Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 viewsReviewer Duty 2
Reviewer Duty 2
Uploaded by
Santos Kyla Patricia T.The document outlines the three stages of labor and birth:
1) The first stage includes early labor and active labor as contractions become stronger and more frequent and the cervix dilates from 1-6 cm.
2) The second stage is when the baby is delivered as the mother finds a comfortable pushing position and the cervix dilates from 6-10 cm.
3) The third stage involves delivering the placenta after birth. Complications during pregnancy can include conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, infections, and sexually transmitted diseases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Skeleton-Worksheet KEY ANSWERDocument4 pagesSkeleton-Worksheet KEY ANSWERjustine alina50% (2)
- 9th Month of PregnancyDocument2 pages9th Month of PregnancyVicky OZNo ratings yet
- IRAC Formulas PDFDocument7 pagesIRAC Formulas PDFroy rebosuraNo ratings yet
- AOI Drift Indicator SystemDocument4 pagesAOI Drift Indicator SystemahnafNo ratings yet
- Stages of Labor & Delivery and Danger Signs of Labor: Week 11 ReportersDocument30 pagesStages of Labor & Delivery and Danger Signs of Labor: Week 11 ReportersMushy_ayaNo ratings yet
- Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation: Are You Thinking About Getting Pregnant?Document2 pagesArchives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation: Are You Thinking About Getting Pregnant?Victor LCNo ratings yet
- Medicinenet: Labor and Delivery Early and Later Signs of Labor ApproachingDocument27 pagesMedicinenet: Labor and Delivery Early and Later Signs of Labor ApproachingNamal No OorNo ratings yet
- Stages of Labour and DeliveryDocument5 pagesStages of Labour and DeliveryChennulNo ratings yet
- What Happens During The First Stage of Labor?Document5 pagesWhat Happens During The First Stage of Labor?ZIAN LABADIANo ratings yet
- Genetic FactorsDocument21 pagesGenetic FactorsMutaganda Ami fideleNo ratings yet
- Stages of Labor Nursing ConsiderationsDocument5 pagesStages of Labor Nursing Considerationsneleh gray100% (2)
- ZzftsoutslDocument26 pagesZzftsoutslCariology YuNo ratings yet
- What Is A Normal DeliveryDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Normal DeliveryVincentus BinNo ratings yet
- Research MethodsDocument6 pagesResearch MethodsDesmond Grasie ZumankyereNo ratings yet
- The Four Stages of LaborDocument12 pagesThe Four Stages of LaborEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- 4 Theories of Labor Onset 0 Signs of LaborDocument13 pages4 Theories of Labor Onset 0 Signs of Labormamsh KlangNo ratings yet
- Pamphlet 2Document2 pagesPamphlet 2api-345915599100% (1)
- Green Pink Handdrawn Style Journey Through The Stages of Pregnancy Education Presentation inDocument19 pagesGreen Pink Handdrawn Style Journey Through The Stages of Pregnancy Education Presentation intreyshaeyjNo ratings yet
- Normal Labour and Birth UohDocument148 pagesNormal Labour and Birth UohCaamir Dek HaybeNo ratings yet
- Normal Labour and Birth Uoh 2023Document159 pagesNormal Labour and Birth Uoh 2023Caamir Dek HaybeNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cesarean Delivery? Reasons For A Cesarean Delivery IncludeDocument12 pagesWhat Is A Cesarean Delivery? Reasons For A Cesarean Delivery IncludeMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Care After Normal DeliveryDocument7 pagesPostpartum Care After Normal DeliveryJennifer MagzNo ratings yet
- Normal LaborDocument8 pagesNormal LaborNishaThakuri100% (2)
- SDL - 4.pdf AnotherDocument3 pagesSDL - 4.pdf AnotherJose Troy NgoaNo ratings yet
- Pre Term Case OlieDocument10 pagesPre Term Case OlieKimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Preg Terms and DefDocument6 pagesPreg Terms and Defvienny kayeNo ratings yet
- OB Stages of Labor and Care in The Stages of Labor With VideoDocument45 pagesOB Stages of Labor and Care in The Stages of Labor With VideodsmagallanesNo ratings yet
- Normal Ob NursingDocument29 pagesNormal Ob NursingEdz Votefornoymar Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery: By: Ma. Kizianne Krystel ManioDocument43 pagesLabor and Delivery: By: Ma. Kizianne Krystel ManioJohn Christian LasalitaNo ratings yet
- Case 2 Guide Questions ChangedDocument9 pagesCase 2 Guide Questions ChangedReyzel PahunaoNo ratings yet
- Caesarian SectionDocument1 pageCaesarian SectionjosephosmandaudaNo ratings yet
- Bubble HeDocument13 pagesBubble HeJoemay Belle CabanelaNo ratings yet
- Induction of Labour Guide PDFDocument56 pagesInduction of Labour Guide PDFlealelgaviNo ratings yet
- JESSA My ReportDocument3 pagesJESSA My ReportMapzy RiveraNo ratings yet
- Definition of LaborDocument2 pagesDefinition of LaborYullie RachmawatieNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Case Study 5 QuestionsDocument6 pagesGroup 2 Case Study 5 QuestionsChadd Vyllmorr VillarinNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Normal Spontaneous Deliver Cil Rmle IiDocument31 pagesCase Presentation: Normal Spontaneous Deliver Cil Rmle IiJose Bryan NacillaNo ratings yet
- LABOR - Labor Is The Process of Childbirth, Starting With Contractions of The Uterus and Ending With Signs of Labor Preliminary Labor: One Hour To A Full Month or More Before LaborDocument6 pagesLABOR - Labor Is The Process of Childbirth, Starting With Contractions of The Uterus and Ending With Signs of Labor Preliminary Labor: One Hour To A Full Month or More Before LaborDianneNo ratings yet
- Perineal Tear Placenta Accreta 1Document8 pagesPerineal Tear Placenta Accreta 1ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Labor and DeliveryDocument5 pagesLabor and DeliveryKayciie CristobalNo ratings yet
- The First Stage of LaborDocument5 pagesThe First Stage of LaborReyna Mee AhiyasNo ratings yet
- Period Power - CompressedDocument20 pagesPeriod Power - Compressedsubhendumohanty2798No ratings yet
- Skills Building Maternal and Child Care: Prepared By: Angeli Joy V. MontonDocument61 pagesSkills Building Maternal and Child Care: Prepared By: Angeli Joy V. MontonboinkjilijoyNo ratings yet
- Normal Labour 400lDocument102 pagesNormal Labour 400lAbdullahi Suleiman MakaNo ratings yet
- O Lightening Probably Occurs Early in Primiparas Because of Tight Abdominal Muscles. inDocument2 pagesO Lightening Probably Occurs Early in Primiparas Because of Tight Abdominal Muscles. inMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- Safari - 25 Jun 2024 at 09:48Document1 pageSafari - 25 Jun 2024 at 09:48adamasoule81No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledFaustina ValerieNo ratings yet
- Edu550 - Child Development: Child Birth - Types of DeliveryDocument16 pagesEdu550 - Child Development: Child Birth - Types of Deliveryसंजेश सुधेश शर्माNo ratings yet
- DR Case Presentation FinalDocument35 pagesDR Case Presentation FinalLord Allen B. GomezNo ratings yet
- Physiology and Management of 1St Stage of LabourDocument5 pagesPhysiology and Management of 1St Stage of LabourSucharita PandaNo ratings yet
- Essential Newborn CareDocument5 pagesEssential Newborn CareJig PirameNo ratings yet
- Definition of Labor Riza Dwi RachmawatiDocument4 pagesDefinition of Labor Riza Dwi Rachmawatiriza dwi rachmawatiNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cesarean Delivery? Reasons For A Cesarean Delivery IncludeDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Cesarean Delivery? Reasons For A Cesarean Delivery IncludeMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Vaginal ChildbirthDocument7 pagesVaginal Childbirtharvyquinday20No ratings yet
- What Do You Want To Know About Pregnancy?Document6 pagesWhat Do You Want To Know About Pregnancy?BAYUFIJRIENo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Midterm ResourcesDocument16 pagesNCM 107 Midterm ResourcesJohnrex MartinezNo ratings yet
- 8 Uterine Prolapse by HINADocument34 pages8 Uterine Prolapse by HINAmasalakhan555No ratings yet
- Bab 2 BundaDocument20 pagesBab 2 BundaNurul UlfahNo ratings yet
- 1 Presumptive Signs and Symptoms of PregnancyDocument13 pages1 Presumptive Signs and Symptoms of PregnancyTherese ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Group 9 - Stages of PregnancyDocument8 pagesGroup 9 - Stages of PregnancyDara Arabella AndalesNo ratings yet
- ErwerDocument2 pagesErwerTREO TESTNo ratings yet
- It's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookFrom EverandIt's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Nursing Care PlansDocument16 pagesNursing Care PlansSantos Kyla Patricia T.No ratings yet
- NSTP ReviewDocument1 pageNSTP ReviewSantos Kyla Patricia T.No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans ...Document16 pagesNursing Care Plans ...Santos Kyla Patricia T.No ratings yet
- NSTP ReviewDocument1 pageNSTP ReviewSantos Kyla Patricia T.No ratings yet
- Reviewer DutyDocument9 pagesReviewer DutySantos Kyla Patricia T.No ratings yet
- 1000 Advanced Vocabulary List (For Advanced Students)Document79 pages1000 Advanced Vocabulary List (For Advanced Students)hasimah5768100% (1)
- 3 Object Oriented Modeling and DesignDocument9 pages3 Object Oriented Modeling and DesignMaya M SNo ratings yet
- advtJRF DIPAS212023Document4 pagesadvtJRF DIPAS212023Rathod Chandra SekharNo ratings yet
- Chassis EUROCASE ML-5410 Middle Tower Full ATX Mainboard Supported, 7 Slots, PSU InsDocument5 pagesChassis EUROCASE ML-5410 Middle Tower Full ATX Mainboard Supported, 7 Slots, PSU InsGuran MaricioNo ratings yet
- Etymology of Directions in Tamil and SanskritDocument17 pagesEtymology of Directions in Tamil and SanskritRavi VararoNo ratings yet
- Essay Topic - Distance LearningDocument3 pagesEssay Topic - Distance LearningFalling stonesNo ratings yet
- Voice Controlled Wheelchair: Project ReportDocument52 pagesVoice Controlled Wheelchair: Project Reportmughees sarwar awanNo ratings yet
- KP Astrology-Denial of Child Birth-4Document7 pagesKP Astrology-Denial of Child Birth-4rahul106No ratings yet
- Secrets of The Abundant Life SermonDocument4 pagesSecrets of The Abundant Life SermonJohnmarc Prince Montano100% (2)
- Midterm Exam For Form 3 CompleteDocument8 pagesMidterm Exam For Form 3 CompleteCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Topic: Assessment of Rehman Medical College Students Attitude Towards Social Media Usage. AbstractDocument10 pagesTopic: Assessment of Rehman Medical College Students Attitude Towards Social Media Usage. AbstractKhalid Khan YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- 1495310-Mdke9 SeriesDocument34 pages1495310-Mdke9 Seriesnhu@nhuNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Study On Loss Processes in Solar CellsDocument11 pagesA Detailed Study On Loss Processes in Solar CellsFernando DiasNo ratings yet
- Chinox 168: AntioxidantDocument2 pagesChinox 168: AntioxidantDanilo CunhaNo ratings yet
- Case Study - 5Q Group 2Document5 pagesCase Study - 5Q Group 2ZulkifliyJamil100% (3)
- The Gateway Experience®: Wave IV-AdventureDocument4 pagesThe Gateway Experience®: Wave IV-AdventureEvan SchowNo ratings yet
- Examinations, Medical Treatment and Ship MedicineDocument15 pagesExaminations, Medical Treatment and Ship Medicineanshul_sharma_5No ratings yet
- Sample CV For Purchase ManagerDocument3 pagesSample CV For Purchase ManagerVijay Kumar100% (1)
- Inhibition of Methicillin-Resistant StaphylococcusDocument7 pagesInhibition of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcusdaniel_siitompulNo ratings yet
- Paranormal Evidences-Are They Justified EditedDocument16 pagesParanormal Evidences-Are They Justified EditedLakshmi PrabaNo ratings yet
- Practical - 4: CS341 Artificial Intelligence Lab ManualDocument12 pagesPractical - 4: CS341 Artificial Intelligence Lab Manual18DCS074 MANN PATELNo ratings yet
- The Magnificent Maldives: Read The Text and Answer The Questions BelowDocument2 pagesThe Magnificent Maldives: Read The Text and Answer The Questions BelowtiareNo ratings yet
- CC103 Engineering Surveying 1 Chapter 2Document15 pagesCC103 Engineering Surveying 1 Chapter 2Xendra AqeylaaNo ratings yet
- Company Profile of Pama PersadaDocument2 pagesCompany Profile of Pama PersadairsyadjamaludinNo ratings yet
- Scope of WorkDocument5 pagesScope of WorkKausik DewanNo ratings yet
- Online Shop Use Case ReportDocument8 pagesOnline Shop Use Case ReportTolu OlusakinNo ratings yet
- 3 Experiment ChemistryDocument30 pages3 Experiment ChemistryThangavel SarujanNo ratings yet
Reviewer Duty 2
Reviewer Duty 2
Uploaded by
Santos Kyla Patricia T.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesThe document outlines the three stages of labor and birth:
1) The first stage includes early labor and active labor as contractions become stronger and more frequent and the cervix dilates from 1-6 cm.
2) The second stage is when the baby is delivered as the mother finds a comfortable pushing position and the cervix dilates from 6-10 cm.
3) The third stage involves delivering the placenta after birth. Complications during pregnancy can include conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, infections, and sexually transmitted diseases.
Original Description:
Aseptic Technique
Original Title
REVIEWER DUTY 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines the three stages of labor and birth:
1) The first stage includes early labor and active labor as contractions become stronger and more frequent and the cervix dilates from 1-6 cm.
2) The second stage is when the baby is delivered as the mother finds a comfortable pushing position and the cervix dilates from 6-10 cm.
3) The third stage involves delivering the placenta after birth. Complications during pregnancy can include conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, infections, and sexually transmitted diseases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesReviewer Duty 2
Reviewer Duty 2
Uploaded by
Santos Kyla Patricia T.The document outlines the three stages of labor and birth:
1) The first stage includes early labor and active labor as contractions become stronger and more frequent and the cervix dilates from 1-6 cm.
2) The second stage is when the baby is delivered as the mother finds a comfortable pushing position and the cervix dilates from 6-10 cm.
3) The third stage involves delivering the placenta after birth. Complications during pregnancy can include conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, infections, and sexually transmitted diseases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
The main principles of Your contractions will become stronger,
closer together and regular. Your legs
aseptic technique include: might cramp, and you might feel
assessing the potential bio contamination risks nauseated.
decontaminating tools, surfaces, and key parts
active labor:
protecting yourself and others from spreading
pathogens Change positions
wearing personal protective equipment (PPE) Roll on a large rubber ball (birthing
creating and working within aseptic fields ball)
(germ-free spaces) Take a warm shower or bath
using non-touch techniques whenever possible Take a walk, stopping to breathe
avoiding cross-contamination through contractions
Have a gentle massage between
contractions
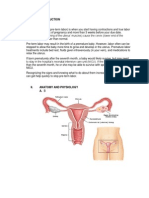
Stage 1: Early labor and
active labor Stage 2: The birth of your
The first stage of labor and birth occurs baby
when you begin to feel persistent
It's time! You'll deliver your baby during
contractions. These contractions become
stronger, more regular and more frequent
the second stage of labor.
over time. When it's time to push, you may experiment
with different positions until you find one
Early labor that feels best. You can push while
During early labor, your cervix dilates squatting, sitting, kneeling — even on your
and effaces. You'll likely feel mild, hands and knees.
irregular contractions.
Stage 3: Delivery of the
As your cervix begins to open, you might
notice a clear pink or slightly bloody
placenta
discharge from your vagina. After your baby is born, you'll likely feel
a great sense of relief. You might hold
early labor:
the baby in your arms or on your
abdomen. Cherish the moment. But a lot
Go for a walk
is still happening. During the third stage
Take a shower or bath
of labor, you will deliver the placenta.
Listen to relaxing music
Try breathing or relaxation Signs and symptoms of placental
techniques taught in childbirth class
abruption include:
Change positions
Vaginal bleeding, although there
Active labor might not be any
During active labor, your cervix will
Abdominal pain
dilate from 6 centimeters (cm) to 10 cm.
Back pain Some examples of common diseases
Uterine tenderness or rigidity and conditions that can cause
complications during your pregnancy
Uterine contractions, often coming
include:
one right after another
diabetes
Some of the most common
complications of pregnancy cancer
include: high blood pressure
high blood pressure infections
gestational diabetes sexually transmitted diseases,
including HIV
preeclampsia
kidney problems
preterm labor
epilepsy
a loss of pregnancy, or
miscarriage anemia
Some examples of common
diseases and conditions that can
cause complications during your
pregnancy include:
diabetes
cancer
high blood pressure
infections
sexually transmitted diseases,
including HIV
kidney problems
epilepsy
anemia
You might also like
- Skeleton-Worksheet KEY ANSWERDocument4 pagesSkeleton-Worksheet KEY ANSWERjustine alina50% (2)
- 9th Month of PregnancyDocument2 pages9th Month of PregnancyVicky OZNo ratings yet
- IRAC Formulas PDFDocument7 pagesIRAC Formulas PDFroy rebosuraNo ratings yet
- AOI Drift Indicator SystemDocument4 pagesAOI Drift Indicator SystemahnafNo ratings yet
- Stages of Labor & Delivery and Danger Signs of Labor: Week 11 ReportersDocument30 pagesStages of Labor & Delivery and Danger Signs of Labor: Week 11 ReportersMushy_ayaNo ratings yet
- Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation: Are You Thinking About Getting Pregnant?Document2 pagesArchives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation: Are You Thinking About Getting Pregnant?Victor LCNo ratings yet
- Medicinenet: Labor and Delivery Early and Later Signs of Labor ApproachingDocument27 pagesMedicinenet: Labor and Delivery Early and Later Signs of Labor ApproachingNamal No OorNo ratings yet
- Stages of Labour and DeliveryDocument5 pagesStages of Labour and DeliveryChennulNo ratings yet
- What Happens During The First Stage of Labor?Document5 pagesWhat Happens During The First Stage of Labor?ZIAN LABADIANo ratings yet
- Genetic FactorsDocument21 pagesGenetic FactorsMutaganda Ami fideleNo ratings yet
- Stages of Labor Nursing ConsiderationsDocument5 pagesStages of Labor Nursing Considerationsneleh gray100% (2)
- ZzftsoutslDocument26 pagesZzftsoutslCariology YuNo ratings yet
- What Is A Normal DeliveryDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Normal DeliveryVincentus BinNo ratings yet
- Research MethodsDocument6 pagesResearch MethodsDesmond Grasie ZumankyereNo ratings yet
- The Four Stages of LaborDocument12 pagesThe Four Stages of LaborEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- 4 Theories of Labor Onset 0 Signs of LaborDocument13 pages4 Theories of Labor Onset 0 Signs of Labormamsh KlangNo ratings yet
- Pamphlet 2Document2 pagesPamphlet 2api-345915599100% (1)
- Green Pink Handdrawn Style Journey Through The Stages of Pregnancy Education Presentation inDocument19 pagesGreen Pink Handdrawn Style Journey Through The Stages of Pregnancy Education Presentation intreyshaeyjNo ratings yet
- Normal Labour and Birth UohDocument148 pagesNormal Labour and Birth UohCaamir Dek HaybeNo ratings yet
- Normal Labour and Birth Uoh 2023Document159 pagesNormal Labour and Birth Uoh 2023Caamir Dek HaybeNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cesarean Delivery? Reasons For A Cesarean Delivery IncludeDocument12 pagesWhat Is A Cesarean Delivery? Reasons For A Cesarean Delivery IncludeMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Care After Normal DeliveryDocument7 pagesPostpartum Care After Normal DeliveryJennifer MagzNo ratings yet
- Normal LaborDocument8 pagesNormal LaborNishaThakuri100% (2)
- SDL - 4.pdf AnotherDocument3 pagesSDL - 4.pdf AnotherJose Troy NgoaNo ratings yet
- Pre Term Case OlieDocument10 pagesPre Term Case OlieKimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Preg Terms and DefDocument6 pagesPreg Terms and Defvienny kayeNo ratings yet
- OB Stages of Labor and Care in The Stages of Labor With VideoDocument45 pagesOB Stages of Labor and Care in The Stages of Labor With VideodsmagallanesNo ratings yet
- Normal Ob NursingDocument29 pagesNormal Ob NursingEdz Votefornoymar Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery: By: Ma. Kizianne Krystel ManioDocument43 pagesLabor and Delivery: By: Ma. Kizianne Krystel ManioJohn Christian LasalitaNo ratings yet
- Case 2 Guide Questions ChangedDocument9 pagesCase 2 Guide Questions ChangedReyzel PahunaoNo ratings yet
- Caesarian SectionDocument1 pageCaesarian SectionjosephosmandaudaNo ratings yet
- Bubble HeDocument13 pagesBubble HeJoemay Belle CabanelaNo ratings yet
- Induction of Labour Guide PDFDocument56 pagesInduction of Labour Guide PDFlealelgaviNo ratings yet
- JESSA My ReportDocument3 pagesJESSA My ReportMapzy RiveraNo ratings yet
- Definition of LaborDocument2 pagesDefinition of LaborYullie RachmawatieNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Case Study 5 QuestionsDocument6 pagesGroup 2 Case Study 5 QuestionsChadd Vyllmorr VillarinNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Normal Spontaneous Deliver Cil Rmle IiDocument31 pagesCase Presentation: Normal Spontaneous Deliver Cil Rmle IiJose Bryan NacillaNo ratings yet
- LABOR - Labor Is The Process of Childbirth, Starting With Contractions of The Uterus and Ending With Signs of Labor Preliminary Labor: One Hour To A Full Month or More Before LaborDocument6 pagesLABOR - Labor Is The Process of Childbirth, Starting With Contractions of The Uterus and Ending With Signs of Labor Preliminary Labor: One Hour To A Full Month or More Before LaborDianneNo ratings yet
- Perineal Tear Placenta Accreta 1Document8 pagesPerineal Tear Placenta Accreta 1ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Labor and DeliveryDocument5 pagesLabor and DeliveryKayciie CristobalNo ratings yet
- The First Stage of LaborDocument5 pagesThe First Stage of LaborReyna Mee AhiyasNo ratings yet
- Period Power - CompressedDocument20 pagesPeriod Power - Compressedsubhendumohanty2798No ratings yet
- Skills Building Maternal and Child Care: Prepared By: Angeli Joy V. MontonDocument61 pagesSkills Building Maternal and Child Care: Prepared By: Angeli Joy V. MontonboinkjilijoyNo ratings yet
- Normal Labour 400lDocument102 pagesNormal Labour 400lAbdullahi Suleiman MakaNo ratings yet
- O Lightening Probably Occurs Early in Primiparas Because of Tight Abdominal Muscles. inDocument2 pagesO Lightening Probably Occurs Early in Primiparas Because of Tight Abdominal Muscles. inMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- Safari - 25 Jun 2024 at 09:48Document1 pageSafari - 25 Jun 2024 at 09:48adamasoule81No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledFaustina ValerieNo ratings yet
- Edu550 - Child Development: Child Birth - Types of DeliveryDocument16 pagesEdu550 - Child Development: Child Birth - Types of Deliveryसंजेश सुधेश शर्माNo ratings yet
- DR Case Presentation FinalDocument35 pagesDR Case Presentation FinalLord Allen B. GomezNo ratings yet
- Physiology and Management of 1St Stage of LabourDocument5 pagesPhysiology and Management of 1St Stage of LabourSucharita PandaNo ratings yet
- Essential Newborn CareDocument5 pagesEssential Newborn CareJig PirameNo ratings yet
- Definition of Labor Riza Dwi RachmawatiDocument4 pagesDefinition of Labor Riza Dwi Rachmawatiriza dwi rachmawatiNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cesarean Delivery? Reasons For A Cesarean Delivery IncludeDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Cesarean Delivery? Reasons For A Cesarean Delivery IncludeMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Vaginal ChildbirthDocument7 pagesVaginal Childbirtharvyquinday20No ratings yet
- What Do You Want To Know About Pregnancy?Document6 pagesWhat Do You Want To Know About Pregnancy?BAYUFIJRIENo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Midterm ResourcesDocument16 pagesNCM 107 Midterm ResourcesJohnrex MartinezNo ratings yet
- 8 Uterine Prolapse by HINADocument34 pages8 Uterine Prolapse by HINAmasalakhan555No ratings yet
- Bab 2 BundaDocument20 pagesBab 2 BundaNurul UlfahNo ratings yet
- 1 Presumptive Signs and Symptoms of PregnancyDocument13 pages1 Presumptive Signs and Symptoms of PregnancyTherese ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Group 9 - Stages of PregnancyDocument8 pagesGroup 9 - Stages of PregnancyDara Arabella AndalesNo ratings yet
