Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsPleural Effusion & Thoracentesis
Pleural Effusion & Thoracentesis
Uploaded by
vishalmakadiaPleural effusion occurs when there is an excessive accumulation of fluid in the pleural space surrounding the lungs, usually greater than 15ml. This prevents full lung expansion and decreases gas exchange. Common causes are pneumonia and heart failure. Signs include chest pain with breathing, shortness of breath, reduced breath sounds, and dullness to percussion on exam. Thoracentesis is a procedure to drain the fluid where a needle is inserted between the ribs into the pleural space. Patients stop blood thinners beforehand and get a chest x-ray before and after. After the procedure, deep breathing helps reinflate the lungs and lying on the unaffected side is recommended to promote drainage. Potential complications include pneumothorax and hyperres
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Unit 06 Assessment of Thorax and LungDocument55 pagesUnit 06 Assessment of Thorax and Lunghuma100% (1)
- Respiratory - Pleural Effusion & ThoracentesisDocument1 pageRespiratory - Pleural Effusion & Thoracentesissaed.hadidosmanNo ratings yet
- NCM103 - 2016 - Lecture2 - Response To Altered Respiratory FunctionDocument128 pagesNCM103 - 2016 - Lecture2 - Response To Altered Respiratory FunctionrimeoznekNo ratings yet
- CPAC SON HA 7 Thorax 1Document59 pagesCPAC SON HA 7 Thorax 1misshalieediiNo ratings yet
- Lungs and Thorax Assessment - PPTX RAHEEM KHANDocument60 pagesLungs and Thorax Assessment - PPTX RAHEEM KHANRabia IsrafilNo ratings yet
- Final Death Note - Compre NotesDocument1,550 pagesFinal Death Note - Compre NotesSteph TabasaNo ratings yet
- Thorax and Lung - LectureDocument60 pagesThorax and Lung - LectureТаншолпан ШохбутоваNo ratings yet
- Chest Tubes: From Indication To RemovalDocument49 pagesChest Tubes: From Indication To Removaldara octavianiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory ExaminationDocument8 pagesRespiratory ExaminationKelly ReyesNo ratings yet
- Pneumothorax-and-HemothoraxDocument14 pagesPneumothorax-and-HemothoraxEzra MaeNo ratings yet
- Anatomo-Physiological Peculiarities of The Respiratory System. Percussion of The Lungs.Document40 pagesAnatomo-Physiological Peculiarities of The Respiratory System. Percussion of The Lungs.Hetvi PatelNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Case of Respiratoey SystemDocument105 pagesApproach To A Case of Respiratoey SystemprashuNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation MethodsDocument9 pagesOxygenation MethodswowsamanthaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory FailureDocument5 pagesRespiratory Failureta CNo ratings yet
- lung and thorax assess - (Autosaved) .مرحباDocument26 pageslung and thorax assess - (Autosaved) .مرحباmamduohkamel8No ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Fisik Sistem Pernapasan: Equipment NeededDocument78 pagesPemeriksaan Fisik Sistem Pernapasan: Equipment Neededsri karinaNo ratings yet
- Trauma Thorax: Oleh: Moch. Achwandi, M.Kep - NS., CWCSDocument52 pagesTrauma Thorax: Oleh: Moch. Achwandi, M.Kep - NS., CWCSMariSstan EM HaNo ratings yet
- resp د. وفاءDocument22 pagesresp د. وفاءProf. Wafaa Mohammed Al-AttarNo ratings yet
- Respiratory ExamDocument6 pagesRespiratory Exam95kscbyqxmNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination in Respiratory SystemDocument84 pagesPhysical Examination in Respiratory SystemDr-i BarreNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument38 pagesRespiratory Systemjsreyes.402No ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument61 pagesThe Respiratory SystemLuna JadeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument57 pagesRespiratory SystemAngelica RevilNo ratings yet
- CU11 Funda Week 13 Respiratory SystemDocument70 pagesCU11 Funda Week 13 Respiratory System97fcqmnnmnNo ratings yet
- What To Ask:: Infection (LRTI)Document11 pagesWhat To Ask:: Infection (LRTI)habbouraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - THORAX AND LUNGSDocument2 pagesLesson 6 - THORAX AND LUNGSKuldip GillNo ratings yet
- Trauma Thorax: Oleh: Moch. Achwandi, M.Kep - NS., CWCSDocument51 pagesTrauma Thorax: Oleh: Moch. Achwandi, M.Kep - NS., CWCSMas sobah SobahNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Assessment PDFDocument53 pagesRespiratory System Assessment PDFJay RomeNo ratings yet
- COPD - Case PresentationDocument68 pagesCOPD - Case PresentationJaslir MendozaNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Respiratory SystemDocument35 pagesExamination of The Respiratory SystemRashhmi Karthodi100% (3)
- Assessment of Respiratory System: Submitted by Pankaj Singh Rana Nurse Practitioner in Critical Care, SrhuDocument80 pagesAssessment of Respiratory System: Submitted by Pankaj Singh Rana Nurse Practitioner in Critical Care, SrhuMary Christine Estrada CabactulanNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Pengantar PF ParuDocument62 pagesKuliah Pengantar PF Parugagah152No ratings yet
- ASSESSING THORAX and LUNGSDocument25 pagesASSESSING THORAX and LUNGSPrincess AñabezaNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan ThoraxDocument27 pagesPemeriksaan ThoraxYaasinta ArlaesNo ratings yet
- Pulmunology FADocument39 pagesPulmunology FAJaankiNo ratings yet
- Cme Trauma Management ZakwanDocument44 pagesCme Trauma Management ZakwansyasyaNo ratings yet
- Lungs and ThoracicDocument66 pagesLungs and ThoracicJoyce Jacobe0% (1)
- Chest and LungsDocument49 pagesChest and LungsChala KeneNo ratings yet
- Thorax and The LungsDocument30 pagesThorax and The Lungschifunndo charles100% (1)
- Pemeriksaan Fisik ParuDocument7 pagesPemeriksaan Fisik ParuLila WatiningrumNo ratings yet
- STUDY GUIDE 2 OXYGENATION Operaña EllayzaDocument5 pagesSTUDY GUIDE 2 OXYGENATION Operaña EllayzaOPERAñA ELLAYZA RB DECANONo ratings yet
- LungsDocument12 pagesLungselman.rifatNo ratings yet
- Respiratory AssessmentDocument79 pagesRespiratory AssessmentKarlo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Trauma Thorax: Oleh: Moch. Achwandi, M.Kep - NS., CWCSDocument52 pagesTrauma Thorax: Oleh: Moch. Achwandi, M.Kep - NS., CWCSMariSstan EM HaNo ratings yet
- Assessmentr of Lungs - ThoraxDocument41 pagesAssessmentr of Lungs - ThoraxAdnan KareemNo ratings yet
- Approach To Breathlessness: Mentor - EP DR Maslina HO - Izzad Bin AzlanDocument18 pagesApproach To Breathlessness: Mentor - EP DR Maslina HO - Izzad Bin AzlanizadalanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System (Physical Examination)Document30 pagesRespiratory System (Physical Examination)Noor Ahmad AhadiNo ratings yet
- Chest ExaminationDocument14 pagesChest Examinationsajad abasewNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Assessment & DiagnosticsDocument9 pagesRespiratory Assessment & DiagnosticsAngellene GraceNo ratings yet
- Revised Chapter-5 - Google Slide - Respiratory SystemDocument30 pagesRevised Chapter-5 - Google Slide - Respiratory SystemJaded KaysarNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan ThoraxDocument27 pagesPemeriksaan ThoraxSubchanPrasetyoNo ratings yet
- 4 RSDocument16 pages4 RSzabdullahstud1No ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Pulmonary Anatomy, Physiology and Assessment (Hemo)Document39 pagesTopic 1 - Pulmonary Anatomy, Physiology and Assessment (Hemo)Ben JilhanoNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDocument26 pagesThe Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemMonica Angelique SalayoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument23 pagesRespiratory SystemSaraNo ratings yet
- Respi ExaminationDocument3 pagesRespi ExaminationvignaaarumugamNo ratings yet
- Respiratory AssessmentDocument43 pagesRespiratory AssessmentLui Andrei AnilaNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPleural Effusion, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
Pleural Effusion & Thoracentesis
