Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Your
Your
Uploaded by
Yashdeep Singh.kCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Management of Post Facial Paralysis Synkinesis 1St Edition Babak Azizzadeh MD Facs Full ChapterDocument67 pagesManagement of Post Facial Paralysis Synkinesis 1St Edition Babak Azizzadeh MD Facs Full Chaptercatherine.green419100% (6)
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Uric AcidDocument5 pagesLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Uric AcidBalraj EnjamuriNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Bad Ragaz Ring Method Gamper Lambeck Chapter 4 Comp Aq TH (2010)Document29 pagesBad Ragaz Ring Method Gamper Lambeck Chapter 4 Comp Aq TH (2010)Talia Gil Villafuerte100% (2)
- 1 Diabetes Screening PO4047576719 696Document4 pages1 Diabetes Screening PO4047576719 696rishiranjan04No ratings yet
- Report f642c 1704009629273Document16 pagesReport f642c 1704009629273Er Sumit SiwatchNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: 19 Years / FemaleDocument3 pagesLaboratory Test Report: 19 Years / Femalesneha sahaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference IntervalDocument15 pagesBiochemistry: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference IntervalAshutoshNo ratings yet
- EGAC0401Document5 pagesEGAC0401bhanuprasadbkNo ratings yet
- Apollo247 249052700 LabreportDocument7 pagesApollo247 249052700 LabreportASHWAQ JAANNo ratings yet
- SnehaDocument3 pagesSneharazeena salamNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Report: FinalDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Report: Finalpraveen04715717No ratings yet
- LabReportNew - 2024-03-18T184949.154Document1 pageLabReportNew - 2024-03-18T184949.154desarajit72No ratings yet
- Mrs Nandhinidevi.M 04007180: Sid No. Patient ID 0400005449Document2 pagesMrs Nandhinidevi.M 04007180: Sid No. Patient ID 040000544911F10 RUCHITA MAARANNo ratings yet
- Clinical Biochemistry: Test Report Reg - No Age Name::: Reg - Date Collection:: Received: 15-Jul-2019 / 09:25 AMDocument8 pagesClinical Biochemistry: Test Report Reg - No Age Name::: Reg - Date Collection:: Received: 15-Jul-2019 / 09:25 AMAnuradha KommojuNo ratings yet
- Client0249 22024271868Document1 pageClient0249 22024271868dharusen082001No ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Fasting Plasma Glucose: 120Document1 pageLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Fasting Plasma Glucose: 120sanath kumarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Biochemistry: Sumit Omkant Nile ,, MRDocument2 pagesClinical Biochemistry: Sumit Omkant Nile ,, MRShivRaj Omkant NileNo ratings yet
- Client0249 22024271867Document1 pageClient0249 22024271867dharusen082001No ratings yet
- 1-Diabetes Package Advanced - PO2935562681-323Document11 pages1-Diabetes Package Advanced - PO2935562681-323Dr. Saurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Subba Lakshmi Kotturu 249951126 CompleteReportDocument1 pageSubba Lakshmi Kotturu 249951126 CompleteReportsaikrupa27No ratings yet
- Efbu2630Document4 pagesEfbu2630Aniruddh NagaNo ratings yet
- Report ViewerDocument1 pageReport ViewerArslan Baig100% (1)
- Department of Biochemistry Campaign Diabetic Check (With PP)Document2 pagesDepartment of Biochemistry Campaign Diabetic Check (With PP)gsm2008No ratings yet
- Department of Biochemistry Campaign Diabetic Panel: Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range MethodDocument4 pagesDepartment of Biochemistry Campaign Diabetic Panel: Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range Methodgsm2008No ratings yet
- Department of Biochemistry Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. RangeDocument5 pagesDepartment of Biochemistry Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. RangeSudhanshuNo ratings yet
- Nnyy3999 PDFDocument2 pagesNnyy3999 PDFAshwin SagarNo ratings yet
- 1-Diabetes Screening - PO3210290160-291Document4 pages1-Diabetes Screening - PO3210290160-291Jawed IqubalNo ratings yet
- Interpretation: S03 - FPSC DILSHAD COLONY (C004263143) J-50 Dilshad Colony, DelhiDocument6 pagesInterpretation: S03 - FPSC DILSHAD COLONY (C004263143) J-50 Dilshad Colony, DelhiAll VIDEOS TechNo ratings yet
- Department of Laboratory Services: Patient Name Uhidno/Ipno Lab No/Manualno Collectiondate Receiving DateDocument1 pageDepartment of Laboratory Services: Patient Name Uhidno/Ipno Lab No/Manualno Collectiondate Receiving DateSachin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Report GNDocument3 pagesReport GNPawan MadhesiyaNo ratings yet
- Iranbadsha Khan SugarDocument1 pageIranbadsha Khan Sugarmdasmaulseikh8No ratings yet
- Report-21YP86307 LOKANATH 03jun2021 122926Document1 pageReport-21YP86307 LOKANATH 03jun2021 122926AnkushNo ratings yet
- Report (4) - 231026 - 181327Document5 pagesReport (4) - 231026 - 181327Sandeep KrishnaNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument3 pagesReportPawan MadhesiyaNo ratings yet
- Department of Clinical Biochemistry: Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) 169 MG/DLDocument1 pageDepartment of Clinical Biochemistry: Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) 169 MG/DLakhilNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument4 pagesReportVibrant PixelsNo ratings yet
- Report 190a3 1695110951228Document13 pagesReport 190a3 1695110951228Mohd Jaffer ShareefNo ratings yet
- Name: Mrs. SABA 681 Patient UID.: 816567: Biochemistry Test Name Results Unit Bio. Ref. IntervalDocument2 pagesName: Mrs. SABA 681 Patient UID.: 816567: Biochemistry Test Name Results Unit Bio. Ref. Intervalshaykh basharatNo ratings yet
- Petersen Et Al 2020 High Dose Glucagon Has Hemodynamic Effects Regardless of Cardiac Beta Adrenoceptor Blockade ADocument27 pagesPetersen Et Al 2020 High Dose Glucagon Has Hemodynamic Effects Regardless of Cardiac Beta Adrenoceptor Blockade AputraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Fasting Plasma Glucose: 136Document1 pageLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Fasting Plasma Glucose: 136sanath kumarNo ratings yet
- 1-Diabetes Package - PO2693771771-269Document6 pages1-Diabetes Package - PO2693771771-269KishoreNo ratings yet
- LFT (Liver Function Test) : Biological Reference Results Units Test NameDocument4 pagesLFT (Liver Function Test) : Biological Reference Results Units Test Namemetepraju0210No ratings yet
- Clinical PathologyDocument1 pageClinical PathologyhmddNo ratings yet
- Report bc90b 1710052260449Document11 pagesReport bc90b 1710052260449muralinaiduNo ratings yet
- Report Eaaf4 1695467677147Document16 pagesReport Eaaf4 1695467677147Mohd Jaffer ShareefNo ratings yet
- Wa0037.Document2 pagesWa0037.lakshNo ratings yet
- TB Gurung72436565-2296573Document8 pagesTB Gurung72436565-2296573KeHar RajPutNo ratings yet
- Po3979242722 431Document8 pagesPo3979242722 431NEETFIXNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument28 pagesCombinepdfNEETFIXNo ratings yet
- Test Report: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Ref. Interval SpecimenDocument2 pagesTest Report: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Ref. Interval SpecimensumaNo ratings yet
- LabReportNew - 2023-09-08T160827.328Document3 pagesLabReportNew - 2023-09-08T160827.328viraj kshirsagarNo ratings yet
- Daksha ChavdaDocument3 pagesDaksha ChavdaKetan ChavdaNo ratings yet
- CMP95Document3 pagesCMP95mohnish aryanNo ratings yet
- PdfText (12) - 2022-07-15T231607.346Document2 pagesPdfText (12) - 2022-07-15T231607.346Mr. BLACKNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument2 pagesReportshifa nasrinNo ratings yet
- 1 Tuga HipoDocument7 pages1 Tuga HipoekaNo ratings yet
- Smart Full Body Checkup: Test Description Value(s) Unit(s) Reference RangeDocument13 pagesSmart Full Body Checkup: Test Description Value(s) Unit(s) Reference RangeShamsher SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Https Tdiagnostics - Telangana.gov - in ViewFiles - Aspx ReportId HK9UQ4C5ZEZ7ICEuNXmyPwDocument8 pagesHttps Tdiagnostics - Telangana.gov - in ViewFiles - Aspx ReportId HK9UQ4C5ZEZ7ICEuNXmyPwKuncham LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Department of Biochemistry-Routine: Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range MethodDocument10 pagesDepartment of Biochemistry-Routine: Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range MethodbfdfndfNo ratings yet
- Report 1690018110488Document2 pagesReport 1690018110488Krishna ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Nilesh Karani 13295 29-10-2023 20231029084151 StationerypdfmergedDocument22 pagesNilesh Karani 13295 29-10-2023 20231029084151 StationerypdfmergedsteelblackNo ratings yet
- Management of Palm Oil PestDocument11 pagesManagement of Palm Oil PestMohamad Syu'ib SyaukatNo ratings yet
- Sample Weekly Planner 2Document9 pagesSample Weekly Planner 2api-662941487No ratings yet
- Capitulo 2 Ista Reglas Internacionales SemillasDocument52 pagesCapitulo 2 Ista Reglas Internacionales SemillasmaritzaNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper Class-Xii Bio-Technology (045) SESSION 2019-20Document6 pagesSample Question Paper Class-Xii Bio-Technology (045) SESSION 2019-20Sudamini JhaNo ratings yet
- EcoCRM A Recombinant CRM197 Carrier ProteinDocument1 pageEcoCRM A Recombinant CRM197 Carrier ProteinRamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- H3C - Abstract Book 12302014-V2Document204 pagesH3C - Abstract Book 12302014-V2AAPI ConventionNo ratings yet
- Handwriting Saying - OralDocument1 pageHandwriting Saying - OralEsther FernandezNo ratings yet
- Speaking Test Avcn 1: Unit 1: Hospital StaffDocument5 pagesSpeaking Test Avcn 1: Unit 1: Hospital StaffHoàng Huy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Intro - EstroG-100 Pres FullDocument60 pagesIntro - EstroG-100 Pres FulllilingNo ratings yet
- 2007 Bakker y Demorouti State of The ArtDocument120 pages2007 Bakker y Demorouti State of The ArtScott SommerNo ratings yet
- Kidney Structure and FunctionDocument68 pagesKidney Structure and FunctionAsmara Syed100% (1)
- What Has Modern Ecosystem Theory To Offer To Cleaner Production, Industrial Ecology and Society The Views of An EcologistDocument15 pagesWhat Has Modern Ecosystem Theory To Offer To Cleaner Production, Industrial Ecology and Society The Views of An EcologistMilenoNo ratings yet
- The Semantics of Morphological RelationsDocument65 pagesThe Semantics of Morphological RelationsDương Bùi100% (1)
- Ebook Cultural Anthropology Canadian 2Nd Edition Robbins Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument34 pagesEbook Cultural Anthropology Canadian 2Nd Edition Robbins Test Bank Full Chapter PDFengagerscotsmangk9jt100% (9)
- Community and Environmental HealthDocument26 pagesCommunity and Environmental HealthMary Grace AgueteNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 GranulopoiesisDocument9 pagesLecture2 GranulopoiesisAfifa Prima GittaNo ratings yet
- Heterospory in PteridophytesDocument4 pagesHeterospory in PteridophytesTANMOY SARKARNo ratings yet
- Humastar300sr enDocument3 pagesHumastar300sr enNghi NguyenNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Synthetic Thought: Takshashila EssayDocument42 pagesThe Evolution of Synthetic Thought: Takshashila EssayLINDYLL PONO100% (1)
- Blank2021 Article MarkerAllergensInHymenopteraVeDocument13 pagesBlank2021 Article MarkerAllergensInHymenopteraVeAna-Maria DuMiNo ratings yet
- WDR-Weaver Dice RulebookDocument29 pagesWDR-Weaver Dice RulebookAzazelNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment Entrepreneurship Program of Diploma in Administrative Management Business Plan: ProposalDocument8 pagesGroup Assignment Entrepreneurship Program of Diploma in Administrative Management Business Plan: ProposalMuhammad ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Advances in Prostaglandin, Leukotriene, and Other Bioactive Lipid ResearchDocument243 pagesAdvances in Prostaglandin, Leukotriene, and Other Bioactive Lipid ResearchCarmen PopaNo ratings yet
- A Self-Assembled Nanoscale Robotic Arm Controlled by Electric FieldsDocument6 pagesA Self-Assembled Nanoscale Robotic Arm Controlled by Electric FieldsRegiane FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Mold and Mildew QA Understanding Mold in Your HousevnoznDocument3 pagesMold and Mildew QA Understanding Mold in Your Housevnoznliftvision70No ratings yet
- Ecozone Dichotomous KeyDocument3 pagesEcozone Dichotomous Keyqmtkqz72vhNo ratings yet
- IIB Sant Pau 2020 WebDocument336 pagesIIB Sant Pau 2020 WebAinhoa GaNo ratings yet
- Bioreaction Engineering PrinciplesDocument554 pagesBioreaction Engineering PrinciplesSaman100% (13)
Your
Your
Uploaded by
Yashdeep Singh.kOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Your
Your
Uploaded by
Yashdeep Singh.kCopyright:
Available Formats
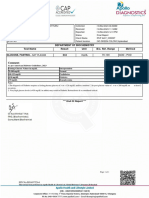
Pattient ID : 102217913 Registration Date : 18/12/2022 14:26:07
Patient Name : Ms. NAVLEEN KAUR Sample Collected On : 18/12/2022 14:27:31
Sex / Age : Female 14 Yrs Sample Received On : 18/12/2022 14:27:33
Client Name : Report Released on : 18/12/2022 16:54:43
Ref. By : DR NALINI JAIN Aadhar/ Passport No :
Test Name Result Unit Biological Ref Interval
BIOCHEMISTRY
PLASMA GLUCOSE (FASTING) 86 mg/dl 70 - 110
Hexokinase
Interpretation (In accordance with the American Diabetes Association guidelines):
. A fasting plasma glucose level below 100 mg/dl is considered normal.
. A fasting plasma glucose between 100-126 mg/dl is considered as glucose intolerant or pre diabetic. A fasting and postprandial blood sugar
test (after consumption of 75 gm of glucose) is recommended for all such patients.
. A fasting plasma glucose above 126 mg/dl is highly suggestive of a diabetic state. A repeat fasting test is strongly recommended for all such
patients. A fasting plasma glucose level in excess of 126 mg/dl on both the occasions is confirmatory of a diabetic state.
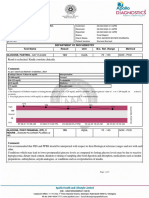
SEROLOGY
INSULIN FASTING 17.5 mIU/L 5.0 - 25.0
CLIA
INTERPRETATION-
Insulin is a peptide hormone with a molecular weight of approximately 6000 daltons. It is secreted by the B-cells of the pancreas and passes
into circulation via the portal vein and the liver. Insulin is generally released in pulses, with the parallel glucose cycle normally about 2 minutes
ahead of the insulin cycle.
The Insulin molecule consists of two polypeptide chains, the alpha-chain with 21 and the beta-chain with 30 amino acids. Biosynthesis of the
hormone takes place in the beta-cells of the islets of Langerhans in the form of single-chain preproinsulin, which is immediately cleaved to
give proinsulin. Specific proteases cleave proinsulin to insulin and C-peptide which pass into the bloodstream simultaneously. Circulating
insulin has a half-life of 3-5 minutes and is preferentially degraded in the liver, whereas inactivation or excertion of proinsulin and C-peptide
mainly takes place in the kidneys.Serum Insulin determinations are mainly performed on patients with symptoms of hypoglycemia.
A disorder in insulin metabolism leads to massive infuencing of a number of metabolic processes. A too low concentration of free, biologically
active insulin can lead to the development of diabetes mellitus. Possible causes of this include destruction of the beta-cells (type I diabetes),
reduced activity of the insulin, or reduced pancreatic synthesis (type II), circulating antibodies to insulin, delayed release of insulin or the
absence (or inadequacy) of insulin receptors.
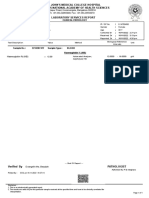
*** End of Report ***
Dr. Maneesh Goyal
Please correlate the results with clinical history of the patient. Not for medico-legal purpose. M.D. (Pathology)
Consultant Pathology
Page No: 1 of 1
You might also like
- Management of Post Facial Paralysis Synkinesis 1St Edition Babak Azizzadeh MD Facs Full ChapterDocument67 pagesManagement of Post Facial Paralysis Synkinesis 1St Edition Babak Azizzadeh MD Facs Full Chaptercatherine.green419100% (6)
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Uric AcidDocument5 pagesLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Uric AcidBalraj EnjamuriNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Bad Ragaz Ring Method Gamper Lambeck Chapter 4 Comp Aq TH (2010)Document29 pagesBad Ragaz Ring Method Gamper Lambeck Chapter 4 Comp Aq TH (2010)Talia Gil Villafuerte100% (2)
- 1 Diabetes Screening PO4047576719 696Document4 pages1 Diabetes Screening PO4047576719 696rishiranjan04No ratings yet
- Report f642c 1704009629273Document16 pagesReport f642c 1704009629273Er Sumit SiwatchNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: 19 Years / FemaleDocument3 pagesLaboratory Test Report: 19 Years / Femalesneha sahaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference IntervalDocument15 pagesBiochemistry: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference IntervalAshutoshNo ratings yet
- EGAC0401Document5 pagesEGAC0401bhanuprasadbkNo ratings yet
- Apollo247 249052700 LabreportDocument7 pagesApollo247 249052700 LabreportASHWAQ JAANNo ratings yet
- SnehaDocument3 pagesSneharazeena salamNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Report: FinalDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Report: Finalpraveen04715717No ratings yet
- LabReportNew - 2024-03-18T184949.154Document1 pageLabReportNew - 2024-03-18T184949.154desarajit72No ratings yet
- Mrs Nandhinidevi.M 04007180: Sid No. Patient ID 0400005449Document2 pagesMrs Nandhinidevi.M 04007180: Sid No. Patient ID 040000544911F10 RUCHITA MAARANNo ratings yet
- Clinical Biochemistry: Test Report Reg - No Age Name::: Reg - Date Collection:: Received: 15-Jul-2019 / 09:25 AMDocument8 pagesClinical Biochemistry: Test Report Reg - No Age Name::: Reg - Date Collection:: Received: 15-Jul-2019 / 09:25 AMAnuradha KommojuNo ratings yet
- Client0249 22024271868Document1 pageClient0249 22024271868dharusen082001No ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Fasting Plasma Glucose: 120Document1 pageLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Fasting Plasma Glucose: 120sanath kumarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Biochemistry: Sumit Omkant Nile ,, MRDocument2 pagesClinical Biochemistry: Sumit Omkant Nile ,, MRShivRaj Omkant NileNo ratings yet
- Client0249 22024271867Document1 pageClient0249 22024271867dharusen082001No ratings yet
- 1-Diabetes Package Advanced - PO2935562681-323Document11 pages1-Diabetes Package Advanced - PO2935562681-323Dr. Saurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Subba Lakshmi Kotturu 249951126 CompleteReportDocument1 pageSubba Lakshmi Kotturu 249951126 CompleteReportsaikrupa27No ratings yet
- Efbu2630Document4 pagesEfbu2630Aniruddh NagaNo ratings yet
- Report ViewerDocument1 pageReport ViewerArslan Baig100% (1)
- Department of Biochemistry Campaign Diabetic Check (With PP)Document2 pagesDepartment of Biochemistry Campaign Diabetic Check (With PP)gsm2008No ratings yet
- Department of Biochemistry Campaign Diabetic Panel: Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range MethodDocument4 pagesDepartment of Biochemistry Campaign Diabetic Panel: Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range Methodgsm2008No ratings yet
- Department of Biochemistry Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. RangeDocument5 pagesDepartment of Biochemistry Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. RangeSudhanshuNo ratings yet
- Nnyy3999 PDFDocument2 pagesNnyy3999 PDFAshwin SagarNo ratings yet
- 1-Diabetes Screening - PO3210290160-291Document4 pages1-Diabetes Screening - PO3210290160-291Jawed IqubalNo ratings yet
- Interpretation: S03 - FPSC DILSHAD COLONY (C004263143) J-50 Dilshad Colony, DelhiDocument6 pagesInterpretation: S03 - FPSC DILSHAD COLONY (C004263143) J-50 Dilshad Colony, DelhiAll VIDEOS TechNo ratings yet
- Department of Laboratory Services: Patient Name Uhidno/Ipno Lab No/Manualno Collectiondate Receiving DateDocument1 pageDepartment of Laboratory Services: Patient Name Uhidno/Ipno Lab No/Manualno Collectiondate Receiving DateSachin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Report GNDocument3 pagesReport GNPawan MadhesiyaNo ratings yet
- Iranbadsha Khan SugarDocument1 pageIranbadsha Khan Sugarmdasmaulseikh8No ratings yet
- Report-21YP86307 LOKANATH 03jun2021 122926Document1 pageReport-21YP86307 LOKANATH 03jun2021 122926AnkushNo ratings yet
- Report (4) - 231026 - 181327Document5 pagesReport (4) - 231026 - 181327Sandeep KrishnaNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument3 pagesReportPawan MadhesiyaNo ratings yet
- Department of Clinical Biochemistry: Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) 169 MG/DLDocument1 pageDepartment of Clinical Biochemistry: Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) 169 MG/DLakhilNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument4 pagesReportVibrant PixelsNo ratings yet
- Report 190a3 1695110951228Document13 pagesReport 190a3 1695110951228Mohd Jaffer ShareefNo ratings yet
- Name: Mrs. SABA 681 Patient UID.: 816567: Biochemistry Test Name Results Unit Bio. Ref. IntervalDocument2 pagesName: Mrs. SABA 681 Patient UID.: 816567: Biochemistry Test Name Results Unit Bio. Ref. Intervalshaykh basharatNo ratings yet
- Petersen Et Al 2020 High Dose Glucagon Has Hemodynamic Effects Regardless of Cardiac Beta Adrenoceptor Blockade ADocument27 pagesPetersen Et Al 2020 High Dose Glucagon Has Hemodynamic Effects Regardless of Cardiac Beta Adrenoceptor Blockade AputraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Fasting Plasma Glucose: 136Document1 pageLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Fasting Plasma Glucose: 136sanath kumarNo ratings yet
- 1-Diabetes Package - PO2693771771-269Document6 pages1-Diabetes Package - PO2693771771-269KishoreNo ratings yet
- LFT (Liver Function Test) : Biological Reference Results Units Test NameDocument4 pagesLFT (Liver Function Test) : Biological Reference Results Units Test Namemetepraju0210No ratings yet
- Clinical PathologyDocument1 pageClinical PathologyhmddNo ratings yet
- Report bc90b 1710052260449Document11 pagesReport bc90b 1710052260449muralinaiduNo ratings yet
- Report Eaaf4 1695467677147Document16 pagesReport Eaaf4 1695467677147Mohd Jaffer ShareefNo ratings yet
- Wa0037.Document2 pagesWa0037.lakshNo ratings yet
- TB Gurung72436565-2296573Document8 pagesTB Gurung72436565-2296573KeHar RajPutNo ratings yet
- Po3979242722 431Document8 pagesPo3979242722 431NEETFIXNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument28 pagesCombinepdfNEETFIXNo ratings yet
- Test Report: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Ref. Interval SpecimenDocument2 pagesTest Report: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Ref. Interval SpecimensumaNo ratings yet
- LabReportNew - 2023-09-08T160827.328Document3 pagesLabReportNew - 2023-09-08T160827.328viraj kshirsagarNo ratings yet
- Daksha ChavdaDocument3 pagesDaksha ChavdaKetan ChavdaNo ratings yet
- CMP95Document3 pagesCMP95mohnish aryanNo ratings yet
- PdfText (12) - 2022-07-15T231607.346Document2 pagesPdfText (12) - 2022-07-15T231607.346Mr. BLACKNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument2 pagesReportshifa nasrinNo ratings yet
- 1 Tuga HipoDocument7 pages1 Tuga HipoekaNo ratings yet
- Smart Full Body Checkup: Test Description Value(s) Unit(s) Reference RangeDocument13 pagesSmart Full Body Checkup: Test Description Value(s) Unit(s) Reference RangeShamsher SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Https Tdiagnostics - Telangana.gov - in ViewFiles - Aspx ReportId HK9UQ4C5ZEZ7ICEuNXmyPwDocument8 pagesHttps Tdiagnostics - Telangana.gov - in ViewFiles - Aspx ReportId HK9UQ4C5ZEZ7ICEuNXmyPwKuncham LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Department of Biochemistry-Routine: Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range MethodDocument10 pagesDepartment of Biochemistry-Routine: Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range MethodbfdfndfNo ratings yet
- Report 1690018110488Document2 pagesReport 1690018110488Krishna ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Nilesh Karani 13295 29-10-2023 20231029084151 StationerypdfmergedDocument22 pagesNilesh Karani 13295 29-10-2023 20231029084151 StationerypdfmergedsteelblackNo ratings yet
- Management of Palm Oil PestDocument11 pagesManagement of Palm Oil PestMohamad Syu'ib SyaukatNo ratings yet
- Sample Weekly Planner 2Document9 pagesSample Weekly Planner 2api-662941487No ratings yet
- Capitulo 2 Ista Reglas Internacionales SemillasDocument52 pagesCapitulo 2 Ista Reglas Internacionales SemillasmaritzaNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper Class-Xii Bio-Technology (045) SESSION 2019-20Document6 pagesSample Question Paper Class-Xii Bio-Technology (045) SESSION 2019-20Sudamini JhaNo ratings yet
- EcoCRM A Recombinant CRM197 Carrier ProteinDocument1 pageEcoCRM A Recombinant CRM197 Carrier ProteinRamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- H3C - Abstract Book 12302014-V2Document204 pagesH3C - Abstract Book 12302014-V2AAPI ConventionNo ratings yet
- Handwriting Saying - OralDocument1 pageHandwriting Saying - OralEsther FernandezNo ratings yet
- Speaking Test Avcn 1: Unit 1: Hospital StaffDocument5 pagesSpeaking Test Avcn 1: Unit 1: Hospital StaffHoàng Huy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Intro - EstroG-100 Pres FullDocument60 pagesIntro - EstroG-100 Pres FulllilingNo ratings yet
- 2007 Bakker y Demorouti State of The ArtDocument120 pages2007 Bakker y Demorouti State of The ArtScott SommerNo ratings yet
- Kidney Structure and FunctionDocument68 pagesKidney Structure and FunctionAsmara Syed100% (1)
- What Has Modern Ecosystem Theory To Offer To Cleaner Production, Industrial Ecology and Society The Views of An EcologistDocument15 pagesWhat Has Modern Ecosystem Theory To Offer To Cleaner Production, Industrial Ecology and Society The Views of An EcologistMilenoNo ratings yet
- The Semantics of Morphological RelationsDocument65 pagesThe Semantics of Morphological RelationsDương Bùi100% (1)
- Ebook Cultural Anthropology Canadian 2Nd Edition Robbins Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument34 pagesEbook Cultural Anthropology Canadian 2Nd Edition Robbins Test Bank Full Chapter PDFengagerscotsmangk9jt100% (9)
- Community and Environmental HealthDocument26 pagesCommunity and Environmental HealthMary Grace AgueteNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 GranulopoiesisDocument9 pagesLecture2 GranulopoiesisAfifa Prima GittaNo ratings yet
- Heterospory in PteridophytesDocument4 pagesHeterospory in PteridophytesTANMOY SARKARNo ratings yet
- Humastar300sr enDocument3 pagesHumastar300sr enNghi NguyenNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Synthetic Thought: Takshashila EssayDocument42 pagesThe Evolution of Synthetic Thought: Takshashila EssayLINDYLL PONO100% (1)
- Blank2021 Article MarkerAllergensInHymenopteraVeDocument13 pagesBlank2021 Article MarkerAllergensInHymenopteraVeAna-Maria DuMiNo ratings yet
- WDR-Weaver Dice RulebookDocument29 pagesWDR-Weaver Dice RulebookAzazelNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment Entrepreneurship Program of Diploma in Administrative Management Business Plan: ProposalDocument8 pagesGroup Assignment Entrepreneurship Program of Diploma in Administrative Management Business Plan: ProposalMuhammad ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Advances in Prostaglandin, Leukotriene, and Other Bioactive Lipid ResearchDocument243 pagesAdvances in Prostaglandin, Leukotriene, and Other Bioactive Lipid ResearchCarmen PopaNo ratings yet
- A Self-Assembled Nanoscale Robotic Arm Controlled by Electric FieldsDocument6 pagesA Self-Assembled Nanoscale Robotic Arm Controlled by Electric FieldsRegiane FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Mold and Mildew QA Understanding Mold in Your HousevnoznDocument3 pagesMold and Mildew QA Understanding Mold in Your Housevnoznliftvision70No ratings yet
- Ecozone Dichotomous KeyDocument3 pagesEcozone Dichotomous Keyqmtkqz72vhNo ratings yet
- IIB Sant Pau 2020 WebDocument336 pagesIIB Sant Pau 2020 WebAinhoa GaNo ratings yet
- Bioreaction Engineering PrinciplesDocument554 pagesBioreaction Engineering PrinciplesSaman100% (13)