Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science - Reviewer
Science - Reviewer
Uploaded by
Tora Raa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesBirds reproduce sexually through mating. Fertilization occurs inside the female bird's cloaca, where the egg and sperm meet. The fertilized egg develops inside the cloaca and is later laid. Many animals undergo metamorphosis as they develop, passing through different growth stages like egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Common examples provided are the life cycles of butterflies, mosquitoes, frogs, insects, and dragonflies, which all have different metamorphosis processes. Climate change, deforestation, and pollution are some of the main threats causing animal extinction.
Original Description:
Science for grade 5 mini reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBirds reproduce sexually through mating. Fertilization occurs inside the female bird's cloaca, where the egg and sperm meet. The fertilized egg develops inside the cloaca and is later laid. Many animals undergo metamorphosis as they develop, passing through different growth stages like egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Common examples provided are the life cycles of butterflies, mosquitoes, frogs, insects, and dragonflies, which all have different metamorphosis processes. Climate change, deforestation, and pollution are some of the main threats causing animal extinction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesScience - Reviewer
Science - Reviewer
Uploaded by
Tora RaaBirds reproduce sexually through mating. Fertilization occurs inside the female bird's cloaca, where the egg and sperm meet. The fertilized egg develops inside the cloaca and is later laid. Many animals undergo metamorphosis as they develop, passing through different growth stages like egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Common examples provided are the life cycles of butterflies, mosquitoes, frogs, insects, and dragonflies, which all have different metamorphosis processes. Climate change, deforestation, and pollution are some of the main threats causing animal extinction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
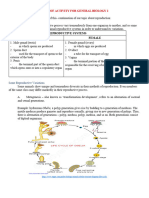
2ND QUARTERLY EXAMS Reproduction in Birds
REVIEWER IN “SCIENCE” Birds produce sexually through mating, like
mammals.
Cloaca
-REPRODUCTION IN ANIMALS-
The hollow chamber inside the male and
female bird where the egg cell and sperm cells
Sexual Reproduction meet, and the fertilized ovum becomes the nucleus
of the egg.
The process wherein a male and a female
animal of the same kind mate to reproduce Part of the bird where the egg develops.
offspring.
Incubation
Fertilization
Process by which the egg of the animal is
The sperm cell of the male and the egg cell kept warm and develops into a baby animal.
of the female unite to produce a fertilized ovum or
Hatchling
a zygote.
A newly hatched bird
External Fertilization
Fertilization that occurs outside the body of
the female animal. -METAMORPHOSIS-
Example: fishes and frogs which
release their egg and sperm cell in the water.
Metamorphosis
The process in which the animal passes
Reproduction in Fishes through different changes in growth.
Fishes undergo both external and internal Kinds of Metamorphosis:
fertilization.
1. Complete metamorphosis
INTERNAL FERTILIZATION: 2. Incomplete metamorphosis
The female fish have an organ that Complete Metamorphosis
allows the transfer of the sperm cell to the female
Has four stages of development: 1) egg 2)
body.
larva 3) pupa and 4) adult
Egg hatches inside the female’s
Example: butterfly, bees, beetles
body.
Incomplete Metamorphosis
EXTERNAL FERTILIZATION
Chas three stages: 1) egg 2) nymph 3) adult
Bony fishes reproduce through
insect
external fertilization.
Example: cockroach, dragonfly, grasshopper
Hermaphrodites
An animal which has both male and female
reproductive organs. Reproduction And Life Cycle of Frogs
Spawning Season (Mating Season) Frogs
The time during which the sperm cell from Belong to the group of amphibians
the male and the egg cell from the female are
Undergo metamorphosis wherein much
released in the water
physical challenges occur as part of growth and
Mouthbreeders development.
the fish’ special way of protecting their egg 3 Organs of Male Frog Reproduction System
by placing their egg in their mouths until the eggs
1) Testes – where sperm is produced
are hatched.
2) Urinary duct – carry urine STAGE 4: ADULT BUTTERFLY (IMAGO)
3) Cloaca – where sperm and urine exit the
- Chrysalis opens and a butterfly comes
body.
out
2 Organs of Female Frog Reproduction System - Butterfly dries its wings and allow blood
to pump into it before flying
1) Oviduct – a tube through which the ova
pass from the ovary to the uterus or to the NOTE:
outside of the body.
Pheromone - a chemical substance released by the
2) Ovaries – where eggs are produced and
male butterfly to signal courtship.
stored.
