Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 viewsAdvantages of Bus Topology
Advantages of Bus Topology
Uploaded by
Prashant BalcharanBus topology has several advantages for networking including:
1) It is easy and inexpensive to connect new devices to the linear network.
2) It is cheaper to implement than other network topologies since it requires less cable.
3) The failure of one device does not disrupt the entire network.
4) No hubs or switches are needed since data flows freely along the backbone.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Group Number:-3: Team Mates NamesDocument41 pagesGroup Number:-3: Team Mates NamesManish GautamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Setting Up The NetworkDocument133 pagesLesson 8 Setting Up The NetworkLeu NameNo ratings yet
- Network Technology: M.S Raza MohamedDocument8 pagesNetwork Technology: M.S Raza Mohamedrazamohamed1No ratings yet
- Topology 1Document2 pagesTopology 1mcsm-f18-055No ratings yet
- CFC CIA 1 NotesDocument15 pagesCFC CIA 1 Notessaksham sondhiNo ratings yet
- Bus Topology: Topology. Organizations Using This Type of Topology Will Generally UseDocument4 pagesBus Topology: Topology. Organizations Using This Type of Topology Will Generally Usehadi fASIALNo ratings yet
- CN 4340703 Gtu Questionpaper SolutionDocument67 pagesCN 4340703 Gtu Questionpaper Solution32 - Shadab X - ANo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Assignment 1 - SuhaibDocument49 pagesUnit 11 Assignment 1 - Suhaibapi-537398914No ratings yet
- What Is A Network Operating SystemDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Network Operating SystemJay-r MatibagNo ratings yet
- Network PDFDocument66 pagesNetwork PDFq_riusNo ratings yet
- Access To Remote Information Person-To-Person Communication Interactive Entertainment Electronic CommerceDocument10 pagesAccess To Remote Information Person-To-Person Communication Interactive Entertainment Electronic CommerceNhia ObleaNo ratings yet
- Access To Remote Information Person-To-Person Communication Interactive Entertainment Electronic CommerceDocument10 pagesAccess To Remote Information Person-To-Person Communication Interactive Entertainment Electronic CommerceNhia ObleaNo ratings yet
- Access To Remote Information Person-To-Person Communication Interactive Entertainment Electronic CommerceDocument10 pagesAccess To Remote Information Person-To-Person Communication Interactive Entertainment Electronic CommerceNhia ObleaNo ratings yet
- Administer Network HardwareDocument62 pagesAdminister Network HardwareMintesnot AdeNo ratings yet
- Networking and Telecommunication (Part 2)Document40 pagesNetworking and Telecommunication (Part 2)Vivien Margareth FaustinoNo ratings yet
- A Computer Network Is A Group of Computer Systems and Other Computing Hardware Devices That Are Linked Together Through Communication Channels To Facilitate Communication and ResourceDocument7 pagesA Computer Network Is A Group of Computer Systems and Other Computing Hardware Devices That Are Linked Together Through Communication Channels To Facilitate Communication and Resource2nablsNo ratings yet
- Network Systems & Protocols: Task 1Document12 pagesNetwork Systems & Protocols: Task 1qwerty2711No ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORK Cyber CrimeDocument6 pagesINTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORK Cyber CrimeAkriti SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkingDocument4 pagesComputer Networkingkitderoger_391648570No ratings yet
- Intro. To Networking & Network DevicesDocument33 pagesIntro. To Networking & Network DevicesAyodeleNo ratings yet
- Work TopologyDocument20 pagesWork Topologyporanchakma514No ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument12 pagesLab ManualRai HessyNo ratings yet
- LAN DesignDocument6 pagesLAN DesignLeanne RuthNo ratings yet
- LAN TopologiesDocument11 pagesLAN TopologiesStephen NthigaNo ratings yet
