Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Bontrager
1 Bontrager
Uploaded by
Guntur Aji PrasetyoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Bontrager
1 Bontrager
Uploaded by
Guntur Aji PrasetyoCopyright:
Available Formats
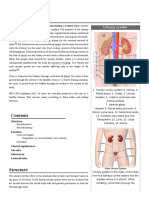
526 CHAP TER 14 UR R S ST M V p U CTUR
RADIOGRAP HIC
ANATOMY
Urinary Sys te m S upra re na l
Radiographic examinations of the urinary system are among the (a dre na l) gla nd
common contrast medium procedures performed in radiology
departments. The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two
ureters (u-re′-ter1 or yoo-ret′-er2 ), one urinary bladder, and one Le ft kidne y
urethra (u-re′-thrah 1 or yoo-re′-thra 2 ) (Fig. 14.1).
Le ft ure te r
OT : Determine which of the possible pronunciations of these terms is
(are) most common in your region.
The two kidneys and the ureters are organs that lie in the ret-
roperitoneal space. These two bean-shaped organs lie on either
side of the vertebral column in the most posterior part of the Urina ry bla dde r
abdominal cavity. The right kidney is generally slightly lower or more
inferior than the left because of the presence of the liver. Superior Ure thra
and medial to each kidney is a su rarenal (adrenal) gland. These
Rig ht Le ft
important glands of the endocrine system are located in the fatty
capsule that surrounds each kidney. Fig.
14.1 Urinary system, anterior view.
Each kidney is connected to the single urinary bladder by its
own ureter. Waste material, in the form of urine, travels from the
kidneys to the bladder via these two narrow tubes, termed ureters.
The saclike urinary bladder serves as a reservoir that stores urine
until it can be eliminated from the body via the urethra.
The Latin designation for kidney is ren, and renal is an adjective S ple e n Live r
that is commonly used to refer to the kidney.
K S
The various organs of the urinary system and their relationship
to the bony skeleton are shown from the back in Fig. 14.2 and
from the left side in Fig. 14.3. The posteriorly placed kidneys lie in
the upper posterior abdomen on either side of the vertebral column.
The right kidney is positioned posterior to the lower portion of the
liver. The left kidney is positioned posterior to the inferior border
of the s leen (see Fig. 14.2). The lower rib cage thus forms a
protective enclosure for the kidneys.
Le ft Rig ht
UR T RS
Most of each ureter lies anterior to its respective kidney. The ureters Fig.
14.2 Urinary system, posterior view.
follow the natural curve of the vertebral column. Each ureter initially
curves anteriorly, following the lumbar lordotic curvature, and then
curves posteriorly on entering the pelvis. After passing into the Ante rio r Po s te rio r
pelvis, each ureter follows the sacrococcygeal curve before entering Le ft kidne y
the posterolateral aspect of the bladder.
UR THR
14 The urethra connects the bladder to the exterior. The urethra exits Le ft ure te r
from the body inferior to the symphysis pubis.
The entire urinary system is posterior to or below the peritoneum.
The kidneys and ureters are retroperitoneal structures, whereas the
bladder and urethra are infraperitoneal structures.
Urina ry bla dde r
Ure thra
Fig.
14.3 Urinary system, lateral view.
You might also like
- NEO, April 01, 2021 Volume 22, Issue 4Document70 pagesNEO, April 01, 2021 Volume 22, Issue 4Majo EscobarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Urinary Tract BaruDocument68 pagesAnatomy of Urinary Tract BaruAdya ArradikhaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyCris Joe Rollorata DumagalNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument55 pagesUrinary SystemDiamante MhayaleneNo ratings yet
- Kidney and Ureter: L.R. AronsonDocument22 pagesKidney and Ureter: L.R. AronsonDiana GranadaNo ratings yet
- Anatomia RiñonDocument6 pagesAnatomia RiñonJeaneth LanzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Kidney and Ureter: Basic ScienceDocument6 pagesAnatomy of The Kidney and Ureter: Basic ScienceAsfahani LatiefahNo ratings yet
- Yusi - Anatomy of The Urinary Tract 2009 12-7Document129 pagesYusi - Anatomy of The Urinary Tract 2009 12-7abstabsNo ratings yet
- Erbil Polytechnic UniversityDocument21 pagesErbil Polytechnic Universitygashbin MahdyNo ratings yet
- Basic Human Anatomy: Lesson 8: Urogenital SystemDocument19 pagesBasic Human Anatomy: Lesson 8: Urogenital SystemIshita SinghNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy,: Renal /urinary SystemDocument62 pagesHuman Anatomy,: Renal /urinary Systemsapana shresthaNo ratings yet
- Kidney: PDF Generated At: Sun, 26 Jan 2014 03:55:26 UTCDocument15 pagesKidney: PDF Generated At: Sun, 26 Jan 2014 03:55:26 UTCVijay RajendiranNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody Urinary SystemDocument15 pagesVisibleBody Urinary SystemPiotr SotomskiNo ratings yet
- 2 BontragerDocument1 page2 BontragerGuntur Aji PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument14 pagesUrinary SystemCharli ParachinniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document3 pagesChapter 6John ErickNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument9 pagesUrinary SystemCailah Sofia SelausoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Kidney and UreterDocument6 pagesAnatomy of The Kidney and UreterMario Ivan De la Cruz LaraNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy, Histology and Development of The Kidney PDFDocument14 pagesThe Anatomy, Histology and Development of The Kidney PDFredderdatNo ratings yet
- Topik 2 2021Document26 pagesTopik 2 2021AnnisNo ratings yet
- Urinary System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesUrinary System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBDNo ratings yet
- Anatomy N Physiology of UtiDocument6 pagesAnatomy N Physiology of UtiMarjorie PalaganasNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Kidney and ExcretionDocument57 pagesPhysiology of Kidney and ExcretionWenny KalamiNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument11 pagesThe Urinary SystemwaplNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology URINARY TRACTDocument28 pagesAnatomy & Physiology URINARY TRACTabdullatifNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary SystemDocument26 pagesGenitourinary SystemKharismatul MaghvirohNo ratings yet
- Two Kidneys: Extract Waste From The Blood and Balance Body FluidDocument5 pagesTwo Kidneys: Extract Waste From The Blood and Balance Body FluidDani PhilipNo ratings yet
- KidneyDocument40 pagesKidneyOlaifa victorNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary SystemDocument23 pagesGenitourinary SystemRisma ZulfianiNo ratings yet
- Function of The Urinary SystemDocument7 pagesFunction of The Urinary SystemMary EnsomoNo ratings yet
- UT AnatomyDocument35 pagesUT AnatomyAngel SaraNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument4 pagesUrinary SystemMohammed Keyarul IslamNo ratings yet
- Mr. Diaz Medical English II: WWW - Usat.edu - PeDocument10 pagesMr. Diaz Medical English II: WWW - Usat.edu - PelakjdlkaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 The Urinary SystemDocument43 pagesChapter 4 The Urinary Systemsomebody_maNo ratings yet
- Bab II Referat BSKDocument26 pagesBab II Referat BSKSandara ParkNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Urinary System orDocument18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Urinary System orFatima Dacalos FuerzasNo ratings yet
- Ivp Intravenous PyelographyDocument16 pagesIvp Intravenous PyelographyLuisa ManaloNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology 1 1aDocument88 pagesRenal Physiology 1 1afentaw melkieNo ratings yet
- DR Laxman Khanal Bpkihs 07-06-2013Document86 pagesDR Laxman Khanal Bpkihs 07-06-2013Bilal YimamNo ratings yet
- RKJ Excretory 1Document14 pagesRKJ Excretory 1Black WidowNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument4 pagesUrinary SystemAntonioNo ratings yet
- Materi Urinary System Bhs InggrisDocument8 pagesMateri Urinary System Bhs InggrisMelany LtrNo ratings yet
- PINK Cream and Green Illustrative Science Project PresentationDocument31 pagesPINK Cream and Green Illustrative Science Project Presentationereneovalerozo22No ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument3 pagesUrinary SystemCh'an Rak KhunNo ratings yet
- The Urinary System: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityDocument44 pagesThe Urinary System: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityRahmawati HamudiNo ratings yet
- Retroperitoneal Space TopographyDocument27 pagesRetroperitoneal Space TopographyAhmad AnsariNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument3 pagesAnaphyKenneth DelorinoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Bladder, Urethra, Adrenals, Blood VesselsDocument47 pagesUrinary Bladder, Urethra, Adrenals, Blood VesselsrajeevshamNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument10 pagesUrinary SystemElyka Alivan Valdez PolonioNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument8 pagesUrinary SystemTana OquendoNo ratings yet
- Seminar Cs 15 NovDocument24 pagesSeminar Cs 15 Novzeenatn1995No ratings yet
- Kidney AnatomyDocument55 pagesKidney AnatomyMohammad zreadNo ratings yet
- Sys RénalDocument25 pagesSys RénalGregory GebertNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Urinary Tract Systems - 20240117 - 125604 - 0000Document44 pagesAnatomy of Urinary Tract Systems - 20240117 - 125604 - 0000Sneha ThiagarajanNo ratings yet
- Radi 583 Paper Final Draft - HicksDocument26 pagesRadi 583 Paper Final Draft - Hicksapi-356393960No ratings yet
