Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 Product of Genetically Modified Organism
1 Product of Genetically Modified Organism
Uploaded by
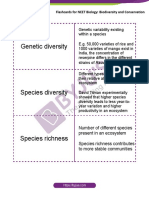
Julius Bien Mendoza1) The document discusses genetic diversity, species diversity, and ecosystem diversity. Genetic diversity refers to variation within a species, species diversity refers to the variety of species in a location, and ecosystem diversity refers to the habitats that support different species.
2) Examples of each type of diversity are provided, such as varieties of mango illustrating genetic diversity and Australia's Great Barrier Reef demonstrating high species diversity.
3) The key differences between in situ and ex situ conservation are explained. In situ conservation maintains species in their natural habitats, while ex situ conservation occurs outside the original habitat and provides protection, medical care, and control over reproduction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Chapter 1 The Science of Biology, Raven Biology 9th Edition Chapter OutlineDocument10 pagesChapter 1 The Science of Biology, Raven Biology 9th Edition Chapter Outlinemaxpilecki100% (2)
- Product of Genetically Modified OrganismDocument2 pagesProduct of Genetically Modified OrganismJulius Bien MendozaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 - VIS Chart - Online VersionDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 4 - VIS Chart - Online VersionJoão victor Baldanzi silvaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer BioconDocument3 pagesReviewer BioconVersace Luestro de GraciaNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Evolution GZ 2018 ChsDocument56 pagesGenetics and Evolution GZ 2018 ChsSayali PatilNo ratings yet
- Bio 14 NotesDocument7 pagesBio 14 NotesCielo EugenioNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Zoolog 1 PDFDocument15 pagesAssignment of Zoolog 1 PDFSyed Haider Ali Shah SheraziNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-3 AsynchronousDocument3 pagesWorksheet-3 AsynchronousadamcabasNo ratings yet
- SCI8 - Q4 - M4 - Concept of A SpeciesDocument20 pagesSCI8 - Q4 - M4 - Concept of A SpeciesdonescatherinejoyNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity NewDocument64 pagesBiodiversity NewJe Lan NieNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Conservation PDFDocument7 pagesBiodiversity and Conservation PDFDeepikaNo ratings yet
- SR4758Document9 pagesSR4758smrutishree25No ratings yet
- 23 BiodiversityDocument8 pages23 Biodiversitysalihundamravikumar100No ratings yet
- Lesson-4 - Ecosystem BiodiversityDocument19 pagesLesson-4 - Ecosystem BiodiversityIrah May CruzatNo ratings yet
- Biological Diversity 1Document108 pagesBiological Diversity 1Dave McMordieNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Its ConservationDocument30 pagesBiodiversity and Its ConservationPratik VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Envi Scie Midterm ReviewerDocument3 pagesEnvi Scie Midterm ReviewerJayce TanNo ratings yet
- A. Human Activities & Stability of EcosystemsDocument7 pagesA. Human Activities & Stability of EcosystemsJames Philip RelleveNo ratings yet
- Week 6 7 Science BiodiversityDocument10 pagesWeek 6 7 Science BiodiversityMarlon James TobiasNo ratings yet
- Activity-3 1Document3 pagesActivity-3 1Paul Jastine RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Activity 22-23-24-25 StsDocument8 pagesActivity 22-23-24-25 StsMarizuela QuidayNo ratings yet
- Biodiverity and Conservation PDF SummarizedDocument15 pagesBiodiverity and Conservation PDF SummarizedmohtashimahmNo ratings yet
- Group 8 HW3 Environmental ScienceDocument21 pagesGroup 8 HW3 Environmental ScienceVy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- T SC 2549805 Science Knowledge Organiser Evolution and Inheritance Year 6 Ver 4Document2 pagesT SC 2549805 Science Knowledge Organiser Evolution and Inheritance Year 6 Ver 4eronkyleNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument18 pagesReportjuvy anne PobleteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Biodiversity (Form 2 KSSM)Document31 pagesChapter 1 - Biodiversity (Form 2 KSSM)scribdudal81% (77)
- Week 2 - Biodiversity PDFDocument4 pagesWeek 2 - Biodiversity PDFjennyNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Biodiversity: Environmental Science 1Document4 pagesWeek 2 Biodiversity: Environmental Science 1Ethan RosarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-5 Environmental ReviewerDocument5 pagesChapter 4-5 Environmental ReviewerJade Chris Tine AnitoNo ratings yet
- Ecological Management 1Document4 pagesEcological Management 1AJAYI PETERNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Fascinating World of Reptiles Habitat Species Nutrition Reproduction and StructurDocument7 pagesExploring The Fascinating World of Reptiles Habitat Species Nutrition Reproduction and Structursanjivdutta626No ratings yet
- Diversity of Living World: Very Short Answer QuestionsDocument9 pagesDiversity of Living World: Very Short Answer Questionsgowtham metikotiNo ratings yet
- WB8 Sci SAMPLE-74-138Document65 pagesWB8 Sci SAMPLE-74-138lengocthuytien0725No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Community Ecology PDFDocument92 pagesChapter 3 Community Ecology PDFnurul syafiyah binti yusoffNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Its ConservationDocument55 pagesBiodiversity and Its ConservationlibrarianNo ratings yet
- Bab IiiDocument3 pagesBab IiiVenty HabibieNo ratings yet
- Habitat and Adaptation: Structural Adaptation, Just As The Limbs of BirdsDocument1 pageHabitat and Adaptation: Structural Adaptation, Just As The Limbs of BirdsGatcha GamesNo ratings yet
- CommunitiesDocument40 pagesCommunitiesCHERRY LYN BELGIRANo ratings yet
- BIODDocument5 pagesBIODJedan TopiagonNo ratings yet
- C 1Document59 pagesC 1mafe1432No ratings yet
- Biology Unit 4Document30 pagesBiology Unit 4Kayleen PerdanaNo ratings yet
- LEC BiodiversityDocument2 pagesLEC BiodiversityMariz RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Arzadon Iv - Quirino - V - Reflection Paper1 - Ese150 - Section A27Document10 pagesArzadon Iv - Quirino - V - Reflection Paper1 - Ese150 - Section A27Quirino Arzadon IVNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and ConservationDocument46 pagesBiodiversity and ConservationrajeshwariNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 - Bio-DiversityDocument12 pagesLesson 12 - Bio-DiversitySwarnapaliliyanageNo ratings yet
- Science - Form - 2 1 27 10 27Document18 pagesScience - Form - 2 1 27 10 27Gan Wei ShengNo ratings yet
- Science, Technology, and Society Lecture 5: Biodiversity and Human SocietyDocument4 pagesScience, Technology, and Society Lecture 5: Biodiversity and Human Societyjennylyn karunungan100% (1)
- Mechanism of Evolution: Charles DarwinDocument10 pagesMechanism of Evolution: Charles DarwinChristine FayeNo ratings yet
- Bio1 - Unit 1 LectureDocument7 pagesBio1 - Unit 1 LectureCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Marine Biology and Resource ConservationDocument420 pagesMarine Biology and Resource ConservationleavesmoonNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity - HandoutsDocument1 pageBiodiversity - Handoutsjoan marie PeliasNo ratings yet
- Adaptation: Survival of The FittestDocument29 pagesAdaptation: Survival of The FittestDanielle ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Climate and Adaptation in Tropical RainforestDocument9 pagesClimate and Adaptation in Tropical Rainforesthweta173No ratings yet
- Biodiversity, Classification and Conservation: BiologyDocument41 pagesBiodiversity, Classification and Conservation: BiologyAnggraeni Kusuma WardaniNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document65 pagesGroup 1025wilmelNo ratings yet
- Gannar, Mi. Biodiversity. Realnareal (Repaired)Document19 pagesGannar, Mi. Biodiversity. Realnareal (Repaired)Emely RomualdoNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity of FreshwaterDocument5 pagesBiodiversity of FreshwaterErica GamePlayNo ratings yet
- U1L4 - Keystone Species Critical ReadingDocument4 pagesU1L4 - Keystone Species Critical Readingyohomieyougood123No ratings yet
- Scie 102 Envi - Sci Midterm Week - 6 Part - 1Document32 pagesScie 102 Envi - Sci Midterm Week - 6 Part - 1Jayce TanNo ratings yet
- Mid EnvDocument8 pagesMid EnvSachya GhoshNo ratings yet
- Gned10 ReviewerDocument4 pagesGned10 ReviewerJulius Bien MendozaNo ratings yet
- Malunggay FriesDocument11 pagesMalunggay FriesJulius Bien MendozaNo ratings yet
- Product of Genetically Modified OrganismDocument2 pagesProduct of Genetically Modified OrganismJulius Bien MendozaNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified OrganismDocument1 pageGenetically Modified OrganismJulius Bien MendozaNo ratings yet
- Aristotle - Vol. 02 - Posterior Analytics (V. Tredennick Loeb. 1960)Document784 pagesAristotle - Vol. 02 - Posterior Analytics (V. Tredennick Loeb. 1960)jcaballero67% (3)
- (FINAL) Local Demo Lesson PlanDocument15 pages(FINAL) Local Demo Lesson Planclent girayNo ratings yet
- Western Central Pacific: Fao Species Identification Guide For Fishery PurposesDocument2 pagesWestern Central Pacific: Fao Species Identification Guide For Fishery PurposesDhea AmandaNo ratings yet
- Bio Factsheet 297 ExtinctionDocument2 pagesBio Factsheet 297 ExtinctionSue Adames de VelascoNo ratings yet
- Cob-Ch11 EvolutionDocument36 pagesCob-Ch11 EvolutiongaryNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Sa Gen BioDocument4 pagesReviewer Sa Gen BioSmythNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity For Cot 1Document4 pagesBiodiversity For Cot 1Trisha Melrose MilanesNo ratings yet
- Las 7 Bio2 PDFDocument14 pagesLas 7 Bio2 PDFPeanut BlobNo ratings yet
- The Rise of The Evolution FraudDocument224 pagesThe Rise of The Evolution FraudSamscribdingNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity HotspotDocument4 pagesBiodiversity Hotspotabhijit joshiNo ratings yet
- Keys - THE GENUS CORTINARIUS I by P D OrtonDocument82 pagesKeys - THE GENUS CORTINARIUS I by P D Ortonbobapera074No ratings yet
- Coridius Nepalensis Coridius Singhalanus C. ChinensisDocument8 pagesCoridius Nepalensis Coridius Singhalanus C. ChinensisHiren GogoiNo ratings yet
- GENBIO2 Mod.17 Cladistic SystemDocument15 pagesGENBIO2 Mod.17 Cladistic SystemBea Bayona JoloNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Animals and SpiecesDocument7 pagesConservation of Animals and SpiecescontactjhovinNo ratings yet
- Praktis Biologi Bab 8 T5?Document4 pagesPraktis Biologi Bab 8 T5?NURHANA KOH BINTI ABDULLAH MoeNo ratings yet
- Wang Zhang 2019 Two New Reticuluma From ChinaDocument7 pagesWang Zhang 2019 Two New Reticuluma From ChinakrisztinahorNo ratings yet
- Mendoza WebquestDocument3 pagesMendoza Webquestapi-267645354No ratings yet
- Megharbi Et Al 2021Document11 pagesMegharbi Et Al 2021Ghizlene HafedNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Checkpoint 1 AssignmentDocument4 pagesUnit 4 Checkpoint 1 AssignmentAndrew MNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasi Dan Komposisi Fitoplankton Di Danau LimanDocument8 pagesKlasifikasi Dan Komposisi Fitoplankton Di Danau LimanRoury El-FathNo ratings yet
- AlishaDocument41 pagesAlishaGirl StruggleNo ratings yet
- Alice in The Land of PlantsDocument384 pagesAlice in The Land of PlantsWellington FavaNo ratings yet
- Snakes of The World A Supplement by Boundy Jeff WallachDocument284 pagesSnakes of The World A Supplement by Boundy Jeff WallachRoullienNo ratings yet
- BIO153 16 Tutorial 9 PDFDocument19 pagesBIO153 16 Tutorial 9 PDFUsama AdnanNo ratings yet
- ESS - Topic 3.2Document30 pagesESS - Topic 3.2Pol Ayra FuenteNo ratings yet
- An Update of Wallace's Zoogeographic Regions of The WorldDocument6 pagesAn Update of Wallace's Zoogeographic Regions of The WorldsongkoroNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Taxonomic Survey of Aquatic Plants of Feni District, BangladeshDocument9 pagesPreliminary Taxonomic Survey of Aquatic Plants of Feni District, Bangladeshshuvo devNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument13 pagesBiodiversityNiveditha VinodNo ratings yet
- Living Things and Their EnvironmentDocument3 pagesLiving Things and Their EnvironmentVergzMonch EspielNo ratings yet
1 Product of Genetically Modified Organism
1 Product of Genetically Modified Organism
Uploaded by
Julius Bien Mendoza0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pages1) The document discusses genetic diversity, species diversity, and ecosystem diversity. Genetic diversity refers to variation within a species, species diversity refers to the variety of species in a location, and ecosystem diversity refers to the habitats that support different species.