- Computer Network BasicsDocument29 pagesComputer Network BasicsGOPI backbencherNo ratings yet
- TLE ICT 10 - Network Topologies - Activity SheetDocument7 pagesTLE ICT 10 - Network Topologies - Activity SheetGioSanBuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- CN QB AnswersDocument20 pagesCN QB AnswersKhushi TharaniNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument10 pagesComputer NetworksBhavishya KumiliNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument13 pagesAssignmentsterlinghayat14No ratings yet
- Holiday HomeworkDocument22 pagesHoliday Homeworkh2462915No ratings yet
- Nguyễn Quốc An (BKC18348) - Assignment 1 NetworkingDocument13 pagesNguyễn Quốc An (BKC18348) - Assignment 1 NetworkingKatonguyenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document15 pagesLesson 3Kean Rafael MarianoNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks 1Document18 pagesComputer Networks 1Edwin NfehNo ratings yet
- NetworkDocument14 pagesNetworkAmit ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Stevenson College - Graded Unit-1Document53 pagesStevenson College - Graded Unit-1karagenski0% (1)
- Bus TopologyDocument6 pagesBus Topologylea_eazeNo ratings yet
- Topology: Chapter - 5Document12 pagesTopology: Chapter - 5RoopaNo ratings yet
- DCC NotesDocument28 pagesDCC NotesOm SutarNo ratings yet
- Star Topology: Types of Network Topologies Ethernet Local Area Networks RouterDocument4 pagesStar Topology: Types of Network Topologies Ethernet Local Area Networks RouterNishil VijayanNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture FileDocument49 pagesComputer Architecture FileFunsuk VangduNo ratings yet
- Networking: Two Types of Networking ConfigurationDocument8 pagesNetworking: Two Types of Networking ConfigurationEdajBass AmadeoNo ratings yet
- What Is Topology or Network Topology?Document25 pagesWhat Is Topology or Network Topology?Mimi Rubia AvilaNo ratings yet
- Study About Basic of Network (Topologies) and Types of network-LAN, Man, WanDocument11 pagesStudy About Basic of Network (Topologies) and Types of network-LAN, Man, WanAnonymous aQxekTRNo ratings yet
- NetwokingDocument38 pagesNetwokingPooja Dhiman100% (1)
- Networking Assignment 2 Course HeroDocument37 pagesNetworking Assignment 2 Course Heroksav yadavNo ratings yet
- Local Area Network (Lan)Document6 pagesLocal Area Network (Lan)luqmanNo ratings yet
- Network ArchitectureDocument2 pagesNetwork ArchitectureMonika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Adminstrate Network and Hardware PeripherialsDocument18 pagesAdminstrate Network and Hardware PeripherialsDark KnightNo ratings yet
- 12 IpDocument9 pages12 IpGoogle DoodleNo ratings yet
- Topology StarDocument3 pagesTopology StarSyafiq FauziNo ratings yet
- Computer TopologyDocument14 pagesComputer TopologytamnumakamseuNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Ii: Computer NetworksDocument8 pagesAssignment - Ii: Computer NetworksAashish RaghunathNo ratings yet
- DCC NotesDocument15 pagesDCC NotesOm SutarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks-4Document6 pagesIntroduction To Networks-4deepheat_008No ratings yet
- Network Topology DiagramDocument7 pagesNetwork Topology DiagramSatvik SalatNo ratings yet
- CJ TechDocument6 pagesCJ TechYasmien Cel AuroNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document37 pagesUnit 1narasimharao P.V.No ratings yet
- Network DocumentDocument8 pagesNetwork Documentwilliam.hartNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Dimensioning of Mobile Wireless Networks: From GSM to LTEFrom EverandModeling and Dimensioning of Mobile Wireless Networks: From GSM to LTENo ratings yet
- US April'23 PAKET BDocument12 pagesUS April'23 PAKET BProject P2BanjaranNo ratings yet
- ChawlaDocument449 pagesChawlarajamannar322No ratings yet
- Koh, Khee Meng - Tay Eng Guan, - Dong, F. M - Introduction To Graph Theory - Solutions Manual-World Scientific Publishing Company (2008 - 2007)Document262 pagesKoh, Khee Meng - Tay Eng Guan, - Dong, F. M - Introduction To Graph Theory - Solutions Manual-World Scientific Publishing Company (2008 - 2007)vahide khodadiNo ratings yet
- Innovative Offerings For Membrane and Thermal Desalination PlantsDocument24 pagesInnovative Offerings For Membrane and Thermal Desalination Plantscvolkan1No ratings yet
- MCQDocument274 pagesMCQgganyan67% (3)
- KP Astrology-Denial of Child Birth-4Document7 pagesKP Astrology-Denial of Child Birth-4rahul106No ratings yet
- BRAPDocument5 pagesBRAPrkkask01No ratings yet
- Roland VSCDR-1880 Turbo StartDocument1 pageRoland VSCDR-1880 Turbo StarthighlanderoneNo ratings yet
- List of DictionariesDocument38 pagesList of DictionariesSaraPhoenixNo ratings yet
- Lecture3 - Logic Operation FundamentalsDocument64 pagesLecture3 - Logic Operation FundamentalsTrần Quốc ToảnNo ratings yet
- Practical-1: AIM: Implement A Program Which Can Decrypt The Original Message From The GivenDocument65 pagesPractical-1: AIM: Implement A Program Which Can Decrypt The Original Message From The GivenprogrammerNo ratings yet
- HDM Stuttgart Vorlage ThesisDocument5 pagesHDM Stuttgart Vorlage ThesisLuz Martinez100% (2)
- 9701 Oct Nov 2011 All Mark SchemesDocument90 pages9701 Oct Nov 2011 All Mark SchemesRobert EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Design of A Two-Stage Cycloidal Gear Reducer WithDocument14 pagesDesign of A Two-Stage Cycloidal Gear Reducer WithAlejandro ChavezNo ratings yet
- Modeling Roundabout Intersections - AUGI - The World's Largest CAD & BIM User GroupDocument9 pagesModeling Roundabout Intersections - AUGI - The World's Largest CAD & BIM User GroupSantosh RaiNo ratings yet
- TareekhePakistan 2ndDocument141 pagesTareekhePakistan 2ndAHMAD RAZANo ratings yet
- Adaptogenic Activity of Caesalpinia Bonduc Seed Extracts in RatsDocument5 pagesAdaptogenic Activity of Caesalpinia Bonduc Seed Extracts in RatssugindavidrajNo ratings yet
- Exterior Derivative - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument8 pagesExterior Derivative - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAlbert QuaedaNo ratings yet
- Excipient PT FinalDocument14 pagesExcipient PT FinalPreeti Wavikar-Panhale100% (1)
- Climate DLLDocument2 pagesClimate DLLlucky may100% (1)
- Scope of WorkDocument5 pagesScope of WorkKausik DewanNo ratings yet
- Essay Topic - Distance LearningDocument3 pagesEssay Topic - Distance LearningFalling stonesNo ratings yet
- MGMT100S2 2019 - With Lecture Schedule PDFDocument8 pagesMGMT100S2 2019 - With Lecture Schedule PDFAkshayScamlattiNo ratings yet
- Search Help Exit How ToDocument18 pagesSearch Help Exit How Tobra_mxoNo ratings yet
- Definition of Research, Characteristics of Research, Research Process and Functions of Research Definition of ResearchDocument2 pagesDefinition of Research, Characteristics of Research, Research Process and Functions of Research Definition of ResearchNinda SNo ratings yet
- XXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXX XX Dsfasdfasdf Res: 00000000000Document3 pagesXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXX XX Dsfasdfasdf Res: 00000000000asksrsinfotechNo ratings yet
- Note Semelles JumeléesDocument6 pagesNote Semelles JumeléeslionelNo ratings yet
- The Way of The Worl1Document1 pageThe Way of The Worl1Maria Olivia GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Sex Is Binary EssayDocument6 pagesSex Is Binary EssayAshleigh SchumanNo ratings yet
- Pub - Green Advertising and Green Public Relations As Integration PropagandaDocument16 pagesPub - Green Advertising and Green Public Relations As Integration PropagandagbthomasonNo ratings yet
Advantages of Bus Topology
Advantages of Bus Topology
Uploaded by
Prashant Balcharan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views2 pagesBus topology has several advantages for networking including:
1) It is easy and inexpensive to connect new devices to the linear network.
2) It is cheaper to implement than other network topologies since it requires less cable.
3) The failure of one device does not disrupt the entire network.
4) No hubs or switches are needed since data flows freely along the backbone.
Original Description:
Original Title
advantages of bus topology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBus topology has several advantages for networking including:
1) It is easy and inexpensive to connect new devices to the linear network.
2) It is cheaper to implement than other network topologies since it requires less cable.
3) The failure of one device does not disrupt the entire network.
4) No hubs or switches are needed since data flows freely along the backbone.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views2 pagesAdvantages of Bus Topology
Advantages of Bus Topology
Uploaded by
Prashant BalcharanBus topology has several advantages for networking including:
1) It is easy and inexpensive to connect new devices to the linear network.
2) It is cheaper to implement than other network topologies since it requires less cable.
3) The failure of one device does not disrupt the entire network.
4) No hubs or switches are needed since data flows freely along the backbone.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Prashant Balcharan
IT RESEARCH
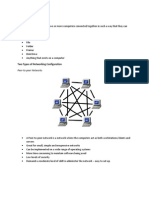
Advantages of Bus topology
1. It is easy to connect a device to the network.
If the computer or peripheral has the appropriate connection mechanism,
then it can be easily added to the network. The new device connects to the
linear bus topology and becomes part of the network immediately. For
those who need a temporary network that can be setup quickly, there isn’t
a better option that is available right now. If several users need mutual
access to a printer, adding the printer to the network meets that need
immediately.
2. It is cheaper than other network options.
Compared to ring, star, or hybrid networks, bus topology is the cheapest to
implement. That is because it requires less cable length than the other
network options. Although terminators are required at both ends of the
backbone to ensure the network can function properly, it is still easy and
affordable to install when a small network is required.
3. The failure of one station does not affect the rest of the network.
If one computer or peripheral should fail when using bus topology, the rest
of the network is not affected by this change in performance. The linear
nature of the network means that each unit transmits to the backbone and
that data is then available to the other units that remain connected. This
makes it an effective way to share uninterrupted communication.
4. No hubs or switches are required.
With bus topology, the linear nature of the network allows data to flow
freely throughout the network. Although this limits outside connections, it
does create a localized network that can effectively work with each terminal
that has been connected. A central file server is used instead of hubs and
switches, which means there are fewer points of potential failure that must
be managed with this setup compared to others.
5. Extensions can be made to the network.
The size and scope of bus topology is naturally limited. It can, however, be
extended quite easily. Joining cable with a repeater or connector allows for
additional peripherals or computers to be added to the network. Although
this can increase the number of packet collisions that may occur, it is a
simplified solution that can get people up and working quickly and for a
minimal overall cost.
6. Multiple nodes can be installed without difficulty.
For a small network, another option that is often considered is point-to-point
topology. Bus topology has an advantage here because it supports multiple
nodes instead of just 2 nodes. That is how the original form of an Ethernet
network came about. 10Base2, which is popularly known as “thinnet,”
utilizes bus topology to create a local area network that can be used to
form departments or working groups.
7. Multiple peripherals can be supported through bus topology.
Routers, printers, and other data devices can be connected to this network
in addition to computers or terminals. This can increase the speed of
productivity because instead of sending commands to a centralized
network, a command can be sent directly to the needed peripheral. A print
command from a computer, for example, can stay local and improve
production speed, which keeps workers more productive over time.
8. Wiring terminators take no power requirements.
The terminators that are used for most bus topology systems are passive
devices. They’re made of resistors and capacitors, which means there isn’t
a power requirement that must be met. This makes it easy to install a
simple LAN at virtually any location where networking would be beneficial
to a department or working group.
