo 3 - Perimeter Area of Composite FiguresDocument11 pagesIntro Geo 3 - Perimeter Area of Composite FiguresTariq ZuhlufNo ratings yet
- 2016NJSLS-M Grade3Document17 pages2016NJSLS-M Grade3Gene HermanNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Mathematics Continues To Build Upon The Foundation Laid in Previous Grades and Introduces New Concepts To Further Develop StudentsDocument2 pagesGrade 4 Mathematics Continues To Build Upon The Foundation Laid in Previous Grades and Introduces New Concepts To Further Develop Studentsk.sophearakNo ratings yet
- Cot Math6 LPDocument7 pagesCot Math6 LPancla.sheena.marie.bNo ratings yet
- Ac Maths Yr4 PlanDocument4 pagesAc Maths Yr4 PlanDinusha BRITTONo ratings yet
- Mathematics Yr 10 Curriculum Maps Term 1Document1 pageMathematics Yr 10 Curriculum Maps Term 1mihirNo ratings yet
- Sample Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesSample Lesson PlanHartoyoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Grade 6: X Y) To Describe Relationships BetweenDocument7 pagesMathematics - Grade 6: X Y) To Describe Relationships Betweenapi-365969613No ratings yet
- Ued400 Biggs Crystal Stage 3 and Final Unit Design MathDocument7 pagesUed400 Biggs Crystal Stage 3 and Final Unit Design Mathapi-539423238No ratings yet
- How To Read The Grade Level Standards: Number and Operations in Base Ten 3.NbtDocument4 pagesHow To Read The Grade Level Standards: Number and Operations in Base Ten 3.NbtmohammadNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Grade 4Document78 pagesMathematics - Grade 4Zaimin Yaz MarchessaNo ratings yet
- IM G6 U1 Unpacking The UnitDocument8 pagesIM G6 U1 Unpacking The UnitProf. David G.No ratings yet
- Math 7 Week 7Document15 pagesMath 7 Week 7Rey Mark RamosNo ratings yet
- Standard 4. Understands and Applies Basic and AdvancedDocument2 pagesStandard 4. Understands and Applies Basic and AdvancedanilbajnathNo ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics 3 q4 w6Document4 pagesDLL Mathematics 3 q4 w6Chelsea JaymaNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 DLL MATH 5 Q4 Week 3Document8 pagesGrade 5 DLL MATH 5 Q4 Week 3Jeward TorregosaNo ratings yet
- PLN 9 U4Document1 pagePLN 9 U4Dylan wiazmuNo ratings yet
- SUPO UbD Geometry Gr10 JIsaacson WAPA-2012Document13 pagesSUPO UbD Geometry Gr10 JIsaacson WAPA-2012Sergio Cuautle JuarezNo ratings yet
- K - 12 Curriculum For Mathematics - Grade 7Document37 pagesK - 12 Curriculum For Mathematics - Grade 7Hezra Mae HermosillaNo ratings yet
- Work Schedule Maths Gr1Document24 pagesWork Schedule Maths Gr1casandraassanahNo ratings yet
- 2016NJSLS-M Grade2Document16 pages2016NJSLS-M Grade2Gene HermanNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 DLL MATH 5 Q4 Week 3Document8 pagesGrade 5 DLL MATH 5 Q4 Week 3shiela pandacNo ratings yet
- In Grade 5 MathematicsDocument2 pagesIn Grade 5 Mathematicsk.sophearakNo ratings yet
- Ued400 Watkins Math Final Unit PlanDocument10 pagesUed400 Watkins Math Final Unit Planapi-656628418No ratings yet
- New Jersey Student Learning Standards Mathematics - Grade 6Document18 pagesNew Jersey Student Learning Standards Mathematics - Grade 6Terrence AkinolaNo ratings yet
- The Learner Will Select and Use Appropriate Tools To Measure Two-And Three - Dimensional FiguresDocument8 pagesThe Learner Will Select and Use Appropriate Tools To Measure Two-And Three - Dimensional FiguresNeha SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit RationaleDocument6 pagesUnit Rationaleapi-463739721No ratings yet
- Term 3 Maths Unit PlanDocument7 pagesTerm 3 Maths Unit Planapi-558132010No ratings yet
- Mathematics - Grade 1Document63 pagesMathematics - Grade 1Charlou Mae TabundaNo ratings yet
- Math Standards Adopted 1997 7Document6 pagesMath Standards Adopted 1997 7establoid1169No ratings yet
- Empyrean School Kharghar Lesson Plan Guidelines: PurposesDocument3 pagesEmpyrean School Kharghar Lesson Plan Guidelines: PurposesHarleen KaurNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 3 - Q4 - W6Document4 pagesDLL - Mathematics 3 - Q4 - W6Jenivive ParcasioNo ratings yet
- Math 130 College MathematicsDocument5 pagesMath 130 College MathematicsGathai MundiaNo ratings yet
- Class 4 WorksheetDocument2 pagesClass 4 WorksheetYuvraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan TemplateDocument15 pagesUnit Plan Templateapi-354426240No ratings yet
- Aitchison Admissions Guide 2020 21 PDFDocument19 pagesAitchison Admissions Guide 2020 21 PDFbilalahmed78No ratings yet
- Jason Howes Tws Learning ObjectivesDocument2 pagesJason Howes Tws Learning Objectivesapi-664138535No ratings yet
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 5From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 5No ratings yet
- Unit Review 03Document2 pagesUnit Review 03Jijo JosephNo ratings yet
- Sine Rule and Cosine Rule Clicker PracticeDocument18 pagesSine Rule and Cosine Rule Clicker PracticeJijo JosephNo ratings yet
- SYMMETRYDocument5 pagesSYMMETRYJijo JosephNo ratings yet
- Similarity - GeometryDocument8 pagesSimilarity - GeometryJijo JosephNo ratings yet
- Congruent Meaning in MathsDocument5 pagesCongruent Meaning in MathsJijo JosephNo ratings yet
- What Are CoordinatesDocument6 pagesWhat Are CoordinatesJijo JosephNo ratings yet
- CPWD Specifications 1Document454 pagesCPWD Specifications 1vikas00707No ratings yet
- Testing The Concentration of Soda Ash and Hydrogen Peroxide - Titrimatric MeDocument2 pagesTesting The Concentration of Soda Ash and Hydrogen Peroxide - Titrimatric MemanlekNo ratings yet
- Gr. 3 - Matter and Energy - HW PacketDocument12 pagesGr. 3 - Matter and Energy - HW PacketTrudie PanNo ratings yet
- Media PrepDocument4 pagesMedia Prepzeljkoac8686No ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document10 pagesExperiment 1Katherine CaspeNo ratings yet
- WOMA Technical Data All Pumps en MedidasDocument11 pagesWOMA Technical Data All Pumps en MedidasEd CalheNo ratings yet
- MeasurementsDocument34 pagesMeasurementsjoshua bravoNo ratings yet
- Egyptian CurriculumDocument24 pagesEgyptian CurriculumAsri DwitaNo ratings yet
- Aa O Level Chemistry Notes Watermarked Protected PDFDocument68 pagesAa O Level Chemistry Notes Watermarked Protected PDFShifa RizwanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: General Physics-Making Measurements: Measurements and Scientific ClaimsDocument24 pagesUnit 1: General Physics-Making Measurements: Measurements and Scientific ClaimsAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- ASTM D7710-14 Standard Test Method For Determination of Volume and Density of Rigid and Irregularity Shaped Molded Cellular MaterialsDocument3 pagesASTM D7710-14 Standard Test Method For Determination of Volume and Density of Rigid and Irregularity Shaped Molded Cellular Materialsynmer_cervantes0% (1)
- ITHHBCMC10AEM-Prepare Hot and Cold DessertsDocument89 pagesITHHBCMC10AEM-Prepare Hot and Cold DessertsBunda RinaNo ratings yet
- BOM - Bills: Inv. ItemDocument10 pagesBOM - Bills: Inv. ItemGuru PrasadNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Secondary 1 CheckpointDocument16 pagesCambridge Secondary 1 CheckpointAlghresi GroupNo ratings yet
- Math7 q2 Week1 EnhancedDocument14 pagesMath7 q2 Week1 EnhancedCindy Buraga PanagaNo ratings yet
- Annual Mathematics Revision QuestionsDocument13 pagesAnnual Mathematics Revision QuestionsshamnathNo ratings yet
- BS 443-82Document12 pagesBS 443-82Sanath WijerathneNo ratings yet
- ConversionDocument2 pagesConversionwindocloudNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 Areas and Volumes (Word Problems)Document13 pagesUnit 14 Areas and Volumes (Word Problems)bemdasNo ratings yet
- Yr 9 Exams PDFDocument112 pagesYr 9 Exams PDFSnifflesNo ratings yet
- Fuel Consumption Hyster Rev3Document7 pagesFuel Consumption Hyster Rev3crash2804No ratings yet
- Chemistry in Focus A Molecular View of Our World 5th Edition Tro Solutions ManualDocument10 pagesChemistry in Focus A Molecular View of Our World 5th Edition Tro Solutions ManualBrettStoutxcqdi100% (12)
- Angka PentingDocument45 pagesAngka PentingoktaNo ratings yet
- Instructions For The User, Installer and Technical Service: Control Box Sun BDocument32 pagesInstructions For The User, Installer and Technical Service: Control Box Sun BmikcomiNo ratings yet
- Decimals Notes02044947Document30 pagesDecimals Notes02044947rajgems007No ratings yet
- Q2 Mathematics 7 AS - Week 1Document13 pagesQ2 Mathematics 7 AS - Week 1Emerald Jane FielNo ratings yet
Haisham ICP
Haisham ICP
Uploaded by
Jijo Joseph0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views6 pagesThis document outlines Mohammed Haisham's grade 8 outcomes, indicators, and assessment criteria for several math topics. The topics covered include money, length, mass, capacity, perimeter, area, 3D shapes, and 2D shapes. For each topic, 1-7 indicators are provided to demonstrate competency, as well as the assessment method which includes formative assessments, integrated learning, and self/peer assessments.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines Mohammed Haisham's grade 8 outcomes, indicators, and assessment criteria for several math topics. The topics covered include money, length, mass, capacity, perimeter, area, 3D shapes, and 2D shapes. For each topic, 1-7 indicators are provided to demonstrate competency, as well as the assessment method which includes formative assessments, integrated learning, and self/peer assessments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views6 pagesHaisham ICP
Haisham ICP
Uploaded by
Jijo JosephThis document outlines Mohammed Haisham's grade 8 outcomes, indicators, and assessment criteria for several math topics. The topics covered include money, length, mass, capacity, perimeter, area, 3D shapes, and 2D shapes. For each topic, 1-7 indicators are provided to demonstrate competency, as well as the assessment method which includes formative assessments, integrated learning, and self/peer assessments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 6
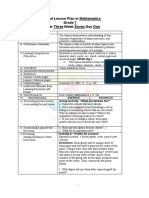
Mohammed Haisham Grade 8
OUTCOMES INDICATORS ASSESMENT CRITERIA PROCEDURE ASSESMENT
OR
METHOD
Recognise, sort and 1. Converts amounts of money. 1. Teacher’s Cross- FORMATIVE
order coins and 2. Partitions money values up to direction Curricular and ASSESMENT
notes with different MVR. 100, using MVR. 10 notes Integrated
face values. Carry out and MVR. 1 coins. 2. Through hands- Learning
simple transactions. 3. Solves 3 step word problems in on experience
Record money the context of money, and
amounts and solves 3 explain how the problem was 3. Through
step word problems solved. examples
and explains the followed by
process. practice.
Understand and use 1. Converts metres to 1. Through Integrated FORMATIVE
the vocabulary centimetres. examples Learning ASSESMENT
related to length. 2. Uses standard units to measure followed by
Know and use and solve problems in a variety practice.
relationships of contexts.
between familiar 3. Solves problems involving
units. Draw and length in a variety of contexts,
measure lines using standard units
accurately. Suggest a
suitable unit and
measuring
equipment, record
estimates and
readings from scales
to a suitable degree
of accuracy. Solve
problems involving
length and distances.
Understand and use 1. Uses the abbreviation for 1. Teacher’s Integrated FORMATIVE
the vocabulary kilogram (kg) and gram (g) in direction Learning ASSESMENT
related to mass recording masses of objects. 2. Through
(weight); suggest a 2. Begins to read the numbered examples
suitable unit and divisions on a scale, and followed by
equipment, record interprets the divisions practice.
estimates and between them.
readings from scales 3. Records masses of objects
to a suitable degree using decimal notation as a
of accuracy, know decimal of kilograms
and use relationships 4. Weighs different amounts of
between familiar water
units and solve 5. Solve problems involving mass
problems involving in a variety of contexts, using
mass. standard units.
Mohammed Haisham Grade 8
Understand and use 1. Orders three or more 1. Teacher’s Integrated FORMATIVE
the vocabulary containers according to direction Learning ASSESMENT
related to capacity; their capacity 2. Through
suggest a suitable 2. Suggests things that could examples
unit to estimate or be measured using litres, followed by
measure capacity; millilitres practice.
record estimates and 3. Finds and describes the
readings from scales relationship between
to a suitable degree millilitre, cubic centimetre
of accuracy. Know and litre.
and use relationships 4. Uses the abbreviation for
between familiar litre (l) and millilitre (ml) in
units. Solve problems recording capacities.
involving capacity . 5. Begins to read the
numbered divisions on a
scale, and interpret the
divisions between them.
(Eg: on a scale from 0 to 25
with intervals of 1 shown
but only the divisions 0, 5,
10, 15 and 20 numbered).
6. Records capacities using
decimal notation as a
decimal of litres. Eg: 1500
ml as 1.500 l
7. Solve problems involving
capacity in a variety of
contexts, using standard
units.
Know the meaning of 1. Uses the term “perimeter” 1. Through Cross- FORMATIVE
perimeter. Estimate to describe the total hands-on Curricular ASSESMENT
and measure the distance around a shape. experience learning
perimeter of simple 2. Estimates and measures
shapes. the perimeter of flat
shapes / places in
centimetres and metres.
Know the meaning of 1. Uses vocabulary related to 1. Through Cross- FORMATIVE
area. Measure the area. hands-on Curricular and ASSESMENT
area of simple shapes 2. Compares area of shapes experience Integrated
using arbitrary units. by placing one shape on Learning
Estimate and top of another.
measure the area of 3. Covers surfaces with
simple shapes. identical shapes without
gaps or overlaps.
4. Measures areas of a flat
surfaces (regular and
irregular shapes) using
arbitrary units.
Mohammed Haisham Grade 8
5. Explains the reason why
area is measured in square
units.
6. Makes a metre square
using news paper.
7. Finds areas by counting
squares.
8. Forms different shapes of
equal area
9. Measures, compares, and
records areas using a
square-centimetre grid
overlay
Recognise, name, 1. Uses mathematical learn and apply Integrated Self and
sort, and make vocabulary to describe 3D mathematical Learning peer
models of 3D objects objects (cubes, cuboids, processes. assessment
and describe them cylinders, spheres, Quizzes
using everyday hemisphere, cones, prism
language. and pyramid) and sort in
different ways on their
attributes such as faces,
corners and edges.
2. Collects examples of cubes,
cuboids, cylinders, spheres,
hemisphere, cones, prism
and pyramid and match
them to name labels.
3. Finds the number of
vertices, edges, and faces
of 3D objects.
4. Selects cubes, cuboids,
cylinders, spheres,
hemisphere, cones, prism
and pyramid from a
collection of 3D objects.
5. Recognises and describes
3D objects displayed
differently. Eg: objects in a
feely bag.
6. Identifies 3D shapes from
pictures of them in
different positions and
orientations.
7. Uses cubes to build
‘double-layered’ solids
from pictures.
Mohammed Haisham Grade 8
8. Makes skeleton models of
cubes and cuboids using
iloshi and modelling clay.
9. Recognises that 3D objects
look different from
different views.
10. Sketches top, front and
side views of cuboids,
cylinders and spheres
Recognise, name, 1. Uses mathematical learn and apply Integrated Self and
sort, and make vocabulary to describe 2D mathematical Learning peer
models of 2D objects shapes (circles, rectangles, processes. assessment
and describe them squares, triangles, Quizzes
using everyday pentagons, hexagons,
language. heptagons, octagons,
quadrilaterals and semi
circles).
2. Collects examples of
circles, rectangles, squares,
triangles, pentagons,
hexagon, octagon,
quadrilateral and semi-
circle and match them to
name labels.
3. Sort a set of flat shapes
according to properties. Eg:
the numbers of vertices or
sides, whether the sides
are the same length,
whether or not at least one
angle is a right angle,
whether or not a shape has
a line of symmetry
4. Arranges attribute blocks
so that the next block has
one difference in attribute
to the previous one
5. Draws a recognisable
pentagons, hexagon and
octagons.
6. Makes symmetrical
patterns with two lines of
symmetry at right angles by
folding and cutting paper.
7. Recognise and draws more
than one line of symmetry
of a shape which has more
than one line of symmetry
Mohammed Haisham Grade 8
and recognises shapes with
no lines of symmetry.
8. Sketches the reflection of a
simple 2-D shape in a
mirror line along one edge,
using a mirror to help
complete it.
Identify angles, 1. Uses paper right angle to learn and apply Integrated Self and
recognise and make identify angles less than, mathematical Learning peer
right angles and greater than or same as a processes. assessment
make turns to right angle. Quizzes
clockwise and 2. Sorts 2D shapes according
anticlockwise to whether they have all,
directions. some or no right angles.
3. Sorts angles of different
sizes i.e. sectors of
different radii.
4. Identifies and marks the
size of angles as small or
big in a given polygon.
5. Uses a paper right angle to
draw right angles and to
identify right angles in 2-D
shapes and in the
environment
6. Compare angles with a
right angle.
7. Recognises that a straight
line is equivalent to two
right angles.
8. Orders angles of different
sizes by superimposing.
Mohammed Haisham Grade 8
You might also like
- G9 U1 Math MYP Unit Planner 20182019Document6 pagesG9 U1 Math MYP Unit Planner 20182019Ayuu Nur AfifahNo ratings yet
- Tro Chapter E - Study GuideDocument6 pagesTro Chapter E - Study GuideRyan Diaz0% (1)
- Olympiad Sample Paper 4: Useful for Olympiad conducted at School, National & International levelsFrom EverandOlympiad Sample Paper 4: Useful for Olympiad conducted at School, National & International levelsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- To Calculate A Quick Budget Price For A Stainless Steel Tank That Includes The FollowingDocument18 pagesTo Calculate A Quick Budget Price For A Stainless Steel Tank That Includes The Followingjayvijay009No ratings yet
- General Formula For Hydroponic Nutrient Stock SolutionDocument3 pagesGeneral Formula For Hydroponic Nutrient Stock Solutionalvaro100% (1)
- 10 Fao 1-6 ManualsDocument1,164 pages10 Fao 1-6 Manualsshahid ali100% (1)
- Grade 3 Unit 5 Scope and SequenceDocument9 pagesGrade 3 Unit 5 Scope and SequencereemaNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Mathematics CurriculumDocument2 pagesYear 10 Mathematics CurriculumJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Target Sheet For Term 1Document2 pagesGrade 6 Target Sheet For Term 1manilaNo ratings yet
- Common Core Math Standards Jigsaw 3rd GradeDocument2 pagesCommon Core Math Standards Jigsaw 3rd Gradeapi-28847298No ratings yet
- Math Distribution Plan Syllabus 4 2022-2023Document5 pagesMath Distribution Plan Syllabus 4 2022-2023katyaNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument31 pagesMathematicskgotsoncengaNo ratings yet
- Intro Geo 4 - Surface Area NetsDocument8 pagesIntro Geo 4 - Surface Area NetsTariq ZuhlufNo ratings yet
- Subject - Mathematics Level A2 Class - V Lesson - 1 (The Fish Tale) Worksheet - 1Document40 pagesSubject - Mathematics Level A2 Class - V Lesson - 1 (The Fish Tale) Worksheet - 1Mayur ChhagNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Term 2 Mathematics SchemesDocument21 pagesGrade 6 Term 2 Mathematics SchemescyberkaplongNo ratings yet
- 2 Grade (US) or Year 3 (UK) : A Full Month of Real Life Problem Solving!Document32 pages2 Grade (US) or Year 3 (UK) : A Full Month of Real Life Problem Solving!Jwan DelawiNo ratings yet
- Beaa 3 CFB 5 e 957 DCDocument12 pagesBeaa 3 CFB 5 e 957 DCapi-296345301No ratings yet
- 2016NJSLS-M Grade4Document17 pages2016NJSLS-M Grade4Gene HermanNo ratings yet
- Shapes and Symmetry LessonplanDocument5 pagesShapes and Symmetry LessonplananilbajnathNo ratings yet
- Math High School Algebra IDocument3 pagesMath High School Algebra IAzwa NadhiraNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Unit 2 Scope and SequenceDocument11 pagesGrade 4 Unit 2 Scope and SequencereemaNo ratings yet
- Gr34measurement 1Document5 pagesGr34measurement 1api-334498218No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Introductory Geomet Ry: Identify Geometric Attributes & VolumeDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Introductory Geomet Ry: Identify Geometric Attributes & VolumeTariq ZuhlufNo ratings yet
- PLN 6 U3Document1 pagePLN 6 U3Dylan wiazmuNo ratings yet
- Class 8Document130 pagesClass 8Ajmal NayabNo ratings yet
- Unit PlannerDocument5 pagesUnit Plannerapi-523656984No ratings yet
- Intro Geo 3 - Perimeter Area of Composite FiguresDocument11 pagesIntro Geo 3 - Perimeter Area of Composite FiguresTariq ZuhlufNo ratings yet
- 2016NJSLS-M Grade3Document17 pages2016NJSLS-M Grade3Gene HermanNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Mathematics Continues To Build Upon The Foundation Laid in Previous Grades and Introduces New Concepts To Further Develop StudentsDocument2 pagesGrade 4 Mathematics Continues To Build Upon The Foundation Laid in Previous Grades and Introduces New Concepts To Further Develop Studentsk.sophearakNo ratings yet
- Cot Math6 LPDocument7 pagesCot Math6 LPancla.sheena.marie.bNo ratings yet
- Ac Maths Yr4 PlanDocument4 pagesAc Maths Yr4 PlanDinusha BRITTONo ratings yet
- Mathematics Yr 10 Curriculum Maps Term 1Document1 pageMathematics Yr 10 Curriculum Maps Term 1mihirNo ratings yet
- Sample Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesSample Lesson PlanHartoyoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Grade 6: X Y) To Describe Relationships BetweenDocument7 pagesMathematics - Grade 6: X Y) To Describe Relationships Betweenapi-365969613No ratings yet
- Ued400 Biggs Crystal Stage 3 and Final Unit Design MathDocument7 pagesUed400 Biggs Crystal Stage 3 and Final Unit Design Mathapi-539423238No ratings yet
- How To Read The Grade Level Standards: Number and Operations in Base Ten 3.NbtDocument4 pagesHow To Read The Grade Level Standards: Number and Operations in Base Ten 3.NbtmohammadNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Grade 4Document78 pagesMathematics - Grade 4Zaimin Yaz MarchessaNo ratings yet
- IM G6 U1 Unpacking The UnitDocument8 pagesIM G6 U1 Unpacking The UnitProf. David G.No ratings yet
- Math 7 Week 7Document15 pagesMath 7 Week 7Rey Mark RamosNo ratings yet
- Standard 4. Understands and Applies Basic and AdvancedDocument2 pagesStandard 4. Understands and Applies Basic and AdvancedanilbajnathNo ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics 3 q4 w6Document4 pagesDLL Mathematics 3 q4 w6Chelsea JaymaNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 DLL MATH 5 Q4 Week 3Document8 pagesGrade 5 DLL MATH 5 Q4 Week 3Jeward TorregosaNo ratings yet
- PLN 9 U4Document1 pagePLN 9 U4Dylan wiazmuNo ratings yet
- SUPO UbD Geometry Gr10 JIsaacson WAPA-2012Document13 pagesSUPO UbD Geometry Gr10 JIsaacson WAPA-2012Sergio Cuautle JuarezNo ratings yet
- K - 12 Curriculum For Mathematics - Grade 7Document37 pagesK - 12 Curriculum For Mathematics - Grade 7Hezra Mae HermosillaNo ratings yet
- Work Schedule Maths Gr1Document24 pagesWork Schedule Maths Gr1casandraassanahNo ratings yet
- 2016NJSLS-M Grade2Document16 pages2016NJSLS-M Grade2Gene HermanNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 DLL MATH 5 Q4 Week 3Document8 pagesGrade 5 DLL MATH 5 Q4 Week 3shiela pandacNo ratings yet
- In Grade 5 MathematicsDocument2 pagesIn Grade 5 Mathematicsk.sophearakNo ratings yet
- Ued400 Watkins Math Final Unit PlanDocument10 pagesUed400 Watkins Math Final Unit Planapi-656628418No ratings yet
- New Jersey Student Learning Standards Mathematics - Grade 6Document18 pagesNew Jersey Student Learning Standards Mathematics - Grade 6Terrence AkinolaNo ratings yet
- The Learner Will Select and Use Appropriate Tools To Measure Two-And Three - Dimensional FiguresDocument8 pagesThe Learner Will Select and Use Appropriate Tools To Measure Two-And Three - Dimensional FiguresNeha SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit RationaleDocument6 pagesUnit Rationaleapi-463739721No ratings yet
- Term 3 Maths Unit PlanDocument7 pagesTerm 3 Maths Unit Planapi-558132010No ratings yet
- Mathematics - Grade 1Document63 pagesMathematics - Grade 1Charlou Mae TabundaNo ratings yet
- Math Standards Adopted 1997 7Document6 pagesMath Standards Adopted 1997 7establoid1169No ratings yet
- Empyrean School Kharghar Lesson Plan Guidelines: PurposesDocument3 pagesEmpyrean School Kharghar Lesson Plan Guidelines: PurposesHarleen KaurNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 3 - Q4 - W6Document4 pagesDLL - Mathematics 3 - Q4 - W6Jenivive ParcasioNo ratings yet
- Math 130 College MathematicsDocument5 pagesMath 130 College MathematicsGathai MundiaNo ratings yet
- Class 4 WorksheetDocument2 pagesClass 4 WorksheetYuvraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan TemplateDocument15 pagesUnit Plan Templateapi-354426240No ratings yet
- Aitchison Admissions Guide 2020 21 PDFDocument19 pagesAitchison Admissions Guide 2020 21 PDFbilalahmed78No ratings yet
- Jason Howes Tws Learning ObjectivesDocument2 pagesJason Howes Tws Learning Objectivesapi-664138535No ratings yet
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 5From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 5No ratings yet
- Unit Review 03Document2 pagesUnit Review 03Jijo JosephNo ratings yet
- Sine Rule and Cosine Rule Clicker PracticeDocument18 pagesSine Rule and Cosine Rule Clicker PracticeJijo JosephNo ratings yet
- SYMMETRYDocument5 pagesSYMMETRYJijo JosephNo ratings yet
- Similarity - GeometryDocument8 pagesSimilarity - GeometryJijo JosephNo ratings yet
- Congruent Meaning in MathsDocument5 pagesCongruent Meaning in MathsJijo JosephNo ratings yet
- What Are CoordinatesDocument6 pagesWhat Are CoordinatesJijo JosephNo ratings yet
- CPWD Specifications 1Document454 pagesCPWD Specifications 1vikas00707No ratings yet
- Testing The Concentration of Soda Ash and Hydrogen Peroxide - Titrimatric MeDocument2 pagesTesting The Concentration of Soda Ash and Hydrogen Peroxide - Titrimatric MemanlekNo ratings yet
- Gr. 3 - Matter and Energy - HW PacketDocument12 pagesGr. 3 - Matter and Energy - HW PacketTrudie PanNo ratings yet
- Media PrepDocument4 pagesMedia Prepzeljkoac8686No ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document10 pagesExperiment 1Katherine CaspeNo ratings yet
- WOMA Technical Data All Pumps en MedidasDocument11 pagesWOMA Technical Data All Pumps en MedidasEd CalheNo ratings yet
- MeasurementsDocument34 pagesMeasurementsjoshua bravoNo ratings yet
- Egyptian CurriculumDocument24 pagesEgyptian CurriculumAsri DwitaNo ratings yet
- Aa O Level Chemistry Notes Watermarked Protected PDFDocument68 pagesAa O Level Chemistry Notes Watermarked Protected PDFShifa RizwanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: General Physics-Making Measurements: Measurements and Scientific ClaimsDocument24 pagesUnit 1: General Physics-Making Measurements: Measurements and Scientific ClaimsAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- ASTM D7710-14 Standard Test Method For Determination of Volume and Density of Rigid and Irregularity Shaped Molded Cellular MaterialsDocument3 pagesASTM D7710-14 Standard Test Method For Determination of Volume and Density of Rigid and Irregularity Shaped Molded Cellular Materialsynmer_cervantes0% (1)
- ITHHBCMC10AEM-Prepare Hot and Cold DessertsDocument89 pagesITHHBCMC10AEM-Prepare Hot and Cold DessertsBunda RinaNo ratings yet
- BOM - Bills: Inv. ItemDocument10 pagesBOM - Bills: Inv. ItemGuru PrasadNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Secondary 1 CheckpointDocument16 pagesCambridge Secondary 1 CheckpointAlghresi GroupNo ratings yet
- Math7 q2 Week1 EnhancedDocument14 pagesMath7 q2 Week1 EnhancedCindy Buraga PanagaNo ratings yet
- Annual Mathematics Revision QuestionsDocument13 pagesAnnual Mathematics Revision QuestionsshamnathNo ratings yet
- BS 443-82Document12 pagesBS 443-82Sanath WijerathneNo ratings yet
- ConversionDocument2 pagesConversionwindocloudNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 Areas and Volumes (Word Problems)Document13 pagesUnit 14 Areas and Volumes (Word Problems)bemdasNo ratings yet
- Yr 9 Exams PDFDocument112 pagesYr 9 Exams PDFSnifflesNo ratings yet
- Fuel Consumption Hyster Rev3Document7 pagesFuel Consumption Hyster Rev3crash2804No ratings yet
- Chemistry in Focus A Molecular View of Our World 5th Edition Tro Solutions ManualDocument10 pagesChemistry in Focus A Molecular View of Our World 5th Edition Tro Solutions ManualBrettStoutxcqdi100% (12)
- Angka PentingDocument45 pagesAngka PentingoktaNo ratings yet
- Instructions For The User, Installer and Technical Service: Control Box Sun BDocument32 pagesInstructions For The User, Installer and Technical Service: Control Box Sun BmikcomiNo ratings yet
- Decimals Notes02044947Document30 pagesDecimals Notes02044947rajgems007No ratings yet
- Q2 Mathematics 7 AS - Week 1Document13 pagesQ2 Mathematics 7 AS - Week 1Emerald Jane FielNo ratings yet