2) Examples of each type of diversity are provided, such as varieties of mango illustrating genetic diversity and Australia's Great Barrier Reef demonstrating high species diversity.
3) The key differences between in situ and ex situ conservation are explained. In situ conservation maintains species in their natural habitats, while ex situ conservation occurs outside the original habitat and provides protection, medical care, and control over reproduction.
Original Description:
1 product of Genetically Modified Organism
Original Title
1 product of Genetically Modified Organism
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The document discusses genetic diversity, species diversity, and ecosystem diversity. Genetic diversity refers to variation within a species, species diversity refers to the variety of species in a location, and ecosystem diversity refers to the habitats that support different species.
2) Examples of each type of diversity are provided, such as varieties of mango illustrating genetic diversity and Australia's Great Barrier Reef demonstrating high species diversity.
3) The key differences between in situ and ex situ conservation are explained. In situ conservation maintains species in their natural habitats, while ex situ conservation occurs outside the original habitat and provides protection, medical care, and control over reproduction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pages1 Product of Genetically Modified Organism
1 Product of Genetically Modified Organism
Uploaded by
Julius Bien Mendoza1) The document discusses genetic diversity, species diversity, and ecosystem diversity. Genetic diversity refers to variation within a species, species diversity refers to the variety of species in a location, and ecosystem diversity refers to the habitats that support different species.
2) Examples of each type of diversity are provided, such as varieties of mango illustrating genetic diversity and Australia's Great Barrier Reef demonstrating high species diversity.
3) The key differences between in situ and ex situ conservation are explained. In situ conservation maintains species in their natural habitats, while ex situ conservation occurs outside the original habitat and provides protection, medical care, and control over reproduction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Republic of the Philippines
CAVITE STATE UNIVERSITY-CCAT
Cavite College of Arts and Trades Campus
Rosario, Cavite
DEPARTMENT OF ARTS AND SCIENCES
GNED 06: SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY, AND SOCIETY
LESSON 4: Genetically Modified Organism
Name: Lady Anne A. Rabin
Course/Year/Sec.: BSBM 201-E
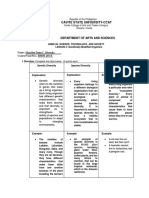
I. Direction. Complete the table below. 10 points each.
Genetic Diversity Species Diversity Ecosystem Diversity
Explanation: Explanation: Explanation:
● Genetic diversity, ● Species diversity
based on the word refers to the ● Ecosystem diversity
itself, refers to the diversity of plants refers to the habitat
diversity of each and animals of each species. All
animal or plant that according to their living organisms
has its own set of biological have diversity when
genes. It means that organization, which it comes to
all living things we call species that ecosystems
have diversity live in a particular because they have
because of their location. different responses,
different genetic tolerances, and
characteristics. needs when it
comes to their
habitats.
Example: Example: Example:
● The varieties of
mango, which ● A good example of Some scenarios that show
include the carabao species diversity is ecosystem diversity are the
mango, the indian Australia's Great following:
mango, the Barrier Reef, which
alphonso mango, contains the world's ● Dogs can't live
the kesar mango, largest collection of underwater, but
and far too many coral reefs, with 400 whales can.
others to list, are a types of coral, 1,500 ● A polar bear can't
good example of species of fish, and live in a tropical
genetic diversity. 4,000 types of area, but a jaguar
The reason why mollusks. can.
there are many
different types of
mango is because
farmers used to do
plant breeding to
produce a new
hybrid variety by
crossing two
dissimilar varieties.
It helps us bring
together the
features of both
varieties in a single
hybrid.
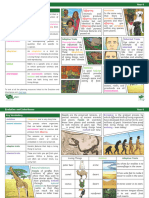
II. Using the Venn Diagram, compare and contrast In situ conservation to Ex situ Conservation. 10 points.
In Situ Conservation Ex Situ
Conservation
This type of conservation
refers to conserving living This type of conservation refers
Its goal is to
organisms in their natural or to the conservation of living
conserve all
original habitat so that when organisms outside of their
living natural or original habitat so that
the time comes that they are
ready to be released, their
species. they can have someone who will
behavior and ways of survival control their species, assess
are all natural, like how they them for medical attention, and
used to be. protect them from predators.
Prepared by:
ROMMEL MARIANO
Instructor, DAS
You might also like
- Chapter 1 The Science of Biology, Raven Biology 9th Edition Chapter OutlineDocument10 pagesChapter 1 The Science of Biology, Raven Biology 9th Edition Chapter Outlinemaxpilecki100% (2)
- Product of Genetically Modified OrganismDocument2 pagesProduct of Genetically Modified OrganismJulius Bien MendozaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 - VIS Chart - Online VersionDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 4 - VIS Chart - Online VersionJoão victor Baldanzi silvaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer BioconDocument3 pagesReviewer BioconVersace Luestro de GraciaNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Evolution GZ 2018 ChsDocument56 pagesGenetics and Evolution GZ 2018 ChsSayali PatilNo ratings yet
- Bio 14 NotesDocument7 pagesBio 14 NotesCielo EugenioNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Zoolog 1 PDFDocument15 pagesAssignment of Zoolog 1 PDFSyed Haider Ali Shah SheraziNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-3 AsynchronousDocument3 pagesWorksheet-3 AsynchronousadamcabasNo ratings yet
- SCI8 - Q4 - M4 - Concept of A SpeciesDocument20 pagesSCI8 - Q4 - M4 - Concept of A SpeciesdonescatherinejoyNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity NewDocument64 pagesBiodiversity NewJe Lan NieNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Conservation PDFDocument7 pagesBiodiversity and Conservation PDFDeepikaNo ratings yet
- SR4758Document9 pagesSR4758smrutishree25No ratings yet
- 23 BiodiversityDocument8 pages23 Biodiversitysalihundamravikumar100No ratings yet
- Lesson-4 - Ecosystem BiodiversityDocument19 pagesLesson-4 - Ecosystem BiodiversityIrah May CruzatNo ratings yet
- Biological Diversity 1Document108 pagesBiological Diversity 1Dave McMordieNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Its ConservationDocument30 pagesBiodiversity and Its ConservationPratik VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Envi Scie Midterm ReviewerDocument3 pagesEnvi Scie Midterm ReviewerJayce TanNo ratings yet
- A. Human Activities & Stability of EcosystemsDocument7 pagesA. Human Activities & Stability of EcosystemsJames Philip RelleveNo ratings yet
- Week 6 7 Science BiodiversityDocument10 pagesWeek 6 7 Science BiodiversityMarlon James TobiasNo ratings yet
- Activity-3 1Document3 pagesActivity-3 1Paul Jastine RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Activity 22-23-24-25 StsDocument8 pagesActivity 22-23-24-25 StsMarizuela QuidayNo ratings yet
- Biodiverity and Conservation PDF SummarizedDocument15 pagesBiodiverity and Conservation PDF SummarizedmohtashimahmNo ratings yet
- Group 8 HW3 Environmental ScienceDocument21 pagesGroup 8 HW3 Environmental ScienceVy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- T SC 2549805 Science Knowledge Organiser Evolution and Inheritance Year 6 Ver 4Document2 pagesT SC 2549805 Science Knowledge Organiser Evolution and Inheritance Year 6 Ver 4eronkyleNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument18 pagesReportjuvy anne PobleteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Biodiversity (Form 2 KSSM)Document31 pagesChapter 1 - Biodiversity (Form 2 KSSM)scribdudal81% (77)
- Week 2 - Biodiversity PDFDocument4 pagesWeek 2 - Biodiversity PDFjennyNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Biodiversity: Environmental Science 1Document4 pagesWeek 2 Biodiversity: Environmental Science 1Ethan RosarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-5 Environmental ReviewerDocument5 pagesChapter 4-5 Environmental ReviewerJade Chris Tine AnitoNo ratings yet
- Ecological Management 1Document4 pagesEcological Management 1AJAYI PETERNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Fascinating World of Reptiles Habitat Species Nutrition Reproduction and StructurDocument7 pagesExploring The Fascinating World of Reptiles Habitat Species Nutrition Reproduction and Structursanjivdutta626No ratings yet
- Diversity of Living World: Very Short Answer QuestionsDocument9 pagesDiversity of Living World: Very Short Answer Questionsgowtham metikotiNo ratings yet
- WB8 Sci SAMPLE-74-138Document65 pagesWB8 Sci SAMPLE-74-138lengocthuytien0725No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Community Ecology PDFDocument92 pagesChapter 3 Community Ecology PDFnurul syafiyah binti yusoffNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Its ConservationDocument55 pagesBiodiversity and Its ConservationlibrarianNo ratings yet
- Bab IiiDocument3 pagesBab IiiVenty HabibieNo ratings yet
- Habitat and Adaptation: Structural Adaptation, Just As The Limbs of BirdsDocument1 pageHabitat and Adaptation: Structural Adaptation, Just As The Limbs of BirdsGatcha GamesNo ratings yet
- CommunitiesDocument40 pagesCommunitiesCHERRY LYN BELGIRANo ratings yet
- BIODDocument5 pagesBIODJedan TopiagonNo ratings yet
- C 1Document59 pagesC 1mafe1432No ratings yet
- Biology Unit 4Document30 pagesBiology Unit 4Kayleen PerdanaNo ratings yet
- LEC BiodiversityDocument2 pagesLEC BiodiversityMariz RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Arzadon Iv - Quirino - V - Reflection Paper1 - Ese150 - Section A27Document10 pagesArzadon Iv - Quirino - V - Reflection Paper1 - Ese150 - Section A27Quirino Arzadon IVNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and ConservationDocument46 pagesBiodiversity and ConservationrajeshwariNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 - Bio-DiversityDocument12 pagesLesson 12 - Bio-DiversitySwarnapaliliyanageNo ratings yet
- Science - Form - 2 1 27 10 27Document18 pagesScience - Form - 2 1 27 10 27Gan Wei ShengNo ratings yet
- Science, Technology, and Society Lecture 5: Biodiversity and Human SocietyDocument4 pagesScience, Technology, and Society Lecture 5: Biodiversity and Human Societyjennylyn karunungan100% (1)
- Mechanism of Evolution: Charles DarwinDocument10 pagesMechanism of Evolution: Charles DarwinChristine FayeNo ratings yet
- Bio1 - Unit 1 LectureDocument7 pagesBio1 - Unit 1 LectureCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Marine Biology and Resource ConservationDocument420 pagesMarine Biology and Resource ConservationleavesmoonNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity - HandoutsDocument1 pageBiodiversity - Handoutsjoan marie PeliasNo ratings yet
- Adaptation: Survival of The FittestDocument29 pagesAdaptation: Survival of The FittestDanielle ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Climate and Adaptation in Tropical RainforestDocument9 pagesClimate and Adaptation in Tropical Rainforesthweta173No ratings yet
- Biodiversity, Classification and Conservation: BiologyDocument41 pagesBiodiversity, Classification and Conservation: BiologyAnggraeni Kusuma WardaniNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document65 pagesGroup 1025wilmelNo ratings yet
- Gannar, Mi. Biodiversity. Realnareal (Repaired)Document19 pagesGannar, Mi. Biodiversity. Realnareal (Repaired)Emely RomualdoNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity of FreshwaterDocument5 pagesBiodiversity of FreshwaterErica GamePlayNo ratings yet
- U1L4 - Keystone Species Critical ReadingDocument4 pagesU1L4 - Keystone Species Critical Readingyohomieyougood123No ratings yet
- Scie 102 Envi - Sci Midterm Week - 6 Part - 1Document32 pagesScie 102 Envi - Sci Midterm Week - 6 Part - 1Jayce TanNo ratings yet
- Mid EnvDocument8 pagesMid EnvSachya GhoshNo ratings yet
- Gned10 ReviewerDocument4 pagesGned10 ReviewerJulius Bien MendozaNo ratings yet
- Malunggay FriesDocument11 pagesMalunggay FriesJulius Bien MendozaNo ratings yet
- Product of Genetically Modified OrganismDocument2 pagesProduct of Genetically Modified OrganismJulius Bien MendozaNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified OrganismDocument1 pageGenetically Modified OrganismJulius Bien MendozaNo ratings yet
- Aristotle - Vol. 02 - Posterior Analytics (V. Tredennick Loeb. 1960)Document784 pagesAristotle - Vol. 02 - Posterior Analytics (V. Tredennick Loeb. 1960)jcaballero67% (3)
- (FINAL) Local Demo Lesson PlanDocument15 pages(FINAL) Local Demo Lesson Planclent girayNo ratings yet
- Western Central Pacific: Fao Species Identification Guide For Fishery PurposesDocument2 pagesWestern Central Pacific: Fao Species Identification Guide For Fishery PurposesDhea AmandaNo ratings yet
- Bio Factsheet 297 ExtinctionDocument2 pagesBio Factsheet 297 ExtinctionSue Adames de VelascoNo ratings yet
- Cob-Ch11 EvolutionDocument36 pagesCob-Ch11 EvolutiongaryNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Sa Gen BioDocument4 pagesReviewer Sa Gen BioSmythNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity For Cot 1Document4 pagesBiodiversity For Cot 1Trisha Melrose MilanesNo ratings yet
- Las 7 Bio2 PDFDocument14 pagesLas 7 Bio2 PDFPeanut BlobNo ratings yet
- The Rise of The Evolution FraudDocument224 pagesThe Rise of The Evolution FraudSamscribdingNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity HotspotDocument4 pagesBiodiversity Hotspotabhijit joshiNo ratings yet
- Keys - THE GENUS CORTINARIUS I by P D OrtonDocument82 pagesKeys - THE GENUS CORTINARIUS I by P D Ortonbobapera074No ratings yet
- Coridius Nepalensis Coridius Singhalanus C. ChinensisDocument8 pagesCoridius Nepalensis Coridius Singhalanus C. ChinensisHiren GogoiNo ratings yet
- GENBIO2 Mod.17 Cladistic SystemDocument15 pagesGENBIO2 Mod.17 Cladistic SystemBea Bayona JoloNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Animals and SpiecesDocument7 pagesConservation of Animals and SpiecescontactjhovinNo ratings yet
- Praktis Biologi Bab 8 T5?Document4 pagesPraktis Biologi Bab 8 T5?NURHANA KOH BINTI ABDULLAH MoeNo ratings yet
- Wang Zhang 2019 Two New Reticuluma From ChinaDocument7 pagesWang Zhang 2019 Two New Reticuluma From ChinakrisztinahorNo ratings yet
- Mendoza WebquestDocument3 pagesMendoza Webquestapi-267645354No ratings yet
- Megharbi Et Al 2021Document11 pagesMegharbi Et Al 2021Ghizlene HafedNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Checkpoint 1 AssignmentDocument4 pagesUnit 4 Checkpoint 1 AssignmentAndrew MNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasi Dan Komposisi Fitoplankton Di Danau LimanDocument8 pagesKlasifikasi Dan Komposisi Fitoplankton Di Danau LimanRoury El-FathNo ratings yet
- AlishaDocument41 pagesAlishaGirl StruggleNo ratings yet
- Alice in The Land of PlantsDocument384 pagesAlice in The Land of PlantsWellington FavaNo ratings yet
- Snakes of The World A Supplement by Boundy Jeff WallachDocument284 pagesSnakes of The World A Supplement by Boundy Jeff WallachRoullienNo ratings yet
- BIO153 16 Tutorial 9 PDFDocument19 pagesBIO153 16 Tutorial 9 PDFUsama AdnanNo ratings yet
- ESS - Topic 3.2Document30 pagesESS - Topic 3.2Pol Ayra FuenteNo ratings yet
- An Update of Wallace's Zoogeographic Regions of The WorldDocument6 pagesAn Update of Wallace's Zoogeographic Regions of The WorldsongkoroNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Taxonomic Survey of Aquatic Plants of Feni District, BangladeshDocument9 pagesPreliminary Taxonomic Survey of Aquatic Plants of Feni District, Bangladeshshuvo devNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument13 pagesBiodiversityNiveditha VinodNo ratings yet
- Living Things and Their EnvironmentDocument3 pagesLiving Things and Their EnvironmentVergzMonch EspielNo ratings yet