Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Classi
Classi
Uploaded by
SEIYADU IBRAHIM KOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Classi
Classi
Uploaded by
SEIYADU IBRAHIM KCopyright:
Available Formats
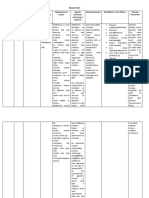
Overview of antidiabetic drugs
Class Mechanism of action Side effects Contraindications
Lactic acidosis
Weight loss Chronic kidney disease
Gastrointestinal Liver failure
Enhances the effect of complaints are common Metformin must be paused
Biguanide (metformin) insulin (e.g. diarrhea, abdominal before administration of
cramps) iodinated contrast medium
Reduced vitamin B12 and major surgery.
absorption
Severe cardiovascular
Risk of hypoglycemia
comorbidity
Weight gain
Increase insulin secretion Obesity
Sulfonylureas (e.g., Hematological changes:
from pancreatic β-cells Sulfonamide allergy
glyburide, glimepiride) agranulocytosis,
(particularly long-acting
hemolysis
substances)
Increase insulin secretion Risk of hypoglycemia
Meglitinides (nateglinide, Severe renal or liver failure
from pancreatic β-cells Weight gain
repaglinide)
Gastrointestinal
Inhibit GLP-1 degradation
complaints Liver failure
→ promotes glucose-
DPP-4 inhibitors Pancreatitis Moderate to severe renal
dependent insulin
(saxagliptin, sitagliptin) Headache, dizziness failure
secretion
Arthralgia
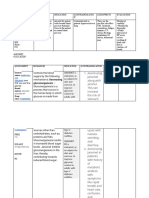
Class Mechanism of action Side effects Contraindications
Nausea
Preexisting, symptomatic
GLP-1 agonists (incretin Direct stimulation of the Increased risk of
gastrointestinal motility
mimetic drugs: exenatide, GLP-1 receptor pancreatitis and possibly
disorders
liraglutide, albiglutide) pancreatic cancer
Genital yeast infections
SGLT-2 inhibitors Increased glucosuria and urinary tract Chronic kidney disease
(canagliflozin, through the inhibition of infections Recurrent urinary tract
dapagliflozin, SGLT-2 in the kidney Polyuria and dehydration infections
empagliflozin) Diabetic ketoacidosis
Any preexisting intestinal
Gastrointestinal
conditions (e.g.,
Reduce intestinal glucose complaints (flatulence,
Alpha-glucosidase inflammatory bowel
absorption diarrhea, feeling of
inhibitors (acarbose) disease)
satiety)
Severe renal failure
Reduce insulin resistance
through the stimulation of Weight gain
PPARs (peroxisome Edema
Congestive heart failure
Thiazolidinediones proliferator-activated Cardiac failure
Liver failure
(pioglitazone) receptors) Increased risk of bone
Increase transcription of fractures (osteoporosis)
adipokines
Reduce glucagon release
Risk of hypoglycemia
Amylin analogs Reduce gastric emptying Gastroparesis
Nausea
(pramlintide) Increase satiety
You might also like
- 10-11 - Anti-Hyperlipidemic Drugs (Summary SAQ and MCQS)Document6 pages10-11 - Anti-Hyperlipidemic Drugs (Summary SAQ and MCQS)Purvak Mahajan100% (1)
- Drug Study (Ranitidine, Metoclopramide, Ketorolac, and Omeprazole)Document8 pagesDrug Study (Ranitidine, Metoclopramide, Ketorolac, and Omeprazole)Akisan0% (1)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Comprehensive Nursing Assessment ToolDocument7 pagesComprehensive Nursing Assessment ToolRamesh KandagatlaNo ratings yet
- Doctor-Scientist On Kangen PDFDocument22 pagesDoctor-Scientist On Kangen PDFfredyagussusanto100% (2)
- Magic SEADocument72 pagesMagic SEAPete Puza82% (22)
- Beck Protocol Handbook PDFDocument85 pagesBeck Protocol Handbook PDFkousti67% (3)
- ArbovirusesDocument74 pagesArbovirusesmulatumelese100% (1)
- Overview of Antidiabetic Drugs: Insulin Hyperglycemic Diabetes MellitusDocument14 pagesOverview of Antidiabetic Drugs: Insulin Hyperglycemic Diabetes Mellitus4760rkNo ratings yet
- Antidiabetic Drug 1 190517142411Document17 pagesAntidiabetic Drug 1 190517142411salehaNo ratings yet
- Significant: BullousDocument6 pagesSignificant: BullousMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Summary Drugs Table - GERR BlockDocument2 pagesSummary Drugs Table - GERR BlockRiley WestwoodNo ratings yet
- Antidiabetic Drugs - AMBOSSDocument13 pagesAntidiabetic Drugs - AMBOSSOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- Non-Insulin Management of Diabetes MellitusDocument15 pagesNon-Insulin Management of Diabetes MellitusrogeracasusoNo ratings yet
- Metformin Drug StudyDocument1 pageMetformin Drug StudyRose Echevarria67% (3)
- Drug Study 2Document5 pagesDrug Study 2Bani Ann Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Treatment: PancreatitisDocument2 pagesDiabetes Treatment: PancreatitisSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MetforminDocument3 pagesDrug Study Metforminbryan.zabala.mnlNo ratings yet
- Step 3 - PharmacologyDocument10 pagesStep 3 - PharmacologyLauren LevyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SitagliptinDocument3 pagesDrug Study SitagliptinEzron Kendrick Duran50% (2)
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesNathaniel John Rebollos SuladayNo ratings yet
- Leveraging GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Options To Advance Glycemic and Extraglycemic Goals in Type 2 DiabetesDocument34 pagesLeveraging GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Options To Advance Glycemic and Extraglycemic Goals in Type 2 DiabetesMagdy GabrNo ratings yet
- Dyslipidemia SummaryDocument6 pagesDyslipidemia SummaryJan Angela BaylonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug Studyjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MsDocument10 pagesDrug Study MsAbie Jewel Joy RoqueNo ratings yet
- Linagliptin - DRUG STUDYDocument1 pageLinagliptin - DRUG STUDYAcads useNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GlyburideDocument5 pagesDrug Study GlyburideSchyna Marielle VitaleNo ratings yet
- Nursing School Drug Chart PDFDocument13 pagesNursing School Drug Chart PDFBapi mirabeau kumbuin100% (1)
- Tableau Antidiabetiques 2018 enDocument1 pageTableau Antidiabetiques 2018 enpraefatioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study #1Document7 pagesDrug Study #1Sarah Kaye BañoNo ratings yet
- GI Elimination Medication Cards 1Document4 pagesGI Elimination Medication Cards 1方郝建No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyAilah Mae Dela Cruz0% (1)
- Diabetes Drugs ComparisonDocument3 pagesDiabetes Drugs Comparisonshahd ?No ratings yet
- Diabetes Drugs ComparisonDocument3 pagesDiabetes Drugs Comparisonshahd ?No ratings yet
- Dams Manipal Endo PPT For StudentsDocument11 pagesDams Manipal Endo PPT For StudentsdeepikaNo ratings yet
- MetoclopramideDocument1 pageMetoclopramideYanejoulce SacanleNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Drug Class Mechanism of Action Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument7 pagesDrug Name Drug Class Mechanism of Action Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationJhucyl Mae GalvezNo ratings yet
- Table 1. Antihyperglycemic Agents For Use in Type 2 DiabetesDocument5 pagesTable 1. Antihyperglycemic Agents For Use in Type 2 DiabeteszeiarraNo ratings yet
- Shock Acute Myocardial Infarction Septicemia Precautions Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument3 pagesShock Acute Myocardial Infarction Septicemia Precautions Diabetic KetoacidosisArienne_Mae_A__6554No ratings yet
- Drug Index Patient 2203Document3 pagesDrug Index Patient 2203Arienne_Mae_A__6554No ratings yet
- Of Active Duodenal Ulcer: 40 MG PO orDocument3 pagesOf Active Duodenal Ulcer: 40 MG PO orAbie Jewel Joy RoqueNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument6 pagesDiabetes Mellitusmaham jahangirNo ratings yet
- New DrugsDocument6 pagesNew DrugsZymer Lee AbasoloNo ratings yet
- Fa 2022 2Document8 pagesFa 2022 2Ransu SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study #2Document3 pagesDrug Study #2Sarah Kaye BañoNo ratings yet
- Atorvastatin Calcium Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument3 pagesAtorvastatin Calcium Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComEloisa BretañaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SitagliptinDocument2 pagesDrug Study SitagliptinAl Theó0% (1)
- 4A Drug SheetDocument14 pages4A Drug SheetTherese PagayNo ratings yet
- Drug Ana LaraDocument2 pagesDrug Ana LaralarapaulineNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 4. GI Tract PharmacologyDocument52 pagesLecture - 4. GI Tract PharmacologyRohaan SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1012 Endocrine Drug Table For Nurse StudyingDocument1 page1012 Endocrine Drug Table For Nurse StudyingJavier PulidoNo ratings yet
- m.10b Drugs Used in Gastrointestinal Diseases 03-26-18 (Table)Document3 pagesm.10b Drugs Used in Gastrointestinal Diseases 03-26-18 (Table)Dasha VeeNo ratings yet
- Table 173-3 - Agents Used For Treatment of Type 1 or Type 2 DiDocument2 pagesTable 173-3 - Agents Used For Treatment of Type 1 or Type 2 DiKiran ShelkeNo ratings yet
- Mini Case Study RuliuDocument26 pagesMini Case Study Ruliuapi-300681452No ratings yet
- Table 9.1 Details of Non-Insulin Agents Used in Pharmacological Therapy in Type 2 DiabetesDocument1 pageTable 9.1 Details of Non-Insulin Agents Used in Pharmacological Therapy in Type 2 DiabetesAmila ShyamalNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Sheet Patient Name: BALDESTOY, Benedict Age: 19 Years Old Sex: Male Diagnosis: Hepatoma CAP-MRDocument5 pagesPharmacological Sheet Patient Name: BALDESTOY, Benedict Age: 19 Years Old Sex: Male Diagnosis: Hepatoma CAP-MRIngrid NicolasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (3rd Rot.) (GMC) - JSGSDocument6 pagesDrug Study (3rd Rot.) (GMC) - JSGSJohannes SantosNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Pills How To Take How They Work Side Effects of NoteDocument2 pagesDiabetes Pills How To Take How They Work Side Effects of NoteLaurensia Erlina NataliaNo ratings yet
- CHFDocument12 pagesCHFganda akoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument20 pagesDrug StudyRoland YusteNo ratings yet
- Week 26 James Banting Insulin: TissueDocument12 pagesWeek 26 James Banting Insulin: Tissuedragtoss2No ratings yet
- Diabetic Recipes for One and TwoFrom EverandDiabetic Recipes for One and TwoRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- AntibioticsDocument1 pageAntibioticsSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Anti Anxiety DrugsDocument1 pageAnti Anxiety DrugsSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Common ICU DripsDocument1 pageCommon ICU DripsSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Anti Coagulants DrugsDocument1 pageAnti Coagulants DrugsSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- AnesthesiaDocument1 pageAnesthesiaSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Insulin PensDocument1 pageInsulin PensSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- DOCDocument1 pageDOCSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Statin ComparisionDocument1 pageStatin ComparisionSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Statin TherapyDocument1 pageStatin TherapySEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
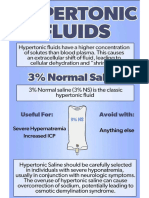
- Hypertonic FluidsDocument1 pageHypertonic FluidsSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Anti Biotics CounsellingDocument1 pageAnti Biotics CounsellingSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Irritable Bowel SyndromeDocument12 pagesIrritable Bowel SyndromeSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Drug of Choice Antibiotics Part 3Document11 pagesDrug of Choice Antibiotics Part 3SEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Diseases Caused by Virus, Bacteria, Protozoa and WormsDocument1 pageDiseases Caused by Virus, Bacteria, Protozoa and WormsSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument11 pagesOsteoporosisSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Platelets CVDDocument1 pagePlatelets CVDSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic CompleteDocument1 pageAntibiotic CompleteSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument9 pagesPneumoniaSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- CHFDocument1 pageCHFSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Pharmacist NotesDocument115 pagesPharmacist NotesSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Patient Counselling A Pharmacist GuideDocument12 pagesPatient Counselling A Pharmacist GuideSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Teratogenic Drugs To Avoid Before ConceptionDocument14 pagesTeratogenic Drugs To Avoid Before ConceptionSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Medical MnemonicsDocument8 pagesMedical MnemonicsSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Medications During BreastfeedingDocument17 pagesMedications During BreastfeedingSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Medications During PregnancyDocument16 pagesMedications During PregnancySEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Side Effects of Common DrugsDocument13 pagesSide Effects of Common DrugsSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinsonian DrugsDocument5 pagesAntiparkinsonian Drugskv 14No ratings yet
- Drug of ChoiceDocument12 pagesDrug of ChoiceSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Endocrine MedicineDocument8 pagesEndocrine MedicineSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Mangement of CV ConditionsDocument9 pagesMangement of CV ConditionsSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- CNS and ANSDocument36 pagesCNS and ANSLEBADISOS KATE PRINCESSNo ratings yet
- Associations Between Body Weight and Personality Disorders in A Nationally Representative SampleDocument8 pagesAssociations Between Body Weight and Personality Disorders in A Nationally Representative SampleKamu Ri ChiNo ratings yet
- Public CVDocument6 pagesPublic CVapi-519356630No ratings yet
- Angeles MeatProcessingDocument38 pagesAngeles MeatProcessingAnonymous gO6PtzXa6No ratings yet
- Final Health Care Associated InfectionDocument23 pagesFinal Health Care Associated Infectionramanand chaudharyNo ratings yet
- So-Called Cellulite: An Invented Disease : Female MaleDocument9 pagesSo-Called Cellulite: An Invented Disease : Female MaleRacovițăNo ratings yet
- Clean CVDocument25 pagesClean CVassssadfNo ratings yet
- Sabir Research Paper 3Document8 pagesSabir Research Paper 3Sabir Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- 20 Things That Someone With An Eating Disorder Wishes They Were Able To Tell YouDocument10 pages20 Things That Someone With An Eating Disorder Wishes They Were Able To Tell Youmorgs39No ratings yet
- Surgical Management of Dilocated Lens: Mohammad Ghoreishi, MDDocument15 pagesSurgical Management of Dilocated Lens: Mohammad Ghoreishi, MDwawan 88No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 9 Grade Jag 2019Document22 pagesLesson Plan 9 Grade Jag 2019Astrid GomezNo ratings yet
- Overview of The 8th Edition TNM Classification For Head and Neck CancerDocument13 pagesOverview of The 8th Edition TNM Classification For Head and Neck CancerGatot Widyatmo100% (1)
- Drug Study PyrazinamideDocument1 pageDrug Study PyrazinamideEphraim MaravillaNo ratings yet
- CDC Syringe Services Programs InformationDocument2 pagesCDC Syringe Services Programs InformationLeslie RubinNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic Disease of The NewbornDocument2 pagesHemorrhagic Disease of The NewbornsucirahmiiiiiiNo ratings yet
- Assoni2021 Article CurrentStageInTheDevelopmentOfDocument19 pagesAssoni2021 Article CurrentStageInTheDevelopmentOfSeksi IlmiahNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper For Guns, Germs, and Steel by Jared DaimondDocument5 pagesReaction Paper For Guns, Germs, and Steel by Jared Daimondsunshine roblesNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument80 pagesImmunologyMaged HusseinNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Answer Key PINK PACOP 2005Document48 pagesPharmacology Answer Key PINK PACOP 2005Shane KimNo ratings yet
- CGHS Rates - TrivandrumDocument79 pagesCGHS Rates - Trivandrumimran kureshiNo ratings yet
- Hifu and Liposunix Combine MachineDocument29 pagesHifu and Liposunix Combine MachineAnisia StefanNo ratings yet
- Introductiontothe Immune SystemDocument25 pagesIntroductiontothe Immune SystemUyên HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Serum: Levels of Creatine PhosphokinaseDocument2 pagesSerum: Levels of Creatine PhosphokinaseDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Optometry: Accommodative and Binocular Dysfunctions: Prevalence in A Randomised Sample of University StudentsDocument9 pagesOptometry: Accommodative and Binocular Dysfunctions: Prevalence in A Randomised Sample of University StudentsShyannaNo ratings yet
- Wesleyan University-Philippines College of Nursing A.Y. 2022-2023Document30 pagesWesleyan University-Philippines College of Nursing A.Y. 2022-2023Jasmin DaclagNo ratings yet