- ErwerDocument2 pagesErwerTREO TESTNo ratings yet
- It's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookFrom EverandIt's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Nursing Care PlansDocument16 pagesNursing Care PlansSantos Kyla Patricia T.No ratings yet
- NSTP ReviewDocument1 pageNSTP ReviewSantos Kyla Patricia T.No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans ...Document16 pagesNursing Care Plans ...Santos Kyla Patricia T.No ratings yet
- NSTP ReviewDocument1 pageNSTP ReviewSantos Kyla Patricia T.No ratings yet
- Reviewer DutyDocument9 pagesReviewer DutySantos Kyla Patricia T.No ratings yet
- 1000 Advanced Vocabulary List (For Advanced Students)Document79 pages1000 Advanced Vocabulary List (For Advanced Students)hasimah5768100% (1)
- 3 Object Oriented Modeling and DesignDocument9 pages3 Object Oriented Modeling and DesignMaya M SNo ratings yet
- advtJRF DIPAS212023Document4 pagesadvtJRF DIPAS212023Rathod Chandra SekharNo ratings yet
- Chassis EUROCASE ML-5410 Middle Tower Full ATX Mainboard Supported, 7 Slots, PSU InsDocument5 pagesChassis EUROCASE ML-5410 Middle Tower Full ATX Mainboard Supported, 7 Slots, PSU InsGuran MaricioNo ratings yet
- Etymology of Directions in Tamil and SanskritDocument17 pagesEtymology of Directions in Tamil and SanskritRavi VararoNo ratings yet
- Essay Topic - Distance LearningDocument3 pagesEssay Topic - Distance LearningFalling stonesNo ratings yet
- Voice Controlled Wheelchair: Project ReportDocument52 pagesVoice Controlled Wheelchair: Project Reportmughees sarwar awanNo ratings yet
- KP Astrology-Denial of Child Birth-4Document7 pagesKP Astrology-Denial of Child Birth-4rahul106No ratings yet
- Secrets of The Abundant Life SermonDocument4 pagesSecrets of The Abundant Life SermonJohnmarc Prince Montano100% (2)
- Midterm Exam For Form 3 CompleteDocument8 pagesMidterm Exam For Form 3 CompleteCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Topic: Assessment of Rehman Medical College Students Attitude Towards Social Media Usage. AbstractDocument10 pagesTopic: Assessment of Rehman Medical College Students Attitude Towards Social Media Usage. AbstractKhalid Khan YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- 1495310-Mdke9 SeriesDocument34 pages1495310-Mdke9 Seriesnhu@nhuNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Study On Loss Processes in Solar CellsDocument11 pagesA Detailed Study On Loss Processes in Solar CellsFernando DiasNo ratings yet
- Chinox 168: AntioxidantDocument2 pagesChinox 168: AntioxidantDanilo CunhaNo ratings yet
- Case Study - 5Q Group 2Document5 pagesCase Study - 5Q Group 2ZulkifliyJamil100% (3)
- The Gateway Experience®: Wave IV-AdventureDocument4 pagesThe Gateway Experience®: Wave IV-AdventureEvan SchowNo ratings yet
- Examinations, Medical Treatment and Ship MedicineDocument15 pagesExaminations, Medical Treatment and Ship Medicineanshul_sharma_5No ratings yet
- Sample CV For Purchase ManagerDocument3 pagesSample CV For Purchase ManagerVijay Kumar100% (1)
- Inhibition of Methicillin-Resistant StaphylococcusDocument7 pagesInhibition of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcusdaniel_siitompulNo ratings yet
- Paranormal Evidences-Are They Justified EditedDocument16 pagesParanormal Evidences-Are They Justified EditedLakshmi PrabaNo ratings yet
- Practical - 4: CS341 Artificial Intelligence Lab ManualDocument12 pagesPractical - 4: CS341 Artificial Intelligence Lab Manual18DCS074 MANN PATELNo ratings yet
- The Magnificent Maldives: Read The Text and Answer The Questions BelowDocument2 pagesThe Magnificent Maldives: Read The Text and Answer The Questions BelowtiareNo ratings yet
- CC103 Engineering Surveying 1 Chapter 2Document15 pagesCC103 Engineering Surveying 1 Chapter 2Xendra AqeylaaNo ratings yet
- Company Profile of Pama PersadaDocument2 pagesCompany Profile of Pama PersadairsyadjamaludinNo ratings yet
- Scope of WorkDocument5 pagesScope of WorkKausik DewanNo ratings yet
- Online Shop Use Case ReportDocument8 pagesOnline Shop Use Case ReportTolu OlusakinNo ratings yet
- 3 Experiment ChemistryDocument30 pages3 Experiment ChemistryThangavel SarujanNo ratings yet