Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.6 2.7 Animal Plant Cells
2.6 2.7 Animal Plant Cells
Uploaded by
Aida Fithriyatur RohmahOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.6 2.7 Animal Plant Cells
2.6 2.7 Animal Plant Cells
Uploaded by
Aida Fithriyatur RohmahCopyright:
Available Formats
AnimalEuKAryotic
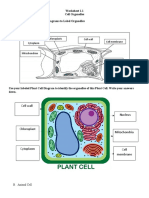
Topic 1.2: Cell vs Plant Cell Cells
Cell Structure
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
Golgi body Smooth ER Nucleus Rough ER
Lysosome
Mitochondrion
Rough ER Cytosol
Smooth ER
Nucleolus Ribosome
Cytosol
(80S)
Nucleus
Membrane
Golgi body Membrane
80S Ribosome
Mitochondrion Vacuole Chloroplast Cell wall
Animal Cell Plant Cell
Micrographs
Eukaryote Micrographs
Golgi complex Chloroplast
Animal Cell (exocrine gland cell) ER (rough) Mitochondrion Plant Cell (palisade mesophyll)
Organelles
Organelles Animalversus
Animal vs Plant CellsCells
Plant
Organelles are compartmentalised structures that serve specific purposes Animal Cells Plant Cells
Examples of eukaryotic organelles include: ︎No chloroplast Have chloroplast
• 80S ribosomes – Responsible for protein synthesis (translation)
• Nucleus – Stores genetic information (site of transcription) No cell wall Cell wall (cellulose)
• Mitochondria – Site of aerobic respiration (ATP production)
• Endoplasmic reticulum – Transports materials between organelles No plasmodesmata Plasmodesmata
• Golgi complex – Sorts, stores, modifies & exports secretory products
• Centrosomes – Involved in cell division (mitosis and meiosis) Temporary vacuoles Large central vacuole
Organelles found only in specific cell types include: Cholesterol present No cholesterol in
• Chloroplasts – Site of photosynthesis (plant cells only) in the cell membrane the cell membrane
• Lysosomes – Breakdown of macromolecules (animal cells)
Glucose → glycogen Glucose → starch
You might also like
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells AnswersDocument3 pagesProkaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells Answersboney75% (4)
- Crooks & Sanjaya 2006 Connectivity ConservationDocument10 pagesCrooks & Sanjaya 2006 Connectivity ConservationIvan SanchezNo ratings yet
- Chicken Genetics Gizmo - ExploreLearningDocument4 pagesChicken Genetics Gizmo - ExploreLearninghsjhsfjdhNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Eukaryotic CellsDocument1 page1.2 Eukaryotic CellsKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- Biology For Engineers: 8.1 What Is A Cell?Document3 pagesBiology For Engineers: 8.1 What Is A Cell?Sunidhi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Bab 2 Tingkatan 1Document58 pagesBab 2 Tingkatan 1azizahembong84No ratings yet
- Plant and Animal CellDocument24 pagesPlant and Animal CellMichel Jay Arguelles EspulgarNo ratings yet
- Plant Animal Cell DiagramsDocument5 pagesPlant Animal Cell Diagramssalagi28No ratings yet
- Cell Notes Class 9Document18 pagesCell Notes Class 9Anshu DashNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1.1 Cell OrganelleDocument2 pagesWorksheet 1.1 Cell OrganelleCyndel TindoyNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellDocument16 pagesAnimal and Plant CellDarlNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1 Plant & Animal CellsDocument16 pagesGrade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1 Plant & Animal CellsTodd SilversteinNo ratings yet
- Unique Structure Organelles: Bacteria Cell 3 Common Things FlagellaDocument1 pageUnique Structure Organelles: Bacteria Cell 3 Common Things FlagellaBiNo ratings yet
- 4 Structures and OrganellesDocument5 pages4 Structures and Organellessalmasadiq2008No ratings yet
- The Cell ActivitiesDocument3 pagesThe Cell Activitiestiareximena0308No ratings yet
- Cell Bio SLDocument103 pagesCell Bio SLkrhimkrNo ratings yet
- Modular Worksheet FinalDocument66 pagesModular Worksheet FinalJouichiro Masamune100% (3)
- Biomedical 01Document26 pagesBiomedical 01api-3706483No ratings yet
- Plant and Animal CellDocument16 pagesPlant and Animal CellWilfredo Arcala Jr.No ratings yet
- CytologyDocument39 pagesCytologyEggNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1 Plant & Animal Cells PDFDocument16 pagesGrade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1 Plant & Animal Cells PDFDavid Jhonson BasnilloNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1 Plant & Animal CellsDocument16 pagesGrade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1 Plant & Animal CellsSandWich TutorialsNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument27 pagesCell Structure and Cell OrganisationAzmaniza AdnanNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cells: Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1Document16 pagesPlant and Animal Cells: Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1wallacedaniyahbNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument32 pagesCell Organellesapi-565439029No ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cells: Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1Document27 pagesPlant and Animal Cells: Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1Reinalyn MendozaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology - Unit - 1Document19 pagesCell Biology - Unit - 1shivangipurohitNo ratings yet
- ch.2 Cell Structure and OrganizationDocument45 pagesch.2 Cell Structure and OrganizationMaha YounusNo ratings yet
- Introduction CellDocument48 pagesIntroduction CellabdNo ratings yet
- Bio105 L1Document38 pagesBio105 L1Aryam AlenziNo ratings yet
- 2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsDocument37 pages2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsJuan Jaylou AnteNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1 Plant & Animal CellsDocument52 pagesGrade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1 Plant & Animal CellsFritzel NavarroNo ratings yet
- Plant Animal CellsDocument19 pagesPlant Animal Cellsits jycdlcrzNo ratings yet
- Cells Review Ws AnswersDocument4 pagesCells Review Ws AnswersTongtun TuntunNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument10 pagesCELLMAAYER MUHAMMADNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellDocument44 pagesAnimal and Plant CellSittie hessa Hadji muslimenNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jul 23, 2023Document12 pagesAdobe Scan Jul 23, 2023yogyatapathak408No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument18 pagesChapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeTownship TownshipNo ratings yet
- Cell - Structure AND FunctionsDocument63 pagesCell - Structure AND FunctionsAdvayNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document3 pagesActivity 3enaniacanoNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 PDFDocument45 pagesUnit 4 PDFSUSHANT SenNo ratings yet
- Tour of The CellDocument60 pagesTour of The Celladisty sncNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY REVIEWE-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesBIOLOGY REVIEWE-WPS OfficeLeanna DaneNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs EukaryoteDocument48 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryotesunifeb128075No ratings yet
- Introduction To Eukaryotic CellDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Eukaryotic CellKali Shankar SinghNo ratings yet
- Module I-Cocepts in BiologyDocument46 pagesModule I-Cocepts in BiologyManan MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Cell TopicDocument29 pagesCell TopicChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- Cell TopicDocument29 pagesCell TopicChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- Cell QuizDocument3 pagesCell QuizEuan CruzNo ratings yet
- Starter: What Is A Cell?Document10 pagesStarter: What Is A Cell?Jomarie Noguerra IINo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Plant and Animal CellsDocument10 pagesLesson 1 Plant and Animal CellsReynold GajusanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Plant and Animal CellsDocument10 pagesLesson 1 Plant and Animal CellsAlfred SolajesNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument18 pagesCells현성JacobNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellDocument41 pagesAnimal and Plant CellSabrina LavegaNo ratings yet
- Cells Study Guide PDFDocument2 pagesCells Study Guide PDFhussein saripNo ratings yet
- Ch8 Class 8 Science Worksheet With Solutions Super Duper Notes PDFDocument16 pagesCh8 Class 8 Science Worksheet With Solutions Super Duper Notes PDFTanmay NathNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure - Bio - Yr91Document18 pagesCell Structure - Bio - Yr91Aameena FarhanNo ratings yet
- Zoo101 (Lec) Assignment - Cell Growth and ReproductionDocument11 pagesZoo101 (Lec) Assignment - Cell Growth and ReproductionJanaCasandra ManitiNo ratings yet
- Knowing The Foundation of LifeDocument47 pagesKnowing The Foundation of LifeAlkhair SangcopanNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument4 pagesCell StructurerueNo ratings yet
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Ans 1.4&1.5 Muscles & JointsDocument2 pagesAns 1.4&1.5 Muscles & JointsAida Fithriyatur RohmahNo ratings yet
- Ans 1.3 The Human SkeletonDocument2 pagesAns 1.3 The Human SkeletonAida Fithriyatur RohmahNo ratings yet
- Ans 1.4&1.5 Muscles & JointsDocument2 pagesAns 1.4&1.5 Muscles & JointsAida Fithriyatur RohmahNo ratings yet
- Ans 1.2 Human Organ SystemsDocument2 pagesAns 1.2 Human Organ SystemsAida Fithriyatur RohmahNo ratings yet
- Ans 1.1 Plant OrgansDocument1 pageAns 1.1 Plant OrgansAida Fithriyatur RohmahNo ratings yet
- 2.1 2.6 2.7 Plant & Animal CellsDocument4 pages2.1 2.6 2.7 Plant & Animal CellsAida Fithriyatur RohmahNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1.2 Human Organ SystemsDocument2 pagesWorksheet 1.2 Human Organ SystemsAida Fithriyatur RohmahNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1.4&1.5 Muscles & JointsDocument2 pagesWorksheet 1.4&1.5 Muscles & JointsAida Fithriyatur RohmahNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2.1 2.6 2.7 Living Things and CellsDocument3 pagesWorksheet 2.1 2.6 2.7 Living Things and CellsAida Fithriyatur RohmahNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1.1 Plant OrgansDocument1 pageWorksheet 1.1 Plant OrgansAida Fithriyatur RohmahNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1.3 The Human SkeletonDocument2 pagesWorksheet 1.3 The Human SkeletonAida Fithriyatur RohmahNo ratings yet
- Summary 1.4 & 1.5Document1 pageSummary 1.4 & 1.5Aida Fithriyatur RohmahNo ratings yet
- RELATIVE - CLAUSE - REDUCTION (Автосохраненный)Document3 pagesRELATIVE - CLAUSE - REDUCTION (Автосохраненный)dina masaripowaNo ratings yet
- m2 l2. Check in ActivityDocument2 pagesm2 l2. Check in ActivityTiffany SelirioNo ratings yet
- Mcqs of PsychologyDocument45 pagesMcqs of PsychologyAHSAN JUTTNo ratings yet
- Oxalic Acid, A Molecule at The Crossroads of Bacterial-Fungal InteractionsDocument29 pagesOxalic Acid, A Molecule at The Crossroads of Bacterial-Fungal InteractionsTetty Arsety GuluhNo ratings yet
- Electron Transfer in BiologyDocument20 pagesElectron Transfer in BiologyVani KaushikNo ratings yet
- Biosafety During Industrial ProductionDocument19 pagesBiosafety During Industrial ProductionGirish Wasudev Ghugare67% (3)
- PONCE - Module 1 - BSN-2 - A18Document7 pagesPONCE - Module 1 - BSN-2 - A18Ponce Kristel Mae ONo ratings yet
- Epigenesis To EpigeneticsDocument38 pagesEpigenesis To EpigeneticsAditi DasNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic TranslationDocument24 pagesEukaryotic TranslationCj ScarletNo ratings yet
- Digestive System 2Document7 pagesDigestive System 2SlaheddineNo ratings yet
- Bifidobacterium Asteroides PRL2011 Genome Analysis Reveals Clues For Colonization of The Insect GutDocument14 pagesBifidobacterium Asteroides PRL2011 Genome Analysis Reveals Clues For Colonization of The Insect Guttissue88No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Bio 12 PDFDocument17 pagesUnit 2 Bio 12 PDFAbdul-Raheem KabalanNo ratings yet
- Identification Et Antibiogramme VITEK2Document4 pagesIdentification Et Antibiogramme VITEK2Bertrand Soppo YokiNo ratings yet
- Selection of Shade-Tolerant Tomato GenotypesDocument6 pagesSelection of Shade-Tolerant Tomato GenotypesShailendra RajanNo ratings yet
- Cotton Production Guideline PDFDocument32 pagesCotton Production Guideline PDFEvans Katuta Mpundu Jr.No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle ControlDocument13 pagesCell Cycle ControlCaue LimaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid MCQ With AnswersDocument4 pagesAmino Acid MCQ With AnswersPrince AsanteNo ratings yet
- Sci 9 q1 Module 3 - RemovedDocument14 pagesSci 9 q1 Module 3 - RemovedClaire AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Capabilities BrochureDocument12 pagesLife Sciences Capabilities BrochurePatrick WingertNo ratings yet
- BG. 6 - Semester (Batch: 2018) : Session:2020-21: (Timetable: BSC-BSCN)Document2 pagesBG. 6 - Semester (Batch: 2018) : Session:2020-21: (Timetable: BSC-BSCN)Narayan BarmanNo ratings yet
- Microbiology The Human Experience 1st Edition Zarrintaj Test BankDocument17 pagesMicrobiology The Human Experience 1st Edition Zarrintaj Test Bankzacharymeliora0h86100% (33)
- Collecting Human Subjects Ethics and The Archive in The History of Science and The Historical Life SciencesDocument10 pagesCollecting Human Subjects Ethics and The Archive in The History of Science and The Historical Life SciencesJéssica PinaNo ratings yet
- Histology Male-1Document1 pageHistology Male-1Yu Tung TsaiNo ratings yet
- The Human Machine by RL Bijlani, SK ManchandaDocument176 pagesThe Human Machine by RL Bijlani, SK ManchandaMUSKANNo ratings yet
- 4-Bacteria-Nutrition-Growth and CultureDocument40 pages4-Bacteria-Nutrition-Growth and Cultureaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Power of Infant Brain Hensch 2016 HarvardDocument6 pagesPower of Infant Brain Hensch 2016 HarvardMariela IrizarryNo ratings yet
- Ans 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument33 pagesAns 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsAdewaleNo ratings yet
- Als Et Al - 2023 - Depression Pathophysiology, Risk Prediction of Recurrence and ComorbidDocument39 pagesAls Et Al - 2023 - Depression Pathophysiology, Risk Prediction of Recurrence and Comorbidkeon.arbabi.altNo ratings yet