- UNIT 10 (Urinary System)Document6 pagesUNIT 10 (Urinary System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy RCR1 RenalDocument3 pagesAnatomy RCR1 RenaleamcrawleyNo ratings yet
- Struktur Dan Mekanisme Sistem UrinariaDocument15 pagesStruktur Dan Mekanisme Sistem UrinariaElva patabangNo ratings yet
- Renal Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument15 pagesRenal Anatomy and PhysiologySapna JainNo ratings yet
- Sistem Perkemihan - Hendriyan Sh. B.InggrisDocument13 pagesSistem Perkemihan - Hendriyan Sh. B.InggrisHaniyyahNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle StructureDocument38 pagesSkeletal Muscle Structuretoyy100% (1)
- Interactive PowerpointDocument12 pagesInteractive PowerpointRahul DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Cleavage: Types and PatternsDocument15 pagesCleavage: Types and PatternstrivikramraoNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 The Respiratory System: Learning OutcomesDocument9 pagesUnit 7 The Respiratory System: Learning OutcomesDeolita BadiangNo ratings yet
- A Cell Is Like A FactoryDocument13 pagesA Cell Is Like A FactoryNoralyn Ngislawan-GunnawaNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument22 pagesHeartNunoAlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Review of The Major and Minor Salivary Glands, Part 1 - Anatomy, Infectious, and Inflammatory ProcessesDocument8 pagesReview of The Major and Minor Salivary Glands, Part 1 - Anatomy, Infectious, and Inflammatory ProcessesPao AlexaNo ratings yet
- The Finale: Multiple Choice: Anatomy & Physiology Coloring WorkbookDocument3 pagesThe Finale: Multiple Choice: Anatomy & Physiology Coloring WorkbookJonash Morales0% (1)
- BIO 235 Syllabus Fall 2014Document4 pagesBIO 235 Syllabus Fall 2014Fan WuNo ratings yet
- Studies oDocument81 pagesStudies oRisha Meilinda MarpaungNo ratings yet
- Boron - Medical PhysiologyDocument13 pagesBoron - Medical PhysiologyOlgaBulat0% (6)
- Full Chapter The Little Book of Valuation How To Value A Company Pick A Stock and Profit Little Books Big Profits 2Nd Edition Aswath Damodaran PDFDocument25 pagesFull Chapter The Little Book of Valuation How To Value A Company Pick A Stock and Profit Little Books Big Profits 2Nd Edition Aswath Damodaran PDFdavid.levey889100% (2)
- RH Isoimmunization DR SamiraDocument37 pagesRH Isoimmunization DR Samiragynaecology2010100% (2)
- Phylum Aschelminthes (Nemathelminthes / Nematoda)Document15 pagesPhylum Aschelminthes (Nemathelminthes / Nematoda)Aditya KaleNo ratings yet
- 01.nobel 2002-Cacti. Biology and Uses (LIVRO)Document45 pages01.nobel 2002-Cacti. Biology and Uses (LIVRO)Anne KarolineNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption NotesDocument60 pagesDigestion and Absorption NotesAstha AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Nerve Supply of TeethDocument45 pagesNerve Supply of TeethJayakumar Patil0% (3)
- Endocrine System: Theoretical HandoutDocument153 pagesEndocrine System: Theoretical HandoutAmy AmyNo ratings yet
- Strength Training For Soccer (Bram Swinnen) (Z-Library) - 29Document1 pageStrength Training For Soccer (Bram Swinnen) (Z-Library) - 29guypetro6No ratings yet
- Unit 3, Human Anatomy and Physiology 1, B Pharmacy 1st Sem, Carewell PharmaDocument27 pagesUnit 3, Human Anatomy and Physiology 1, B Pharmacy 1st Sem, Carewell Pharmadeekshigowda07No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The TeethDocument8 pagesAnatomy of The Teethjitariandrei68No ratings yet
- 1 - 2 - Module 1 (Neuroanatomy) - Part 1 - Learning Objectives and Overview of Neuroanatomy (27-46)Document14 pages1 - 2 - Module 1 (Neuroanatomy) - Part 1 - Learning Objectives and Overview of Neuroanatomy (27-46)Rodrigo Eberhart Musaio SommaNo ratings yet
- Tarabi, Maria Kiara B. Tarabi II-10 RLE 1 Ma'am Cortez-Ramos 10/8/10Document5 pagesTarabi, Maria Kiara B. Tarabi II-10 RLE 1 Ma'am Cortez-Ramos 10/8/10Kiara TarabiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Roles in Reproductive and Sexual HealthDocument43 pagesNursing Roles in Reproductive and Sexual HealthKisses Joyce AlmazarNo ratings yet
- 1pages From The Anatomy of Stretching, Seco - Walker, BradDocument6 pages1pages From The Anatomy of Stretching, Seco - Walker, BradFatimah SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Brown FatDocument26 pagesBrown Fatno.1tracy843450% (2)
- Montfort Senior Secondary School: Sundaranadappu, SivagangaiDocument9 pagesMontfort Senior Secondary School: Sundaranadappu, SivagangaiRoss GellerNo ratings yet
- Hernias: General Features To All Types of HerniasDocument19 pagesHernias: General Features To All Types of Herniashussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System ExamDocument4 pagesEndocrine System ExamNirmala Josephine100% (1)