Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Singlephaseinverter
Singlephaseinverter
Uploaded by
Praveen Kumar PandeyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Singlephaseinverter
Singlephaseinverter
Uploaded by
Praveen Kumar PandeyCopyright:
Available Formats
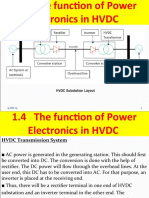
SINGLE PHASE FULL WAVE INVERTER
Circuit Simulation done by
J.LEON BOSCO RAJ, Assistant professor
Department of EEE,
St.Xavier’s Catholic College of Engineering, Nagercoil
Theory
DC to AC converters is known as inverters. The function of an inverter is to change a
DC input voltage to a symmetrical ac output voltage of desired magnitude and frequency.
The output voltage could be variable or fixed frequency. A variable output voltage can be
obtained by varying the input DC voltage and maintaining the gain of the inverter constant.
On the other hand, if the DC input voltage is fixed and it is not controllable, a variable
voltage can be obtained by varying the gain of the inverter, which is normally accomplished
by pulse-width-modulation (PWM) control within the inverter.
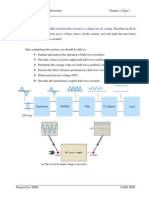
A single phase bridge voltage source inverter is shown in Figure 1. It consists of four
choppers T4 and the four inverse parallel diodes D1, D2, D3, D4.. When the switches and
are turned on simultaneously for a duration , the input voltage appears across
the load and the current flows from point a to b. If the switches and are turned on for a
duration , the voltage across the load is reversed and the current through the load
flows from point b to a. The voltage and current waveforms across the resistive load are
shown in Figure 2.
Figure 1 Circuit diagram of Single phase inverter
Figure 2 Output waveform
Figure 3: Schematic view of Buck converter in eSim
Simulation results
1) Ngspice Plots
Figure 4: Input voltage wave form
Figure 5: Output voltage wave form
2. Python Plots:
Figure 6: Python plot for input and output voltage waveform
Reference
Power Electronic circuits, Devices and Applications, Muhammed H. Rashid, Third Edition,
Pearson Publishers.
You might also like
- Course - Section: - ECE20L-2 - E06 Group Number: Group MembersDocument11 pagesCourse - Section: - ECE20L-2 - E06 Group Number: Group MembersLuch ÜNo ratings yet
- Active Power Factor Correction Technique For Single Phase Full Bridge RectifierDocument6 pagesActive Power Factor Correction Technique For Single Phase Full Bridge RectifierAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- Ec1355 Esd EceDocument31 pagesEc1355 Esd EceSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Modified Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation For Modified Z-Source InverterDocument4 pagesModified Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation For Modified Z-Source InverterAvinash GpNo ratings yet
- Ac-Dc ConvertersDocument7 pagesAc-Dc ConvertersJessica PGNo ratings yet
- Diode Rectifier Then Provides A Full-WaveDocument4 pagesDiode Rectifier Then Provides A Full-Waveprem035No ratings yet
- Resonant DC-DC Converting Controller Santhosh112Document21 pagesResonant DC-DC Converting Controller Santhosh112SanthoshNo ratings yet
- Bi-Dirctional Acdc Converter Based On Neutral Point ClampedDocument6 pagesBi-Dirctional Acdc Converter Based On Neutral Point ClampedphieuxuatkhoNo ratings yet
- Present 2Document35 pagesPresent 2Jayesh JainNo ratings yet
- DC - AC Converter - ADocument15 pagesDC - AC Converter - Abishnu prasad muniNo ratings yet
- IE Mod 01 PowerSupplyDocument25 pagesIE Mod 01 PowerSupplyRy AnNo ratings yet
- ENGG 184.12 Lab Activity 4 - Manlapaz & DolalasDocument3 pagesENGG 184.12 Lab Activity 4 - Manlapaz & DolalasJuan Glicerio C. ManlapazNo ratings yet
- ECE20L - 2 - Expt4Document10 pagesECE20L - 2 - Expt4Niko de LemosNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Full InverterDocument5 pagesSingle Phase Full InverterKinza MallickNo ratings yet
- Choppers & Ac ControllersDocument28 pagesChoppers & Ac Controllersves vegasNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument119 pagesIlovepdf MergedkushalNo ratings yet
- BasicsOfPowerElectronicCircuits ConvertersDocument9 pagesBasicsOfPowerElectronicCircuits ConvertersDhananjay LimayeNo ratings yet
- SPWMDocument5 pagesSPWMKiran Kumar NallamekalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5.4 InverterDocument5 pagesChapter 5.4 InverterSandeep JoshiNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Interface For PV SysteDocument7 pagesPower Electronics Interface For PV SysteSreepadam PadamNo ratings yet
- Split Supply Single Phase Uncontrolled Full Wave Rectifier (Ass PE)Document3 pagesSplit Supply Single Phase Uncontrolled Full Wave Rectifier (Ass PE)Miz AelyfhaNo ratings yet
- Boost Converter: Project FileDocument3 pagesBoost Converter: Project FilevackyvipinNo ratings yet
- AEI Power Module 3 NoteDocument35 pagesAEI Power Module 3 NoteNandu JagguNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Bridge VSIDocument13 pagesSingle Phase Bridge VSIRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- REEEFFFSESDocument6 pagesREEEFFFSESezradural99No ratings yet
- DC To DC Buck and Boost ConverterDocument5 pagesDC To DC Buck and Boost ConverterR ABHISHEKNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Part 1: DC-DC ConverterDocument52 pagesChapter 3 - Part 1: DC-DC ConverterWeehao SiowNo ratings yet
- A Novel Switch Mode Dc-To-Ac Converter With Nonlinear Robust ControlDocument21 pagesA Novel Switch Mode Dc-To-Ac Converter With Nonlinear Robust Controlapi-19799369No ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of Frequency Converter Used in Speed Control of Asynchronous MotorDocument6 pagesModeling and Simulation of Frequency Converter Used in Speed Control of Asynchronous MotorLelosPinelos123No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (Analogue Electronics I)Document7 pagesLecture 3 (Analogue Electronics I)amash.emillyNo ratings yet
- DC-AC ConverterDocument152 pagesDC-AC Converterads jokamNo ratings yet
- A Very High Frequency DC-DC Converter Based On A Class Pfi Resonant InverterDocument10 pagesA Very High Frequency DC-DC Converter Based On A Class Pfi Resonant InvertererdemsecenNo ratings yet
- Inverter PDFDocument84 pagesInverter PDFVenkedesh RNo ratings yet
- Power Factor Corrector For AC To DC Boost Converter: National Conference On Recent Trends in Engineering & TechnologyDocument6 pagesPower Factor Corrector For AC To DC Boost Converter: National Conference On Recent Trends in Engineering & TechnologyAlejandro Navarro CrespinNo ratings yet
- Wave Shaping of Current Using PWM Rectifiers: Mahasweta Bhattacharya, Ashish SrivastavaDocument5 pagesWave Shaping of Current Using PWM Rectifiers: Mahasweta Bhattacharya, Ashish SrivastavaerpublicationNo ratings yet
- Main Objective:: Student Name: Ga Name: Matric NumberDocument19 pagesMain Objective:: Student Name: Ga Name: Matric NumberlionNo ratings yet
- Voltage Harmonic Control of Z-Source Inverter For UPS ApplicationsDocument6 pagesVoltage Harmonic Control of Z-Source Inverter For UPS ApplicationsR.SRIKANTHNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1dDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 1dnorliana salimunNo ratings yet
- DC Power Generation Using Intierior Permanent-Magnet MachiniesDocument6 pagesDC Power Generation Using Intierior Permanent-Magnet MachiniesHosein AshourianNo ratings yet
- Ecgr3155-Experiment 4-Diodes and Bridge RectifiersDocument8 pagesEcgr3155-Experiment 4-Diodes and Bridge RectifiersPhạm Đào Hoàng LongNo ratings yet
- New Type Single-Stage DC Ac InverterDocument5 pagesNew Type Single-Stage DC Ac InverterqiwatingNo ratings yet
- Chapter (Choppers & Inverters) S 1Document4 pagesChapter (Choppers & Inverters) S 1xae778899No ratings yet
- DC-DC Part OneDocument27 pagesDC-DC Part OneAbenezer ZenebeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Part 3: Isolated ConverterDocument28 pagesChapter 2 - Part 3: Isolated ConverterWeehao SiowNo ratings yet
- IAETSD-JARAS High Gain Ratio Hybrid Transformer Based On DC-DC Converter For PV Grid ApplicationsDocument6 pagesIAETSD-JARAS High Gain Ratio Hybrid Transformer Based On DC-DC Converter For PV Grid ApplicationsiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1c (RECTIFIER)Document15 pagesChapter 1c (RECTIFIER)Akmal Amyrul Aizat100% (1)
- Single Phase AC To AC Conversion Without Frequency RestrictionsDocument4 pagesSingle Phase AC To AC Conversion Without Frequency RestrictionsTaniyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document13 pagesUnit 4yamunaoli87No ratings yet
- Assignment # 1 Principles of Steady-State Converter AnalysisDocument20 pagesAssignment # 1 Principles of Steady-State Converter AnalysisMandanas, John MaledrexNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Lab ManualDocument6 pagesPower Electronics: Lab ManualmaryamNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of A Buck-Boost Converters Using IC555Document22 pagesAnalysis and Design of A Buck-Boost Converters Using IC555Eng SamharNo ratings yet
- 201ee235 VIDHARSHANA J MATLAB REPORTDocument5 pages201ee235 VIDHARSHANA J MATLAB REPORTVIDHARSHANA JNo ratings yet
- Hazman Alif Bin HanafiDocument12 pagesHazman Alif Bin HanafiAlice LiewNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument83 pagesReportNikita SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design Considerations of A Buck Converter With A Hysteresis PWM ControllerDocument6 pagesAnalysis and Design Considerations of A Buck Converter With A Hysteresis PWM ControllerRGinanjar Nur RahmatNo ratings yet
- Switching Mode Amplifier For High Voltage Piezo ActuatorDocument3 pagesSwitching Mode Amplifier For High Voltage Piezo ActuatorIjmret JournalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Single Phase InverterDocument20 pagesChapter 3 - Single Phase InverterMuhammad Izz IzzuddinNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Konverter Basic DesignDocument16 pagesDC-DC Konverter Basic DesignTaufik InsaniNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet