Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Parts of Speech
Parts of Speech
Uploaded by
Jhedalyn HilarionOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parts of Speech
Parts of Speech
Uploaded by
Jhedalyn HilarionCopyright:
Available Formats
THE EIGHT PARTS OF SPEECH
There are eight parts of speech in the English language: NOUN, PRONOUN, VERB, ADJECTIVE, ADVERB,
PREPOSITION, CONJUNCTION, AND INTERJECTION.
. A noun is the name of a person, place, thing, or idea.
Nouns have these characteristics:
They are abstract or concrete.
They are proper or common.
Most are singular or plural, but...
Some are collective.
Every noun is either abstract or concrete.
Abstract nouns name things we cannot see, touch, or detect readily through our senses. Abstract
nouns name ideas (existentialism, democracy), measurements (weight, percent), emotions
(love, angst), or qualities (responsibility)
.
Concrete nouns, on the other hand, name persons, including animals (cousins, Roger Rabbit), places
(beach, Chico), or things we can see, touch, or otherwise detect through our senses (smoke, beer).
Every noun is either proper or common.
A proper noun identifies a particular person, animal, place, thing, or idea--Roger Rabbit, for example.
The first letter of each word of a proper noun is capitalized.
A common noun does not name a particular person or thing; rather, it refers to a whole class or type.
Common nouns do not require capitalization.
Proper noun (capitalized) common noun
Sierra Nevada Crystal Wheat is his favorite beer.
The Rooks and the Rangers are our local soccer and baseball teams.
Bidwell Park is one of the largest municipal parks.
Lundberg Family Farm is a sustainable, organic farm.
Most nouns are either singular or plural...
Most nouns are made plural with the addition of s or es. Thus, instructor becomes instructors,
and class becomes classes. Some nouns have irregular plural forms: man becomes men,
and woman becomes women. Child becomes children, and person becomes people.
Many people, both men and women, believe that having children will be a remedy for their existential angst.
Some nouns have the same form in both singular and plural: "A moose is crossing the river. No, wait--
three moose are crossing the river!"
Some nouns are collective.
A collective noun names a collection or group of things. Although a collective noun refers to a group of many
things, it is usually singular in form. We think of a collective noun as singular because its members act in one
accord: The army is withdrawing from those Asian countries that are in negotiations.
PRONOUNS
Pronouns replace nouns. Without them, language would be repetitious, lengthy, and awkward:
President John Kennedy had severe back trouble, and although President John Kennedy approached stairs
gingerly and lifted with care, President John Kennedy did swim and sail, and occasionally President John
Kennedy even managed to play touch football with friends, family members, or co-workers.
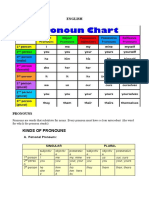
There are six types of pronouns:
1. Personal 4. Reflexive
2. Indefinite 5. Relative
3. Possessive 6. Demonstrative
Personal pronouns also refer to specific persons, places, or things.
First person Second person Third person
Subjective Objective Subjective Objective Subjective Objective
I, we me, us you you he, she, it, they him, her, it, them
Indefinite pronouns refer to general persons, places, or things. Indefinite pronouns all are third-person
pronouns and can be subjects or objects in sentences.
Indefinite pronouns, singular
anyone anybody anything either each
no one nobody nothing another one
someone somebody something any
everyone everybody everything
On the other hand, some indefinite pronouns are plural:
Indefinite pronouns, plural
both few many several
Indefinite pronouns, singular or plural
most any all none some neither
Possessive pronouns
my our your his, her its their whose
mine ours yours his, hers theirs
Reflexive pronouns add emphasis.
Reflexive pronouns
yourself himself, herself, itself
myself ourselves
yourselves themselves
Relative pronouns
that who whoever whose
which whom whomever what
Demonstrative pronouns
this these
that those
All verbs are one of three types:
1. Action verbs Action verbs express physical or mental actions: think, eat, collide, realize, dance.
2. Linking verbs
Another set of linking verbs are those pertaining to our five senses--seeing, tasting, touching, hearing, and
smelling--and how we perceive the world: the verbs appear, seem, look, feel, smell, taste, and sound
1st person (I; we) 2nd person (you) 3rd person (she, he, it; they)
present am; are are is; are
past was; were were was; were
participle [have] been; [had] been [have] been; [had] been [has] been; [had] been
3. Helping verbs
have, has, had
to be: am, are, is, was, were, been
do, does, did
will, shall
would, could, should, can, may, might
You might also like
- Astm C 423Document12 pagesAstm C 423Abhinav AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Jabsco 15780-0000 Parts ListDocument2 pagesJabsco 15780-0000 Parts ListClarence Clar100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English IV - COMPOUND SENTENCEDocument12 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in English IV - COMPOUND SENTENCEMadhie Gre Dela Provi94% (16)
- Pronouns Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesPronouns Lesson PlanAshford Thom100% (1)
- Forgive and Forget PDFDocument410 pagesForgive and Forget PDFhpssomgNo ratings yet
- Clair de Lune (Debussy) Easy Piano Sheet MusicDocument1 pageClair de Lune (Debussy) Easy Piano Sheet MusicSiebert NixNo ratings yet
- Medication Schedule Template 16Document27 pagesMedication Schedule Template 16Maria UlfaNo ratings yet
- PronounDocument27 pagesPronounannisa nurul apNo ratings yet
- Pronouns - Basic NotesDocument4 pagesPronouns - Basic NotesFrancis Guerrero TimbalNo ratings yet
- Unit ThreeDocument9 pagesUnit ThreefaizaNo ratings yet
- Pronouns: Subject: Language Description Code: TESL 1024 Lecturer: DR. Jane Student's Name: Aisha AzmanDocument13 pagesPronouns: Subject: Language Description Code: TESL 1024 Lecturer: DR. Jane Student's Name: Aisha AzmanAisha AzmanNo ratings yet
- English Grammar - 1Document57 pagesEnglish Grammar - 1Alfred MwayutaNo ratings yet
- Kinds of AdverbDocument6 pagesKinds of AdverbBryan CasidoNo ratings yet
- PronounDocument4 pagesPronounmohammadadan424No ratings yet
- PronounsDocument4 pagesPronounsmrs.star999No ratings yet
- Personal Pronoun: You, He, She, It, We They, Me, Him, Her, Us, and Them Are All PersonalDocument12 pagesPersonal Pronoun: You, He, She, It, We They, Me, Him, Her, Us, and Them Are All PersonalWH LimNo ratings yet
- Group 2 PronounDocument29 pagesGroup 2 PronounJacob Clint LipuraNo ratings yet
- Unit Three 3 PronounsDocument9 pagesUnit Three 3 Pronounskatia oussNo ratings yet
- l1 Parts of SpeechDocument54 pagesl1 Parts of SpeechNeilJohn MogatoNo ratings yet
- 08 - 09 October 2020: Understanding Noun and Its TypesDocument8 pages08 - 09 October 2020: Understanding Noun and Its TypesFitri DelitaNo ratings yet
- Communicative English Grammar IIDocument63 pagesCommunicative English Grammar IIAman MatebieNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - S1 - PronounsDocument12 pagesWeek 2 - S1 - PronounsTechnical InformationNo ratings yet
- Prounouns and DeterminersDocument2 pagesProunouns and DeterminersFanni BNo ratings yet
- Pronouns Understanding The Essential Parts of SpeechDocument8 pagesPronouns Understanding The Essential Parts of SpeechHamdan MustafaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument10 pagesParts of SpeechSaikat SahaNo ratings yet
- Indefinite Pronoun - WikipediaDocument7 pagesIndefinite Pronoun - WikipediaShex KingNo ratings yet
- PronounDocument29 pagesPronounAlfa RizkiNo ratings yet
- Pronouns, Verbs, Simple TensesDocument56 pagesPronouns, Verbs, Simple TensesCharoNo ratings yet
- English: Kinds of PronounsDocument9 pagesEnglish: Kinds of PronounsMarynell ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Pronouns 7thDocument3 pagesPronouns 7thNajwa SerhanNo ratings yet
- PRONOUNS.docxDocument3 pagesPRONOUNS.docxJairo Martinez EscalanteNo ratings yet
- PRONOUNSDocument3 pagesPRONOUNSdiakitebocar10No ratings yet
- 4 Word Classes Pronouns Conjunctions Prepositions DeterminersDocument23 pages4 Word Classes Pronouns Conjunctions Prepositions Determinersjangauci123No ratings yet
- Pronoun II 27Document6 pagesPronoun II 27TanmoyNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument3 pagesPronounsFatouNo ratings yet
- English Portofolio PronounDocument2 pagesEnglish Portofolio PronounFirman AdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Types of Pronouns PDFDocument2 pagesTypes of Pronouns PDFSumit ShankarNo ratings yet
- PronounDocument38 pagesPronounAlfa RizkiNo ratings yet
- Pronouns and AdjectivesDocument13 pagesPronouns and AdjectivesAngela Zavala VillalobosNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument4 pagesProjectMicheal FiverrNo ratings yet
- PRONOUNS ReportDocument16 pagesPRONOUNS Reportashik aem ashilNo ratings yet
- PRONOUNSDocument3 pagesPRONOUNSleydi merinoNo ratings yet
- 2ND Pronoun PPT For Guided NotesDocument26 pages2ND Pronoun PPT For Guided NotesAdam SudrajatNo ratings yet
- Green 3D Gradient English Parts of Speech Pronoun Educational PresentationDocument19 pagesGreen 3D Gradient English Parts of Speech Pronoun Educational PresentationNiloufar GholamipourNo ratings yet
- PronounDocument25 pagesPronounJolina VelascoNo ratings yet
- Hers, It, Its, They, Them, Their, Theirs.: Table of Personal PronounsDocument5 pagesHers, It, Its, They, Them, Their, Theirs.: Table of Personal PronounsWolfo ChicoNo ratings yet
- PRONOUNSDocument10 pagesPRONOUNSa_j_sanyalNo ratings yet
- Final Test Vocabulary SummaryDocument25 pagesFinal Test Vocabulary Summarysharencecilia2015No ratings yet
- Pronouns of English Grammar Guides - 95690Document2 pagesPronouns of English Grammar Guides - 95690GemaNo ratings yet
- 00 Parts of SpeechDocument18 pages00 Parts of SpeechBlessie Marie SamontañezNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Pronouns - E9Document4 pagesKinds of Pronouns - E929camziiNo ratings yet
- Biz 1054Document19 pagesBiz 1054qawsedNo ratings yet
- Types of PronounsDocument10 pagesTypes of PronounsJeremy BrownNo ratings yet
- Pronouns: Presented By: Indah Dwiphayanti Nurika Primastuti Rina Astri FaizatyDocument4 pagesPronouns: Presented By: Indah Dwiphayanti Nurika Primastuti Rina Astri FaizatyASTRI FNo ratings yet
- Engl 103Document1 pageEngl 103heartgeoligao13No ratings yet
- Yellow Booklet - Revised 2013 PDFDocument42 pagesYellow Booklet - Revised 2013 PDFBabak EbrahimiNo ratings yet
- Indefinite PronounsDocument20 pagesIndefinite Pronounsprox1maNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech 3Document48 pagesParts of Speech 3Taleb AbboudNo ratings yet
- Parts Od Speech-6-12Document7 pagesParts Od Speech-6-12Prim SalvatoreNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument17 pagesParts of SpeechMaria Alejandra VillamizarNo ratings yet
- A Pronoun Is A Word: Used in Place of A Noun or Another PronounDocument38 pagesA Pronoun Is A Word: Used in Place of A Noun or Another Pronounzain asmatNo ratings yet
- College EngDocument5 pagesCollege EngPatricia SierraNo ratings yet
- PronounDocument5 pagesPronounzk4039271No ratings yet
- Functional English 3. Pronoun and Its TypesDocument21 pagesFunctional English 3. Pronoun and Its Typessawerarahim456No ratings yet
- Kinds of PronounDocument2 pagesKinds of PronounBrito Raj100% (1)
- The Little Magazine RamRamDocument5 pagesThe Little Magazine RamRamJasdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Physical Pendulum - Angular SHM - Solved ProblemsDocument7 pagesPhysical Pendulum - Angular SHM - Solved ProblemsHomayoon GeramifarNo ratings yet
- Sony Kdl-40xbr9 Kdl-46xbr9 Kdl-52xbr9 Ex2m ChassisDocument118 pagesSony Kdl-40xbr9 Kdl-46xbr9 Kdl-52xbr9 Ex2m ChassisAndy WilsonNo ratings yet
- Types of ParentingDocument13 pagesTypes of ParentingViseshNo ratings yet
- Asmaa Mamdouh CVDocument1 pageAsmaa Mamdouh CVAsmaa MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Oma TS MLP V3 - 2 20110719 ADocument128 pagesOma TS MLP V3 - 2 20110719 AkennychanklNo ratings yet
- Jobdesc Project Officer Intern TRACK SDGsDocument2 pagesJobdesc Project Officer Intern TRACK SDGssocmed gistiNo ratings yet
- How To Download A Windows 10 ISO File - PCWorldDocument3 pagesHow To Download A Windows 10 ISO File - PCWorldRajeev BatraNo ratings yet
- Hell by D.L. MoodyDocument7 pagesHell by D.L. MoodyLisaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 FMCC221 - Introduction To International Businesss - Part 1Document19 pages1.2 FMCC221 - Introduction To International Businesss - Part 1Bernie D. TeguenosNo ratings yet
- Course CurriculumDocument3 pagesCourse CurriculumPRASENJIT MUKHERJEENo ratings yet
- Poster FinalDocument1 pagePoster FinalKrish vasisthaNo ratings yet
- Biogas ProductionDocument7 pagesBiogas ProductionFagbohungbe MichaelNo ratings yet
- InnerFiles Current Year PDF 2023Document687 pagesInnerFiles Current Year PDF 2023shravanibagul04No ratings yet
- HMT (U4)Document23 pagesHMT (U4)maniNo ratings yet
- TakeawayDocument6 pagesTakeawayWilman VasquezNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions FinalDocument11 pagesSample Questions FinaldunyaNo ratings yet
- 3700 S 24 Rev 0 ENDocument3 pages3700 S 24 Rev 0 ENJoão CorrêaNo ratings yet
- Edmund Burke Maroon 2/4/18Document1 pageEdmund Burke Maroon 2/4/18Chicago MaroonNo ratings yet
- 0547 s06 TN 3Document20 pages0547 s06 TN 3mstudy123456No ratings yet
- Natural Gas - Pipe SizingDocument6 pagesNatural Gas - Pipe SizinglekakasNo ratings yet
- IRP ReportDocument13 pagesIRP ReportAnkit JajooNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: I've Got Two SistersDocument5 pagesLesson Plan: I've Got Two SistersBianca BybyNo ratings yet
- Understanding Sars-Cov-2-Induced Systemic Amyloidosis: BiorxivDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Sars-Cov-2-Induced Systemic Amyloidosis: BiorxivAntonisNo ratings yet