Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio - CO 6
Bio - CO 6
Uploaded by
Jae Bert UbisoftOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio - CO 6
Bio - CO 6
Uploaded by
Jae Bert UbisoftCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOLOGY 01
Course Outcome 6
REDOX REACTIONS
IMPORTANT TERMS:
Metabolism – has two complementary components
Catabolism – releases energy by splitting complex molecules into smaller components
Anabolism – synthesis of complex molecules from simpler building blocks
Cellular Respiration – catabolic process that converts energy from nutrients to energy stored in ATP
Aerobic Respiration – requires oxygen
1. Glycolysis
2. Formation of acetyl coenzyme
3. Citric acid cycle
4. Electron transport and chemiosmosis
Anaerobic Respiration – does not require oxygen
Fermentation
Ethanol
Glucose + Yeast
Lactic Acid
Lactose + Good Bacteria
AEROBIC RESPIRATION
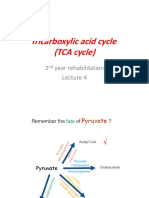
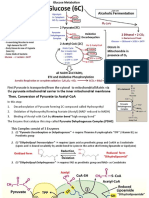
I. GLYCOLYSIS Pyruvate
“ Good Gracious Father Franklin Did Glyca bought 4pin” Pyruvate Kinase 2atp>2adp
Glucose phosphoenolpyruvate
atp>adp Hexokinase Enolase (H2O release)
Glucose 6 phosphate 2 phosphoglycerate
Phosphoglucoisomerase Phosphoglyceromutase
Fructose 6 phosphate 3 phosphoglycerate
atp>adp Phosphofructokinase Phosphoglycerokinase 2atp>2adp
Dihydroxyacetone G3P dehydrogenase
1, 3
Fructose 1, 6 phosphate
biphosphoglycerate
biphosphate Glyceraldehyde 3
phosphate (G3P) 2NAD > 2NADPH
Aldolase Isomerase
Pyruvate Acetyl CoA Citrate
Pyruvate oxidation Oxaloacetate CITRIC ACID Isocitate
CYCLE
Malate “Can I keep Α-Ketoglutarate
selling sex for
Fumerate money officer” Succinyl CoA
Succinate
II. III. ETC
CONVERSION
1 ATP = 1 ATP 1 ATP
1 NADH = 3 ATP 2.5 ATP
1 FADH2 = 2 ATP 1.5 ATP
NET
NAD+ Glycolysis:
FAD AcetylOCOA:
2 and H2O
TCA Cycle:
NAD+ & FAD
2 ATP 2 NADH 3 NADH x 2 =6 NADH
I 2 NADHII III 1 ATP x 2 = 2IVATP
1 FADH2 x 2 = 2 FADH2 ATP Synthase
NADH Succinate COMPUTATION
Cytochrome Cytochrome
Reductase Net
Dehydrogenase Conversion
Reductase Computation
Oxidase
4 ATP 4 ATP 4 ATP
3 ATP
10 NADH 30 ATP
NADH
2 ATP
2 FADH2 4 ATP
FADH 2
TOTAL : 38 ATP
You might also like
- BIOCHEMISTRY - Summary of PathwaysDocument8 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY - Summary of PathwaysWendy Mae100% (10)
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet 2Document2 pagesTranscription and Translation Worksheet 2n1n2n3n50% (2)
- BIO121 Chapter 7 Releasing Chemical EnergyDocument45 pagesBIO121 Chapter 7 Releasing Chemical EnergyggttettanNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis and Kreb CycleDocument34 pagesGlycolysis and Kreb CycleKhazel CasimiroNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis - "EMP Pathway" "Embden Meyerhoff Parnas Pathway" AncientDocument2 pagesGlycolysis - "EMP Pathway" "Embden Meyerhoff Parnas Pathway" AncientKathleene AulidaNo ratings yet
- Cho MetabDocument1 pageCho MetabKarla Faye UcangNo ratings yet
- Bio LectureDocument38 pagesBio LectureDaniel ZederNo ratings yet
- MicroBio Lec Transes 8 9Document7 pagesMicroBio Lec Transes 8 9Kai BarsanaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration ActivityDocument8 pagesCellular Respiration ActivityJOCAS GERALD G. ABARCARNo ratings yet
- ASB0204 Chap 7 - CidDocument42 pagesASB0204 Chap 7 - CidZulhelmiNo ratings yet
- 1M. 2 - Biochemistry - Glycolysis and KrebsDocument4 pages1M. 2 - Biochemistry - Glycolysis and KrebsKate Lynne Camonayan100% (1)
- Cellular Respiration: Biology I FinalsDocument7 pagesCellular Respiration: Biology I FinalsPrimo GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme KatabolismeDocument3 pagesMetabolisme KatabolismeGiska AliyaNo ratings yet
- Carbo ChemDocument123 pagesCarbo ChemHan MichelNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 27: Fatty Acid Degradation: 27.1: Fatty Acids Are Processed in Three StagesDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 27: Fatty Acid Degradation: 27.1: Fatty Acids Are Processed in Three Stagesshyamalee97No ratings yet
- 2 GlycolysisDocument43 pages2 GlycolysisAbdul RaufNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Complete Notes (B.pharm 2nd Sem)Document25 pagesCarbohydrate Complete Notes (B.pharm 2nd Sem)DIPENDRA KUMAR KUSHAWAHANo ratings yet
- Introduction BCHN 222 2022Document39 pagesIntroduction BCHN 222 2022Francisca ManyisaNo ratings yet
- TCA Cycle and ETC 2015 E.C.Document47 pagesTCA Cycle and ETC 2015 E.C.Abdurehman KasimNo ratings yet
- 11 - Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument68 pages11 - Carbohydrate MetabolismcheckmateNo ratings yet
- Engineering of Biological Processes Metabolic Pathways: Pertemuan 2Document26 pagesEngineering of Biological Processes Metabolic Pathways: Pertemuan 2Fauzan RahmanNo ratings yet
- 05 Cell Respiration Fermentation Anaerobic and MoreDocument21 pages05 Cell Respiration Fermentation Anaerobic and MoreneelNo ratings yet
- Asy GlycolysisDocument69 pagesAsy GlycolysisErdem AltunNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism 1Document22 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism 1Affie SaikolNo ratings yet
- Cho L4 (Tca) 2020-2021Document23 pagesCho L4 (Tca) 2020-2021Sara AljadaniNo ratings yet
- Bioc192 2018 s2Document30 pagesBioc192 2018 s2Joel CatlettNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 20 Class Notes Saakaar 20 Batch For IIT JAM 2Document46 pagesBiochemistry 20 Class Notes Saakaar 20 Batch For IIT JAM 2Adeeti RaiNo ratings yet
- Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle: DR Imran SiddiquiDocument10 pagesTricarboxylic Acid Cycle: DR Imran Siddiquiapi-19824406No ratings yet
- Cho L4 (Tca) 2020-2021Document25 pagesCho L4 (Tca) 2020-2021RNo ratings yet
- Cellularrespiration2012 130110052718 Phpapp02Document59 pagesCellularrespiration2012 130110052718 Phpapp02Kimberly Anne PagdangananNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration ActivityDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration Activitymysh grcNo ratings yet
- Engineering of Biological Processes Lecture 1: Metabolic PathwaysDocument27 pagesEngineering of Biological Processes Lecture 1: Metabolic Pathwaysagnarindra01_8550147No ratings yet
- Microbial MetabolismDocument49 pagesMicrobial MetabolismOmelNo ratings yet
- Kreb cycle (2) - ١٢٤٠٢٠Document25 pagesKreb cycle (2) - ١٢٤٠٢٠bastakwyryNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Fermentation 1Document29 pagesCellular Respiration Fermentation 1Lorraine LibioNo ratings yet
- 10 GluconeogenesisDocument18 pages10 GluconeogenesiskulturewearzmNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid CycleDocument20 pagesCitric Acid CycleAastha SinhaNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - Aerobic Cellular RespirationDocument5 pagesGroup 5 - Aerobic Cellular Respirationditucalan.ha2003No ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument19 pagesBiochemistry: Carbohydrate MetabolismALINo ratings yet
- Summarybioo Compressed PDFDocument3 pagesSummarybioo Compressed PDFHassan mohamad Al-bayateNo ratings yet
- 1 Metabolism-BDS2020-student copyDocument33 pages1 Metabolism-BDS2020-student copyFoo Mei FongNo ratings yet
- 2.2 TCA CycleDocument14 pages2.2 TCA Cyclesabirinaly30No ratings yet
- Ch9 Tricardoxylic Acid Cycle LectureDocument16 pagesCh9 Tricardoxylic Acid Cycle Lecturearyanchaudhary77798No ratings yet
- Revisi TerakhirDocument14 pagesRevisi TerakhirSyaiful RizalNo ratings yet
- METABOLISMDocument11 pagesMETABOLISMking untalanNo ratings yet
- Jamiel James Arceno Biochemisty Bsn1BDocument2 pagesJamiel James Arceno Biochemisty Bsn1BjamielNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration PDFDocument85 pagesCellular Respiration PDFmailforprinting101No ratings yet
- DRB 13-14 - Metabolic Pathways Dan EngeeneringDocument43 pagesDRB 13-14 - Metabolic Pathways Dan EngeeneringItsAndrioNo ratings yet
- Lect # 3 GluconeogenesisDocument40 pagesLect # 3 GluconeogenesisUbaid ur Rahman100% (1)
- Facultad de Medicina: Seminario N°4: Ciclo de Los Ácidos Tricarboxílicos Y Metabolismo Del GluucógenoDocument41 pagesFacultad de Medicina: Seminario N°4: Ciclo de Los Ácidos Tricarboxílicos Y Metabolismo Del GluucógenoyeniferNo ratings yet
- 228 Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument43 pages228 Carbohydrate MetabolismAmanullahNo ratings yet
- Different Metabolic PathwaysDocument1 pageDifferent Metabolic PathwaysKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Cell Respiration Glycoloysis and Acetyl CoADocument30 pagesCell Respiration Glycoloysis and Acetyl CoAJ15No ratings yet
- Biochemical PathwaysDocument38 pagesBiochemical PathwaysMarja Shania Galido RañolaNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis and TCA Cycle Enzymes and EC Reference NumbersDocument1 pageGlycolysis and TCA Cycle Enzymes and EC Reference NumbersDr. SHIVA AITHALNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis + Cell Resp SLIDESDocument7 pagesGlycolysis + Cell Resp SLIDESDavid WoodyNo ratings yet
- Cell RespiDocument30 pagesCell Respi11009911No ratings yet
- Ho10 Tca & EtsDocument26 pagesHo10 Tca & EtstresnowahyudienNo ratings yet
- TCA CycleDocument47 pagesTCA CycleMita SeptianiNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Glycolysis Alcoholic Fermentation: Oxidative DecarboxyationDocument19 pagesAnaerobic Glycolysis Alcoholic Fermentation: Oxidative DecarboxyationMadani TawfeeqNo ratings yet
- Bio - CO 4Document5 pagesBio - CO 4Jae Bert UbisoftNo ratings yet
- Math01 - CO 4Document4 pagesMath01 - CO 4Jae Bert UbisoftNo ratings yet
- MATH 01 FormulaDocument3 pagesMATH 01 FormulaJae Bert UbisoftNo ratings yet
- Math04 - CO 4Document1 pageMath04 - CO 4Jae Bert UbisoftNo ratings yet
- Bio - CO 5Document3 pagesBio - CO 5Jae Bert UbisoftNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids Metabolism &: Urea CycleDocument11 pagesAmino Acids Metabolism &: Urea Cyclemuhammad amjadNo ratings yet
- CH 19Document27 pagesCH 19NadunKodikaraNo ratings yet
- Annex 10 Ordinance Fdha Materials and Articles Intended To Come Into Contact With Food StuffsDocument202 pagesAnnex 10 Ordinance Fdha Materials and Articles Intended To Come Into Contact With Food Stuffsjai soniNo ratings yet
- Lupin Product ListDocument6 pagesLupin Product ListIbrahim Mohammad100% (1)
- Pka ChartDocument1 pagePka ChartHimansu BisoiNo ratings yet
- Chem 31.1 FG Post Lab Group 4 Expt. 2Document10 pagesChem 31.1 FG Post Lab Group 4 Expt. 2lazygemNo ratings yet
- Pharma DermaDocument7 pagesPharma DermaDee SarajanNo ratings yet
- The Alkaloids, Vol. 1 - The Chemical SocietyDocument524 pagesThe Alkaloids, Vol. 1 - The Chemical SocietyDimitri100% (1)
- Drug Comment Dosage: Table 44-3. Pediatric Drug DosagesDocument7 pagesDrug Comment Dosage: Table 44-3. Pediatric Drug Dosageschocolat_stripesNo ratings yet
- Missing Page From - Determining Unknown Organic Compound Lab ReportDocument1 pageMissing Page From - Determining Unknown Organic Compound Lab ReportMark RileyNo ratings yet
- Drugs To Watch With WARFARINDocument3 pagesDrugs To Watch With WARFARINRajendra RaiNo ratings yet
- Objectives: CH - OHDocument18 pagesObjectives: CH - OHHarsh TyagiNo ratings yet
- Reagent and CatalysisDocument37 pagesReagent and CatalysisBapu ThoratNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Organic Derivatives of WaterDocument3 pagesWorksheet Organic Derivatives of WaterVenicer BalaodNo ratings yet
- chm510 Experiment 3Document7 pageschm510 Experiment 3Naz Helmi100% (1)
- fORMULARIUM NASIONALDocument12 pagesfORMULARIUM NASIONALKlinik HARAPAN KITA BATAMNo ratings yet
- 13.5 DNA Structure and Protein Synthesis (Biology Only) 2020 StudentsDocument55 pages13.5 DNA Structure and Protein Synthesis (Biology Only) 2020 StudentsBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Chem 113 Lipid ActivityDocument3 pagesChem 113 Lipid ActivityAlliah MendozaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Extra CycloalkanesDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 2 Extra Cycloalkanesellina safian100% (1)
- Chinox 168: AntioxidantDocument2 pagesChinox 168: AntioxidantDanilo CunhaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Chemistry AssignmentDocument23 pagesBiomolecules Chemistry AssignmentArchita PanchalNo ratings yet
- Importacion de Tolueno 2018Document12 pagesImportacion de Tolueno 2018Juan Jose LlamoccaNo ratings yet
- Alkene - Alkynes 1Document39 pagesAlkene - Alkynes 1Hajar MuhamadNo ratings yet
- 2018 01 15 Lijst Antibiotica Met DDDA Informatie (Update 15-01-2018) - 167 PDFDocument11 pages2018 01 15 Lijst Antibiotica Met DDDA Informatie (Update 15-01-2018) - 167 PDFMatthew HsuNo ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument35 pagesCentral Dogmatariqul13017No ratings yet
- 8.0 Gugus KarbonilDocument64 pages8.0 Gugus KarbonilWahyu DinNo ratings yet
- .Degradasi ProteinDocument29 pages.Degradasi ProteinSeffy Yane SuhandaNo ratings yet
- Form Obat Dan AlkesDocument33 pagesForm Obat Dan AlkesTiara Widya NovadilaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Protecting Groups: OTHP/OMOM Protecting GroupDocument7 pagesAlcohol Protecting Groups: OTHP/OMOM Protecting GroupQuốc NguyễnNo ratings yet