Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 viewsARF Table269 4
ARF Table269 4
Uploaded by
purwandinyThis document provides guidelines for managing ischemic and nephrotoxic acute renal failure. It outlines therapies for reversing the causative renal insult, preventing and treating complications like fluid overload and electrolyte abnormalities, addressing nutrition needs, and determining when dialysis is needed. Specific recommendations include restricting sodium and fluid intake, using loop diuretics to manage fluid overload, restricting potassium and phosphorus in the diet, and treating hyperkalemia with insulin and glucose or sodium polystyrene sulphonate if needed. Dialysis should be considered for refractory fluid overload, electrolyte abnormalities, or azotemia above specified levels. Medication dosing also needs adjustment based on renal function.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Syndrome of Inappropriate Secretion of Anti Diuretic HormoneDocument39 pagesSyndrome of Inappropriate Secretion of Anti Diuretic Hormonefarmasi_hmNo ratings yet
- Část Maturity Z Anglického Jazyka - Ústní Část - 18 - Z - Food and Healthy Diet - Interlocutor (New 2013)Document2 pagesČást Maturity Z Anglického Jazyka - Ústní Část - 18 - Z - Food and Healthy Diet - Interlocutor (New 2013)Trill_MoNo ratings yet
- Function Maintain Homeostatic Balance With Respect To Fluids, Electrolytes, and Organic SolutesDocument8 pagesFunction Maintain Homeostatic Balance With Respect To Fluids, Electrolytes, and Organic SolutesNikki SalivioNo ratings yet
- Sec1 Clinical2 (ARF)Document44 pagesSec1 Clinical2 (ARF)ahmedmohamed01153159469No ratings yet
- Terapi CairanDocument30 pagesTerapi CairanNunik Dewi KumalasariNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument43 pagesElectrolyte ImbalanceJoshua JoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine EmergenciesDocument22 pagesEndocrine EmergenciesBen Man JunNo ratings yet
- Medical Nutrition Therapy For Renal Disease 2016Document39 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy For Renal Disease 2016Steven FongNo ratings yet
- Potassium Disorders by AiyraDocument25 pagesPotassium Disorders by AiyraAnndrea IlhamNo ratings yet
- Medical Nutrition Therapy For Renal Disease 2021Document39 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy For Renal Disease 2021Oktaviani Karo SekaliNo ratings yet
- Review: Diagnostic and Treatment of Electrolyte DisturbancesDocument31 pagesReview: Diagnostic and Treatment of Electrolyte DisturbancesalvyandaniNo ratings yet
- Metabolic AlkalosisDocument4 pagesMetabolic AlkalosisCay Sevilla100% (1)
- Nursing 75 Fluid and Electrolyte Exam 2Document6 pagesNursing 75 Fluid and Electrolyte Exam 2chubbygunny_29776413No ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : Myocardial InfarctionDocument5 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : Myocardial InfarctionManju PillaiNo ratings yet
- Potassium ChlorideDocument2 pagesPotassium ChlorideSetiram Zenitram50% (2)
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : BackgroundDocument7 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : BackgroundLeoNo ratings yet
- Pass Critical Care Endocrine Frcem ResourcesDocument41 pagesPass Critical Care Endocrine Frcem ResourcesYoussef SaadNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Disturbance-1Document22 pagesElectrolyte Disturbance-1Doaa Abd El-WahabNo ratings yet
- Management of Potassium Disorders 17706 ArticleDocument4 pagesManagement of Potassium Disorders 17706 ArticlealeNo ratings yet
- Aki and CKD Therapy 2021Document46 pagesAki and CKD Therapy 2021Alfathri YunediNo ratings yet
- S.gaus-Management of Life-Threatening (Kuliah Sistem) 2Document46 pagesS.gaus-Management of Life-Threatening (Kuliah Sistem) 2Ta RaNo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectroltyesDocument45 pagesFluids and ElectroltyesNurhafizah sahidanNo ratings yet
- Materi 7 - Gagal Ginjal AkutDocument30 pagesMateri 7 - Gagal Ginjal AkutTegar Muhamad RifkiNo ratings yet
- CA Vit D MetabolismDocument41 pagesCA Vit D MetabolismPramod N KNo ratings yet
- Medical Nutrition Therapy For Renal Disease 2016Document39 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy For Renal Disease 2016Steven FongNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid TonicityDocument4 pagesIV Fluid TonicityDarylSteffiNo ratings yet
- RenalElectrolytecharts 220906 101323 2Document7 pagesRenalElectrolytecharts 220906 101323 2Saheed jaladeNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Management Of: Kurdistan Higher Council For Medical SpecialtiesDocument6 pagesGuidelines For The Management Of: Kurdistan Higher Council For Medical SpecialtiesCik JaaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Sumolly Anak DavidDocument29 pagesDiuretics: Sumolly Anak Davidfarmasi_hmNo ratings yet
- Gangguan Ginjal AkutDocument29 pagesGangguan Ginjal Akutb3djo_76No ratings yet
- Angela Heithaus, MD, PS Internal Medicine Seattle Healing Arts CenterDocument32 pagesAngela Heithaus, MD, PS Internal Medicine Seattle Healing Arts CenterMarwan M.No ratings yet
- DR Sravan Thondam - HyponatraemiaDocument38 pagesDR Sravan Thondam - HyponatraemiaAndy esNo ratings yet
- Cardiac MedsDocument7 pagesCardiac MedsMary Fair DelcidNo ratings yet
- ACE Inhibitors PrintDocument5 pagesACE Inhibitors PrintBernard TangNo ratings yet
- 0 - Management of Life-Threatening Electrolyte and Metabolic Disturbances 3Document32 pages0 - Management of Life-Threatening Electrolyte and Metabolic Disturbances 3Roqoyyah MursyidNo ratings yet
- Renal Guide and Charts: AlbuminDocument16 pagesRenal Guide and Charts: AlbuminYaima JimenezNo ratings yet
- 2 Fluid and Electrolyte AbnormalityDocument16 pages2 Fluid and Electrolyte AbnormalityGoez Aditya NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Therapy - 2021Document10 pagesFluid Therapy - 2021Madiha MadiNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument2 pagesDrugsKC IgnacioNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument2 pagesDRUG StudyKC IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Management of GoutDocument6 pagesManagement of GoutSeanHong TanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Therapy and ElectroliteDocument36 pagesFluid Therapy and ElectroliteAriefBudimanHidayatNo ratings yet
- Off Tag Assessment (Surgery)Document19 pagesOff Tag Assessment (Surgery)Ahmad LiewNo ratings yet
- HyperkalaemiaDocument6 pagesHyperkalaemiaSSNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Calcium (Autosaved)Document22 pagesDisorders of Calcium (Autosaved)ksNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument4 pagesChronic Kidney DiseasejosephNo ratings yet
- Phys Block 2Document63 pagesPhys Block 2drunkenwukongNo ratings yet
- Management of HypokalemiaDocument6 pagesManagement of HypokalemiaEsraa Abu elelaNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia Algorithm: Onset Rapid ( 48 Hours) : 3% Onset Rapid ( 48 Hours) : May Consider 3% Nac LDocument2 pagesHyponatremia Algorithm: Onset Rapid ( 48 Hours) : 3% Onset Rapid ( 48 Hours) : May Consider 3% Nac Lmina000005100% (1)
- Nutritional Management of Renal Diseases Disease Goals Energy Protein Vitamins/Minerals Fats/FluidsDocument3 pagesNutritional Management of Renal Diseases Disease Goals Energy Protein Vitamins/Minerals Fats/Fluidscbac1990No ratings yet
- Surgery YbDocument67 pagesSurgery YbTamirat geletaNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument3 pagesAcute Renal Failurezainabd1964No ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 12Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 12JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument3 pagesSodium BicarbonateAubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Fluid TherapyDocument9 pagesFluid TherapyMadiha MadiNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- The Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionFrom EverandThe Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionNo ratings yet
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- 2020 The Essential Diets - All Diets in One Book - Ketogenic, Mediterranean, Mayo, Zone Diet, High Protein, Vegetarian, Vegan, Detox, Paleo, Alkaline Diet and Much More: COOKBOOK, #2From Everand2020 The Essential Diets - All Diets in One Book - Ketogenic, Mediterranean, Mayo, Zone Diet, High Protein, Vegetarian, Vegan, Detox, Paleo, Alkaline Diet and Much More: COOKBOOK, #2No ratings yet
- Minilecture Pneumonia 1703Document54 pagesMinilecture Pneumonia 1703purwandinyNo ratings yet
- DHF - CDCDocument105 pagesDHF - CDCpurwandinyNo ratings yet
- DHF - CDC Utk DiprintDocument72 pagesDHF - CDC Utk DiprintpurwandinyNo ratings yet
- SL paraDocument36 pagesSL parapurwandinyNo ratings yet
- Keadaan Kepala-Leher (Revisi)Document54 pagesKeadaan Kepala-Leher (Revisi)purwandinyNo ratings yet
- Komplikasi DMDocument53 pagesKomplikasi DMpurwandinyNo ratings yet
- ARF Table269 2Document3 pagesARF Table269 2purwandinyNo ratings yet
- ARF Table269 1Document2 pagesARF Table269 1purwandinyNo ratings yet
- Problems With DialysisDocument3 pagesProblems With Dialysispurwandiny100% (1)
- 142 Blood Leak AlarmDocument2 pages142 Blood Leak AlarmpurwandinyNo ratings yet
- Easy Vegan Pasta SaladDocument41 pagesEasy Vegan Pasta SaladDiana Madalina LuchianNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Substrate Oxidation Rates in Vivo From Gaseous ExchangeDocument7 pagesCalculation of Substrate Oxidation Rates in Vivo From Gaseous ExchangeRodrigo CastilloNo ratings yet
- NCP MakingDocument2 pagesNCP MakingMinakaNo ratings yet
- Einstein Bros. Bagels Nutrition and Allergen Information: Einstein Noah Restaurant Group, IncDocument6 pagesEinstein Bros. Bagels Nutrition and Allergen Information: Einstein Noah Restaurant Group, InctomtranNo ratings yet
- Media Monitoring SCM (27may20-3.30pm)Document2,605 pagesMedia Monitoring SCM (27may20-3.30pm)Chandra YugoNo ratings yet
- Snack Attack, You Are What You EatDocument1 pageSnack Attack, You Are What You EatRooney SamirNo ratings yet
- Type 2 Diabetes Thesis PDFDocument5 pagesType 2 Diabetes Thesis PDFCollegePapersToBuyUK100% (2)
- Grade 9 PE DLL Week 1Document7 pagesGrade 9 PE DLL Week 1Pagsibigan PO100% (1)
- Analysis of Sugars PDFDocument29 pagesAnalysis of Sugars PDFKhalidNo ratings yet
- Lim 2016Document80 pagesLim 2016Hora GoroNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Food Additives in Sri LankaDocument5 pagesRegulation of Food Additives in Sri LankaBiNtH AbDeeNNo ratings yet
- 8 Tips For Healthy Eating - NHSDocument4 pages8 Tips For Healthy Eating - NHSp100% (1)
- 3.2 Soal Isian SingkatDocument2 pages3.2 Soal Isian SingkatFikriNo ratings yet
- Mud Crab FeedsDocument34 pagesMud Crab FeedsCharles StephenNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions 1 PhotosynthesisDocument17 pagesPractice Questions 1 Photosynthesis사나No ratings yet
- Balanced DietDocument6 pagesBalanced DietsumiinlineNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Final NoteDocument17 pagesNutrition Final Notediemtruc414No ratings yet
- Birac Naarm0147 Big-17 20.Document18 pagesBirac Naarm0147 Big-17 20.Murali KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Abortion BSN 0PR-2: Case Study of BelleDocument27 pagesAbortion BSN 0PR-2: Case Study of BellekervinNo ratings yet
- Cereals and Legume TechnologyDocument23 pagesCereals and Legume TechnologyLê Tất TiếnNo ratings yet
- Obtlp Nutrition Diet Therapy NCM 105 2020-2021 1ST SemDocument11 pagesObtlp Nutrition Diet Therapy NCM 105 2020-2021 1ST Semmirai desuNo ratings yet
- Innovation in Precision Fermentation For Food IngredientsDocument22 pagesInnovation in Precision Fermentation For Food IngredientsBabuskin SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- UNIT 6 How Often Do You ExerciseDocument28 pagesUNIT 6 How Often Do You ExerciseCelis LópezNo ratings yet
- SAARES AguajunDocument23 pagesSAARES AguajunBETTY MIRELLA MURILLO CHOQUENo ratings yet
- MSM Medium Updated 2019Document1 pageMSM Medium Updated 2019ഗീതു സുരേഷ്No ratings yet
- Test Asesmen Literasi Numerasi Tingkat SMPDocument14 pagesTest Asesmen Literasi Numerasi Tingkat SMParaoky100% (3)
- Vol 1 of MCQs E MagazineDocument349 pagesVol 1 of MCQs E MagazineJąhąnząib Khąn Kąkąr100% (1)
- Cacfp Menu AssessmentDocument2 pagesCacfp Menu Assessmentapi-604622509No ratings yet
- Biology Studies On Screening of Suitable Diet For Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera Frugiperda (J. E. Smith)Document4 pagesBiology Studies On Screening of Suitable Diet For Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera Frugiperda (J. E. Smith)VISHAL TIDKENo ratings yet
ARF Table269 4
ARF Table269 4
Uploaded by
purwandiny0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesThis document provides guidelines for managing ischemic and nephrotoxic acute renal failure. It outlines therapies for reversing the causative renal insult, preventing and treating complications like fluid overload and electrolyte abnormalities, addressing nutrition needs, and determining when dialysis is needed. Specific recommendations include restricting sodium and fluid intake, using loop diuretics to manage fluid overload, restricting potassium and phosphorus in the diet, and treating hyperkalemia with insulin and glucose or sodium polystyrene sulphonate if needed. Dialysis should be considered for refractory fluid overload, electrolyte abnormalities, or azotemia above specified levels. Medication dosing also needs adjustment based on renal function.
Original Description:
Original Title
ARF-Table269-4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides guidelines for managing ischemic and nephrotoxic acute renal failure. It outlines therapies for reversing the causative renal insult, preventing and treating complications like fluid overload and electrolyte abnormalities, addressing nutrition needs, and determining when dialysis is needed. Specific recommendations include restricting sodium and fluid intake, using loop diuretics to manage fluid overload, restricting potassium and phosphorus in the diet, and treating hyperkalemia with insulin and glucose or sodium polystyrene sulphonate if needed. Dialysis should be considered for refractory fluid overload, electrolyte abnormalities, or azotemia above specified levels. Medication dosing also needs adjustment based on renal function.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as rtf, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesARF Table269 4
ARF Table269 4
Uploaded by
purwandinyThis document provides guidelines for managing ischemic and nephrotoxic acute renal failure. It outlines therapies for reversing the causative renal insult, preventing and treating complications like fluid overload and electrolyte abnormalities, addressing nutrition needs, and determining when dialysis is needed. Specific recommendations include restricting sodium and fluid intake, using loop diuretics to manage fluid overload, restricting potassium and phosphorus in the diet, and treating hyperkalemia with insulin and glucose or sodium polystyrene sulphonate if needed. Dialysis should be considered for refractory fluid overload, electrolyte abnormalities, or azotemia above specified levels. Medication dosing also needs adjustment based on renal function.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as rtf, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
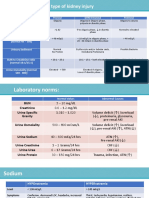
Table 269-4.
Management of Ischemic and Nephrotoxic Acute Renal Failurea
Management Issue Therapy
REVERSE CAUSATIVE RENAL INSULT
Ischemic ARF Restore systemic hemodynamics and renal perfusion
Nephrotoxic ARF Eliminate nephrotoxins
Consider specific measures (e.g., forced alkaline diuresis,
chelators: see text)
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF COMPLICATIONS
Intravascular volume overload Salt (1-2 g/d) and water (usually <1 L/d) restriction
Diuretics (usually loop blockers ± thiazide)
Ultrafiltration or dialysis
Hyponatremia Restriction of enteral free water intake (<1 L/d)
Avoid hypotonic intravenous solutions (including dextrose
solutions)
Hyperkalemia Restriction of dietary K+ intake (usually <40 mmol/d)
Eliminate K+ supplements and K+-sparing diuretics
Potassium-binding ion-exchange resins (e.g., sodium
polystyrene sulphonate)
Glucose (50 mL of 50% dextrose) and insulin (10 units regular)
Sodium bicarbonate (usually 50-100 mmol)
Calcium gluconate (10 mL of 10% solution over 5 min)
Dialysis (with low K+ dialysate)
Metabolic acidosis Restriction of dietary protein (usually 0.6 g/kg per day of high
biologic value)
Sodium bicarbonate (maintain serum bicarbonate >15 mmol/L
or arterial pH >7.2)
Dialysis
Hyperphosphatemia Restriction of dietary phosphate intake (usually <800 mg/d)
Phosphate binding agents (calcium carbonate, aluminum
hydroxide)
Hypocalcemia Calcium carbonate (if symptomatic or if sodium bicarbonate to
be administered)
Calcium gluconate (10-20 mL of 10% solution)
Hypermagnesemia Discontinue Mg2+-containing antacids
Hyperuricemia Treatment usually not necessary [if <890 mmol/L (<15 mg/dL)]
Nutrition Restriction of dietary protein (~0.6 g/kg per day)
Carbohydrate (~100 g/d)
Enteral or parenteral nutrition (if recovery prolonged or patient
very catabolic)
Indications for dialysis Clinical evidence (symptoms or signs) of uremia
Intractable intravascular volume overload
Hyperkalemia or severe acidosis resistant to conservative
measures
?Prophylactic dialysis when urea >100-150 mg/dL or creatinine
>8-10 mg/dL
PRESCRIBING OF MEDICATIONS
Choice of agents Avoid other nephrotoxins, ACE inhibitors, cyclooxygenase
inhibitors, and radiocontrast unless absolute indication and
no alternative agent
Drug dosing Adjust doses and frequency of administration for degree of
renal impairment
a These are general recommendations and must be tailored to needs of individual patients.
You might also like
- Syndrome of Inappropriate Secretion of Anti Diuretic HormoneDocument39 pagesSyndrome of Inappropriate Secretion of Anti Diuretic Hormonefarmasi_hmNo ratings yet
- Část Maturity Z Anglického Jazyka - Ústní Část - 18 - Z - Food and Healthy Diet - Interlocutor (New 2013)Document2 pagesČást Maturity Z Anglického Jazyka - Ústní Část - 18 - Z - Food and Healthy Diet - Interlocutor (New 2013)Trill_MoNo ratings yet
- Function Maintain Homeostatic Balance With Respect To Fluids, Electrolytes, and Organic SolutesDocument8 pagesFunction Maintain Homeostatic Balance With Respect To Fluids, Electrolytes, and Organic SolutesNikki SalivioNo ratings yet
- Sec1 Clinical2 (ARF)Document44 pagesSec1 Clinical2 (ARF)ahmedmohamed01153159469No ratings yet
- Terapi CairanDocument30 pagesTerapi CairanNunik Dewi KumalasariNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument43 pagesElectrolyte ImbalanceJoshua JoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine EmergenciesDocument22 pagesEndocrine EmergenciesBen Man JunNo ratings yet
- Medical Nutrition Therapy For Renal Disease 2016Document39 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy For Renal Disease 2016Steven FongNo ratings yet
- Potassium Disorders by AiyraDocument25 pagesPotassium Disorders by AiyraAnndrea IlhamNo ratings yet
- Medical Nutrition Therapy For Renal Disease 2021Document39 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy For Renal Disease 2021Oktaviani Karo SekaliNo ratings yet
- Review: Diagnostic and Treatment of Electrolyte DisturbancesDocument31 pagesReview: Diagnostic and Treatment of Electrolyte DisturbancesalvyandaniNo ratings yet
- Metabolic AlkalosisDocument4 pagesMetabolic AlkalosisCay Sevilla100% (1)
- Nursing 75 Fluid and Electrolyte Exam 2Document6 pagesNursing 75 Fluid and Electrolyte Exam 2chubbygunny_29776413No ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : Myocardial InfarctionDocument5 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : Myocardial InfarctionManju PillaiNo ratings yet
- Potassium ChlorideDocument2 pagesPotassium ChlorideSetiram Zenitram50% (2)
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : BackgroundDocument7 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : BackgroundLeoNo ratings yet
- Pass Critical Care Endocrine Frcem ResourcesDocument41 pagesPass Critical Care Endocrine Frcem ResourcesYoussef SaadNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Disturbance-1Document22 pagesElectrolyte Disturbance-1Doaa Abd El-WahabNo ratings yet
- Management of Potassium Disorders 17706 ArticleDocument4 pagesManagement of Potassium Disorders 17706 ArticlealeNo ratings yet
- Aki and CKD Therapy 2021Document46 pagesAki and CKD Therapy 2021Alfathri YunediNo ratings yet
- S.gaus-Management of Life-Threatening (Kuliah Sistem) 2Document46 pagesS.gaus-Management of Life-Threatening (Kuliah Sistem) 2Ta RaNo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectroltyesDocument45 pagesFluids and ElectroltyesNurhafizah sahidanNo ratings yet
- Materi 7 - Gagal Ginjal AkutDocument30 pagesMateri 7 - Gagal Ginjal AkutTegar Muhamad RifkiNo ratings yet
- CA Vit D MetabolismDocument41 pagesCA Vit D MetabolismPramod N KNo ratings yet
- Medical Nutrition Therapy For Renal Disease 2016Document39 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy For Renal Disease 2016Steven FongNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid TonicityDocument4 pagesIV Fluid TonicityDarylSteffiNo ratings yet
- RenalElectrolytecharts 220906 101323 2Document7 pagesRenalElectrolytecharts 220906 101323 2Saheed jaladeNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Management Of: Kurdistan Higher Council For Medical SpecialtiesDocument6 pagesGuidelines For The Management Of: Kurdistan Higher Council For Medical SpecialtiesCik JaaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Sumolly Anak DavidDocument29 pagesDiuretics: Sumolly Anak Davidfarmasi_hmNo ratings yet
- Gangguan Ginjal AkutDocument29 pagesGangguan Ginjal Akutb3djo_76No ratings yet
- Angela Heithaus, MD, PS Internal Medicine Seattle Healing Arts CenterDocument32 pagesAngela Heithaus, MD, PS Internal Medicine Seattle Healing Arts CenterMarwan M.No ratings yet
- DR Sravan Thondam - HyponatraemiaDocument38 pagesDR Sravan Thondam - HyponatraemiaAndy esNo ratings yet
- Cardiac MedsDocument7 pagesCardiac MedsMary Fair DelcidNo ratings yet
- ACE Inhibitors PrintDocument5 pagesACE Inhibitors PrintBernard TangNo ratings yet
- 0 - Management of Life-Threatening Electrolyte and Metabolic Disturbances 3Document32 pages0 - Management of Life-Threatening Electrolyte and Metabolic Disturbances 3Roqoyyah MursyidNo ratings yet
- Renal Guide and Charts: AlbuminDocument16 pagesRenal Guide and Charts: AlbuminYaima JimenezNo ratings yet
- 2 Fluid and Electrolyte AbnormalityDocument16 pages2 Fluid and Electrolyte AbnormalityGoez Aditya NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Therapy - 2021Document10 pagesFluid Therapy - 2021Madiha MadiNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument2 pagesDrugsKC IgnacioNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument2 pagesDRUG StudyKC IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Management of GoutDocument6 pagesManagement of GoutSeanHong TanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Therapy and ElectroliteDocument36 pagesFluid Therapy and ElectroliteAriefBudimanHidayatNo ratings yet
- Off Tag Assessment (Surgery)Document19 pagesOff Tag Assessment (Surgery)Ahmad LiewNo ratings yet
- HyperkalaemiaDocument6 pagesHyperkalaemiaSSNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Calcium (Autosaved)Document22 pagesDisorders of Calcium (Autosaved)ksNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument4 pagesChronic Kidney DiseasejosephNo ratings yet
- Phys Block 2Document63 pagesPhys Block 2drunkenwukongNo ratings yet
- Management of HypokalemiaDocument6 pagesManagement of HypokalemiaEsraa Abu elelaNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia Algorithm: Onset Rapid ( 48 Hours) : 3% Onset Rapid ( 48 Hours) : May Consider 3% Nac LDocument2 pagesHyponatremia Algorithm: Onset Rapid ( 48 Hours) : 3% Onset Rapid ( 48 Hours) : May Consider 3% Nac Lmina000005100% (1)
- Nutritional Management of Renal Diseases Disease Goals Energy Protein Vitamins/Minerals Fats/FluidsDocument3 pagesNutritional Management of Renal Diseases Disease Goals Energy Protein Vitamins/Minerals Fats/Fluidscbac1990No ratings yet
- Surgery YbDocument67 pagesSurgery YbTamirat geletaNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument3 pagesAcute Renal Failurezainabd1964No ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 12Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 12JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument3 pagesSodium BicarbonateAubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Fluid TherapyDocument9 pagesFluid TherapyMadiha MadiNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- The Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionFrom EverandThe Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionNo ratings yet
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- 2020 The Essential Diets - All Diets in One Book - Ketogenic, Mediterranean, Mayo, Zone Diet, High Protein, Vegetarian, Vegan, Detox, Paleo, Alkaline Diet and Much More: COOKBOOK, #2From Everand2020 The Essential Diets - All Diets in One Book - Ketogenic, Mediterranean, Mayo, Zone Diet, High Protein, Vegetarian, Vegan, Detox, Paleo, Alkaline Diet and Much More: COOKBOOK, #2No ratings yet
- Minilecture Pneumonia 1703Document54 pagesMinilecture Pneumonia 1703purwandinyNo ratings yet
- DHF - CDCDocument105 pagesDHF - CDCpurwandinyNo ratings yet
- DHF - CDC Utk DiprintDocument72 pagesDHF - CDC Utk DiprintpurwandinyNo ratings yet
- SL paraDocument36 pagesSL parapurwandinyNo ratings yet
- Keadaan Kepala-Leher (Revisi)Document54 pagesKeadaan Kepala-Leher (Revisi)purwandinyNo ratings yet
- Komplikasi DMDocument53 pagesKomplikasi DMpurwandinyNo ratings yet
- ARF Table269 2Document3 pagesARF Table269 2purwandinyNo ratings yet
- ARF Table269 1Document2 pagesARF Table269 1purwandinyNo ratings yet
- Problems With DialysisDocument3 pagesProblems With Dialysispurwandiny100% (1)
- 142 Blood Leak AlarmDocument2 pages142 Blood Leak AlarmpurwandinyNo ratings yet
- Easy Vegan Pasta SaladDocument41 pagesEasy Vegan Pasta SaladDiana Madalina LuchianNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Substrate Oxidation Rates in Vivo From Gaseous ExchangeDocument7 pagesCalculation of Substrate Oxidation Rates in Vivo From Gaseous ExchangeRodrigo CastilloNo ratings yet
- NCP MakingDocument2 pagesNCP MakingMinakaNo ratings yet
- Einstein Bros. Bagels Nutrition and Allergen Information: Einstein Noah Restaurant Group, IncDocument6 pagesEinstein Bros. Bagels Nutrition and Allergen Information: Einstein Noah Restaurant Group, InctomtranNo ratings yet
- Media Monitoring SCM (27may20-3.30pm)Document2,605 pagesMedia Monitoring SCM (27may20-3.30pm)Chandra YugoNo ratings yet
- Snack Attack, You Are What You EatDocument1 pageSnack Attack, You Are What You EatRooney SamirNo ratings yet
- Type 2 Diabetes Thesis PDFDocument5 pagesType 2 Diabetes Thesis PDFCollegePapersToBuyUK100% (2)
- Grade 9 PE DLL Week 1Document7 pagesGrade 9 PE DLL Week 1Pagsibigan PO100% (1)
- Analysis of Sugars PDFDocument29 pagesAnalysis of Sugars PDFKhalidNo ratings yet
- Lim 2016Document80 pagesLim 2016Hora GoroNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Food Additives in Sri LankaDocument5 pagesRegulation of Food Additives in Sri LankaBiNtH AbDeeNNo ratings yet
- 8 Tips For Healthy Eating - NHSDocument4 pages8 Tips For Healthy Eating - NHSp100% (1)
- 3.2 Soal Isian SingkatDocument2 pages3.2 Soal Isian SingkatFikriNo ratings yet
- Mud Crab FeedsDocument34 pagesMud Crab FeedsCharles StephenNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions 1 PhotosynthesisDocument17 pagesPractice Questions 1 Photosynthesis사나No ratings yet
- Balanced DietDocument6 pagesBalanced DietsumiinlineNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Final NoteDocument17 pagesNutrition Final Notediemtruc414No ratings yet
- Birac Naarm0147 Big-17 20.Document18 pagesBirac Naarm0147 Big-17 20.Murali KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Abortion BSN 0PR-2: Case Study of BelleDocument27 pagesAbortion BSN 0PR-2: Case Study of BellekervinNo ratings yet
- Cereals and Legume TechnologyDocument23 pagesCereals and Legume TechnologyLê Tất TiếnNo ratings yet
- Obtlp Nutrition Diet Therapy NCM 105 2020-2021 1ST SemDocument11 pagesObtlp Nutrition Diet Therapy NCM 105 2020-2021 1ST Semmirai desuNo ratings yet
- Innovation in Precision Fermentation For Food IngredientsDocument22 pagesInnovation in Precision Fermentation For Food IngredientsBabuskin SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- UNIT 6 How Often Do You ExerciseDocument28 pagesUNIT 6 How Often Do You ExerciseCelis LópezNo ratings yet
- SAARES AguajunDocument23 pagesSAARES AguajunBETTY MIRELLA MURILLO CHOQUENo ratings yet
- MSM Medium Updated 2019Document1 pageMSM Medium Updated 2019ഗീതു സുരേഷ്No ratings yet
- Test Asesmen Literasi Numerasi Tingkat SMPDocument14 pagesTest Asesmen Literasi Numerasi Tingkat SMParaoky100% (3)
- Vol 1 of MCQs E MagazineDocument349 pagesVol 1 of MCQs E MagazineJąhąnząib Khąn Kąkąr100% (1)
- Cacfp Menu AssessmentDocument2 pagesCacfp Menu Assessmentapi-604622509No ratings yet
- Biology Studies On Screening of Suitable Diet For Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera Frugiperda (J. E. Smith)Document4 pagesBiology Studies On Screening of Suitable Diet For Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera Frugiperda (J. E. Smith)VISHAL TIDKENo ratings yet