NOTE:
Reproduction And Life Cycle of Mosquitoes
Frogs produce sexually through fertilization
outside of the female’s body. METAMORPHOSIS CYCLE OF A MOSQUITO
Female releases eggs into the water, and at
Eggs > Larva > pupa > adult > egg
the same time, male releases sperm into
the water. STAGE 1: EGG
When a frog grows, it becomes a TADPOLE
- Female mosquito can lay 100-300 eggs.
After a month, the tadpole grow legs. As the
- Hatches within 1 to 2 days.
front leg grow, the internal organ changes.
- Eggs are released to the water.
A FROGLET is a tadpole which its tail had
Individual eggs will float.
already disappeared as part of
metamorphosis. It becomes an adult frog. STAGE 2: LARVA
METAMORPHOSIS CYCLE OF A FROG: - Develops within 7 days depending on
the food and temperature
Egg > tadpole > tadpole with back legs > tadpole
- A larva is also known as a WRIGGLER
with front and back legs > froglet with small tail >
- It molts at least 4 times before It
adult frog > egg.
changes into a pupa
STAGE 3: PUPA
Reproduction And Life Cycle of Insects
- Also known as a TUMBLER
METAMORPHOSIS CYCLE OF AN INSECT (ANT): - It can breathe air, but it cannot bite.
- Stays in this stage for 2 days after which
Eggs > larvae > pupae > Queen; or
the skin opens up its back where the
Male; or head and the legs emerge followed by
Worker (female) its body
STAGE 4: ADULT
Reproduction And Metamorphosis of Butterflies - It looks for nectar to feed itself.
- Female mosquito will look for a meal
STAGE 1: EGG blood. After such, it will look for a place
- Butterfly lays eggs on a leaf. After 5 where to digest, rest and lay its eggs.
days, a tiny worm hatches from it.
STAGE 2: CATERPILLAR (LARVA) Reproduction And Life Cycle of Dragonflies
- The easting and growing stage. METAMORPHOSIS CYCLE OF A DRAGON FLY
- Caterpillar sheds its skin 4 to 5 times in a
process called MOLTING Egg > nymphs (larvae) > adult > egg
STAGE 3: CHRYSALIS (PUPA)
- It is brown/green in color.
- Caterpillar is done growing
Dragonfly
- The resting and changing stage into a
butterfly.
has a long slender abdomen, pair of wings 1) CLIMATE CHANGE
and three pair of legs. It has big eyes and - The warming of the planet due
undergoes incomplete metamorphosis. to excessive carbon footprints
creating greenhouse effect.
Male dragonfly attaches the back of his
abdomen into the head of the female. They will fly
2) FORREST DEGRATION
together and find a place o mate
- the conversion of forest lands
into commercial and industrial
development
-ENDANGERED ANIMALS-
3) POLLUTION
Extinction - Contamination of the
environment with chemicals, and
All members of a particular group of living
other emissions made by human
things die.
activity
Endangered Species 4) SOIL DEGRATION
a) SOIL COMPACTION
Categorized to become likely extinct
- Compressed pores that would
Threatened Species otherwise transport water and
air.
Species that most likely will become
- Hinders root growth and causes
endangered in the future.
oxygen deficiency
Found in the environment but are b) SOIL EROSION
decreasing in number. - Wearing away of topsoil.
TIPS FOR HABITAT PROTECTION:
Destruction of Habitat
1) Join campaign for the protection of
Humans destroy the natural environment of animals and their habitats
a living thing. 2) Recycle and reduce energy and good
consumption
Pollution
3) Minimize the use of herbicides and
Contamination of habitats and devastating pesticides
the species. 4) Take care of injured wildlife.
Overhunting
Humans hunting animals for raw materials
and consumption more than what is needed
leaving animals lesser in number.
Exotic Species
An animal arrives into a new habitat from a
foreign place, it brings with it diseases that the
native species cannot fight.
-PROTECTING THE HABITATS OF ANIMALS-
HABITAT
Place where animal lives and gets its
nourishment for survival.
Threats to the Habitats:
You might also like
- Sample Contract of Employment For SpaDocument2 pagesSample Contract of Employment For SpaTora Raa100% (5)
- EAP Grammar in Context: Reading & WritingDocument27 pagesEAP Grammar in Context: Reading & WritingMónica Coirolo50% (2)
- REVIEWER IN SCIENCE 3rd GDocument3 pagesREVIEWER IN SCIENCE 3rd GGab OlarteNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 02 Q4Document7 pagesGen Bio 02 Q4Charles EspiloyNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 04 - Chapter 09Document7 pagesExp SC 04 - Chapter 09megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Q2 W3 SCI 5-Methods of Reproduction (ANIMALs)Document32 pagesQ2 W3 SCI 5-Methods of Reproduction (ANIMALs)Buena Rosario100% (1)
- Reproduction Lesson BioDocument3 pagesReproduction Lesson Biousha leninNo ratings yet
- Hermaphroditism, The Condition of Having Both MaleDocument11 pagesHermaphroditism, The Condition of Having Both Maleaimee mallariNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Students NotesDocument6 pagesLesson 3 ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Students NotesrasingtanyaroseNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Sciences SLHTQ2 3Document9 pagesEarth and Life Sciences SLHTQ2 3Melissa GerzonNo ratings yet
- Animal Reproduction - Sexual ReproductionDocument28 pagesAnimal Reproduction - Sexual ReproductionRachel Jasmine AblanNo ratings yet
- Science 5: Learning Activity Sheet Modes of Reproduction in AnimalsDocument4 pagesScience 5: Learning Activity Sheet Modes of Reproduction in AnimalsLena Beth Tapawan Yap100% (1)
- Animal ReproductionDocument27 pagesAnimal ReproductionMargie B. AlmozaNo ratings yet
- G1-G2 Notes in Dev. BioDocument10 pagesG1-G2 Notes in Dev. BioROMERO, Hannah Grace T.No ratings yet
- Earth and Life Sciences SLHTQ2 3Document7 pagesEarth and Life Sciences SLHTQ2 3Joy Valerie AricayosNo ratings yet
- Science 5 3rd ReviewerDocument2 pagesScience 5 3rd ReviewerEunice VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Module in Science 5 3rd Quarter Week 3Document5 pagesModule in Science 5 3rd Quarter Week 3Ronalyn RuizNo ratings yet
- Fa 3 e 1Document3 pagesFa 3 e 1Pahal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Science: Reproduction in AnimalsDocument21 pagesClass 8 Science: Reproduction in AnimalsJ CNo ratings yet
- Notes Science Modes in ReproductionDocument1 pageNotes Science Modes in Reproductionmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- This Is For GENERAL BIOLOGY 2Document11 pagesThis Is For GENERAL BIOLOGY 2jayyyyyrg16No ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 3: Modes of Reproduction in AnimalsDocument68 pagesScience: Quarter 2 - Module 3: Modes of Reproduction in AnimalsChester Allan EduriaNo ratings yet
- Level of Organization Sample ActivityDocument1 pageLevel of Organization Sample ActivityKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- Science Quarter 2 Module 5Document13 pagesScience Quarter 2 Module 5Zerreitug Elppa100% (2)
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument79 pagesReproduction in Animalsmdudi558No ratings yet
- Els q2 Las Week 3 1Document11 pagesEls q2 Las Week 3 1SeanNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Animals - Class Notes - Pariksha AbhyasDocument78 pagesReproduction in Animals - Class Notes - Pariksha Abhyastechnoharshil201No ratings yet
- 8GS L-9 Reproduction in AnimalsDocument5 pages8GS L-9 Reproduction in AnimalsSis and Bro Adventure & CookeryNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FertilizationDocument4 pagesIntroduction To FertilizationSupermarc OlaguirNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Animal Class 8 NewDocument3 pagesReproduction in Animal Class 8 NewkapsarcNo ratings yet
- Physio HandoutsDocument3 pagesPhysio Handouts丂卂Kㄥ卂爪TEAMNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 NotesDocument17 pagesGeneral Biology 2 NotesAlyssa Mae BinoNo ratings yet
- Honey Bee DevelopmentDocument5 pagesHoney Bee DevelopmentZena KidaneNo ratings yet
- Class 4 - Science Chapter - 4 REPRODUCTION IN ANIMALSDocument10 pagesClass 4 - Science Chapter - 4 REPRODUCTION IN ANIMALSAmisha SenapatiNo ratings yet
- Modes of ReproductionDocument4 pagesModes of ReproductionSayie GulmaticoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument69 pagesReproduction in AnimalsAliya CastroNo ratings yet
- Animal ReproductionDocument31 pagesAnimal ReproductionAmelda Mira BontilaoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER2 5th Grade Science ReviewerDocument3 pagesCHAPTER2 5th Grade Science ReviewerLisette LaoNo ratings yet
- Animal ReproductionDocument46 pagesAnimal Reproductionrufino delacruzNo ratings yet
- Animal Reproduction Not SummarizeDocument4 pagesAnimal Reproduction Not SummarizeKim KardashianNo ratings yet
- CAHPTER 6 NOTES Class 8Document8 pagesCAHPTER 6 NOTES Class 8dasakshyat098No ratings yet
- U4l4 150930151647 Lva1 App6892Document25 pagesU4l4 150930151647 Lva1 App6892DianaRoseAcupeadoNo ratings yet
- 2019 20 Life Cycle of AnimalsDocument25 pages2019 20 Life Cycle of Animalsfareehailhan512No ratings yet
- Pra-Embryonic and Post-Embryonic Development in InsectDocument35 pagesPra-Embryonic and Post-Embryonic Development in Insectdebora herawaty hasibuan100% (1)
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument3 pagesReproduction in Animalsevelynlinda370No ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2Document9 pagesGen Bio 2rigeljoemariealcayraNo ratings yet
- ASC199Document2 pagesASC199Anggita SuryandariNo ratings yet
- Reproduction of AnimalsDocument11 pagesReproduction of AnimalsNOVA LESLIE AGAPAYNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Concise Biology Notes For KVPY, NSEBDocument121 pagesClass 11 Concise Biology Notes For KVPY, NSEBNischal Vir MNo ratings yet
- How Representative Animals ReproduceDocument29 pagesHow Representative Animals ReproduceIMY PAMEROYANNo ratings yet
- MetamorphosisDocument110 pagesMetamorphosisShivaniNo ratings yet
- Term 2 - Grade 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction in AnimalsDocument4 pagesTerm 2 - Grade 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animalsprakashjoshi23aprilNo ratings yet
- Q3 Science ReviewerDocument4 pagesQ3 Science Reviewerprinceraniel.mejiajrNo ratings yet
- WK 9 - 10Document65 pagesWK 9 - 10ALPHEAUS-MBA AwajibenejiNo ratings yet
- Science 5 Lesson 10 Modes of ReproductionDocument34 pagesScience 5 Lesson 10 Modes of ReproductionAlmario DacalcapNo ratings yet
- G-11 PPT P-2Document126 pagesG-11 PPT P-2etsubtarekegn87No ratings yet
- Chapter 10. Edited ReproductionJ Growth and DevelopmentDocument10 pagesChapter 10. Edited ReproductionJ Growth and Development5pn4x4czxnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 9 NotesChahat SanataniNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Animals - TB QuestionsDocument7 pagesReproduction in Animals - TB Questionshafsatabarak.rNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in AnimalsDocument2 pagesSexual Reproduction in Animalsmallorca albertNo ratings yet
- Animal Morphology and Physiology CompressedDocument54 pagesAnimal Morphology and Physiology CompressedJana Elaine HermosoNo ratings yet
- Camp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- CD Bautista Vs SB (No Inordinate Delay)Document1 pageCD Bautista Vs SB (No Inordinate Delay)Tora RaaNo ratings yet
- CD Catamco Vs SB (Inordinate Delay)Document2 pagesCD Catamco Vs SB (Inordinate Delay)Tora RaaNo ratings yet
- CD PP Vs Sergio (Written Interrogatories in Crim Case)Document2 pagesCD PP Vs Sergio (Written Interrogatories in Crim Case)Tora RaaNo ratings yet
- CD Alarilla Vs SB (Delay in PI by OMB)Document2 pagesCD Alarilla Vs SB (Delay in PI by OMB)Tora RaaNo ratings yet
- CD Alarilla Vs Lorenzo (Speedy Disposition)Document2 pagesCD Alarilla Vs Lorenzo (Speedy Disposition)Tora RaaNo ratings yet
- CD PP Vs Ang (Request For Admission in CrimPro)Document1 pageCD PP Vs Ang (Request For Admission in CrimPro)Tora RaaNo ratings yet
- TESDA - Communication (K Caacbay Nootes)Document14 pagesTESDA - Communication (K Caacbay Nootes)Tora RaaNo ratings yet
- Intro To GS TonyDocument5 pagesIntro To GS TonyTora RaaNo ratings yet
- RRL Addendum - SOGIE XkcaacbayDocument3 pagesRRL Addendum - SOGIE XkcaacbayTora RaaNo ratings yet
- CNN - Cover Letter ApplicationDocument1 pageCNN - Cover Letter ApplicationTora RaaNo ratings yet
- ABS-CBN Application - Cover LetterDocument1 pageABS-CBN Application - Cover LetterTora RaaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Prop 011823Document30 pagesThesis Prop 011823Tora RaaNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Film and Student Viewers (ACE THESIS)Document11 pagesPart 1 Film and Student Viewers (ACE THESIS)Tora RaaNo ratings yet
- Intro To GS TonyDocument5 pagesIntro To GS TonyTora RaaNo ratings yet
- Promisory Note To DsaDocument1 pagePromisory Note To DsaTora RaaNo ratings yet
- Cert of Employment RequestDocument1 pageCert of Employment RequestTora RaaNo ratings yet
- Week Two Module 2 DiscussionDocument3 pagesWeek Two Module 2 Discussionadhiambo lucyNo ratings yet
- Energiaelosztok - Energy Distributors MixvillDocument65 pagesEnergiaelosztok - Energy Distributors MixvillJózsef VidaNo ratings yet
- HC700 SDK SpecificationDocument680 pagesHC700 SDK SpecificationTzahiKupfer0% (1)
- Mete AggiesDocument16 pagesMete AggiesJohn Renzel RiveraNo ratings yet
- 2F4Y: Molecular Structure and Energy Levels Formula Sheet Topic 1: Quantum MechanicsDocument2 pages2F4Y: Molecular Structure and Energy Levels Formula Sheet Topic 1: Quantum Mechanicsapi-250366166No ratings yet
- ISO 50001training For Shop 2013 UpdatedDocument46 pagesISO 50001training For Shop 2013 Updatedjawad chraibiNo ratings yet
- Haskell Ebook ReaderDocument1,610 pagesHaskell Ebook ReaderhoogggleeeNo ratings yet
- Assignment4 Solutions Chap6Document7 pagesAssignment4 Solutions Chap6Mohit soniNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Flux Vector PDFDocument15 pagesDesign and Implementation of Flux Vector PDFBelal AshrafNo ratings yet
- Ancient Tomb Lamps Still Found BurningDocument4 pagesAncient Tomb Lamps Still Found Burningolim owletNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis Chemistry Lab PDFDocument9 pagesSalt Analysis Chemistry Lab PDFkushal aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Nama: Dimas Hendrico NIM: 21/475218/PA/20551 Tugas 5 1. Program Rata-Rata Data Dalam ArrayDocument8 pagesNama: Dimas Hendrico NIM: 21/475218/PA/20551 Tugas 5 1. Program Rata-Rata Data Dalam ArrayDimasNo ratings yet
- Kale Mahesh Anant.: Qualification: B.E. Mechanical With Knowledge of CAD-CAEDocument4 pagesKale Mahesh Anant.: Qualification: B.E. Mechanical With Knowledge of CAD-CAEapi-3698788No ratings yet
- 34 Concrete ShearDocument4 pages34 Concrete ShearMario Sajulga Dela CuadraNo ratings yet
- Final Report PlacementDocument14 pagesFinal Report PlacementAndrei-Bogdan PuiuNo ratings yet
- 17mat41 PDFDocument3 pages17mat41 PDFKruthik KoushikNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1998 Biology QuestionsDocument8 pagesKcse 1998 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- According To The ANSI/IEEE 946: Figure 1. 125 VDC System Key DiagramDocument8 pagesAccording To The ANSI/IEEE 946: Figure 1. 125 VDC System Key DiagramDavid MorenoNo ratings yet
- Embedment Strength of Stud PlateDocument3 pagesEmbedment Strength of Stud Platemathu100% (1)
- More Than 5000 Questions Dr. BL Sharma Mathematics PageDocument4 pagesMore Than 5000 Questions Dr. BL Sharma Mathematics Pagerskr_tNo ratings yet
- Handout Physics 101 ForceDocument12 pagesHandout Physics 101 ForceMary Grace AcostaNo ratings yet
- It 3022 (CC) - CS - End - May - 2023Document7 pagesIt 3022 (CC) - CS - End - May - 2023Rachit SrivastavNo ratings yet
- NOTES - GUIDANCE AND COUNSELLING Manual 2021Document30 pagesNOTES - GUIDANCE AND COUNSELLING Manual 2021Mercy GakiiNo ratings yet
- Homelite XL 12Document21 pagesHomelite XL 12Alberto LazzarinNo ratings yet
- Svensk Standard SS-EN ISO 6157-2:2004Document8 pagesSvensk Standard SS-EN ISO 6157-2:2004Hari PrasadNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Scheme 2020term 1Document158 pagesGrade 6 Scheme 2020term 1jordan thunderNo ratings yet
- Peace Corps Administrative Assistant Receptionist - Vacancy AnnouncementDocument1 pagePeace Corps Administrative Assistant Receptionist - Vacancy AnnouncementAccessible Journal Media: Peace Corps DocumentsNo ratings yet
- sgpnr001 enDocument70 pagessgpnr001 enAli AlmukhtarNo ratings yet
- AS4041 ASME B31 - 3 Pipe Wall ThicknessDocument8 pagesAS4041 ASME B31 - 3 Pipe Wall Thicknesscutefrenzy100% (1)