Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maalox
Maalox
Uploaded by
Julia Hermogino0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesThis document provides information about the drug Maalox, including its generic name (aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide), classification (antacid), mechanism of action (neutralizes hydrochloric acid in the stomach), indications (treats acid indigestion, heartburn, gastric hyperacidity), contraindications (renal insufficiency, severe abdominal pain), adverse reactions (nausea, constipation, diarrhea), and nursing responsibilities (assess for allergies or contraindications, monitor for effectiveness and side effects).
Original Description:
fgbgbf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information about the drug Maalox, including its generic name (aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide), classification (antacid), mechanism of action (neutralizes hydrochloric acid in the stomach), indications (treats acid indigestion, heartburn, gastric hyperacidity), contraindications (renal insufficiency, severe abdominal pain), adverse reactions (nausea, constipation, diarrhea), and nursing responsibilities (assess for allergies or contraindications, monitor for effectiveness and side effects).
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesMaalox
Maalox
Uploaded by
Julia HermoginoThis document provides information about the drug Maalox, including its generic name (aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide), classification (antacid), mechanism of action (neutralizes hydrochloric acid in the stomach), indications (treats acid indigestion, heartburn, gastric hyperacidity), contraindications (renal insufficiency, severe abdominal pain), adverse reactions (nausea, constipation, diarrhea), and nursing responsibilities (assess for allergies or contraindications, monitor for effectiveness and side effects).
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Republic of the Philippines
UNIVERSITY OF EASTERN PHILIPPINES
University Town, Northern Samar
COLLEGE of NURSING and ALLIED HEALTH SCIENCES
DRUG ANALYSIS
Name of Patient: ______ Date Admitted: ______ Chief Complaint: ______
Age: ______ Gender: ______ Civil Status: ______ Address: ______ Ward: ______
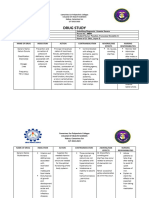
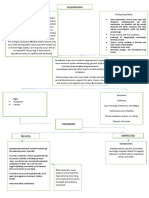
DRUG DATA MECHANISM OF INDICATIONS CONTRAIND DRUG ADVERSE NURSING
ACTION ICATIONS INDICATION REACTIONS RESPONSIBILITIES
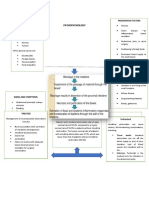
Generic Name: Aluminum Antacid Maalox This medication is This Assess for possible
Aluminum hydroxide, hydroxide is a therapy in should not be used to treat the medication contraindications
magnesium basic inorganic gastric and used in symptoms of too can cause and cautions: any
hydroxide. salt that acts by duodenal patients who much stomach acid nausea, history of allergy to
neutralizing ulcer, gastritis, are severely such as stomach constipation, antacids to prevent
Brand Name: hydrochloric acid heartburn, and debilitated or upset, heartburn, diarrhea, or hypersensitivity
Maalox in gastric gastric suffering and acid headache. reactions; renal
Classification: secretions. hyperacidity. from renal indigestion. It is dysfunction, which
Antacids Aluminum insufficiency, also used to relieve might interfere with
hydroxide is slowly or if there is symptoms of extra the drug’s excretion;
Reference: solubilized in the severe gas such as electrolyte
https:// stomach and abdominal belching, bloating, disturbances, which
nurseslabs.com/ reacts with pain and/or and feelings of could be
antacids/ hydrochloric acid the possibility pressure/ exacerbated by
https:// to form aluminum of bowel discomfort in the effects of the drug;
www.rnpedia.com/ chloride and obstruction. stomach/gut. and current status of
nursing-notes/ water. It also pregnancy or
pharmacology-drug- inhibits the action lactation due to
study-notes/ of pepsin by possible effects on
aluminum-hydroxide/ increasing the pH the fetus
and via or newborn.
adsorption. Perform a physical
Cytoprotective examination to
effects may occur establish baseline
through increases data before
in bicarbonate ion beginning therapy,
(HCO3-) and determine the
prostaglandins. effectiveness of the
therapy, and
evaluate for any
potential adverse
effects associated
with the drug.
Inspect the
abdomen;
auscultate bowel
sounds to ensure GI
motility.
Assess mucous
membrane status to
evaluate potential
problems with
absorption and
hydration.
Monitor laboratory
test results,
including serum
electrolyte levels
and renal function
tests, to monitor for
adverse effects of
the drug and
potential alterations
in excretion that
may necessitate
dose adjustment.
You might also like
- CDS Protocols - KalckerDocument46 pagesCDS Protocols - Kalckerbagus918100% (3)
- MiraLax (Polyethylene Glycol)Document1 pageMiraLax (Polyethylene Glycol)E100% (2)
- Gould, J. 2017towards Understanding The Under-Recognition of Girls and Women On The Autism SpectrumDocument3 pagesGould, J. 2017towards Understanding The Under-Recognition of Girls and Women On The Autism SpectrumBíró ZoltánNo ratings yet
- Medical Evaluation Form 2022Document2 pagesMedical Evaluation Form 2022jimmy p. lamhi50% (2)
- Counselling Fam Comm Disorders PDFDocument11 pagesCounselling Fam Comm Disorders PDFirimes carmelaNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy Ms. IbaleDocument23 pagesDrugstudy Ms. IbaleNabor, MelagroseNo ratings yet
- Megan Culata - GIT Drugs CourseworkDocument18 pagesMegan Culata - GIT Drugs CourseworkMegshieNo ratings yet
- DanicaDocument9 pagesDanicaDaniela CodmNo ratings yet
- PXprofile History Drugstudy PUDDocument8 pagesPXprofile History Drugstudy PUDPaola CruzNo ratings yet
- Campillo-Drug-Study M1Document4 pagesCampillo-Drug-Study M1NICOLE CAMPILLONo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocument2 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementJOHN PEARL FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Body System and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument7 pagesDrugs Affecting The Body System and Nursing ConsiderationsLOVELLE GRACE DE JESUSNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY LactuloseDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY LactuloseBRYCE WILLIAM GONo ratings yet
- Classification Generic Name Brand NameDocument42 pagesClassification Generic Name Brand NameMARIA ROWENA VIA J. LUCENANo ratings yet
- AntacidsDocument7 pagesAntacidsrosita d. ramosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 1 Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesDrug Study 1 Ferrous SulfateKrizzia Mae ColladoNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY-Omeprazole 2Document3 pagesDRUG-STUDY-Omeprazole 2Froo KeruNo ratings yet
- Antacids Are Used To Chemically React With and NeuDocument4 pagesAntacids Are Used To Chemically React With and Neunipheyy dananNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NOt COmpleteDocument6 pagesDrug Study NOt COmpletejiellianemaeNo ratings yet
- DrugsssDocument3 pagesDrugsssLindy JaneNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LactuloseDocument2 pagesDrug Study - LactuloseCath Bril100% (1)
- Case Study in Poorly Differentiated Endometrial Cancer With Dermoid Clear Cell FeaturesDocument20 pagesCase Study in Poorly Differentiated Endometrial Cancer With Dermoid Clear Cell FeaturesjimwelluismNo ratings yet
- X. Medical ManagementDocument12 pagesX. Medical ManagementXy-Za Roy MarieNo ratings yet
- Quigley 2011Document10 pagesQuigley 2011askhaeraniNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY (Ferrous Sulfate)Document3 pagesDRUG-STUDY (Ferrous Sulfate)NicholeGarcesCisnerosNo ratings yet
- Base-Icu Drug-Study-FormDocument27 pagesBase-Icu Drug-Study-FormJennifer AlamonNo ratings yet
- Cabasis1 Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCabasis1 Drug StudyNick James CabasisNo ratings yet
- Antacids: Antacids Are Used To Chemically React With and Neutralize The Acid in The Stomach. They CanDocument6 pagesAntacids: Antacids Are Used To Chemically React With and Neutralize The Acid in The Stomach. They CanKarina MadriagaNo ratings yet
- GI: Diarrhea/loose: Stools, Fulminant Hepatitis, Hepatic Dysfunction, JaundiceDocument3 pagesGI: Diarrhea/loose: Stools, Fulminant Hepatitis, Hepatic Dysfunction, JaundiceDaniela Claire FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - KetoanalougeDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Ketoanalougeliza sianNo ratings yet
- Drug TableDocument1 pageDrug TablehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - DigestiveDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - DigestiveRaynard MaestradoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Med Ward Duty)Document6 pagesDrug Study (Med Ward Duty)Kimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Base-Icu Drug StudyDocument10 pagesBase-Icu Drug StudyJennifer AlamonNo ratings yet
- Interpretations: How To Use Faecal Elastase TestingDocument6 pagesInterpretations: How To Use Faecal Elastase TestingguschinNo ratings yet
- Drug Study and NCP For Eamc Ob-Gyne Ward Case PresDocument4 pagesDrug Study and NCP For Eamc Ob-Gyne Ward Case PresvirnzrobzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyKyle Margaret FloresNo ratings yet
- Case 1: Pneumonia: 1st Sem:PrelimDocument8 pagesCase 1: Pneumonia: 1st Sem:PrelimJemy Tamaño MorongNo ratings yet
- Case 1: Pneumonia: 1st Sem:PrelimDocument8 pagesCase 1: Pneumonia: 1st Sem:PrelimJemy Tamaño MorongNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Drug Monitoring in The ElderlyDocument3 pagesTherapeutic Drug Monitoring in The ElderlyKristine BaringNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing Drug Study Age: 69 Ward/Bed Number:MMSW-2 Impression/Diagnosis: HAP, COPD Acute ExacerbationDocument2 pagesCollege of Nursing Drug Study Age: 69 Ward/Bed Number:MMSW-2 Impression/Diagnosis: HAP, COPD Acute ExacerbationSian AsadaNo ratings yet
- Icu Jendrugiee2Document6 pagesIcu Jendrugiee2Jennifer AlamonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studyfaula rocamoraNo ratings yet
- Final - Food PoisoningDocument10 pagesFinal - Food PoisoningCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- D. PharmaDocument45 pagesD. PharmaShivam Das, Tehsil KulpaharNo ratings yet
- Blumea Balsamifera (L.) DC (NIRPROMP Tablet)Document9 pagesBlumea Balsamifera (L.) DC (NIRPROMP Tablet)Rexel BarramedaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Peptic Ulcer: Ma. Christina T. Alvarez Wup - Bs Nursing Iii-2Document18 pagesCase Presentation Peptic Ulcer: Ma. Christina T. Alvarez Wup - Bs Nursing Iii-2Shane Aileen AngelesNo ratings yet
- Review: Treatment of Constipation in Older PeopleDocument8 pagesReview: Treatment of Constipation in Older PeopleMohd ZulAmirulNo ratings yet
- Name of DrugsDocument3 pagesName of DrugsMiaLynn PangkuNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy Reviews: Pharmacology and Clinical Use of AntacidsDocument5 pagesDrug Therapy Reviews: Pharmacology and Clinical Use of AntacidsAaquib AmirNo ratings yet
- Management of ConstipationDocument3 pagesManagement of ConstipationFarah Balqis BaragbahNo ratings yet
- Lactulose Drug StudyDocument1 pageLactulose Drug StudyJhanine ArellanoNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDYDocument6 pagesDRUGSTUDYMauriceNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Drug Study Ketoanalogue PDF FreeDocument2 pagesComprehensive Drug Study Ketoanalogue PDF FreeYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY PesebreDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY PesebreFrancoise Nicolette PesebreNo ratings yet
- Drug Delivery On Rectal Absorption: Suppositories: Review ArticleDocument7 pagesDrug Delivery On Rectal Absorption: Suppositories: Review ArticleNindah IkaNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Agents PDFDocument32 pagesParathyroid Agents PDFRhodee Kristine DoñaNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Agents PDFDocument32 pagesParathyroid Agents PDFRhodee Kristine DoñaNo ratings yet
- SucralfateDocument10 pagesSucralfateherlika gustineNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyhsiriaNo ratings yet
- Phinma - University of Iloilo College of Allied Health Sciences Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPhinma - University of Iloilo College of Allied Health Sciences Drug Studylhie cabanlitNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyChuchai AmbongNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SorbitolDocument2 pagesDrug Study SorbitolみずNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionFrom EverandHandbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Writing Learning Objectives Nursing - Jan - 2022Document3 pagesWriting Learning Objectives Nursing - Jan - 2022Julia HermoginoNo ratings yet
- Med Surg Learning Plans Angels T DenisDocument13 pagesMed Surg Learning Plans Angels T DenisJulia HermoginoNo ratings yet
- Entrep M3Document8 pagesEntrep M3Julia HermoginoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology 1Document1 pagePathophysiology 1Julia HermoginoNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument1 pageElectrolyte ImbalanceJulia HermoginoNo ratings yet
- Acid ImbaLANCEDocument1 pageAcid ImbaLANCEJulia HermoginoNo ratings yet
- Case Study 92 Breast CancerDocument3 pagesCase Study 92 Breast CancerJulia HermoginoNo ratings yet
- Curie Capstone Origanum Vulgare RevisedDocument32 pagesCurie Capstone Origanum Vulgare RevisedJapet AlcaideNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis PathophysiologyArunNo ratings yet
- Principles of Aerobic ExerciseDocument23 pagesPrinciples of Aerobic ExerciseAmina Sawalmeh100% (2)
- MovicolDocument2 pagesMovicolreadalotbutnowisdomyetNo ratings yet
- Dr. Artrien Adhi Putri, SP.P (K), M.biomedDocument44 pagesDr. Artrien Adhi Putri, SP.P (K), M.biomedNovery SimbolonNo ratings yet
- College of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDocument5 pagesCollege of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Body Weight MonitorDocument15 pagesBody Weight MonitorBimbo Malonzo LabajoNo ratings yet
- Group 8Document14 pagesGroup 8HrishavNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Principles of Athletic Training: A Guide To Evidence-Based Clinical Practice 17th Edition All ChapterDocument43 pagesFull Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Principles of Athletic Training: A Guide To Evidence-Based Clinical Practice 17th Edition All Chaptercawwoopahomi100% (7)
- Management of Pediatric Blunt Abdominal Trauma in A Dutch Level One Trauma CenterDocument14 pagesManagement of Pediatric Blunt Abdominal Trauma in A Dutch Level One Trauma CenterimamNo ratings yet
- Gambaran Radiologi OsteomielitisDocument5 pagesGambaran Radiologi Osteomielitisoktaviana54No ratings yet
- Case Presentation Radicular CystDocument27 pagesCase Presentation Radicular CystVishnu PreethamNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Variations in The Human Paranasal Sinus Region Studied by CTDocument7 pagesAnatomical Variations in The Human Paranasal Sinus Region Studied by CTkhanhlinhNo ratings yet
- Icmr 33930643Document2 pagesIcmr 33930643saicharan reddyNo ratings yet
- PEDIATRIC Drug Formulary 2019-20Document56 pagesPEDIATRIC Drug Formulary 2019-20Eva Marie GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and Drug Abuse Division (ADAD) Substance Use Disorder Treatment Rules Colorado DHSDocument80 pagesAlcohol and Drug Abuse Division (ADAD) Substance Use Disorder Treatment Rules Colorado DHSBrian HarrisNo ratings yet
- The Fastest Way To Sleep?Document7 pagesThe Fastest Way To Sleep?NNorameenNo ratings yet
- Pharma LMRDocument21 pagesPharma LMRAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Consecuencias de La Alimentación Con Fórmula InfantilDocument12 pagesConsecuencias de La Alimentación Con Fórmula InfantilAna M. Garcia CubaNo ratings yet
- TCM Wen Bing ReviewDocument8 pagesTCM Wen Bing ReviewFredy Mardika SenjayaNo ratings yet
- ModernaDocument22 pagesModernagoslugs12No ratings yet
- Drug Presentation On Anti-Hypertensive: All India Institute of Medical and Science New Delhi 2021-2022Document12 pagesDrug Presentation On Anti-Hypertensive: All India Institute of Medical and Science New Delhi 2021-2022Priya SinghNo ratings yet
- More Secret Remedies PDFDocument298 pagesMore Secret Remedies PDFBalakrishna GopinathNo ratings yet
- Inglés II - TP 1 ResueltoDocument15 pagesInglés II - TP 1 ResueltoDani100% (1)
- Heavenly Elixir 1Document63 pagesHeavenly Elixir 1Ryan Lorenzo Garcia PerezNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal DiseaseDocument12 pagesChronic Renal DiseaseNohaira SADANGNo ratings yet