Pleural Effusion & Thoracentesis
Uploaded by
vishalmakadia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pagePleural effusion occurs when there is an excessive accumulation of fluid in the pleural space surrounding the lungs, usually greater than 15ml. This prevents full lung expansion and decreases gas exchange. Common causes are pneumonia and heart failure. Signs include chest pain with breathing, shortness of breath, reduced breath sounds, and dullness to percussion on exam. Thoracentesis is a procedure to drain the fluid where a needle is inserted between the ribs into the pleural space. Patients stop blood thinners beforehand and get a chest x-ray before and after. After the procedure, deep breathing helps reinflate the lungs and lying on the unaffected side is recommended to promote drainage. Potential complications include pneumothorax and hyperres
Original Description:
Nursing
Original Title
12. Pleural Effusion & Thoracentesis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPleural effusion occurs when there is an excessive accumulation of fluid in the pleural space surrounding the lungs, usually greater than 15ml. This prevents full lung expansion and decreases gas exchange. Common causes are pneumonia and heart failure. Signs include chest pain with breathing, shortness of breath, reduced breath sounds, and dullness to percussion on exam. Thoracentesis is a procedure to drain the fluid where a needle is inserted between the ribs into the pleural space. Patients stop blood thinners beforehand and get a chest x-ray before and after. After the procedure, deep breathing helps reinflate the lungs and lying on the unaffected side is recommended to promote drainage. Potential complications include pneumothorax and hyperres
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pagePleural Effusion & Thoracentesis
Pleural Effusion & Thoracentesis
Uploaded by
vishalmakadiaPleural effusion occurs when there is an excessive accumulation of fluid in the pleural space surrounding the lungs, usually greater than 15ml. This prevents full lung expansion and decreases gas exchange. Common causes are pneumonia and heart failure. Signs include chest pain with breathing, shortness of breath, reduced breath sounds, and dullness to percussion on exam. Thoracentesis is a procedure to drain the fluid where a needle is inserted between the ribs into the pleural space. Patients stop blood thinners beforehand and get a chest x-ray before and after. After the procedure, deep breathing helps reinflate the lungs and lying on the unaffected side is recommended to promote drainage. Potential complications include pneumothorax and hyperres
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
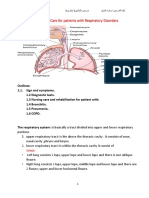
Pleural Effusion & Thoracentesis
Pathophysiology Course
Pathophysiology
Pleural Effusion think Plenty of Fluid in the lung space, specifically fluid
collection in the pleural space greater than 15 mls of fluid. This fluid
prevents full expansion of the lung & results in decreased gas exchange > 15ml
& atelectasis (collapse of the alveoli).
Causes
• Pneumonia (lung infection), which fills the lungs with fluid.
• Heart failure causing pulmonary edema, where heavy fluid
builds up in the lungs.
Signs & Symptoms
L L
KEY SIGNS
DULL RESONANCE FLUID FILLED LUNGS
1. Chest pain during inhalation
2. Dyspnea
3. Diminished breath sounds
4. Dull resonance on percussion
Nursing Interventions BEFORE procedure:
Thoracentesis STOP all blood thinners:
1st
1. Provider places a needle through ● Antiplatelets: aspirin &
an intercostal space (the space clopidogrel
between the ribs) to gently ● Anticoagulants: Warfarin
puncture the lung & drain the fluid! & heparin (enoxaparin)
2. Sign a consent form
3. Chest X ray before & AFTER procedure to compare fluid & lung expansion
AFTER a thoracentesis:
• Deep breaths to help re-expand the lungs & promote adequate oxygen exchange
• Lie on the unaffected lung to keep BAD LUNG UP!
Complications
Pneumothorax
REPORT to HCP
● Asymmetrical chest expansion
& decreased breath sounds on
affected side
● Hyperresonance
● Deviated Trachea Hyperresonance
You might also like
- Unit 06 Assessment of Thorax and LungDocument55 pagesUnit 06 Assessment of Thorax and Lunghuma100% (1)
- Respiratory - Pleural Effusion & ThoracentesisDocument1 pageRespiratory - Pleural Effusion & Thoracentesissaed.hadidosmanNo ratings yet
- NCM103 - 2016 - Lecture2 - Response To Altered Respiratory FunctionDocument128 pagesNCM103 - 2016 - Lecture2 - Response To Altered Respiratory FunctionrimeoznekNo ratings yet
- CPAC SON HA 7 Thorax 1Document59 pagesCPAC SON HA 7 Thorax 1misshalieediiNo ratings yet
- Lungs and Thorax Assessment - PPTX RAHEEM KHANDocument60 pagesLungs and Thorax Assessment - PPTX RAHEEM KHANRabia IsrafilNo ratings yet
- Final Death Note - Compre NotesDocument1,550 pagesFinal Death Note - Compre NotesSteph TabasaNo ratings yet
- Thorax and Lung - LectureDocument60 pagesThorax and Lung - LectureТаншолпан ШохбутоваNo ratings yet
- Chest Tubes: From Indication To RemovalDocument49 pagesChest Tubes: From Indication To Removaldara octavianiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory ExaminationDocument8 pagesRespiratory ExaminationKelly ReyesNo ratings yet
- Pneumothorax-and-HemothoraxDocument14 pagesPneumothorax-and-HemothoraxEzra MaeNo ratings yet
- Anatomo-Physiological Peculiarities of The Respiratory System. Percussion of The Lungs.Document40 pagesAnatomo-Physiological Peculiarities of The Respiratory System. Percussion of The Lungs.Hetvi PatelNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Case of Respiratoey SystemDocument105 pagesApproach To A Case of Respiratoey SystemprashuNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation MethodsDocument9 pagesOxygenation MethodswowsamanthaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory FailureDocument5 pagesRespiratory Failureta CNo ratings yet
- lung and thorax assess - (Autosaved) .مرحباDocument26 pageslung and thorax assess - (Autosaved) .مرحباmamduohkamel8No ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Fisik Sistem Pernapasan: Equipment NeededDocument78 pagesPemeriksaan Fisik Sistem Pernapasan: Equipment Neededsri karinaNo ratings yet
- Trauma Thorax: Oleh: Moch. Achwandi, M.Kep - NS., CWCSDocument52 pagesTrauma Thorax: Oleh: Moch. Achwandi, M.Kep - NS., CWCSMariSstan EM HaNo ratings yet
- resp د. وفاءDocument22 pagesresp د. وفاءProf. Wafaa Mohammed Al-AttarNo ratings yet
- Respiratory ExamDocument6 pagesRespiratory Exam95kscbyqxmNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination in Respiratory SystemDocument84 pagesPhysical Examination in Respiratory SystemDr-i BarreNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument38 pagesRespiratory Systemjsreyes.402No ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument61 pagesThe Respiratory SystemLuna JadeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument57 pagesRespiratory SystemAngelica RevilNo ratings yet
- CU11 Funda Week 13 Respiratory SystemDocument70 pagesCU11 Funda Week 13 Respiratory System97fcqmnnmnNo ratings yet
- What To Ask:: Infection (LRTI)Document11 pagesWhat To Ask:: Infection (LRTI)habbouraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - THORAX AND LUNGSDocument2 pagesLesson 6 - THORAX AND LUNGSKuldip GillNo ratings yet
- Trauma Thorax: Oleh: Moch. Achwandi, M.Kep - NS., CWCSDocument51 pagesTrauma Thorax: Oleh: Moch. Achwandi, M.Kep - NS., CWCSMas sobah SobahNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Assessment PDFDocument53 pagesRespiratory System Assessment PDFJay RomeNo ratings yet
- COPD - Case PresentationDocument68 pagesCOPD - Case PresentationJaslir MendozaNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Respiratory SystemDocument35 pagesExamination of The Respiratory SystemRashhmi Karthodi100% (3)
- Assessment of Respiratory System: Submitted by Pankaj Singh Rana Nurse Practitioner in Critical Care, SrhuDocument80 pagesAssessment of Respiratory System: Submitted by Pankaj Singh Rana Nurse Practitioner in Critical Care, SrhuMary Christine Estrada CabactulanNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Pengantar PF ParuDocument62 pagesKuliah Pengantar PF Parugagah152No ratings yet
- ASSESSING THORAX and LUNGSDocument25 pagesASSESSING THORAX and LUNGSPrincess AñabezaNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan ThoraxDocument27 pagesPemeriksaan ThoraxYaasinta ArlaesNo ratings yet
- Pulmunology FADocument39 pagesPulmunology FAJaankiNo ratings yet
- Cme Trauma Management ZakwanDocument44 pagesCme Trauma Management ZakwansyasyaNo ratings yet
- Lungs and ThoracicDocument66 pagesLungs and ThoracicJoyce Jacobe0% (1)
- Chest and LungsDocument49 pagesChest and LungsChala KeneNo ratings yet
- Thorax and The LungsDocument30 pagesThorax and The Lungschifunndo charles100% (1)
- Pemeriksaan Fisik ParuDocument7 pagesPemeriksaan Fisik ParuLila WatiningrumNo ratings yet
- STUDY GUIDE 2 OXYGENATION Operaña EllayzaDocument5 pagesSTUDY GUIDE 2 OXYGENATION Operaña EllayzaOPERAñA ELLAYZA RB DECANONo ratings yet
- LungsDocument12 pagesLungselman.rifatNo ratings yet
- Respiratory AssessmentDocument79 pagesRespiratory AssessmentKarlo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Trauma Thorax: Oleh: Moch. Achwandi, M.Kep - NS., CWCSDocument52 pagesTrauma Thorax: Oleh: Moch. Achwandi, M.Kep - NS., CWCSMariSstan EM HaNo ratings yet
- Assessmentr of Lungs - ThoraxDocument41 pagesAssessmentr of Lungs - ThoraxAdnan KareemNo ratings yet
- Approach To Breathlessness: Mentor - EP DR Maslina HO - Izzad Bin AzlanDocument18 pagesApproach To Breathlessness: Mentor - EP DR Maslina HO - Izzad Bin AzlanizadalanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System (Physical Examination)Document30 pagesRespiratory System (Physical Examination)Noor Ahmad AhadiNo ratings yet
- Chest ExaminationDocument14 pagesChest Examinationsajad abasewNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Assessment & DiagnosticsDocument9 pagesRespiratory Assessment & DiagnosticsAngellene GraceNo ratings yet
- Revised Chapter-5 - Google Slide - Respiratory SystemDocument30 pagesRevised Chapter-5 - Google Slide - Respiratory SystemJaded KaysarNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan ThoraxDocument27 pagesPemeriksaan ThoraxSubchanPrasetyoNo ratings yet
- 4 RSDocument16 pages4 RSzabdullahstud1No ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Pulmonary Anatomy, Physiology and Assessment (Hemo)Document39 pagesTopic 1 - Pulmonary Anatomy, Physiology and Assessment (Hemo)Ben JilhanoNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDocument26 pagesThe Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemMonica Angelique SalayoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument23 pagesRespiratory SystemSaraNo ratings yet
- Respi ExaminationDocument3 pagesRespi ExaminationvignaaarumugamNo ratings yet
- Respiratory AssessmentDocument43 pagesRespiratory AssessmentLui Andrei AnilaNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPleural Effusion, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet