Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Study of Micro Wave Componets - 3
Study of Micro Wave Componets - 3
Uploaded by
narasimhaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Study of Micro Wave Componets - 3
Study of Micro Wave Componets - 3
Uploaded by
narasimhaCopyright:
Available Formats
MICROWAVE LAB MANUAL ECE DEPARTMENT
STUDY OF MICROWAVE COMPONENTS-3
AIM
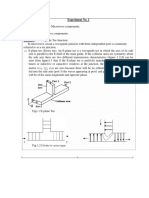
To study the Microwave Components such as E-Plane Tee, H-Plane Tee, Magic Tee, Movable
Short, Matched Termination, Pyramidal wave guide horn antenna in detail.
E PLANE TEE
An E-Plane Tee junction is formed by attaching a
simple waveguide to the broader dimension of a
rectangular waveguide, which already has two
ports. The arms of rectangular waveguides make two
ports called collinear ports i.e., Port1 and Port2, while
the new one, Port3 is called as Side arm or E-arm.T
his E-plane Tee is also called as Series Tee.
As the axis of the side arm is parallel to the electric field,
this junction is called E-Plane Tee junction. This is also
called as Voltage or Series junction. The ports 1 and 2
are 180° out of phase with each other.
Model 3061 E - plane tee are series type T - junction
and consists of three section of wave guide joined
together in order to divide or compare power levels.
The signal entering the first port of this T - junction
will be equally dividing at second and third ports of the same magnitude but in opp.
Phase.
Specifications:
Model No. : X - 3061 Frequency Range (Ghz) : 8.2 - 12.4
WG Type (WR-) : 90 Flange Type (UG/U) : 39
Govt.polytechnic ,Vempalli. Page 1
MICROWAVE LAB MANUAL ECE DEPARTMENT
H - PLANT TEE
An H-Plane Tee junction is formed by cutting narrower dimension of main waveguide
and attaching a side arm. The arms of rectangular waveguides make two ports called
collinear ports i.e., Port1 and Port2, while the new one, Port3 is called as Side arm or H-
arm. This H-plane Tee is also called as Shunt Tee.
As the axis of the side arm is parallel to the magnetic field, this junction is called H-Plane
Tee junction. This is also called as Current junction, as the magnetic field divides itself
into arms.
The cross-sectional details of H-plane tee can be understood by the following figure.
Model 3065 H - Plane Tee are shunt type T - junction for use in conjunction with VSWR
meters, frequency - meters and other detector devices. Like in E-plane tee, the signal fed
through first port of H - plane Tee will be equally divided in magnitude at second and
third ports but in same phase.
Specifications:
Model No. : X - 3065 Frequency Range (GHz) : 8.2 - 12.4
WG Type (WR-) : 90 Flange Type (UG-/U) : 39
Govt.polytechnic ,Vempalli. Page 2
MICROWAVE LAB MANUAL ECE DEPARTMENT
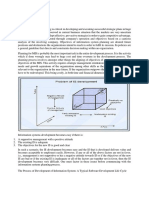
MAGIC TEE
An E-H Plane Tee junction is formed by attaching two simple waveguides one parallel and the
other series, to a rectangular waveguide which already has two ports. This is also called
as Magic Tee, or Hybrid or 3dB coupler.
The arms of rectangular waveguides make two ports called collinear ports i.e., Port 1 and Port
2, while the Port 3 is called as H-Arm or Sum port or Parallel port. Port 4 is called as E-
Arm or Difference port or Series port.
The cross-sectional details of Magic Tee can be understood by the following figure.
The following figure shows the connection made by the side arms to the bi-directional
waveguide to form both parallel and serial ports.
Characteristics of E-H Plane Tee:
If a signal of equal phase and magnitude is sent to port 1 and port 2, then the output at port 4 is
zero and the output at port 3 will be the additive of both the ports 1 and 2.
If a signal is sent to port 4, E−arm, then the power is divided between port 1 and 2 equally but in
opposite phase, while there would be no output at port 3. Hence, S34 = 0.
Govt.polytechnic ,Vempalli. Page 3
MICROWAVE LAB MANUAL ECE DEPARTMENT
If a signal is fed at port 3, then the power is divided between port 1 and 2 equally, while there
would be no output at port 4. Hence, S43 = 0.
If a signal is fed at one of the collinear ports, then there appears no output at the other collinear
port, as the E-arm produces a phase delay and the H-arm produces a phase advance.
So, S12 = S21 = 0.
Model 3045 E - H Tee consists of a section
of wave guide in both series and shunt wave
guide arms, mounted at the exact midpoint
of main arm. Both ends of the section of
wave guide and both arms are flanged on
their ends.
These Tees are employed in balanced
mixers, AFC circuits and impedance
measurement circuits etc. This becomes a
four terminal device where one terminal is
isolated from the input terminal.
Specifications:
Model No. : X - 3045 Frequency Range (Ghz) : 8.2 - 12.4
WG Type (WR-) : 90 Flange Type (UR-/U) : 39
Govt.polytechnic ,Vempalli. Page 4
MICROWAVE LAB MANUAL ECE DEPARTMENT
MOVABLE SHORT:
These are used to obtain a phase reference in the calibration of various experimental
setup and are also used to vary the effective plane of reflection and therefore the phase of
reflected wave. These are also useful in impedance measurement.
Model 4081 movable shorts consists of a section of waveguide, flanged on one end and
terminated with a movable shorting plunger on the other end. By means of this non-
contacting type plunger, a reflection co-efficient of almost unity may be obtained.
Model No. : X - 4081 Frequency Range (GHz) : 8.2 - 12.4
WG Type (WR-) : 90 Flange Type (UG-/U) : 39
Govt.polytechnic ,Vempalli. Page 5
MICROWAVE LAB MANUAL ECE DEPARTMENT
MATCHED TERMINATION:
Matched terminations are used to terminate the waveguide transmission line operating at low
average power. The loads are carefully designed to absorb all the applied power and VSWR of
matched termination is low. These are used in the measurement of reflection coefficient and
where the matched load is required.
Model 4000 are low power and non-reflective type of terminations. It consists of a small and
highly diss-apative taper flap mounted inside the centre of a section of wave guide.
Matched Terminations are useful for USWR measurement of various waveguide components.
These are also employed as dummy and as a precise reference loads with Tee junctions,
directionalcouplers and other similar dividing devices.
Specifications:
Model No. : X - 4000, Freq. Range (Ghz) : 8.2 - 12.4 Max VSWR : 1.04
AV Power : 2W, WG Type (WR-) 90, Flange Type (UG-/U) : 39
Govt.polytechnic ,Vempalli. Page 6
MICROWAVE LAB MANUAL ECE DEPARTMENT
PYRAMIDAL WAVEGUIDE HORN ANTENNA:
A Horn antenna is a type of aperture antenna which is specially designed for microwave
frequencies. The end of the antenna is widened or in the horn shape. Because of this structure,
there is larger directivity so that the emitted signal can be easily transmitted to long distances.
Horn antennas operate in microwave frequency, so the frequency range of these antennas is
super high or ultra-high which ranges from 300 MHz – 30 GHz. These antennas are used as
feed horns for big antennas like parabolic antennas directive antennas, etc.
The benefits of using these antennas are simple design & adjustment, low SWR (standing wave
ratio), moderate directivity, and broad bandwidth. Model 5041 pyramidal Wave guide Horn
antenna consists of waveguide joined to pyramidal section fabricated from brass sheet.
The pyramidal section shapes the energy to concentrate in a specified beam. Wave guide horns
are used as feed horns as radiators for reflectors and lenses and as a pickup antenna for
receiving microwave power.
Horn antenna design can be done with a flared waveguide which is formed as a horn. These are
used to transmit and receive RF microwave signals.
Usually, these are used in combination with waveguide feeds & direct radio waves within a
narrow beam. Here, the flared portion can be in
any shape like square, conical or rectangular.
For proper working, this antenna should be in
minimum size. If the wavelength is very large or
the horn size is very small then the antenna will
not work properly.
In this antenna, the fraction of incident energy
can be radiated from the entry of the waveguide
and the rest of the energy will be reflected back
from the same entry because of the open entry,
the poor impedance matching will exist in
between the space & waveguide.
Govt.polytechnic ,Vempalli. Page 7
MICROWAVE LAB MANUAL ECE DEPARTMENT
So to overcome the drawbacks of the waveguide, its end is opened in an electromagnetic horn
form. So that a smooth transition can be allowed in between the space & waveguide thus
offering better directivity toward the radio wave.
By changing the waveguide like a horn structure, the existing discontinuity in between the
space & waveguide, 377 ohms impedance is eliminated. So this provides the incident energy to
be emitted in the forwarding direction by decreasing the diffraction on the edges. Therefore the
transmitting antenna’s directivity can be enhanced with superior gain.
Specifications:
Model No. : X - 5041 Frequency Range (Ghz)
: 8.2 - 12.4Max VSWR : 1.20 WG Type (WR-) : 90
Flange Type (UG-/U) : 39
Govt.polytechnic ,Vempalli. Page 8
You might also like
- It App Coursera QuizDocument47 pagesIt App Coursera QuizD'Orphic100% (1)
- Notes On Wide-Band Multi-Wire Folded DipolesDocument12 pagesNotes On Wide-Band Multi-Wire Folded DipolesTrinity BaysNo ratings yet
- Helix Colour SM en Ver. 3.20Document86 pagesHelix Colour SM en Ver. 3.20NURILNo ratings yet
- Numpy Pandas Cheatsheet PDFDocument1 pageNumpy Pandas Cheatsheet PDFShailesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Cohen 1992 A Power Primer PDFDocument8 pagesCohen 1992 A Power Primer PDFRicardo LeivaNo ratings yet
- Magic Tee: StructureDocument5 pagesMagic Tee: Structurejhon deenNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 2016 17Document52 pagesLab Manual 2016 17Bhavin V KakaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Passive Microwave Components and NetworksDocument32 pagesChapter Four: Passive Microwave Components and Networksgetahun fentawNo ratings yet
- Waveguide ComponentsDocument22 pagesWaveguide Componentsstatus and songNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - Study of Microwave ComponentsDocument11 pagesExperiment 1 - Study of Microwave ComponentsSai Saswat Sahu100% (1)
- III DECE Advanced Communications LabDocument23 pagesIII DECE Advanced Communications LabKethavath Sakrunaik K100% (1)
- Microwave Engineering: Laboratory ManualDocument60 pagesMicrowave Engineering: Laboratory ManualAayush Kumar KumarNo ratings yet
- Emt LabDocument53 pagesEmt LabEP 104 SOURABH SAMANIYANo ratings yet
- Microwave Components Waveguide Tee E Plane Tee H Plane Tee Magic Tee Hybrid Tee AssignmentDocument14 pagesMicrowave Components Waveguide Tee E Plane Tee H Plane Tee Magic Tee Hybrid Tee Assignmentshwet_vNo ratings yet
- M Micro Owav Ve An ND Ra Adar R: (EE E-326-F F)Document71 pagesM Micro Owav Ve An ND Ra Adar R: (EE E-326-F F)ABHAYNo ratings yet
- MWE Lab Manual FinalDocument48 pagesMWE Lab Manual Finalmaynashah100% (2)
- MW ManualDocument60 pagesMW ManualesesesNo ratings yet
- Slotted Waveguide Antenna Design Using 3D EM SimulationDocument10 pagesSlotted Waveguide Antenna Design Using 3D EM SimulationJuhasz GaborNo ratings yet
- Design of Slotted Waveguide Array Antenna Fed by Power DividerDocument5 pagesDesign of Slotted Waveguide Array Antenna Fed by Power Dividerravi010582No ratings yet
- Viva ManualDocument77 pagesViva ManualSatya Moulika GokavarapuNo ratings yet
- Microwave JunctionsDocument20 pagesMicrowave JunctionsSaraswathi Asirvatham100% (2)
- 40m 10m Delta Loop Antenna Gu3whn Iss 1 3Document9 pages40m 10m Delta Loop Antenna Gu3whn Iss 1 3shubhamformeNo ratings yet
- Microwave & Antenna LabDocument27 pagesMicrowave & Antenna LabhoneyattriNo ratings yet
- Microwave Very Short Wave: 300 MHZ - 300 GHZDocument50 pagesMicrowave Very Short Wave: 300 MHZ - 300 GHZraviNo ratings yet
- TE0320 Labmanual PDFDocument46 pagesTE0320 Labmanual PDFFrew FrewNo ratings yet
- Viva-Voce Questions: Parul DawarDocument11 pagesViva-Voce Questions: Parul DawarNeil PantNo ratings yet
- An Interesting Program: Development of A Circularly Polarised Patch Antenna For 2.45Ghz With Sonnet LiteDocument17 pagesAn Interesting Program: Development of A Circularly Polarised Patch Antenna For 2.45Ghz With Sonnet Liteanon_552241585No ratings yet
- Microwave ComponentsDocument52 pagesMicrowave ComponentsHari HaranNo ratings yet
- MW Manual Practical 1Document6 pagesMW Manual Practical 1Siddhi Kadam100% (1)
- Expt 1Document7 pagesExpt 1Ananyaja DebadiptaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Microwave Waveguides and Components - Lecture 5 Microwave Hybrid CircuitsDocument4 pagesUnit 2 - Microwave Waveguides and Components - Lecture 5 Microwave Hybrid CircuitsLokesh SivakumarNo ratings yet
- Co Axial Fed Microstrip Rectangular PatcDocument6 pagesCo Axial Fed Microstrip Rectangular Patcmahjoubi RabieNo ratings yet
- Secx1037 Unit 5Document22 pagesSecx1037 Unit 5www.saimali8878No ratings yet
- List Some of The Applications of Microwave Technology. AnswerDocument6 pagesList Some of The Applications of Microwave Technology. AnswerFuad al-ahosanNo ratings yet
- Final Microwave Lab Manual McetDocument61 pagesFinal Microwave Lab Manual Mcetsravan_451No ratings yet
- Advanced Communication LabDocument57 pagesAdvanced Communication Labramurama12No ratings yet
- RF File Ary-1 (1) - RemovedDocument25 pagesRF File Ary-1 (1) - RemovedChhaya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mwe Lab Instruction Manual New FinalDocument120 pagesMwe Lab Instruction Manual New Finalkalyan chakravarthyNo ratings yet
- An E Plane Folded Magic Tee For X Band ApplicationsDocument5 pagesAn E Plane Folded Magic Tee For X Band ApplicationsthiyagupsgNo ratings yet
- A Switchable-Frequency Slot-Ring Antenna Element For Designing A Reconfigurable ArrayDocument5 pagesA Switchable-Frequency Slot-Ring Antenna Element For Designing A Reconfigurable ArrayloganathanNo ratings yet
- DuplexerDocument7 pagesDuplexermanishbharti0786100% (2)
- Awp 2marksDocument8 pagesAwp 2marksHema Malini VggNo ratings yet
- Circularly Polarized Microstrip Patch Antenna With Fr4 Substrate in Dual Feed For Wlan ApplicationsDocument5 pagesCircularly Polarized Microstrip Patch Antenna With Fr4 Substrate in Dual Feed For Wlan ApplicationsNageswara Rao ChallaNo ratings yet
- Ring Attenuator Matched Load Twist Bend CornerDocument24 pagesRing Attenuator Matched Load Twist Bend CornerpadmaNo ratings yet
- Antenna Objective QuestionsDocument8 pagesAntenna Objective QuestionsAkanksha Dixit ManodhyaNo ratings yet
- Design and Simulation Based Studies of A Dual Band Antenna For Wlan/Wimax ApplicationDocument5 pagesDesign and Simulation Based Studies of A Dual Band Antenna For Wlan/Wimax ApplicationIjarcet JournalNo ratings yet
- 6 Passive Microwave Components: DefinitionsDocument13 pages6 Passive Microwave Components: DefinitionsYohannes NakachewNo ratings yet
- 118Document8 pages118Suranga Nuwan GoonawardaneNo ratings yet
- Microwave ExperimentDocument10 pagesMicrowave ExperimentsachinNo ratings yet
- Antennas - 4 Types of Antenna PDFDocument36 pagesAntennas - 4 Types of Antenna PDFPraneeth KumarNo ratings yet
- Antenna & Wave PropagationDocument32 pagesAntenna & Wave PropagationGaurav MahNo ratings yet
- Web - Itu.edu - TR Yumakk Downloads Lab Notes Distance Protection v1Document6 pagesWeb - Itu.edu - TR Yumakk Downloads Lab Notes Distance Protection v1sunitharajababuNo ratings yet
- ! Eee 4021 - CH.2Document153 pages! Eee 4021 - CH.2David KanikiNo ratings yet
- Microwave EnggDocument44 pagesMicrowave Enggankita.bhargava007No ratings yet
- Dual-Band Monopole Antenna With Frequency-Tunable Feature For Wimax ApplicationsDocument4 pagesDual-Band Monopole Antenna With Frequency-Tunable Feature For Wimax ApplicationsFirman Nico ChandraNo ratings yet
- A Dual Band Circularly Polarized Rectenna For RF Energy Harvesting ApplicationsDocument7 pagesA Dual Band Circularly Polarized Rectenna For RF Energy Harvesting ApplicationsLALBABU PRASHADNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Portal - Com Autotransformer Connection ExplainedDocument4 pagesElectrical Engineering Portal - Com Autotransformer Connection Explainedraul_bsuNo ratings yet
- Inf2 2Document9 pagesInf2 2Nixon RamonNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection - Part 08Document16 pagesPower System Protection - Part 08Rahul MandalNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- 2.6 VSWR Lab SheetDocument8 pages2.6 VSWR Lab SheetnarasimhaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Lab Sheet Ex-1, ACSDocument8 pages2.1 Lab Sheet Ex-1, ACSnarasimhaNo ratings yet
- State Board of Technical Education & Training Andhra Pradesh:: VijayawadaDocument161 pagesState Board of Technical Education & Training Andhra Pradesh:: VijayawadanarasimhaNo ratings yet
- Ec 310Document203 pagesEc 310narasimhaNo ratings yet
- Study of Micro Wave Components-1Document6 pagesStudy of Micro Wave Components-1narasimhaNo ratings yet
- Business Analysis Study MaterialDocument45 pagesBusiness Analysis Study MaterialnarasimhaNo ratings yet
- Preheat and PWHT Procedure: GlobalDocument12 pagesPreheat and PWHT Procedure: GlobalHendra AwanNo ratings yet
- Secret Symbolism: Hari Kumar January 11, 2013 Toronto, CanadaDocument39 pagesSecret Symbolism: Hari Kumar January 11, 2013 Toronto, CanadaHari Kumar100% (9)
- Virtual Trials and Real-World Evidence Data CollectionDocument4 pagesVirtual Trials and Real-World Evidence Data CollectionRoopali AggarwalNo ratings yet
- 2017 1 27 Governance Officer Temporary Agent AD 7antonis - fysekidisATgmail.com CV PDFDocument8 pages2017 1 27 Governance Officer Temporary Agent AD 7antonis - fysekidisATgmail.com CV PDFvvlakNo ratings yet
- Informal Social Group Influence On Consumer Brand ChoiceDocument4 pagesInformal Social Group Influence On Consumer Brand Choiceapi-484757229100% (2)
- Gases: Behavior & PropertiesDocument35 pagesGases: Behavior & PropertiesAdelia SetianingsihNo ratings yet
- Black and White Minimalist Simple Design Freelancer ResumeDocument3 pagesBlack and White Minimalist Simple Design Freelancer Resumemalaz husseinNo ratings yet
- Monitoring Times 1997 08Document124 pagesMonitoring Times 1997 08Benjamin DoverNo ratings yet
- Ground Penetrating Radar - Shawna Jones, Meghan McGinn, Nicholas RiordanDocument19 pagesGround Penetrating Radar - Shawna Jones, Meghan McGinn, Nicholas RiordanRafael Manfrin MendesNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - PowerPoint PresentationDocument2 pagesLesson Plan - PowerPoint PresentationVicente CarandangNo ratings yet
- 15 Anxiety Worksheets and Workbooks For Teens, Kids, AdultsDocument23 pages15 Anxiety Worksheets and Workbooks For Teens, Kids, AdultsGilang Faisal AndrianNo ratings yet
- FinalPaper SalesPredictionModelforBigMartDocument14 pagesFinalPaper SalesPredictionModelforBigMartGuru KowshikNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Biology 4th Edition by BrookerDocument37 pagesTest Bank For Biology 4th Edition by BrookerShannon Melancon100% (44)
- Ojt Moa and Letter To Industry3Document4 pagesOjt Moa and Letter To Industry3Jeffrey BeloyNo ratings yet
- Methodology For Product Design PDFDocument45 pagesMethodology For Product Design PDFCherun ChesilNo ratings yet
- Upgrading The Academic Performance Using Social Media of Grade 11 Ict Students in Kasiglahan Village Senior HighschoolDocument9 pagesUpgrading The Academic Performance Using Social Media of Grade 11 Ict Students in Kasiglahan Village Senior HighschoolSean NolonNo ratings yet
- Ships' Piping: A Master'S Guide ToDocument32 pagesShips' Piping: A Master'S Guide ToWilliam DaslerNo ratings yet
- Catalog HYUNDAI HGMP (E)Document33 pagesCatalog HYUNDAI HGMP (E)Kostas TressosNo ratings yet
- Mis 3Document5 pagesMis 3peterNo ratings yet
- Self Evaluating Hydro BlastingDocument11 pagesSelf Evaluating Hydro Blastingmmd BusinessNo ratings yet
- HSE Business Plan: Updated November 2020Document40 pagesHSE Business Plan: Updated November 2020sanjeev thadaniNo ratings yet
- Deaerators: TEGO® AirexDocument8 pagesDeaerators: TEGO® AirexjoeNo ratings yet
- Custom Molds IncDocument11 pagesCustom Molds Incapi-326829966No ratings yet
- Statement of Study PlanDocument1 pageStatement of Study PlanNadia Prisillia JuanitaNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentNripesh PokhrelNo ratings yet
- CableDocument7 pagesCablerocketvtNo ratings yet