Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acute Respiratory Failure & ARDS
Acute Respiratory Failure & ARDS
Uploaded by
VishalCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- NCLEX Cram SheetDocument6 pagesNCLEX Cram Sheetaishwariyapokharel55No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesCardiovascular Systemsurviving nursing school100% (2)
- Aiken Strategic Economic Development Action PlanDocument265 pagesAiken Strategic Economic Development Action PlanAiken Chamber0% (1)
- Benign Breast Disease: Douglas J. Marchant, MDDocument20 pagesBenign Breast Disease: Douglas J. Marchant, MDchristel chadidNo ratings yet
- Clinical Nursing JudgmentDocument7 pagesClinical Nursing Judgmentapi-502994344No ratings yet
- SimulationDocument5 pagesSimulationJessFriend100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (Kenneth Regida)Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (Kenneth Regida)Kenneth Anthony Tiu Regida100% (8)
- Asthma - Pathom, Signs & ComlicationsDocument1 pageAsthma - Pathom, Signs & ComlicationsVishalNo ratings yet
- 31 Acid Base Imbalances ABGs II - 230110 - 004938Document2 pages31 Acid Base Imbalances ABGs II - 230110 - 004938JanaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Lung Sounds v2Document1 pageAbnormal Lung Sounds v2Ynah BellaNo ratings yet
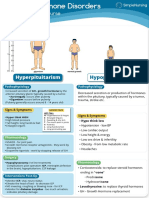
- Growth Hormone DisordersDocument1 pageGrowth Hormone DisordersVishalNo ratings yet
- Blankenhagen-Larson-Taylor Stroke BrochureDocument2 pagesBlankenhagen-Larson-Taylor Stroke Brochureapi-362395776100% (1)
- Nursing Exam Cram Sheet For The NCLEX-RN: 1. Test Information 5. ABG ValuesDocument8 pagesNursing Exam Cram Sheet For The NCLEX-RN: 1. Test Information 5. ABG ValuesManuela GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Testing Strategies For The Nclex-Rn Examination: Chapter OneDocument22 pagesTesting Strategies For The Nclex-Rn Examination: Chapter OneShiraishiNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument48 pagesAssessment of The Cardiovascular Systemkimberlyrwarren8817No ratings yet
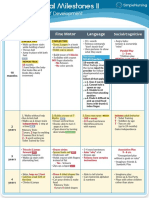
- Visual Chart 2 - Developmental MilestonesDocument1 pageVisual Chart 2 - Developmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- Nervous System AlterationsDocument45 pagesNervous System AlterationsMajesty ParkerNo ratings yet
- 13 2023 Surgery Revised HandoutsDocument26 pages13 2023 Surgery Revised HandoutswesamNo ratings yet
- TonsillitisDocument1 pageTonsillitisVishalNo ratings yet
- BulletsDocument41 pagesBulletsrosepearl ignacioNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Types of Traumatic Brain InjuriesDocument1 pageNursing CS Types of Traumatic Brain InjuriesJazzmine GuraNo ratings yet
- NURS 460 Nursing Licensure Examination Course: Jv7@hawaii - EduDocument5 pagesNURS 460 Nursing Licensure Examination Course: Jv7@hawaii - EduJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction ProblemsDocument29 pagesManagement of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction ProblemsYlanni Coritana100% (1)
- Prioritization LectureDocument6 pagesPrioritization LecturesamNo ratings yet
- Alterations in VentilationDocument10 pagesAlterations in VentilationCharisma Pastor100% (1)
- Visual Chart 1 - Developmental MilestonesDocument1 pageVisual Chart 1 - Developmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes: Irene L. Gardiner, MDDocument48 pagesFluids and Electrolytes: Irene L. Gardiner, MDGabriel Carlo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EarDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EarGunel AliyevaNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base NclexDocument4 pagesAcid-Base NclexDilNo ratings yet
- Focused Neurological Assessment From Simple NursingDocument1 pageFocused Neurological Assessment From Simple NursingAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular AP & Nursing AssessmentDocument24 pagesCardiovascular AP & Nursing AssessmentIssy2703No ratings yet
- BloodDocument9 pagesBloodCailah Sofia SelausoNo ratings yet
- High Yield Surgery Compatible Version-2Document20 pagesHigh Yield Surgery Compatible Version-2zoozsuhai2No ratings yet
- Acid Base Balance: Carol Johns, MSN, RNDocument36 pagesAcid Base Balance: Carol Johns, MSN, RNkatrinasdNo ratings yet
- The Child With Endocrine DysfunctionDocument5 pagesThe Child With Endocrine Dysfunctionhenny1620No ratings yet
- Diabetes Insulin Oral Agents TreatmentDocument1 pageDiabetes Insulin Oral Agents TreatmentAudrey Nicole GabianaNo ratings yet
- Answer: CDocument34 pagesAnswer: CLola OladapoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Overload Student PagesDocument4 pagesFluid Overload Student PagesJess OswaldNo ratings yet
- Perioperative NursingDocument97 pagesPerioperative NursingJames Lavarias SuñgaNo ratings yet
- Ekg InterpretationDocument26 pagesEkg Interpretationpaulzilicous.artNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Quick FactsDocument7 pagesNCLEX Quick FactsMary Aurine FullanteNo ratings yet
- NERVOUS SYSTEM NotesDocument6 pagesNERVOUS SYSTEM NotesAndrea Elaine Joy TorrentoNo ratings yet
- 6 - Basic Care and ComfortDocument15 pages6 - Basic Care and ComfortKristen NateNo ratings yet
- Pharm 1.13 Antidepressant Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePharm 1.13 Antidepressant Cheat SheetEunice CortésNo ratings yet
- Sirs & ModsDocument5 pagesSirs & Modsmarlou agananNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument1 pageHeart FailureTrisha VergaraNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Pre Class Minilecture Lewis 10-2018-2Document27 pagesCardiac Pre Class Minilecture Lewis 10-2018-2Jasmine LiraNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DisorderDocument6 pagesCardiovascular DisorderClara De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemAlliyah SalindoNo ratings yet
- All ConditionsDocument6 pagesAll ConditionsJoya Ruben CamposNo ratings yet
- Basic Chart 1 of 2 - Delopmental MilestonesDocument1 pageBasic Chart 1 of 2 - Delopmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Study GuideDocument9 pagesCardiac Study GuideJane DiazNo ratings yet
- Cardiac PathophysiologyDocument36 pagesCardiac Pathophysiologykim suhoNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Review GuideDocument3 pagesNCLEX Review GuidefallenangelleNo ratings yet
- Endocrine 10-Day Post Live ModulesDocument15 pagesEndocrine 10-Day Post Live ModulesPascal St Peter Nwaorgu100% (2)
- PREPUMASTERKEY (Repaired)Document2,031 pagesPREPUMASTERKEY (Repaired)surviving nursing schoolNo ratings yet
- Cardiac QuestionsDocument13 pagesCardiac Questionsacque100% (1)
- HeartFailure Nursing FIK 2014Document101 pagesHeartFailure Nursing FIK 2014Putri NurlaeliNo ratings yet
- 3 Fluids and Electrolytes PPDocument112 pages3 Fluids and Electrolytes PPjcodoyNo ratings yet
- Sinus Bradycardia: I. Sinus Dysrhythmias Description ManagementDocument4 pagesSinus Bradycardia: I. Sinus Dysrhythmias Description ManagementMargueretti Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid (Hyper & Hypo)Document1 pageParathyroid (Hyper & Hypo)Vishal100% (1)
- Growth Hormone DisordersDocument1 pageGrowth Hormone DisordersVishalNo ratings yet
- Diabetes - Patho, Causes, Signs, LabsDocument1 pageDiabetes - Patho, Causes, Signs, LabsVishalNo ratings yet
- Siadh - Patho, Signs, Causes, TreatmentDocument1 pageSiadh - Patho, Signs, Causes, TreatmentVishalNo ratings yet
- Thyroid (Hyper & Hypo) - Patho, Causes, LabsDocument1 pageThyroid (Hyper & Hypo) - Patho, Causes, LabsVishalNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Patho & SignsDocument1 pagePneumonia Patho & SignsVishalNo ratings yet
- Asthma - Diagnostics & CausesDocument1 pageAsthma - Diagnostics & CausesVishalNo ratings yet
- Basic Chart 1 of 2 - Delopmental MilestonesDocument1 pageBasic Chart 1 of 2 - Delopmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- Asthma - Pathom, Signs & ComlicationsDocument1 pageAsthma - Pathom, Signs & ComlicationsVishalNo ratings yet
- Basic Chart 2 of 2 - Delopmental MilestonesDocument1 pageBasic Chart 2 of 2 - Delopmental MilestonesVishal100% (1)
- TonsillitisDocument1 pageTonsillitisVishalNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Key TermsDocument1 pageRespiratory Key TermsVishalNo ratings yet
- Visual Chart 2 - Developmental MilestonesDocument1 pageVisual Chart 2 - Developmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- Visual Chart 1 - Developmental MilestonesDocument1 pageVisual Chart 1 - Developmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- SCIDDocument10 pagesSCIDIbrahimNo ratings yet
- KasaiDocument7 pagesKasaishalukiriNo ratings yet
- Microbes and Infectious Diseases: Continuous Medical Education Activities Case No. 1Document2 pagesMicrobes and Infectious Diseases: Continuous Medical Education Activities Case No. 1ahmedNo ratings yet
- Nebosh International Diploma in Environmental Management BrochureDocument1 pageNebosh International Diploma in Environmental Management BrochureSahib Singh Chadha0% (1)
- NSTP Group 3 First Aid ReportingDocument44 pagesNSTP Group 3 First Aid ReportingCindy GeverolaNo ratings yet
- Anandhu M AVT Academy 1486Document17 pagesAnandhu M AVT Academy 1486anandmg41No ratings yet
- Reflection Paper Botany LectureDocument1 pageReflection Paper Botany LectureCHARLES RONALD GENATONo ratings yet
- Infective EndocarditisDocument18 pagesInfective EndocarditisLee Foo WengNo ratings yet
- Asian Pacific ScientistsDocument28 pagesAsian Pacific ScientistsMahmood SanglayNo ratings yet
- Ebook Braddoms Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sixth Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Braddoms Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sixth Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFmelinda.warren862100% (34)
- Pia Cayetano: Goan, Danielle Beatrice S. Villanueva, Ruben RochelleDocument11 pagesPia Cayetano: Goan, Danielle Beatrice S. Villanueva, Ruben RochelleDana GoanNo ratings yet
- Dermatoglyphics in Dentistry: A Review: Int J Eth Trauma Victimology 2019 5 (1) :39Document6 pagesDermatoglyphics in Dentistry: A Review: Int J Eth Trauma Victimology 2019 5 (1) :39Rohini TondaNo ratings yet
- Developing An Expert System PDFDocument5 pagesDeveloping An Expert System PDFryfweNo ratings yet
- CSC138 Group Assignment 2Document3 pagesCSC138 Group Assignment 2KIRIT GOVINDARAJA PILLAI 20BCE2404No ratings yet
- Quiz Informatics Sample 04Document2 pagesQuiz Informatics Sample 04janmalexx100% (2)
- Mapeh Worksheet - W2 Health Education 8Document5 pagesMapeh Worksheet - W2 Health Education 8Nathan MasilunganNo ratings yet
- 7.1 TelemedicineDocument19 pages7.1 TelemedicineTrisha BawaNo ratings yet
- Daily Food Log: Date: Weight: Sleep BMI Time Qty FoodDocument7 pagesDaily Food Log: Date: Weight: Sleep BMI Time Qty FoodDiana Ulei-CrișanNo ratings yet
- Advance Managament of Acute Cholecystitis and CholangitisDocument43 pagesAdvance Managament of Acute Cholecystitis and CholangitisWi HardiyantiNo ratings yet
- Amoebiasis DiseaseDocument10 pagesAmoebiasis Diseaseshruti ghordadeNo ratings yet
- Kandungan Gizi Puding Jagung Lapis CoklatDocument1 pageKandungan Gizi Puding Jagung Lapis Coklatdaffa11No ratings yet
- Prevalence of Rifampicin Resistance Tuberculosis and Associated Factors Among Presumptive TB or MDRDocument3 pagesPrevalence of Rifampicin Resistance Tuberculosis and Associated Factors Among Presumptive TB or MDRTigray OutlookNo ratings yet
- Chapter-Ii Review of LiteratureDocument8 pagesChapter-Ii Review of LiteratureANU GRAPHICSNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocument3 pagesDisseminated Intravascular CoagulationArlan Abragan100% (1)
- Gensler Design Forecast 2013Document43 pagesGensler Design Forecast 2013Pete PetrášNo ratings yet
- Medical GasesDocument20 pagesMedical Gasesmagicarray.hrNo ratings yet
- Contoh MotletDocument2 pagesContoh MotletAduy Hudaya WidihasthaNo ratings yet
Acute Respiratory Failure & ARDS
Acute Respiratory Failure & ARDS
Uploaded by
VishalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acute Respiratory Failure & ARDS
Acute Respiratory Failure & ARDS
Uploaded by
VishalCopyright:
Available Formats
Respiratory Failure & ARDS
Pathophysiology Course
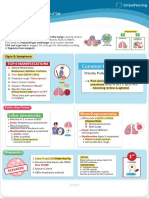
Respiratory Failure
0₂ 0₂
0₂ 0₂
0₂
When the capillaries (little blood vessels in the alveoli) cannot adequately exchange CO2 for Oxygen. 0₂
0₂
Causes
• Infection causes these alveoli to become swollen, inflamed, & filled with mucus
or fluid which blocks gas exchange!
• Clients can present with a common FLU which can progress into pneumonia &
eventually into DEADLY A.R.D.S. - Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Signs & Symptoms MEMORY TRICK Common Exam Question
REsistant to Oxygen Which arterial blood gas (ABG) values
Hypoxemia LOW O2 REfractory Hypoxemia support suspected acute respiratory
failure (ARF)?
#1 Sign = Altered Mental status NCLEX TIP
0₂
0₂
1. PaO2 55 mm Hg, PaCO2 47 mm Hg
0₂
0₂
0₂
2. PaO2 62 mm Hg, PaCO2 32 mm Hg
1. Agitation 3. PaO2 47 mm Hg, PaCO2 63 mm Hg
4. PaO2 82 mm Hg, PaCO2 22 mm Hg
2. Restlessness
3. Confusion Lab Values
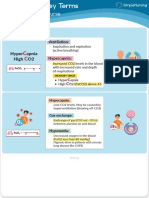
ABG Arterial Blood Gas
ARDS Low PaO2 pH
A B
? High CO2 7.35 7.45
Refractory Hypoxemia
?
?
? ? PaCO₂
B
A
0₂
35 45 63
Low PaO2 = Despite Oxygen delivery ?
C PaO₂
O O 47 80 100
PaO2
CO2
ARDS Pathophysiology
The alveoli become hard due to the capillaries around the Alveoli becoming inflamed O2 CO2
in out
& fluid-filled, creating a leaky barrier, which eventually fills up the little alveoli sac like
a sinking ship! THIS makes it impossible to get oxygen in & to get CO2 OUT!
Eventually clients DIE from hypoxia IF they are not on a ventilator early.
MEMORY TRICK PRIORITY DIAGNOSIS
• ARDS = HARD Alveoli • Impaired gas exchange
Causes Nursing Interventions for ARDS
• Sepsis - bloodborne infection that inflames the entire body
• Respiratory inflammation - pneumonia, inhaled toxin, Mechanical Ventilation
or even aspiration.
• Acute pancreatitis = HIGH risk for developing ARDS NCLEX TIP 0₂ PEEP (positive end-expiratory
pressure)
accidental release of active pancreatic enzymes & cytokines
into the bloodstream - which get sucked into the lungs
causing inflammation.
A.R.F. - ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE
H High Fowler's position (HOB up)
2 types:
0₂
O Oral suctioning & Oxygen
HypOXemic failure LOW O2
(PaO2 60 or LESS) L Listen to lung sounds
HyperCapnic failure HIGH CO2
(PaCO2 Over 50 )
PaO2 <60
Y Yell for help! Notify HCP “provider”
You might also like
- NCLEX Cram SheetDocument6 pagesNCLEX Cram Sheetaishwariyapokharel55No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesCardiovascular Systemsurviving nursing school100% (2)
- Aiken Strategic Economic Development Action PlanDocument265 pagesAiken Strategic Economic Development Action PlanAiken Chamber0% (1)
- Benign Breast Disease: Douglas J. Marchant, MDDocument20 pagesBenign Breast Disease: Douglas J. Marchant, MDchristel chadidNo ratings yet
- Clinical Nursing JudgmentDocument7 pagesClinical Nursing Judgmentapi-502994344No ratings yet
- SimulationDocument5 pagesSimulationJessFriend100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (Kenneth Regida)Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (Kenneth Regida)Kenneth Anthony Tiu Regida100% (8)
- Asthma - Pathom, Signs & ComlicationsDocument1 pageAsthma - Pathom, Signs & ComlicationsVishalNo ratings yet
- 31 Acid Base Imbalances ABGs II - 230110 - 004938Document2 pages31 Acid Base Imbalances ABGs II - 230110 - 004938JanaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Lung Sounds v2Document1 pageAbnormal Lung Sounds v2Ynah BellaNo ratings yet
- Growth Hormone DisordersDocument1 pageGrowth Hormone DisordersVishalNo ratings yet
- Blankenhagen-Larson-Taylor Stroke BrochureDocument2 pagesBlankenhagen-Larson-Taylor Stroke Brochureapi-362395776100% (1)
- Nursing Exam Cram Sheet For The NCLEX-RN: 1. Test Information 5. ABG ValuesDocument8 pagesNursing Exam Cram Sheet For The NCLEX-RN: 1. Test Information 5. ABG ValuesManuela GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Testing Strategies For The Nclex-Rn Examination: Chapter OneDocument22 pagesTesting Strategies For The Nclex-Rn Examination: Chapter OneShiraishiNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument48 pagesAssessment of The Cardiovascular Systemkimberlyrwarren8817No ratings yet
- Visual Chart 2 - Developmental MilestonesDocument1 pageVisual Chart 2 - Developmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- Nervous System AlterationsDocument45 pagesNervous System AlterationsMajesty ParkerNo ratings yet
- 13 2023 Surgery Revised HandoutsDocument26 pages13 2023 Surgery Revised HandoutswesamNo ratings yet
- TonsillitisDocument1 pageTonsillitisVishalNo ratings yet
- BulletsDocument41 pagesBulletsrosepearl ignacioNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Types of Traumatic Brain InjuriesDocument1 pageNursing CS Types of Traumatic Brain InjuriesJazzmine GuraNo ratings yet
- NURS 460 Nursing Licensure Examination Course: Jv7@hawaii - EduDocument5 pagesNURS 460 Nursing Licensure Examination Course: Jv7@hawaii - EduJeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction ProblemsDocument29 pagesManagement of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction ProblemsYlanni Coritana100% (1)
- Prioritization LectureDocument6 pagesPrioritization LecturesamNo ratings yet
- Alterations in VentilationDocument10 pagesAlterations in VentilationCharisma Pastor100% (1)
- Visual Chart 1 - Developmental MilestonesDocument1 pageVisual Chart 1 - Developmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes: Irene L. Gardiner, MDDocument48 pagesFluids and Electrolytes: Irene L. Gardiner, MDGabriel Carlo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EarDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EarGunel AliyevaNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base NclexDocument4 pagesAcid-Base NclexDilNo ratings yet
- Focused Neurological Assessment From Simple NursingDocument1 pageFocused Neurological Assessment From Simple NursingAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular AP & Nursing AssessmentDocument24 pagesCardiovascular AP & Nursing AssessmentIssy2703No ratings yet
- BloodDocument9 pagesBloodCailah Sofia SelausoNo ratings yet
- High Yield Surgery Compatible Version-2Document20 pagesHigh Yield Surgery Compatible Version-2zoozsuhai2No ratings yet
- Acid Base Balance: Carol Johns, MSN, RNDocument36 pagesAcid Base Balance: Carol Johns, MSN, RNkatrinasdNo ratings yet
- The Child With Endocrine DysfunctionDocument5 pagesThe Child With Endocrine Dysfunctionhenny1620No ratings yet
- Diabetes Insulin Oral Agents TreatmentDocument1 pageDiabetes Insulin Oral Agents TreatmentAudrey Nicole GabianaNo ratings yet
- Answer: CDocument34 pagesAnswer: CLola OladapoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Overload Student PagesDocument4 pagesFluid Overload Student PagesJess OswaldNo ratings yet
- Perioperative NursingDocument97 pagesPerioperative NursingJames Lavarias SuñgaNo ratings yet
- Ekg InterpretationDocument26 pagesEkg Interpretationpaulzilicous.artNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Quick FactsDocument7 pagesNCLEX Quick FactsMary Aurine FullanteNo ratings yet
- NERVOUS SYSTEM NotesDocument6 pagesNERVOUS SYSTEM NotesAndrea Elaine Joy TorrentoNo ratings yet
- 6 - Basic Care and ComfortDocument15 pages6 - Basic Care and ComfortKristen NateNo ratings yet
- Pharm 1.13 Antidepressant Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePharm 1.13 Antidepressant Cheat SheetEunice CortésNo ratings yet
- Sirs & ModsDocument5 pagesSirs & Modsmarlou agananNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument1 pageHeart FailureTrisha VergaraNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Pre Class Minilecture Lewis 10-2018-2Document27 pagesCardiac Pre Class Minilecture Lewis 10-2018-2Jasmine LiraNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DisorderDocument6 pagesCardiovascular DisorderClara De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemAlliyah SalindoNo ratings yet
- All ConditionsDocument6 pagesAll ConditionsJoya Ruben CamposNo ratings yet
- Basic Chart 1 of 2 - Delopmental MilestonesDocument1 pageBasic Chart 1 of 2 - Delopmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Study GuideDocument9 pagesCardiac Study GuideJane DiazNo ratings yet
- Cardiac PathophysiologyDocument36 pagesCardiac Pathophysiologykim suhoNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Review GuideDocument3 pagesNCLEX Review GuidefallenangelleNo ratings yet
- Endocrine 10-Day Post Live ModulesDocument15 pagesEndocrine 10-Day Post Live ModulesPascal St Peter Nwaorgu100% (2)
- PREPUMASTERKEY (Repaired)Document2,031 pagesPREPUMASTERKEY (Repaired)surviving nursing schoolNo ratings yet
- Cardiac QuestionsDocument13 pagesCardiac Questionsacque100% (1)
- HeartFailure Nursing FIK 2014Document101 pagesHeartFailure Nursing FIK 2014Putri NurlaeliNo ratings yet
- 3 Fluids and Electrolytes PPDocument112 pages3 Fluids and Electrolytes PPjcodoyNo ratings yet
- Sinus Bradycardia: I. Sinus Dysrhythmias Description ManagementDocument4 pagesSinus Bradycardia: I. Sinus Dysrhythmias Description ManagementMargueretti Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid (Hyper & Hypo)Document1 pageParathyroid (Hyper & Hypo)Vishal100% (1)
- Growth Hormone DisordersDocument1 pageGrowth Hormone DisordersVishalNo ratings yet
- Diabetes - Patho, Causes, Signs, LabsDocument1 pageDiabetes - Patho, Causes, Signs, LabsVishalNo ratings yet
- Siadh - Patho, Signs, Causes, TreatmentDocument1 pageSiadh - Patho, Signs, Causes, TreatmentVishalNo ratings yet
- Thyroid (Hyper & Hypo) - Patho, Causes, LabsDocument1 pageThyroid (Hyper & Hypo) - Patho, Causes, LabsVishalNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Patho & SignsDocument1 pagePneumonia Patho & SignsVishalNo ratings yet
- Asthma - Diagnostics & CausesDocument1 pageAsthma - Diagnostics & CausesVishalNo ratings yet
- Basic Chart 1 of 2 - Delopmental MilestonesDocument1 pageBasic Chart 1 of 2 - Delopmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- Asthma - Pathom, Signs & ComlicationsDocument1 pageAsthma - Pathom, Signs & ComlicationsVishalNo ratings yet
- Basic Chart 2 of 2 - Delopmental MilestonesDocument1 pageBasic Chart 2 of 2 - Delopmental MilestonesVishal100% (1)
- TonsillitisDocument1 pageTonsillitisVishalNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Key TermsDocument1 pageRespiratory Key TermsVishalNo ratings yet
- Visual Chart 2 - Developmental MilestonesDocument1 pageVisual Chart 2 - Developmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- Visual Chart 1 - Developmental MilestonesDocument1 pageVisual Chart 1 - Developmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- SCIDDocument10 pagesSCIDIbrahimNo ratings yet
- KasaiDocument7 pagesKasaishalukiriNo ratings yet
- Microbes and Infectious Diseases: Continuous Medical Education Activities Case No. 1Document2 pagesMicrobes and Infectious Diseases: Continuous Medical Education Activities Case No. 1ahmedNo ratings yet
- Nebosh International Diploma in Environmental Management BrochureDocument1 pageNebosh International Diploma in Environmental Management BrochureSahib Singh Chadha0% (1)
- NSTP Group 3 First Aid ReportingDocument44 pagesNSTP Group 3 First Aid ReportingCindy GeverolaNo ratings yet
- Anandhu M AVT Academy 1486Document17 pagesAnandhu M AVT Academy 1486anandmg41No ratings yet
- Reflection Paper Botany LectureDocument1 pageReflection Paper Botany LectureCHARLES RONALD GENATONo ratings yet
- Infective EndocarditisDocument18 pagesInfective EndocarditisLee Foo WengNo ratings yet
- Asian Pacific ScientistsDocument28 pagesAsian Pacific ScientistsMahmood SanglayNo ratings yet
- Ebook Braddoms Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sixth Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Braddoms Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sixth Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFmelinda.warren862100% (34)
- Pia Cayetano: Goan, Danielle Beatrice S. Villanueva, Ruben RochelleDocument11 pagesPia Cayetano: Goan, Danielle Beatrice S. Villanueva, Ruben RochelleDana GoanNo ratings yet
- Dermatoglyphics in Dentistry: A Review: Int J Eth Trauma Victimology 2019 5 (1) :39Document6 pagesDermatoglyphics in Dentistry: A Review: Int J Eth Trauma Victimology 2019 5 (1) :39Rohini TondaNo ratings yet
- Developing An Expert System PDFDocument5 pagesDeveloping An Expert System PDFryfweNo ratings yet
- CSC138 Group Assignment 2Document3 pagesCSC138 Group Assignment 2KIRIT GOVINDARAJA PILLAI 20BCE2404No ratings yet
- Quiz Informatics Sample 04Document2 pagesQuiz Informatics Sample 04janmalexx100% (2)
- Mapeh Worksheet - W2 Health Education 8Document5 pagesMapeh Worksheet - W2 Health Education 8Nathan MasilunganNo ratings yet
- 7.1 TelemedicineDocument19 pages7.1 TelemedicineTrisha BawaNo ratings yet
- Daily Food Log: Date: Weight: Sleep BMI Time Qty FoodDocument7 pagesDaily Food Log: Date: Weight: Sleep BMI Time Qty FoodDiana Ulei-CrișanNo ratings yet
- Advance Managament of Acute Cholecystitis and CholangitisDocument43 pagesAdvance Managament of Acute Cholecystitis and CholangitisWi HardiyantiNo ratings yet
- Amoebiasis DiseaseDocument10 pagesAmoebiasis Diseaseshruti ghordadeNo ratings yet
- Kandungan Gizi Puding Jagung Lapis CoklatDocument1 pageKandungan Gizi Puding Jagung Lapis Coklatdaffa11No ratings yet
- Prevalence of Rifampicin Resistance Tuberculosis and Associated Factors Among Presumptive TB or MDRDocument3 pagesPrevalence of Rifampicin Resistance Tuberculosis and Associated Factors Among Presumptive TB or MDRTigray OutlookNo ratings yet
- Chapter-Ii Review of LiteratureDocument8 pagesChapter-Ii Review of LiteratureANU GRAPHICSNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocument3 pagesDisseminated Intravascular CoagulationArlan Abragan100% (1)
- Gensler Design Forecast 2013Document43 pagesGensler Design Forecast 2013Pete PetrášNo ratings yet
- Medical GasesDocument20 pagesMedical Gasesmagicarray.hrNo ratings yet
- Contoh MotletDocument2 pagesContoh MotletAduy Hudaya WidihasthaNo ratings yet