Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 viewsESC133 Unit 2
ESC133 Unit 2
Uploaded by
Ronda StewartCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- AmplifierDocument3 pagesAmplifierRonda StewartNo ratings yet
- Unit - II Quantum MechanicsDocument14 pagesUnit - II Quantum MechanicsRonda StewartNo ratings yet
- ArraysDocument3 pagesArraysRonda StewartNo ratings yet
- Adalita Bhase KannadaDocument5 pagesAdalita Bhase KannadaRonda StewartNo ratings yet
- Basic Java Programming S and S IA1Document4 pagesBasic Java Programming S and S IA1Ronda StewartNo ratings yet
- LASER Notes (Dec-2022) - 1Document20 pagesLASER Notes (Dec-2022) - 1Ronda StewartNo ratings yet
- Spherical Refracting Surfaces TheoryDocument6 pagesSpherical Refracting Surfaces TheoryRonda StewartNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 NotesDocument16 pagesUnit-2 NotesRonda StewartNo ratings yet
- Maths Lab RecordDocument3 pagesMaths Lab RecordRonda StewartNo ratings yet
- Spherical Mirrors MCQ SolutionsDocument12 pagesSpherical Mirrors MCQ SolutionsRonda StewartNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics (MCQS)Document21 pagesWave Optics (MCQS)Ronda StewartNo ratings yet
- 2nd Pu Notes - 2021-06-19T064153.704Document161 pages2nd Pu Notes - 2021-06-19T064153.704Ronda StewartNo ratings yet
- Combination of Resistances: Circuit Diagram: Series Combination Experiment No.:7A Date: Aim: - Apparatus RequiredDocument4 pagesCombination of Resistances: Circuit Diagram: Series Combination Experiment No.:7A Date: Aim: - Apparatus RequiredRonda StewartNo ratings yet
ESC133 Unit 2
ESC133 Unit 2
Uploaded by
Ronda Stewart0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views30 pagesOriginal Title
ESC133 Unit 2 (2)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views30 pagesESC133 Unit 2
ESC133 Unit 2
Uploaded by
Ronda StewartCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 30
Unit 2: Power Suppuies
eee
— Power is the backbone £ any electronie syste and
the power supply is what feeds the system.
This chapter gis an inbeduchon to the flower Gupp
Civcuits that we come across in cur laty life
> Any electronic deurce congrsts of & power Supply unit
cohich provicles the required “cimount of AC oF DC
Power Supply to various sections Of that electronic
device.
Need for Power Supplies
There ave many small seckons present in the
Electronic devices” Buech as computer, television,
CRO ete. but all f those seckons doesn't need 230v
AC Supply cohich ube get from mains
— Gnstecd one or more Sections may need o42V De
@hile Bome others ma
meed O Sov bc
> Sn order 40 provicle “the
enquired de voltages, the
ney 230v_AC ly has to be Conwrted into pure
oc fe the usage
= The f
Power Supply units serve the game purpose
Parts of a Power Supply
> The block clagram of a d-¢ power Supply is shown
in $g- below:
> S$ consists
f step-down transformer, se ctifier,
weservoty and ve Hage regulator as shown.
24
Smo. Smocthed
High raed a Mapes cee Be" Reqd
A
vig ac v J v J
v7 Rectifrer| 4 Resevvo Voting
[tray Req o
Block diagram La Dc power Suppl
cranstomer Rechfied Ej Lteved i
hg oa SR cupat g
Block clragram of a dC powey Supply showing
Prinuiple Components ,
—> From the above block ditgrams, we can observe that
transfinmer i& present atthe inital Stage
> A transformer has c pyimeny coil te whith input ic
ge and a Secondang coil se which the output i's
Collected
> Tn our power Supply Cireuits , we use the Step-down
francbmen Lop Oppropriate tums ratio), as we need 40
lowey the AC power to DC
>The output of thts step-down transformey will be less
In power and this will be gun cs-the Input. to the next
Becton, cellecl Rechfier
22
Mol
— Whenever there arises the need +0 conurt an_Ac
to DC power, a wechfier civeuit comes forthe vesctee:
> A simple Pas function dicde acts as a rectifier:
The forwarcl biasme cand veverse biasmg conclitins
Of the clicde makes -the rectification.
>The ac output from the transformer secondary is
then cectified sng gili¢on rectifier cliodes to
Procluce an cinsmoothed output (pulsatng de)as
Shown above in fig
>The pulsedierde output comma from rechfier element
Consists Of unwanted ac ©) nents
>This ac component has to be completely removed in
order to get pure _de- output
> So, the op of rectifier (pulsering de) is then fed as
‘input fo meact sechon te, Reservoir /Smoothmg filter,
cohich remeves the QC component present in The
rectified output and allows the de Component to
reach the load
>The ment and the Cast_Stage in power Supply
System is the Rege actos Part
> As we aebserve that the op of Reserucir, (smocthong
fitter is not pure dew
ih order to gob punect form of de op, ox need te poss
the pulsatnd’ de ofp from filter RE into the voltage
regulator Stage.
> A yoltaye regulater is Such a deuice that maintains
constant “outpitt voltage, instead of cry ond of
fluctuations in the Input voltage beng applied
23
Met.
Sumenerny
he high voltage ac is fed to Gkpdewn trarsfermer, which
intutin gives low Voltage ac- Z
>The low voltage ac Cofp frum bensfermey) 1s fed as
input to ment Stage ie: Rectifier crrceart This will
ve the pulscrhng de cuctput: which consists. both
‘ac_and de Components -
> then the ojp of rectifier ts fad as input 4 newt Stage
hey Reservoir /smoothng filter Ceapacitor) .-
>The Capaciter helps fo smooth Out the voltage Pulses
Procuced by the cechifien-
+t Coften based on Zener
—> Foally a stabiligmg chreei
dliocle) ides a. Bases output voltage.
Rectifiers
= Reclificedion ts the process of convrimg ac supply
into pure de Suppl
Te. perform this, we need a rectifier circuit
> A diocle is used as reckifyng clement to construct
the rectifier_civeuit
> Gepending onthe ofp and ne diodes usage,
the rectifier cinuits are Classifrd inte theo main
pes
> Haig wae Re
> Half wave rechfier cht recifies nyo haf cyl
Of the input Supply eohereas Full wave rectifier cht
rectifieS both the half Cycles Of input suppl
and Full eoave Rectifier
24
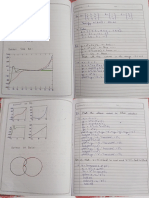
Half hlave Rectifier (HWIR)
>The mame half- eave rechfier itself States that
the rectification’ is dene onl eset ie positive
OB neq octive sr Of the input supply cycle
Set
a i Seas
fee Derg te bl ee
primary cit ms =
Nae Secendany coi bavas TNE nocmese Ze,
meteor
— Ar altematnes tnpuk votlage ts applied via a transfowmer
be
ta Binge diode connecked tn Series with o load resister RL
> During the positive hal, le Of the input, diocle
becomes forward biased and on effectiely behave tke
ao closed Sith.
> Current sarts flowng inthe dtredton shown cibove
‘Cfror Cathode +0 ama)
Uber cliode is finverd biased, the volta across
this Ve and the output voHage is ae eSTaT Vr
— Ideal condition.
<— Practical Condition (st)
Aime et Secondary =
Met
> During negative half cycle of input, cliocle becomes
S negative _
reverse phased causing e dhe to act like an
open Switch 2 show chove
7 No current flow in reverse biased diode amdition.
> No=ov letdeat Condition
Vo. Tad < Prackeal Condition:
where
Tr= gmall weverse coment duety mtreri
ge comes. f
?
& RL =v high resictance
> From the lip ¥ op waveforms , we obsone that diode Di
conducts Con) for ~~ Positive half cyele of ip and
doesn't Conducts Cofe) for every negative half eycle of
Inpeks
the cutpit will be pulsating which is taken Geross
the load resistor CRL)- .
Fat ewe Rectifier (FUR)
> Unfortunately, the half wave mectifier crreuit is
relatively inefficient as concuchen takes Place ~
on altefhate “half cycles
> A better recifier Ovrongement exould make use of bots
positie and megative half cycles:
> The full-wave rechfier Circuits offer a considerabie
improvement. over -thery half-ecave wrectffer Counterparts.
There ove two basic firms F FAR
ey OEE Cty Centre Tapped) Biphase Rectifier
wi Bridge Reck fren
© Contre Tapped | Bi-phase Rechfor ™
Duying —vé hal cle. =
Paving ve ef eye 5 i |
Tnpuk — oukpute voovefors
>The civeuit 5 essentially conbnedton of two half
wouNe civeuits
> Fe cibove figs shows a Simple bi -phace|Contre tppect
anctifier
> Mains volt (24qov) Is appived to the primory of
vch has bo identical secondary
step-down transformer whi
wwinclinys, each providing equal amount of vollape-
= During positive half oy cycle ff input voltage, point ‘A’ will be
poorivd with respect areas B ie
-
> Similarly point 'B' will be positive with respect ty — MO
point 'c?
> Gn this condlttron , drode. Dy Conducts (ON) eahile
Do_will mot_condluct CoFe).
> Dy ts -frward biased and load current (1) flows
from the top_of the tra er_gecondlons through D1,
cUnnugh Re from top to bottom, ard back tothe fansfermer
Centre tap as shown in fig above.
> Unthis, the current 1s due to diode ‘Da’,
> Girwng ive haf cyele of the input ‘Vellage, point
0 wilt be Positive with respect to point A’
> So thts Cmdriton, diode Da elit beceme fimeard biased
cincl conclucts CON) ewhile diode Dy will become reverse
biased and mot _conclucts CofE).
prased
> Ie flows fiom the bottom terminal of the transformer
sermaaniy: Honus Do, trou Re fem top to bettom,
and back“ +o the tvansfermey centre bap. as shown in fig:
> Inthis, the current 1s due fe diode! Do’
7 From 4his we can observe that , Positive halt cycles
A oor postive Ralf acyeeal
uct gets rectified by Di and every mneqtve half egeles of
put gees rectified by Da
> The e6uit is thet current is routed! Heeugh the load
in the Game Clirecron Cop te bettom) for Goth _haif cycles
operation, thus we get Successive positive half Cgoles
in the output as séen above
> The load current foyp waveform is the gum of individual
diode cements fievsing in comresponclng half cycles
ao
5 The cenbe-tagred transformer used in Bi-phase civcuit,
ts usually more Compler ,excpensive and requires more
Space thal additional drocles oe
So, a bridge rectifier 16 the clyauit most frequently used
Thre avoids the neecl to have boo seperate secondary
windings
n> The bridge vectifier Crveutt is essertrally & FOR frit,
using 4diodes, forming the arms of an electrical bridge
>To one _cliagonal ofthe bridge, the ac voltage is aj lied
, age f= appli
throw F adlafet sccondodh al The reckified! ct vetage
ts Laken fror the other dliagonal of the bridge as
Shown above &
>The 4 diedes connected eoith therr Anowhead Symcls “Mt
alll pointing toward the positive output terminal
the citait. + #
>The fullecove bridge rectf ent iS 1
he ge rectifier cavongement 15 a5 shown
> Mains voltage is applied tothe prima a step-down
beansformes reo Ot
> The Secmdeny utnemg provides ms voltage as before
> Boing posiine half cycle of pst voltage, pomt A
coil! bil positive with respect * pome ‘et
> Tn thie Condition, diodes 04 ond Da_comducts ond
clioces Ds and Dy vot Conducts:
> The load current Ch) flows fro positive input termincal(A)
Urrough Ds to Re, and then through Ru and D2, back
40 Regative input_terminal(s)
One DP ROR =) current flow
> Note that,the direction of the load current through
Re is from top 40 bottom:
> aaa dhis time, positive termmal of inp ts applied
+ cathocle of P4 and negate terminal of input ts
applied -to Anode of Da “Hence Py and Ds are
reverse biased + a ea
7 Tn this, the cusrent
> Bag negative half cycle of inpud. votige, point!"
will be positive with respect t point_A’
> fo this condition, cliodes D3 and Dy Conducts (on)
‘and aliodes Da and D2 doesn't conducts (OFF).
D1_and D2 Coesnt conan
ic due-to diodes Dg ancl D2
Met
> The lead current Cr.) flows from positie Input
termmal (B) ‘through Da to RL, and then through Re
Grd Dy back 10 megatve input terminal (a) "~~
03 RO =) Cement flow»
A
> Note that, the direction of the load current through
Re ts agate fron top to batten.
> During this time, Positive termmal of input ts applred
to catidde of Do and negate termina! of input is
applied to ancole of Da. Hence Da and D3 are
severse biased:
> Sn this, the curment ts due to cliodes Ds and Dy.
> fis seen Pat luring bot elf cycles Of the inpuct
the eutput_temmmal polar is always positive at
the op of RL and megatv® at the bottom:
> Both positiveand negative half-cycles Othe input
ave passed to the output
> The repatie half’ qycles ove inverted, sothect the
output Fe a coninucus Sones of positive half
ee of Sinusoidal voltages
Capacitas Fitter Crreuit
Th. power Supply block dragram clearly explams that
a ears Pd ceded ofter the well er chreuit
Gilt now we have. seen Bree different types OF oediffer
ciranits-
> The outputs of cl these aectifier circuits contams
Some vipple(ac component):
>This az component has to be completely removed
order to get pure de output
a
> 80, we neecl a chreit that Bmoothens the sectifred
oukput into a pure de signal
> A filter ciraiit is one ewhich removes the ae
Component present in the rectified cxetput and allows
the dle Component to reach the. load
>The following frure shows the finchonality ofa
filter circuit
ow
ie
“Ww r\ Filter [eh
; > Circuit fe} .
Rackifed oF An ideal filter o/e
Gi pilter crvcuit és constructed etsing too main
Componente, induckerand capacitor
> An Tnducter allows’ de and blocks ac
Gln Capaciter allows ac and blocks de
> Wle use capaciter filter because of it small Size ¢
fess power Consumption
> Bs he charadorstes of cxpacitor St # allows ae
Sat blocks de , 60 we have fo connect 7% alwoags in
cuts,
parallel with gesistive load, RL rm cectifien
Half Wave Rectifier ewith Gapacitor Filter
° i
Nin
7 T i
= le. CTE ROVE paper’ er
vl Lope |
A.
Ve=Ne lek
with jo) ry cohen
é| 1
é
30
> The above fie’ shows a HOR circuit with a sin
capacitor filter Co) and a load resister (RL) and
che Input, output coaveforms
> Bermg pesitre half cycle of input Signal (vin), the
diede We becnes fonccrel bined anal tarts cnduchng -
— Spthis condition, the Capacitor ts charged alinost to
the mncotimum peak value of input “oltage Vm -
Ves Vm < Ideal condition
Ve = Vin-Ve < Practical Condition-
where Ve is the drop Ff diode 0
Gouitt in potentsal)
e the : ch ;
7 Once the Capacitor gets Dargis airy hold the value
for longer time as its clischarging time ts greater wrt
charging HME by tnocasng QE ‘me enstont-
> Wben the instantaneous [eve of input vottage Cot rode
anede) falls belo Vi, the diode becomes reverse—
biased “because the capacitor voHage Ve (at diode
cathode) semains close to \m:
—> With the diode reverse ~brased , there ts No Capacitor
¢ to clischa
chargmg cament, and Capacitor be
tir te load wesistor(Rs). Bo Ve. fussing? ys
@S Shon: in above WA! eee
> The diode remams evorse -biased (as Ve decreases)
ee fag fae te
the Wegative half cycle , and the first part next
posititd half cycle agar enti the instantaneous level
of Vio, becomes gente than Ve once mow -
mae Me beenees qeater-thon Ye ere Gee
dliade gou info. fravard biased! cand alerts Teonduchng.
capaci get hax back to Vm in
ae tn the citer + ear Vm
—o of ‘deal conden and Um-VE) fn Cose of
pratt T conclition «
> This. procest Gonttnuous how long Vin is present -
~The argng_ and Teclorg and dscharging of the Capacitor Cause the
W if Itage ,
Shall jngrease and Secrease. nthe cape
which i= also he circatt: output VOR G
arallel connecton 28 shown in abore Arograms
Pp
Fa toe Recir city Capaitor Giter”
obke half wae rectifors,
EwWRis requires filter
Circuit im ardor to convert
the op eoareform rte Aivect
© volta
Eres we > The fouure shows Fur
fier crreuit witha reservoir
ieee Capacitor
\
Neste Losiertny 7 This operates exactly
as expleuned fer the
half. coave reckon creuit
a “wih ofp inforkant
exceptrons
The only diffrence isthe, in HuoR only one half
cycle (either He or —Ve) Of the input AC current coill
Charge the capacitor But in full weve. rectifior, both
positive_and negate hal? cycles of the tof Top AC
mena oe
> Diasng. positive half cycle of meat Cin, the
drocle Da becomes forvard ard cea and Dr D2_ becomes
weerse biased
> Sn tis comdttion, Dysarts Conductsres and capacitor
Gets _chenged swith mamimum peak. value of Vin #-25\n
and holdsthe _chaged walue for longer time asit
> When the Instantaneous acts ‘input ‘vol (at
diode Di anode) falls below Os becomes
severse biased because the erica woltage Ve
Cal diode Dy Cattede) remains Close to Yin.
> ht thie conditon, bot diodes Di and De will be %
qeurrse_biased-and capacitey begins te Arscha
thro load reststo¥ (RY). So Ve falls slowly as
shown above
> Gs half. cycle of mput voltage Cm),
the clic role Ba becomes or biased, and Bs becomes
meverse biased: brased-
> Sp this Condition, Da Starts Condacing and capacitor
again gets charged with marimar value of Vn.
and holds i:
cl
— When the instantaneous lee of ane; i inj
eoltage (ect altode Da anode) falls below Vm
Da becomes reverse biased , because the aaa
Govoes Capacitor Ve. Ve (at diode Dz cedhode) vemams
Close to mantimum Vm
he this Condition , aga bot Ps and 0;tutll be in
ins 0 discharge
reverse biased: and Capacitor
Louk through lo load Tesistor (Ru) as Shown above
Slory
Note: Cpaciter charges oxhen any one diedle becomes
and gar! Conductor
== Frrward_biast.
only cohen both drades
Capaciter_oltscharges, only
becomes reverse Biased dnd Stops conductng.
tdge Rectifier volth Capacitos Fitter
Bri
wl B.< ee ee
Vtg Mio
‘ Pty ae 4 =
The aboe figure shows the brid ne roith & capacitor
filter
> Trpat_and oubpet voaveforms axe Same as FIR with‘ filter
cycle of inp voltage \iny diodes Dy
cd Baring posttne hal
and Dz becomes tar biased ane! staves Conducting
wshere as clredes D3 and Dy becomes reverse biased
ancl doesn't conducts
> So wis condition, Capaciter gets _chargeel {0 the raniman MCL
‘value of input voHage, Vin.
— When the instantaneous Level of positive tmput votage
Cat dliocles Dy and Or anode) falls below Vm, Dy and
Da becomes reverse biased.
> Ht this Conditions, alt the olicdes O1,P2,D3 and Dp will
be in reverse biased and capacitor begins to discharge
tts value Ve trough R G
7 a negative hal} ile of input voHage( vin) , the cliodes
Da and! Dy becomes forward biased and Dy and Do
aoe braseck.
— 10tth this, Capaciter again
peak value of input woHtage, Vm:
= When the instantaneous Level of ne
Cat dliccles Ds and Dg anode)
Dy becomes reverse biasecl
char to the ronimum
ive input volta
alls below Vm, Dascodt
—> Gn this Condiiton, ayam all diodes will be in reverse
biasecl and helps oacita to dlischarge its walue Ve
Through Re: coma
ener Giode MoLinge fequlators
ee
“Ganrent
V2 = Zener Breakdown y
1 ‘4
* wi
trodes Tomer
imam Zener camer
Wanimune Zener carmen
Va = yevere bias v
ee Tvs reverse coment
Tenax] ———] “Vr chnactostns WG = frvvrrd les vig
Jf = foswerd current
ocle builtin vtg.
37
Mee
> The zener diode, ts used! In ike "reverse bias" oy
reverse breakdown mode ise, diode's anode connects
to negative Guppl
= From the Vl chawactertstics eave above , we can
Bee that the zener citode has a region in its reverse
bias characteristics of almost a Gnstant: negative
Volta ex ferdicss of the value OF the current
flow thro gh the diode
=> Ghis vol remains almost constant even with
large changes in Current providing the zener dicdes
current wemains between the breakdown current
Temi and its Teme Carent voting)
7s Obitiy of the Zenen clade ‘& onbro!_itseyp
can be used 40 gaat effect to requlate or stabilise
avelage source agamst Supply Soa aia
—> The voltage cross the diode in breakdown regiem
is almost int tums aut to be an imBortant_
Characteristic Of zener diede as it can be usecl the
are epee applicedrons
>The funchon of 2 voltage regulator is to provide a
constcint output WoHlage tea {oad connected in paral
‘with dlicde in spite of the wipples inthe Supply voltoge
or variations fn the load cerment
3s
Regulated
RL output Vo=V2
Zener Diode Voltage Regulater
>The ciruit f Zener oegaleter is as ghuwn above:
—> St ammsists of an unrequlatect input voltage vin)
Connected to carrent limiting cesistor (Rs) , 0 Zener
diode CDs) in parallel with load _nesistor (RL).
—> $n order t work as a volta julater, the
following conditions must be Satisfied
1) Zener clicde must be reverse biased.
2) Input voltage (Vind must be
breakdowo voltage (V2)
BDrAhe load cument (1) Should be Less-than
Tecman). 7
water than zener
> Since RL onel Dgleener diode) are i> parallel
oHage acwes Qi = VoHage across Di
ey [Vo eVz
> Fro above equation we find that Vo remains constant
exen if Vin happens to change due to the Pluchatins in
andegulated vollge:
ze
> From above fgure it canbe seen that
Is-T2+Te
* [Ze= Ts-TU
Regulotio with varying Vin Line Regutetson)
> fy this Condition, load parameters cre made Constant
mony line Pavameters are varied
— with this Te_and RL will be made constant
- | Tg = Iz + Teenstant|
> When Vie inoreases, Is also increases. This will
effect Tae and I_
ie es Ti_ts made constant, the overall effect
will on Iz. herefore Tz_inoveases.
> Ele long os the current Hhrvoug® zener cliode is
between Tamm and Temen, the voltage acres it
is constant. Bo Tz can inorease only upko Temert.
vs oil be Controlled Cetseent: limiting
aeSistor Re
> Bimilarly , when Vin cleeweases , Is also decseasey.
—> with this Ze also decreases vith Ty constant
> Te can clecwease only tll Temn.
— Hence Vol is made constant ,
Liesignmg Curent Limiting Resistor (Rs) ne
> Since the cerwent through zener diode varies with
change Tm Input voltage to have proper Curent troup,
.
>This has to be taken between two extreme cases
“thus, [Remin £Rs £ Remax
> lalhen a locid CRL) ts connected ,the zeney current (Tz)
will fall as cument ts diverted into-the load resistance.
> Te_should not fall below minienam carment recting:
of zener dice (Lemin)
— Similarly, Iz_will_ rise incase of Increase inthe
rp nage tr). Te should mot etceec| Temane
Current cresting of zener dlrode
> Sn order to clo 86, the resistor Rs ghould be selected
proper
>the vesisters Re and RL forms the potential divides
metwork in the aboe wtqulater circuit
> The. ratio of Rs “to Re ts Hus important
> At the point at which the crreutt fat begins
voy to regulate
V2 = Vie Re
FRE
“thus the maximum valueof Rs can be calculated as
as
Mee
Ri+Rs = Vin Re
Vz
“Roa VinRL _ Q,
—
=Rivi
re eae
> The power lissipated In the zener diode, will be
ae
— Hence the minimum value of Re can be caleuted
as
Renin = Nin-V2 _ Min-V2 _(Vin-Ve) xve
Te ei aaa
2
a Remin = NinVe Vz rohere Poman rsthe
Raman — |mase- rated power
‘tssipated fir diede
Numerical:
4) A Sv zener cliode has a mortimum atecl Power
dissipation & SoomW. If ‘the cliode is to be used in
a simple ter circuit to Supply a regulated. SV
aving a resistance of 400-- Determine
bo a load
a guitable ‘value of Series vesister for opercten In
Congunchoo sith a Supply. F WV:
Sold: Given: Pemen= Soom, V2=SV, R= 400-4,
\lin= ave
man = Vin 4) = 400x/9 _
Gar Ot (UD geccad a)
age
mc
Va-V2 _ (axs)-5? _
Pema Soon” 0S
Hence a suitable value of Rs would be [550%]
Coveraged value),
2) Ifa W zener diode ts to be used In a simple shunt
regulator circuit to supply a load havmg a nomial
aesistance f 300-2,determwne the mentimam value oF
Senter resistor fer operedson in Conpunchvo with a Bupply
of isv
sol?: Given, V2=4V, RL= 300-2, Vin=45V
Remon = RUC -1)
e Ss
300( -t)
Reman = 200 2
Output Resistance and Voltage Regulation.
Due eae
The output resistance of a power Supply ts clefined as
change in output Voltage clivitled by the Corresponds
Ree sees
Rout = change % op
Change top Curvent
43
> Te voltage regulation Of & power supply te
given by the relation ship:
Regulation = Change in opp voltage toot é
Change in fp voltage
Numeriaal-
Y The followng data was obtained dering o. test
carried out o% Ade power supply +
YD Load test
Output voltage (mo load) =12V
Output voltage (2A load cwment) = 11.5V.
) Requledren test
Output vol Cmeins input, 220v) =12¥
Output vol Cameatns input, 200V) = 14-9V.
GBetermine @) the equivalent oudput resistance of
Power Supply and cb) the megulation oP the power
Supply
SolD:
Rout = AM 19-445
aiimoaome ge
& Regulater = oe oe
AVin — jo-200 "20%"
= [ose
44
Voltage Giluttipliers
+The voltage maltipli¢r Is an electronic eiruut that
delivers the output voltage whose amplitude ts
“two, Hives ov move Hine! .greciter than the amplitude
% the input voltage
> St converts the (ao Ac voltage into high De voltage
— & rs madeup of diodes andl capacitors .
> Voltage multpliors has differnt stages. Each Sage
feqmate up of ene dliocle and one capacitor.
= Although it te usual in electronic circuits to use
oltage transformer to incatease a voltage
= Sometimes a suitable Step-up transformer required
fr high voltage appiicatvons may not always be
ava ithe IP eo, Pds sige and power consumption
will be more
= One alternative approach is to use a diode voltage
multiplier Circufé” which Increases or 'steps—up' the
‘Voltage without the we Of & transfermer-
pes of Novtage Mulupliens
D Voltage Doubler
© Voltage Tripler:
4s
Ma
Nottage Doubler
C2
>The above circuit ghows a voltage doubler
a Burg the positive half cycle of mp voltage Vin,
diocle “Dj becomes forward biased and Stet condlucting
= §naris Condition, capacitor ‘ch’ Starts changing uP.
dong oTFage im!
aoith montimum peak. value Of Secon
> Because there is mo return path fax ccpaciter'ci'to
discharge into, it aemams fully chev acing 08
Storage device with. the voltage Supply
> Bharng the ego bull eye of put weHage, dete
‘Da becomes reverse biased! blackigy the clischargi
of Ch while cliode ‘Dz becomes forward bused vt
Starts condluctog-, chargtng up copactter ‘ca
> Buk because there fsa voltage across capacitor'cy
already exual to the peat input voltage Vag, Capacitor
“Ca! Changes fo twice the peak voltage value of ped
Siqmal-
he cletailed working of voltage chubler *s ae
Shawn below with verreaits and analysts
46
cyeNee
4
“Ope
Neq = Vm
gt
During det
—Ve4 — Vm +Vie2 = 0
= Veg = Vm+Vea,
= Vint im
G=2Vm
a agate ha
half cycle.
ee -
47
> The abowe figures Shows the vollage trpplerand — MC
auorkng of Hin three dliffennt Stages
a Gung dot postne half cyole of mput voltage Vi,
dicdle ‘By’ becomes forward biasecl andl heels Coclucing,
charging up the capacitor'Cy! 08 shown above
2 Wen = veo]
eS Bron dot negate half cyole of mput voltage Vin,
diode "Di becomes reverse biased, while dlfede Da
becomes forward biased cind starts
erward lolased One &
up ‘the Capacitor Ca os shown above
conducting »
Chargin
—Ve4 - Vin +e = 0
2 Veg = VmtVeg = VinetVm =|
7 Baring nent C2nd) positive half cyste off inpuck voltege Vin,
diode Da Conducts , shite cltodes Ds ind Ds becomes
Yeverce biased. because of the Capacitor polarity (ve>
Across thetr (D4 anel Ds) Anodes
= nabs Condition, the forward biased diode Ds sfemts
Changing Up the capacitor C3 ca shown above
Neo a=W Hey +VE3 =O
[ovm
2 MC3= Veg +Vm —Vea
= 2m +Vim Vn
“Wes =2Vm
As there is no return path for any capacitors Ce ,C> ,C3)
te discharge rye mena fal Shane ch a
devices 7
Stom Wee
Sromge eve ie
| Noltage Tripler —s |
Nea =Vm \eg=2Vr0
Fe vl Gy
face cs
Von Vou L\o. Da
| co
Veg=2Vm
AA Nottage Doubler I
n
<-$->>
From the above civeult, we can observe that
ot Cy we get vm
ct wept 2m [eg Ca]
ak C3 we get 2vin, bo get thrice the Ppt vollage
we havet add Vex cind Vea, as they are Connected fn
. ‘Senter -
Meg 4Veq = Vine 2Vm =[3Vm
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- AmplifierDocument3 pagesAmplifierRonda StewartNo ratings yet
- Unit - II Quantum MechanicsDocument14 pagesUnit - II Quantum MechanicsRonda StewartNo ratings yet
- ArraysDocument3 pagesArraysRonda StewartNo ratings yet
- Adalita Bhase KannadaDocument5 pagesAdalita Bhase KannadaRonda StewartNo ratings yet
- Basic Java Programming S and S IA1Document4 pagesBasic Java Programming S and S IA1Ronda StewartNo ratings yet
- LASER Notes (Dec-2022) - 1Document20 pagesLASER Notes (Dec-2022) - 1Ronda StewartNo ratings yet
- Spherical Refracting Surfaces TheoryDocument6 pagesSpherical Refracting Surfaces TheoryRonda StewartNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 NotesDocument16 pagesUnit-2 NotesRonda StewartNo ratings yet
- Maths Lab RecordDocument3 pagesMaths Lab RecordRonda StewartNo ratings yet
- Spherical Mirrors MCQ SolutionsDocument12 pagesSpherical Mirrors MCQ SolutionsRonda StewartNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics (MCQS)Document21 pagesWave Optics (MCQS)Ronda StewartNo ratings yet
- 2nd Pu Notes - 2021-06-19T064153.704Document161 pages2nd Pu Notes - 2021-06-19T064153.704Ronda StewartNo ratings yet
- Combination of Resistances: Circuit Diagram: Series Combination Experiment No.:7A Date: Aim: - Apparatus RequiredDocument4 pagesCombination of Resistances: Circuit Diagram: Series Combination Experiment No.:7A Date: Aim: - Apparatus RequiredRonda StewartNo ratings yet