Reference:
Gaille, L. (2019, 16 december). 17 Advantages and Disadvantages of Bus Topology. Vitanna.
Geraadpleegd op 28 mei 2022, van https://vittana.org/17-advantages-and-
disadvantages-of-bus-topology
You might also like
- Group Number:-3: Team Mates NamesDocument41 pagesGroup Number:-3: Team Mates NamesManish GautamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Setting Up The NetworkDocument133 pagesLesson 8 Setting Up The NetworkLeu NameNo ratings yet
- Network Technology: M.S Raza MohamedDocument8 pagesNetwork Technology: M.S Raza Mohamedrazamohamed1No ratings yet
- Topology 1Document2 pagesTopology 1mcsm-f18-055No ratings yet
- CFC CIA 1 NotesDocument15 pagesCFC CIA 1 Notessaksham sondhiNo ratings yet
- Bus Topology: Topology. Organizations Using This Type of Topology Will Generally UseDocument4 pagesBus Topology: Topology. Organizations Using This Type of Topology Will Generally Usehadi fASIALNo ratings yet
- CN 4340703 Gtu Questionpaper SolutionDocument67 pagesCN 4340703 Gtu Questionpaper Solution32 - Shadab X - ANo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Assignment 1 - SuhaibDocument49 pagesUnit 11 Assignment 1 - Suhaibapi-537398914No ratings yet
- What Is A Network Operating SystemDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Network Operating SystemJay-r MatibagNo ratings yet
- Network PDFDocument66 pagesNetwork PDFq_riusNo ratings yet
- Access To Remote Information Person-To-Person Communication Interactive Entertainment Electronic CommerceDocument10 pagesAccess To Remote Information Person-To-Person Communication Interactive Entertainment Electronic CommerceNhia ObleaNo ratings yet
- Access To Remote Information Person-To-Person Communication Interactive Entertainment Electronic CommerceDocument10 pagesAccess To Remote Information Person-To-Person Communication Interactive Entertainment Electronic CommerceNhia ObleaNo ratings yet
- Access To Remote Information Person-To-Person Communication Interactive Entertainment Electronic CommerceDocument10 pagesAccess To Remote Information Person-To-Person Communication Interactive Entertainment Electronic CommerceNhia ObleaNo ratings yet
- Administer Network HardwareDocument62 pagesAdminister Network HardwareMintesnot AdeNo ratings yet
- Networking and Telecommunication (Part 2)Document40 pagesNetworking and Telecommunication (Part 2)Vivien Margareth FaustinoNo ratings yet
- A Computer Network Is A Group of Computer Systems and Other Computing Hardware Devices That Are Linked Together Through Communication Channels To Facilitate Communication and ResourceDocument7 pagesA Computer Network Is A Group of Computer Systems and Other Computing Hardware Devices That Are Linked Together Through Communication Channels To Facilitate Communication and Resource2nablsNo ratings yet
- Network Systems & Protocols: Task 1Document12 pagesNetwork Systems & Protocols: Task 1qwerty2711No ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORK Cyber CrimeDocument6 pagesINTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORK Cyber CrimeAkriti SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkingDocument4 pagesComputer Networkingkitderoger_391648570No ratings yet
- Intro. To Networking & Network DevicesDocument33 pagesIntro. To Networking & Network DevicesAyodeleNo ratings yet
- Work TopologyDocument20 pagesWork Topologyporanchakma514No ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument12 pagesLab ManualRai HessyNo ratings yet
- LAN DesignDocument6 pagesLAN DesignLeanne RuthNo ratings yet
- LAN TopologiesDocument11 pagesLAN TopologiesStephen NthigaNo ratings yet
- Computer Network BasicsDocument29 pagesComputer Network BasicsGOPI backbencherNo ratings yet
- TLE ICT 10 - Network Topologies - Activity SheetDocument7 pagesTLE ICT 10 - Network Topologies - Activity SheetGioSanBuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- CN QB AnswersDocument20 pagesCN QB AnswersKhushi TharaniNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument10 pagesComputer NetworksBhavishya KumiliNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument13 pagesAssignmentsterlinghayat14No ratings yet
- Holiday HomeworkDocument22 pagesHoliday Homeworkh2462915No ratings yet
- Nguyễn Quốc An (BKC18348) - Assignment 1 NetworkingDocument13 pagesNguyễn Quốc An (BKC18348) - Assignment 1 NetworkingKatonguyenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document15 pagesLesson 3Kean Rafael MarianoNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks 1Document18 pagesComputer Networks 1Edwin NfehNo ratings yet
- NetworkDocument14 pagesNetworkAmit ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Stevenson College - Graded Unit-1Document53 pagesStevenson College - Graded Unit-1karagenski0% (1)
- Bus TopologyDocument6 pagesBus Topologylea_eazeNo ratings yet
- Topology: Chapter - 5Document12 pagesTopology: Chapter - 5RoopaNo ratings yet
- DCC NotesDocument28 pagesDCC NotesOm SutarNo ratings yet
- Star Topology: Types of Network Topologies Ethernet Local Area Networks RouterDocument4 pagesStar Topology: Types of Network Topologies Ethernet Local Area Networks RouterNishil VijayanNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture FileDocument49 pagesComputer Architecture FileFunsuk VangduNo ratings yet
- Networking: Two Types of Networking ConfigurationDocument8 pagesNetworking: Two Types of Networking ConfigurationEdajBass AmadeoNo ratings yet
- What Is Topology or Network Topology?Document25 pagesWhat Is Topology or Network Topology?Mimi Rubia AvilaNo ratings yet
- Study About Basic of Network (Topologies) and Types of network-LAN, Man, WanDocument11 pagesStudy About Basic of Network (Topologies) and Types of network-LAN, Man, WanAnonymous aQxekTRNo ratings yet
- NetwokingDocument38 pagesNetwokingPooja Dhiman100% (1)
- Networking Assignment 2 Course HeroDocument37 pagesNetworking Assignment 2 Course Heroksav yadavNo ratings yet
- Local Area Network (Lan)Document6 pagesLocal Area Network (Lan)luqmanNo ratings yet
- Network ArchitectureDocument2 pagesNetwork ArchitectureMonika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Adminstrate Network and Hardware PeripherialsDocument18 pagesAdminstrate Network and Hardware PeripherialsDark KnightNo ratings yet
- 12 IpDocument9 pages12 IpGoogle DoodleNo ratings yet
- Topology StarDocument3 pagesTopology StarSyafiq FauziNo ratings yet
- Computer TopologyDocument14 pagesComputer TopologytamnumakamseuNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Ii: Computer NetworksDocument8 pagesAssignment - Ii: Computer NetworksAashish RaghunathNo ratings yet
- DCC NotesDocument15 pagesDCC NotesOm SutarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks-4Document6 pagesIntroduction To Networks-4deepheat_008No ratings yet
- Network Topology DiagramDocument7 pagesNetwork Topology DiagramSatvik SalatNo ratings yet
- CJ TechDocument6 pagesCJ TechYasmien Cel AuroNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document37 pagesUnit 1narasimharao P.V.No ratings yet
- Network DocumentDocument8 pagesNetwork Documentwilliam.hartNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Dimensioning of Mobile Wireless Networks: From GSM to LTEFrom EverandModeling and Dimensioning of Mobile Wireless Networks: From GSM to LTENo ratings yet
- US April'23 PAKET BDocument12 pagesUS April'23 PAKET BProject P2BanjaranNo ratings yet
- ChawlaDocument449 pagesChawlarajamannar322No ratings yet
