Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oxidation
Oxidation
Uploaded by
Maria0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesMany metals react with oxygen to form metal oxides through oxidation reactions. Oxygen can be removed from metal oxides through reduction reactions, such as reacting copper oxide with carbon to form copper and carbon dioxide. Displacement reactions occur when a more reactive metal, like magnesium, displaces a less reactive metal like copper from its compounds in solution, forming magnesium sulfate and metallic copper.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMany metals react with oxygen to form metal oxides through oxidation reactions. Oxygen can be removed from metal oxides through reduction reactions, such as reacting copper oxide with carbon to form copper and carbon dioxide. Displacement reactions occur when a more reactive metal, like magnesium, displaces a less reactive metal like copper from its compounds in solution, forming magnesium sulfate and metallic copper.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesOxidation
Oxidation
Uploaded by
MariaMany metals react with oxygen to form metal oxides through oxidation reactions. Oxygen can be removed from metal oxides through reduction reactions, such as reacting copper oxide with carbon to form copper and carbon dioxide. Displacement reactions occur when a more reactive metal, like magnesium, displaces a less reactive metal like copper from its compounds in solution, forming magnesium sulfate and metallic copper.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
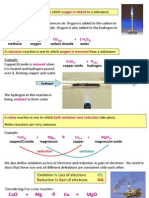
Oxidation, reduction and displacement reactions
Reactions of metals with oxygen
Many metals react with oxygen to make metal oxides. For
example, magnesium burns rapidly in air:
Magnesium + oyxgen → magnesium oxide
2Mg(s) + O2(g) → 2MgO(s)
The reactions are oxidation reactions because the metal gains
oxygen.
Oxygen can be removed from metal oxides in chemical
reactions. For example:
Copper oxide + carbon → copper + carbon dioxide
2CuO(s) + C(s) → 2Cu(l) + CO2(g)
In this reaction, carbon is oxidised because it gains oxygen. At
the same time, copper oxide is reduced because oxygen is
removed from it.
Oxidation is the gain of oxygen. Reduction is the loss of
oxygen.
Displacement in solutions
A more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from
its compounds. For example, magnesium is more reactive than
copper. It displaces copper from copper sulfate solution:
Magnesium + copper sulfate → magnesium sulfate + copper
Mg(s) + CuSO4(aq) → MgSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
In this displacement reaction:
magnesium becomes coated with copper
the blue colour of the solution fades as blue copper sulfate
solution is replaced by colourless magnesium sulfate
solution
You might also like
- Metals IGCSE NotesDocument27 pagesMetals IGCSE NotesMisbah Kamran100% (1)
- Reactivity Series 9 RVDocument20 pagesReactivity Series 9 RVbtz4d95wbkNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Redox, Reactivity Series and AnalysisDocument20 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Redox, Reactivity Series and AnalysisChemistryKlipz93% (14)
- Acid and MetalDocument2 pagesAcid and MetalMariaNo ratings yet
- Reactivity SeriesDocument10 pagesReactivity SeriesZeedan MohammedNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and ReductionDocument39 pagesOxidation and ReductionlisalisoNo ratings yet
- Contents:: Oxidation and Reduction Oxidizing and Reducing Agent Process of OxidationDocument12 pagesContents:: Oxidation and Reduction Oxidizing and Reducing Agent Process of OxidationMUHAMMAD NABEEL ARIFNo ratings yet
- 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes: Reactivity of MetalsDocument6 pages4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes: Reactivity of MetalsJadyn Mc SweenNo ratings yet
- D 4-4-Chemical-Changes-TrilogyDocument5 pagesD 4-4-Chemical-Changes-Trilogyishikagajjar123No ratings yet
- 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes: Reactivity of MetalsDocument6 pages4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes: Reactivity of MetalsJadyn Mc SweenNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Chemical ChangesDocument6 pages4.4 Chemical Changesdynamiccosmic7No ratings yet
- Reactivity SeriesDocument16 pagesReactivity SeriesmarkmchemNo ratings yet
- Reactivity LO's and IGCSE NotesDocument10 pagesReactivity LO's and IGCSE Notesm.sarmadrehanNo ratings yet
- The Reactivity Series NotesDocument6 pagesThe Reactivity Series NotesJo PatrickNo ratings yet
- Chap 9Document17 pagesChap 9Tun Lin AungNo ratings yet
- Reactivity SeriesDocument42 pagesReactivity SeriesGhadeer AlkhayatNo ratings yet
- Reactivity SeriesDocument5 pagesReactivity SeriesTAKUNDA MARIMENo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 7Document5 pagesScience Chapter 7kejungwooNo ratings yet
- Oxidation & Reduction - Redox Reactions - Oxidation: Oxygen Atoms From The Oxygen Molecules in Air E.GDocument4 pagesOxidation & Reduction - Redox Reactions - Oxidation: Oxygen Atoms From The Oxygen Molecules in Air E.Ghussein hajiNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and ReductionDocument8 pagesOxidation and Reductionray469859No ratings yet
- Reactivity Series-DisplacementDocument16 pagesReactivity Series-Displacementmeganekokun kawaiiNo ratings yet
- REACTIVITY SERIES FULL CompleteDocument6 pagesREACTIVITY SERIES FULL CompleteSanbir SaadNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals - Chemical Properties NotesDocument13 pagesMetals and Non-Metals - Chemical Properties NotesDhyan ShahNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 6 WJEC (England) Chemistry GCSEDocument6 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 6 WJEC (England) Chemistry GCSEReaktivic gaishnikovicNo ratings yet
- Reactivity CAU ResearchDocument4 pagesReactivity CAU ResearchmitchofmagicNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument14 pagesQuestion Bankashok pradhan0% (1)
- Metal ReactivityDocument30 pagesMetal ReactivityMin Nyo SinNo ratings yet
- METALSDocument12 pagesMETALSjpkaomeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Metals and Non MetalsDocument17 pagesChapter 3 - Metals and Non Metalskush96122No ratings yet
- MetalsDocument11 pagesMetalsZenoxu 7zNo ratings yet
- REDOX Reaction: CombustionDocument13 pagesREDOX Reaction: Combustionanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Metals in SoilDocument12 pagesMetals in SoilHina AftabNo ratings yet
- Chem F5 Chapter 3 (2020)Document39 pagesChem F5 Chapter 3 (2020)JΞτΗασ0% (1)
- Combination ReactionsDocument7 pagesCombination Reactionstaurus_nikita4484No ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals - NotesDocument13 pagesMetals and Non Metals - NotesmittalshivamNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument34 pagesChemistryvzqyr66ck5No ratings yet
- UNIT-10 Metals: The Reactivity Series of MetalsDocument9 pagesUNIT-10 Metals: The Reactivity Series of MetalsTravel UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- Chap 5Document11 pagesChap 5Tun Lin AungNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations: Chapter - 1Document8 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations: Chapter - 1Samradh Singh 9-H DPSKNo ratings yet
- EM - 10th Science Notes 2018-19-1Document153 pagesEM - 10th Science Notes 2018-19-1Nagesh EinsteinNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument322 pagesScienceIssmeh FatimaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument12 pagesMetals and Non MetalsMuzafar ahmadNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES Question and AnswerDocument6 pagesPHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES Question and AnswerKunal SumukNo ratings yet
- Physical Changes and Chemical Changes: (MG) +oxygen (O2) Magnesium Oxide (Mgo)Document2 pagesPhysical Changes and Chemical Changes: (MG) +oxygen (O2) Magnesium Oxide (Mgo)prartana smNo ratings yet
- Wa0002Document3 pagesWa0002brendabjematiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document3 pagesUnit 7api-282526559No ratings yet
- REDOX REACTIONS NOTES-Unit 8Document13 pagesREDOX REACTIONS NOTES-Unit 8muralidharhegdenorthsquareNo ratings yet
- Chap-1-Chemical Reaction and EqDocument8 pagesChap-1-Chemical Reaction and Eqapi-400692183No ratings yet
- Edexcel AS Chemistry Note 3 - Different Types of ReactionDocument7 pagesEdexcel AS Chemistry Note 3 - Different Types of ReactionSajaniNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3.04: Particles and Chemical Equation 2Document17 pagesUnit - 3.04: Particles and Chemical Equation 2Ayman HassanNo ratings yet
- Displacement Reactions G8Document14 pagesDisplacement Reactions G8diamehta1512No ratings yet
- The Reactivity Series of Metals and Its ApplicationsDocument14 pagesThe Reactivity Series of Metals and Its ApplicationsSaadiah MohammadNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS Notes 1710928665Document11 pagesCHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS Notes 1710928665Chinmayi mamathaNo ratings yet
- Reactivity Series of Metals: Reactions of Metals Effect of Heat On Metal CarbonatesDocument24 pagesReactivity Series of Metals: Reactions of Metals Effect of Heat On Metal CarbonatesCarl Agape DavisNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text: By: Dwiyanti Octaviani Farrah Nabila F Malik Farhan Nazhara Ardhan Roikhan Azhari Syifa FauziahDocument28 pagesExplanation Text: By: Dwiyanti Octaviani Farrah Nabila F Malik Farhan Nazhara Ardhan Roikhan Azhari Syifa Fauziahsyifa fauziahNo ratings yet
- Unit 2B.6 Mining and RefiningDocument20 pagesUnit 2B.6 Mining and RefiningPualeilehuaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes 3 Chapter - Materials: Metals and Non MetalsDocument6 pagesChemistry Notes 3 Chapter - Materials: Metals and Non MetalsRuby SisodiyaNo ratings yet
- Yr10 Redox Reactions SlidesDocument12 pagesYr10 Redox Reactions SlidesKahan BNo ratings yet
- Chm101: Introductory Chemistry 1 MODULE 1: Methods of Science Lecture Four: Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument34 pagesChm101: Introductory Chemistry 1 MODULE 1: Methods of Science Lecture Four: Types of Chemical ReactionsOluwabusolami Akinola100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Acid and MetalDocument2 pagesAcid and MetalMariaNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument1 pageElectrolysisMariaNo ratings yet
- Aluminium ExtractionDocument2 pagesAluminium ExtractionMariaNo ratings yet
- ExtractionDocument1 pageExtractionMariaNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionDocument1 pageRedox ReactionMariaNo ratings yet
- JohalDocument1 pageJohalMariaNo ratings yet