Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lung Cancer
Lung Cancer
Uploaded by
vishalmakadiaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Special Operations Forces Medical HandbookFrom EverandSpecial Operations Forces Medical HandbookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Concept Map LungDocument1 pageConcept Map LungThea Eya FayeNo ratings yet
- Thyroid CancerDocument5 pagesThyroid CancerZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- The Radiology Handbook: A Pocket Guide to Medical ImagingFrom EverandThe Radiology Handbook: A Pocket Guide to Medical ImagingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Pathogenesis and Clinical ManifestationDocument4 pagesPathogenesis and Clinical ManifestationkrismaevelNo ratings yet
- Oncology AssignmentDocument18 pagesOncology AssignmentAngeline EspinasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Conditions ChartDocument1 pageRespiratory Conditions ChartAmanda MuchaNo ratings yet
- PATH - Lung Cancer (7p)Document7 pagesPATH - Lung Cancer (7p)Cristopher NivelaNo ratings yet
- 09 Prof - Barmawi H - Carcinoma, Efusi PleuraDocument48 pages09 Prof - Barmawi H - Carcinoma, Efusi PleuraRama BiomantaraNo ratings yet
- Lung & Mediastinal CancerDocument50 pagesLung & Mediastinal Cancercharlesy T0% (1)
- Lung Cancer (Bronchogenic Carcinoma) : Topic OutlineDocument3 pagesLung Cancer (Bronchogenic Carcinoma) : Topic OutlineKdamnz100% (1)
- Dr. Handoko T, SPP: Sub Departemen Penyakit Paru Dan AlergiDocument54 pagesDr. Handoko T, SPP: Sub Departemen Penyakit Paru Dan AlergiMUHAMMAD BAGIR ALJUFRINo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Transitional Cell CarcinomaDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of Transitional Cell CarcinomaJheanAlphonsineT.MeansNo ratings yet
- Thyroid NodulesDocument56 pagesThyroid NodulesSri Kombong100% (2)
- Cheat Sheet For CancerDocument4 pagesCheat Sheet For CancerEffie Cloe Marie BitengNo ratings yet
- Kanker Pada Perempuan: DR - Hariadi, Spog - K.Onk Rsud Ulin / FK Unlam BanjarmasinDocument68 pagesKanker Pada Perempuan: DR - Hariadi, Spog - K.Onk Rsud Ulin / FK Unlam BanjarmasinNor AinaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary CancerDocument1 pagePulmonary CancerjoeNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi Tumor: By: Agus SantosaDocument26 pagesPatofisiologi Tumor: By: Agus SantosaAnonymous BFjVBgN3No ratings yet
- Tonsil Cancer: Cedars-Sinai ResourceDocument4 pagesTonsil Cancer: Cedars-Sinai ResourceSiRa DiktaraNo ratings yet
- Ferrets Oncology-MainDocument26 pagesFerrets Oncology-MainJOAQUINALONZOPEREIRANo ratings yet
- DR - Dr. Tahan P.H.,: FK UWK Surabaya Januari 2014Document30 pagesDR - Dr. Tahan P.H.,: FK UWK Surabaya Januari 2014Chen SiongNo ratings yet
- Pedia RespiDocument2 pagesPedia RespiKerby RosasNo ratings yet
- Cups Neck by Dr. Musaib MushtaqDocument42 pagesCups Neck by Dr. Musaib MushtaqDr. Musaib MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology:: Symptoms Mechanism and PathophysiologyDocument7 pagesPathophysiology:: Symptoms Mechanism and PathophysiologyRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Cancer: By: Carolina Vidal, RNDocument49 pagesCancer: By: Carolina Vidal, RNCarolina VidalNo ratings yet
- 1 - Cancer Basics OverviewDocument50 pages1 - Cancer Basics OverviewAlexa RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Block 3.3 Sesi 3 Pathology of Urinary Tract: by Asdos 2011: Vetta Awe Eric Lily Fiko Ghana Ikal Linda May FahmiDocument96 pagesBlock 3.3 Sesi 3 Pathology of Urinary Tract: by Asdos 2011: Vetta Awe Eric Lily Fiko Ghana Ikal Linda May Fahmimail junkNo ratings yet
- NCM 112: (Surgery, CD, I&I, Cellular Aberration) : Lung Cancer (Document8 pagesNCM 112: (Surgery, CD, I&I, Cellular Aberration) : Lung Cancer (Jamaicah N. NagaNo ratings yet
- Patho of CA & Breast CaDocument3 pagesPatho of CA & Breast CaAngeline EspinasNo ratings yet
- Sheet 10 (Lung Tumor)Document40 pagesSheet 10 (Lung Tumor)ardesh abdilleNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck TumoursDocument50 pagesHead and Neck Tumoursene.dubemNo ratings yet
- Glossary Medical TermsDocument18 pagesGlossary Medical Termssazmeeta pantaNo ratings yet
- Back To Basic in Thoracic Surgery: FM Shamji 31-03-2011Document180 pagesBack To Basic in Thoracic Surgery: FM Shamji 31-03-2011mi DaNo ratings yet
- Lung Cancer: I Gede Ketut SajinadiyasaDocument81 pagesLung Cancer: I Gede Ketut Sajinadiyasadr.Dewi Shintaher100% (1)
- 3 1 Neoplasia PDFDocument3 pages3 1 Neoplasia PDFPrabhat GuptaNo ratings yet
- 33 Approach To ADocument6 pages33 Approach To AJanine Vega CalayoNo ratings yet
- Tumor Laring DannyDocument31 pagesTumor Laring DannyCicha Aulia WardaniNo ratings yet
- Tumours of The LarynxDocument90 pagesTumours of The LarynxDrravikumar BhandariNo ratings yet
- ENT ENT Emergencies: High-Pitched, Wheezing Sound Caused by Disrupted AirflowDocument53 pagesENT ENT Emergencies: High-Pitched, Wheezing Sound Caused by Disrupted AirflowYavani KulasinghamNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia: Monoclonal Unregulated, and IrreversibleDocument10 pagesNeoplasia: Monoclonal Unregulated, and Irreversiblehippypsyduck mdNo ratings yet
- Kanker GinekologiDocument81 pagesKanker GinekologiSismi AtyNo ratings yet
- Tumors by SadekDocument22 pagesTumors by SadekAhmed El SayedNo ratings yet
- Efusi Pleura Masif: M Harun Iskandar Medical Faculty Hasanuddin UniversityDocument56 pagesEfusi Pleura Masif: M Harun Iskandar Medical Faculty Hasanuddin UniversityMelody Nethania SutedjaNo ratings yet
- Primary Lung CancerDocument3 pagesPrimary Lung CancerStephanie LocsinNo ratings yet
- Long Cases ADocument24 pagesLong Cases Amieraf mesfinNo ratings yet
- Prostate GlandsDocument3 pagesProstate GlandsDragan PetrovicNo ratings yet
- Notes EntDocument43 pagesNotes Entadriana azmanNo ratings yet
- Lung CancerDocument12 pagesLung CancerKianoosh GhozhmaniNo ratings yet
- Pancoast's Tumor: Sallie Ruth Coleman December 15, 2008Document26 pagesPancoast's Tumor: Sallie Ruth Coleman December 15, 2008agnes trianaNo ratings yet
- Predisposing-Factors 20231129 134609 0000Document1 pagePredisposing-Factors 20231129 134609 0000Mary Mathel Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Ann Pulmo TB !Document2 pagesAnn Pulmo TB !scribd_lostandfoundNo ratings yet
- Lung Ca 2Document9 pagesLung Ca 2AbuobiedaBallaAbusharibNo ratings yet
- Important Topics of ENT For MBBSDocument2 pagesImportant Topics of ENT For MBBSDr.Riashat azimNo ratings yet
- Anal CancerDocument14 pagesAnal Cancerdrsp2001No ratings yet
- Case Report: Severe Exacerbation COPD Without Respiratory FailureDocument20 pagesCase Report: Severe Exacerbation COPD Without Respiratory FailureAsdar Raya RangkutiNo ratings yet
- Case Report Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor of SinonasalDocument84 pagesCase Report Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor of SinonasalAyunita ArifinNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Fecalysis & Chest X-RayDocument12 pagesGroup 3 Fecalysis & Chest X-Ray•TobioChan•No ratings yet
- Colorectal AdenocarcinomaDocument48 pagesColorectal Adenocarcinomamingchuan chuNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer Pap Smear Test Result (Bethesda) : Adenocarcinoma, Growth ofDocument1 pageCervical Cancer Pap Smear Test Result (Bethesda) : Adenocarcinoma, Growth ofJeremiah JustoNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Radiology: A Guide for BeginnersFrom EverandThoracic Radiology: A Guide for BeginnersIacopo CarboneNo ratings yet
Lung Cancer
Lung Cancer
Uploaded by
vishalmakadiaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lung Cancer
Lung Cancer
Uploaded by
vishalmakadiaCopyright:
Available Formats
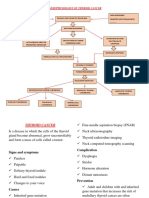
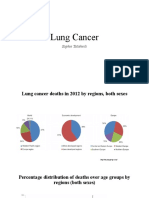
Lung Cancer
Pathophysiology Course
Pathophysiology
Lung cancer or lung carcinoma is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth within lung
tissue. This growth can spread beyond the lung by the process of metastasis into nearby tissue or other parts of
the body.
Carcinoma
Cause
1. 90% smoking
2. Second-hand smoke
3. Exposure to asbestos & other carcinogens
4. Air pollution
90% 5. Family history of lung cancer (genetics)
Early Manifestations A...B...
(Signs & Symptoms)
Persistent, productive cough
Hemoptysis (coughing blood)
Hoarseness in voice
Dysphagia (swallowing difficulties)
Complications
Paraneoplastic syndromes
Metastases
Bone pain
Diagnostics
Imaging: CT scan, MRI, Chest X-ray
Biopsy (sample of tissue)
Notes
You might also like
- Special Operations Forces Medical HandbookFrom EverandSpecial Operations Forces Medical HandbookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Concept Map LungDocument1 pageConcept Map LungThea Eya FayeNo ratings yet
- Thyroid CancerDocument5 pagesThyroid CancerZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- The Radiology Handbook: A Pocket Guide to Medical ImagingFrom EverandThe Radiology Handbook: A Pocket Guide to Medical ImagingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Pathogenesis and Clinical ManifestationDocument4 pagesPathogenesis and Clinical ManifestationkrismaevelNo ratings yet
- Oncology AssignmentDocument18 pagesOncology AssignmentAngeline EspinasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Conditions ChartDocument1 pageRespiratory Conditions ChartAmanda MuchaNo ratings yet
- PATH - Lung Cancer (7p)Document7 pagesPATH - Lung Cancer (7p)Cristopher NivelaNo ratings yet
- 09 Prof - Barmawi H - Carcinoma, Efusi PleuraDocument48 pages09 Prof - Barmawi H - Carcinoma, Efusi PleuraRama BiomantaraNo ratings yet
- Lung & Mediastinal CancerDocument50 pagesLung & Mediastinal Cancercharlesy T0% (1)
- Lung Cancer (Bronchogenic Carcinoma) : Topic OutlineDocument3 pagesLung Cancer (Bronchogenic Carcinoma) : Topic OutlineKdamnz100% (1)
- Dr. Handoko T, SPP: Sub Departemen Penyakit Paru Dan AlergiDocument54 pagesDr. Handoko T, SPP: Sub Departemen Penyakit Paru Dan AlergiMUHAMMAD BAGIR ALJUFRINo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Transitional Cell CarcinomaDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of Transitional Cell CarcinomaJheanAlphonsineT.MeansNo ratings yet
- Thyroid NodulesDocument56 pagesThyroid NodulesSri Kombong100% (2)
- Cheat Sheet For CancerDocument4 pagesCheat Sheet For CancerEffie Cloe Marie BitengNo ratings yet
- Kanker Pada Perempuan: DR - Hariadi, Spog - K.Onk Rsud Ulin / FK Unlam BanjarmasinDocument68 pagesKanker Pada Perempuan: DR - Hariadi, Spog - K.Onk Rsud Ulin / FK Unlam BanjarmasinNor AinaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary CancerDocument1 pagePulmonary CancerjoeNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi Tumor: By: Agus SantosaDocument26 pagesPatofisiologi Tumor: By: Agus SantosaAnonymous BFjVBgN3No ratings yet
- Tonsil Cancer: Cedars-Sinai ResourceDocument4 pagesTonsil Cancer: Cedars-Sinai ResourceSiRa DiktaraNo ratings yet
- Ferrets Oncology-MainDocument26 pagesFerrets Oncology-MainJOAQUINALONZOPEREIRANo ratings yet
- DR - Dr. Tahan P.H.,: FK UWK Surabaya Januari 2014Document30 pagesDR - Dr. Tahan P.H.,: FK UWK Surabaya Januari 2014Chen SiongNo ratings yet
- Pedia RespiDocument2 pagesPedia RespiKerby RosasNo ratings yet
- Cups Neck by Dr. Musaib MushtaqDocument42 pagesCups Neck by Dr. Musaib MushtaqDr. Musaib MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology:: Symptoms Mechanism and PathophysiologyDocument7 pagesPathophysiology:: Symptoms Mechanism and PathophysiologyRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Cancer: By: Carolina Vidal, RNDocument49 pagesCancer: By: Carolina Vidal, RNCarolina VidalNo ratings yet
- 1 - Cancer Basics OverviewDocument50 pages1 - Cancer Basics OverviewAlexa RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Block 3.3 Sesi 3 Pathology of Urinary Tract: by Asdos 2011: Vetta Awe Eric Lily Fiko Ghana Ikal Linda May FahmiDocument96 pagesBlock 3.3 Sesi 3 Pathology of Urinary Tract: by Asdos 2011: Vetta Awe Eric Lily Fiko Ghana Ikal Linda May Fahmimail junkNo ratings yet
- NCM 112: (Surgery, CD, I&I, Cellular Aberration) : Lung Cancer (Document8 pagesNCM 112: (Surgery, CD, I&I, Cellular Aberration) : Lung Cancer (Jamaicah N. NagaNo ratings yet
- Patho of CA & Breast CaDocument3 pagesPatho of CA & Breast CaAngeline EspinasNo ratings yet
- Sheet 10 (Lung Tumor)Document40 pagesSheet 10 (Lung Tumor)ardesh abdilleNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck TumoursDocument50 pagesHead and Neck Tumoursene.dubemNo ratings yet
- Glossary Medical TermsDocument18 pagesGlossary Medical Termssazmeeta pantaNo ratings yet
- Back To Basic in Thoracic Surgery: FM Shamji 31-03-2011Document180 pagesBack To Basic in Thoracic Surgery: FM Shamji 31-03-2011mi DaNo ratings yet
- Lung Cancer: I Gede Ketut SajinadiyasaDocument81 pagesLung Cancer: I Gede Ketut Sajinadiyasadr.Dewi Shintaher100% (1)
- 3 1 Neoplasia PDFDocument3 pages3 1 Neoplasia PDFPrabhat GuptaNo ratings yet
- 33 Approach To ADocument6 pages33 Approach To AJanine Vega CalayoNo ratings yet
- Tumor Laring DannyDocument31 pagesTumor Laring DannyCicha Aulia WardaniNo ratings yet
- Tumours of The LarynxDocument90 pagesTumours of The LarynxDrravikumar BhandariNo ratings yet
- ENT ENT Emergencies: High-Pitched, Wheezing Sound Caused by Disrupted AirflowDocument53 pagesENT ENT Emergencies: High-Pitched, Wheezing Sound Caused by Disrupted AirflowYavani KulasinghamNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia: Monoclonal Unregulated, and IrreversibleDocument10 pagesNeoplasia: Monoclonal Unregulated, and Irreversiblehippypsyduck mdNo ratings yet
- Kanker GinekologiDocument81 pagesKanker GinekologiSismi AtyNo ratings yet
- Tumors by SadekDocument22 pagesTumors by SadekAhmed El SayedNo ratings yet
- Efusi Pleura Masif: M Harun Iskandar Medical Faculty Hasanuddin UniversityDocument56 pagesEfusi Pleura Masif: M Harun Iskandar Medical Faculty Hasanuddin UniversityMelody Nethania SutedjaNo ratings yet
- Primary Lung CancerDocument3 pagesPrimary Lung CancerStephanie LocsinNo ratings yet
- Long Cases ADocument24 pagesLong Cases Amieraf mesfinNo ratings yet
- Prostate GlandsDocument3 pagesProstate GlandsDragan PetrovicNo ratings yet
- Notes EntDocument43 pagesNotes Entadriana azmanNo ratings yet
- Lung CancerDocument12 pagesLung CancerKianoosh GhozhmaniNo ratings yet
- Pancoast's Tumor: Sallie Ruth Coleman December 15, 2008Document26 pagesPancoast's Tumor: Sallie Ruth Coleman December 15, 2008agnes trianaNo ratings yet
- Predisposing-Factors 20231129 134609 0000Document1 pagePredisposing-Factors 20231129 134609 0000Mary Mathel Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Ann Pulmo TB !Document2 pagesAnn Pulmo TB !scribd_lostandfoundNo ratings yet
- Lung Ca 2Document9 pagesLung Ca 2AbuobiedaBallaAbusharibNo ratings yet
- Important Topics of ENT For MBBSDocument2 pagesImportant Topics of ENT For MBBSDr.Riashat azimNo ratings yet
- Anal CancerDocument14 pagesAnal Cancerdrsp2001No ratings yet
- Case Report: Severe Exacerbation COPD Without Respiratory FailureDocument20 pagesCase Report: Severe Exacerbation COPD Without Respiratory FailureAsdar Raya RangkutiNo ratings yet
- Case Report Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor of SinonasalDocument84 pagesCase Report Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor of SinonasalAyunita ArifinNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Fecalysis & Chest X-RayDocument12 pagesGroup 3 Fecalysis & Chest X-Ray•TobioChan•No ratings yet
- Colorectal AdenocarcinomaDocument48 pagesColorectal Adenocarcinomamingchuan chuNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer Pap Smear Test Result (Bethesda) : Adenocarcinoma, Growth ofDocument1 pageCervical Cancer Pap Smear Test Result (Bethesda) : Adenocarcinoma, Growth ofJeremiah JustoNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Radiology: A Guide for BeginnersFrom EverandThoracic Radiology: A Guide for BeginnersIacopo CarboneNo ratings yet