- Koh, Khee Meng - Tay Eng Guan, - Dong, F. M - Introduction To Graph Theory - Solutions Manual-World Scientific Publishing Company (2008 - 2007)Document262 pagesKoh, Khee Meng - Tay Eng Guan, - Dong, F. M - Introduction To Graph Theory - Solutions Manual-World Scientific Publishing Company (2008 - 2007)vahide khodadiNo ratings yet
- Innovative Offerings For Membrane and Thermal Desalination PlantsDocument24 pagesInnovative Offerings For Membrane and Thermal Desalination Plantscvolkan1No ratings yet
- MCQDocument274 pagesMCQgganyan67% (3)
- KP Astrology-Denial of Child Birth-4Document7 pagesKP Astrology-Denial of Child Birth-4rahul106No ratings yet
- BRAPDocument5 pagesBRAPrkkask01No ratings yet
- Roland VSCDR-1880 Turbo StartDocument1 pageRoland VSCDR-1880 Turbo StarthighlanderoneNo ratings yet
- List of DictionariesDocument38 pagesList of DictionariesSaraPhoenixNo ratings yet
- Lecture3 - Logic Operation FundamentalsDocument64 pagesLecture3 - Logic Operation FundamentalsTrần Quốc ToảnNo ratings yet
- Practical-1: AIM: Implement A Program Which Can Decrypt The Original Message From The GivenDocument65 pagesPractical-1: AIM: Implement A Program Which Can Decrypt The Original Message From The GivenprogrammerNo ratings yet
- HDM Stuttgart Vorlage ThesisDocument5 pagesHDM Stuttgart Vorlage ThesisLuz Martinez100% (2)
- 9701 Oct Nov 2011 All Mark SchemesDocument90 pages9701 Oct Nov 2011 All Mark SchemesRobert EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Design of A Two-Stage Cycloidal Gear Reducer WithDocument14 pagesDesign of A Two-Stage Cycloidal Gear Reducer WithAlejandro ChavezNo ratings yet
- Modeling Roundabout Intersections - AUGI - The World's Largest CAD & BIM User GroupDocument9 pagesModeling Roundabout Intersections - AUGI - The World's Largest CAD & BIM User GroupSantosh RaiNo ratings yet
- TareekhePakistan 2ndDocument141 pagesTareekhePakistan 2ndAHMAD RAZANo ratings yet
- Adaptogenic Activity of Caesalpinia Bonduc Seed Extracts in RatsDocument5 pagesAdaptogenic Activity of Caesalpinia Bonduc Seed Extracts in RatssugindavidrajNo ratings yet
- Exterior Derivative - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument8 pagesExterior Derivative - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAlbert QuaedaNo ratings yet
- Excipient PT FinalDocument14 pagesExcipient PT FinalPreeti Wavikar-Panhale100% (1)
- Climate DLLDocument2 pagesClimate DLLlucky may100% (1)
- Scope of WorkDocument5 pagesScope of WorkKausik DewanNo ratings yet
- Essay Topic - Distance LearningDocument3 pagesEssay Topic - Distance LearningFalling stonesNo ratings yet
- MGMT100S2 2019 - With Lecture Schedule PDFDocument8 pagesMGMT100S2 2019 - With Lecture Schedule PDFAkshayScamlattiNo ratings yet
- Search Help Exit How ToDocument18 pagesSearch Help Exit How Tobra_mxoNo ratings yet
- Definition of Research, Characteristics of Research, Research Process and Functions of Research Definition of ResearchDocument2 pagesDefinition of Research, Characteristics of Research, Research Process and Functions of Research Definition of ResearchNinda SNo ratings yet
- XXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXX XX Dsfasdfasdf Res: 00000000000Document3 pagesXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXX XX Dsfasdfasdf Res: 00000000000asksrsinfotechNo ratings yet
- Note Semelles JumeléesDocument6 pagesNote Semelles JumeléeslionelNo ratings yet
- The Way of The Worl1Document1 pageThe Way of The Worl1Maria Olivia GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Sex Is Binary EssayDocument6 pagesSex Is Binary EssayAshleigh SchumanNo ratings yet
- Pub - Green Advertising and Green Public Relations As Integration PropagandaDocument16 pagesPub - Green Advertising and Green Public Relations As Integration PropagandagbthomasonNo ratings yet