Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plant and Animal Hormones
Plant and Animal Hormones
Uploaded by
Esther EkengCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Plant Hormone - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesPlant Hormone - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaCristie SumbillaNo ratings yet
- Study of Plant Hormones and Their Role in Growth and Development.From EverandStudy of Plant Hormones and Their Role in Growth and Development.No ratings yet
- Plant Hormone - WikipediaDocument13 pagesPlant Hormone - WikipediaNageso FitoNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormone: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesPlant Hormone: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediacieda_89No ratings yet
- Plant Hormone: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument8 pagesPlant Hormone: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Hormones in AnimalsDocument8 pagesHormones in AnimalsJAYESH TELANGNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones SummaryDocument11 pagesPlant Hormones SummaryRamesh Kumar MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones 1Document2 pagesPlant Hormones 1Mj AikoNo ratings yet
- Can Plants CommunicateDocument19 pagesCan Plants CommunicateIemaaNaimaaNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth RegulatorsDocument9 pagesPlant Growth RegulatorsDestia Ayu100% (1)
- Lesson 1: Classes of Hormones Self CheckDocument7 pagesLesson 1: Classes of Hormones Self CheckRenz Jian B. MacasiebNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormone Csir Net Notes Merit Life Sciences 85560092620 To JoinDocument18 pagesPlant Hormone Csir Net Notes Merit Life Sciences 85560092620 To Joinmerit tutorials com NET JRF JAM TUTORIALSNo ratings yet
- How Do We Know They Exist?Document11 pagesHow Do We Know They Exist?Saumyaranjan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Phytohormone: Growth in AnimalsDocument7 pagesPhytohormone: Growth in AnimalsAnonymous rq5C3bZkMNo ratings yet
- Plant HormonesDocument38 pagesPlant Hormonesbaha hafizNo ratings yet
- Plant HormonesDocument3 pagesPlant HormonesAbdullah Al MamunNo ratings yet
- Regulating Growth and Development The Plant HormonesDocument30 pagesRegulating Growth and Development The Plant HormonesMoath EnnabNo ratings yet
- Plant HormoneDocument31 pagesPlant HormoneChristine De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- TT PB 6 Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesTT PB 6 Lecture NoteseashelNo ratings yet
- Plant HormonesDocument22 pagesPlant HormonesBelcharle Salom BalangNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Nervous ControlDocument36 pagesChemical and Nervous ControlAlex BlancoNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth Regulators in Agriculture: Department of Agronomy Bahauddin Zakariya University MultanDocument32 pagesPlant Growth Regulators in Agriculture: Department of Agronomy Bahauddin Zakariya University MultanIrfan SuliansyahNo ratings yet
- Science & English G10 Activities SamplesDocument6 pagesScience & English G10 Activities SamplesShane RicoNo ratings yet
- Bio 250 (Systems and Maintenance)Document12 pagesBio 250 (Systems and Maintenance)Amar SafwanNo ratings yet
- Plant hormones Final 1Document33 pagesPlant hormones Final 1ssah4155No ratings yet
- Portfolio IN Histology Laboratory: Submitted To: Tom Anthony Tonguia, RMT Submitted By: Charlene Caro 2A-BsmlsDocument9 pagesPortfolio IN Histology Laboratory: Submitted To: Tom Anthony Tonguia, RMT Submitted By: Charlene Caro 2A-BsmlsFearless AngelNo ratings yet
- PendahuluanDocument11 pagesPendahuluansekarNo ratings yet
- GLUCOSIDEDocument3 pagesGLUCOSIDEAngel Ellene MarcialNo ratings yet
- Plant HormonesDocument10 pagesPlant HormonesAmna MaqboolNo ratings yet
- TT PB 6 Teaching GuideDocument5 pagesTT PB 6 Teaching GuideeashelNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination, Class 10, Module 2.3, PPTDocument19 pagesControl and Coordination, Class 10, Module 2.3, PPTArpithaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Plant Growth RegulatorsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Plant Growth RegulatorsSaad Ahmed SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Growth RegulatorsDocument5 pagesGrowth Regulatorsirfan shahNo ratings yet
- 14.1 Plant Tropisms and Hormonal ControlDocument17 pages14.1 Plant Tropisms and Hormonal ControlRahulKwatraNo ratings yet
- Chemical An Nervous ControlDocument12 pagesChemical An Nervous ControlNikki AlbiosNo ratings yet
- (Bio) 4THDocument21 pages(Bio) 4THZoe CataquizNo ratings yet
- Growth Regulators Functions in Horticultural Crops: Eknaik, V S S V PrasannaDocument6 pagesGrowth Regulators Functions in Horticultural Crops: Eknaik, V S S V PrasannaiajerNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination Plant Hormones (Part 1)Document4 pagesControl and Coordination Plant Hormones (Part 1)qtqutaNo ratings yet
- SIM PlantGrowthHormonesDocument18 pagesSIM PlantGrowthHormonesariel ebreoNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 05 Dec 2022Document8 pagesAdobe Scan 05 Dec 2022Gaurav Raj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth RegulatorsDocument5 pagesPlant Growth RegulatorsRockyNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth RegulatorsDocument28 pagesPlant Growth RegulatorsSurga FirdausNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: Movement in OrganismsDocument7 pagesThe Nervous System: Movement in OrganismsMohd YounusNo ratings yet
- Dr. Macauly - Hormones in PlantsDocument28 pagesDr. Macauly - Hormones in Plantskoromamoses235No ratings yet
- FaizDocument2 pagesFaizFaiz ShahNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth and Development-An IntroductionDocument6 pagesPlant Growth and Development-An IntroductionSenthilkumar PalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Genbio 2Document39 pagesGenbio 2Pawn RookNo ratings yet
- Abdullahi Mohamed AbdiDocument1 pageAbdullahi Mohamed AbdiHussein Mohamed JimcaleNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination: Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesControl and Coordination: Nervous SystemRounak BasuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Control and OordinationDocument5 pagesChemical Control and OordinationprimeeducationalinstituteNo ratings yet
- Physiology 2 Long Question Answer WPS OfficeDocument9 pagesPhysiology 2 Long Question Answer WPS OfficeShamoon HaroonNo ratings yet
- Project Chem 23Document2 pagesProject Chem 23Almas SNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of FeelingsDocument6 pagesBiochemistry of FeelingsAnnija Vecuma-VecoNo ratings yet
- Phytohormone - Types and FunctionsDocument23 pagesPhytohormone - Types and FunctionsminiNo ratings yet
- G2 Unit 2 Variation Standardization of Natural Products Quality Control Origins of Secondary MetaboliteDocument69 pagesG2 Unit 2 Variation Standardization of Natural Products Quality Control Origins of Secondary MetaboliteMa Jessica Allequer LlanoNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To EndocrinologyDocument47 pagesAn Introduction To EndocrinologyAmeng GosimNo ratings yet
- Agri Paper 2Document6 pagesAgri Paper 2VikasNo ratings yet
- Commercial Production of HormonesDocument2 pagesCommercial Production of HormonessumayyaNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth RegulatorsDocument55 pagesPlant Growth RegulatorsXimena Libano0% (1)
- Growth and Development of CropsDocument17 pagesGrowth and Development of CropsSUSHMA PRIYANo ratings yet
- Gamete Formation BIO 101Document3 pagesGamete Formation BIO 101Esther EkengNo ratings yet
- Meaning, Tools and Relevance of PhilosophyDocument3 pagesMeaning, Tools and Relevance of PhilosophyEsther EkengNo ratings yet
- The Need To Move From Fossil Fuel To Alternative EnergyDocument3 pagesThe Need To Move From Fossil Fuel To Alternative EnergyEsther EkengNo ratings yet
- Ossification Centres of The Upper Limb, Importance, and Greenstick FracturesDocument3 pagesOssification Centres of The Upper Limb, Importance, and Greenstick FracturesEsther EkengNo ratings yet
Plant and Animal Hormones
Plant and Animal Hormones
Uploaded by
Esther EkengCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Plant and Animal Hormones
Plant and Animal Hormones
Uploaded by
Esther EkengCopyright:
Available Formats
Plant and Animal Hormones
In plants and animals, hormones can be described as “chemical messengers” in that they are
chemical compounds which regulate the functioning of the organisms by evoking responses
from particular tissues or organs. They are organic substances secreted in both plants and
animals, and aid in homeostasis.
In Plants
Plant hormones are a collection of independent chemical substances that affect the origin and
development of morphological characteristics in plants. They affect growth, flowering, leaf fall,
and maturation amongst other things. P0mt hormones can work in the cell they are secreted
from, or a tissue somewhere else in the plant.
Some major plant hormones are auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid and ethylene.
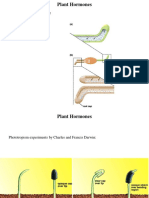
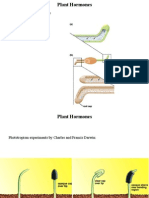
Auxins: hormones responsible for cell elongation in response to light and gravity stimuli
Gibberellins: closely related hormones responsible for seed germination, shoot elongation, and
fruit and flower maturation.
Cytokinins: they promote cytokinesis (cell division), delay senescence in leaf tissues, and
stimulate differentiation of the meristem in shoots and roots.
In Animals
Hormones in animals are coordinated with the endocrine system. It has no ducts, so hormones
are secreted directly into the transport medium and travel long distances to the target organ or
tissue. Hormones communicate changes in target cells by binding to specific hormone
receptors. They are in charge of regulating the internal environment i.e homeostasis, and
complex processes e.g metamorphosis.
References
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/plant-hormones
https://openstax.org/books/biology-2e/pages/37-introduction
You might also like
- Plant Hormone - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesPlant Hormone - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaCristie SumbillaNo ratings yet
- Study of Plant Hormones and Their Role in Growth and Development.From EverandStudy of Plant Hormones and Their Role in Growth and Development.No ratings yet
- Plant Hormone - WikipediaDocument13 pagesPlant Hormone - WikipediaNageso FitoNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormone: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesPlant Hormone: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediacieda_89No ratings yet
- Plant Hormone: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument8 pagesPlant Hormone: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Hormones in AnimalsDocument8 pagesHormones in AnimalsJAYESH TELANGNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones SummaryDocument11 pagesPlant Hormones SummaryRamesh Kumar MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones 1Document2 pagesPlant Hormones 1Mj AikoNo ratings yet
- Can Plants CommunicateDocument19 pagesCan Plants CommunicateIemaaNaimaaNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth RegulatorsDocument9 pagesPlant Growth RegulatorsDestia Ayu100% (1)
- Lesson 1: Classes of Hormones Self CheckDocument7 pagesLesson 1: Classes of Hormones Self CheckRenz Jian B. MacasiebNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormone Csir Net Notes Merit Life Sciences 85560092620 To JoinDocument18 pagesPlant Hormone Csir Net Notes Merit Life Sciences 85560092620 To Joinmerit tutorials com NET JRF JAM TUTORIALSNo ratings yet
- How Do We Know They Exist?Document11 pagesHow Do We Know They Exist?Saumyaranjan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Phytohormone: Growth in AnimalsDocument7 pagesPhytohormone: Growth in AnimalsAnonymous rq5C3bZkMNo ratings yet
- Plant HormonesDocument38 pagesPlant Hormonesbaha hafizNo ratings yet
- Plant HormonesDocument3 pagesPlant HormonesAbdullah Al MamunNo ratings yet
- Regulating Growth and Development The Plant HormonesDocument30 pagesRegulating Growth and Development The Plant HormonesMoath EnnabNo ratings yet
- Plant HormoneDocument31 pagesPlant HormoneChristine De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- TT PB 6 Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesTT PB 6 Lecture NoteseashelNo ratings yet
- Plant HormonesDocument22 pagesPlant HormonesBelcharle Salom BalangNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Nervous ControlDocument36 pagesChemical and Nervous ControlAlex BlancoNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth Regulators in Agriculture: Department of Agronomy Bahauddin Zakariya University MultanDocument32 pagesPlant Growth Regulators in Agriculture: Department of Agronomy Bahauddin Zakariya University MultanIrfan SuliansyahNo ratings yet
- Science & English G10 Activities SamplesDocument6 pagesScience & English G10 Activities SamplesShane RicoNo ratings yet
- Bio 250 (Systems and Maintenance)Document12 pagesBio 250 (Systems and Maintenance)Amar SafwanNo ratings yet
- Plant hormones Final 1Document33 pagesPlant hormones Final 1ssah4155No ratings yet
- Portfolio IN Histology Laboratory: Submitted To: Tom Anthony Tonguia, RMT Submitted By: Charlene Caro 2A-BsmlsDocument9 pagesPortfolio IN Histology Laboratory: Submitted To: Tom Anthony Tonguia, RMT Submitted By: Charlene Caro 2A-BsmlsFearless AngelNo ratings yet
- PendahuluanDocument11 pagesPendahuluansekarNo ratings yet
- GLUCOSIDEDocument3 pagesGLUCOSIDEAngel Ellene MarcialNo ratings yet
- Plant HormonesDocument10 pagesPlant HormonesAmna MaqboolNo ratings yet
- TT PB 6 Teaching GuideDocument5 pagesTT PB 6 Teaching GuideeashelNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination, Class 10, Module 2.3, PPTDocument19 pagesControl and Coordination, Class 10, Module 2.3, PPTArpithaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Plant Growth RegulatorsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Plant Growth RegulatorsSaad Ahmed SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Growth RegulatorsDocument5 pagesGrowth Regulatorsirfan shahNo ratings yet
- 14.1 Plant Tropisms and Hormonal ControlDocument17 pages14.1 Plant Tropisms and Hormonal ControlRahulKwatraNo ratings yet
- Chemical An Nervous ControlDocument12 pagesChemical An Nervous ControlNikki AlbiosNo ratings yet
- (Bio) 4THDocument21 pages(Bio) 4THZoe CataquizNo ratings yet
- Growth Regulators Functions in Horticultural Crops: Eknaik, V S S V PrasannaDocument6 pagesGrowth Regulators Functions in Horticultural Crops: Eknaik, V S S V PrasannaiajerNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination Plant Hormones (Part 1)Document4 pagesControl and Coordination Plant Hormones (Part 1)qtqutaNo ratings yet
- SIM PlantGrowthHormonesDocument18 pagesSIM PlantGrowthHormonesariel ebreoNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 05 Dec 2022Document8 pagesAdobe Scan 05 Dec 2022Gaurav Raj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth RegulatorsDocument5 pagesPlant Growth RegulatorsRockyNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth RegulatorsDocument28 pagesPlant Growth RegulatorsSurga FirdausNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: Movement in OrganismsDocument7 pagesThe Nervous System: Movement in OrganismsMohd YounusNo ratings yet
- Dr. Macauly - Hormones in PlantsDocument28 pagesDr. Macauly - Hormones in Plantskoromamoses235No ratings yet
- FaizDocument2 pagesFaizFaiz ShahNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth and Development-An IntroductionDocument6 pagesPlant Growth and Development-An IntroductionSenthilkumar PalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Genbio 2Document39 pagesGenbio 2Pawn RookNo ratings yet
- Abdullahi Mohamed AbdiDocument1 pageAbdullahi Mohamed AbdiHussein Mohamed JimcaleNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination: Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesControl and Coordination: Nervous SystemRounak BasuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Control and OordinationDocument5 pagesChemical Control and OordinationprimeeducationalinstituteNo ratings yet
- Physiology 2 Long Question Answer WPS OfficeDocument9 pagesPhysiology 2 Long Question Answer WPS OfficeShamoon HaroonNo ratings yet
- Project Chem 23Document2 pagesProject Chem 23Almas SNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of FeelingsDocument6 pagesBiochemistry of FeelingsAnnija Vecuma-VecoNo ratings yet
- Phytohormone - Types and FunctionsDocument23 pagesPhytohormone - Types and FunctionsminiNo ratings yet
- G2 Unit 2 Variation Standardization of Natural Products Quality Control Origins of Secondary MetaboliteDocument69 pagesG2 Unit 2 Variation Standardization of Natural Products Quality Control Origins of Secondary MetaboliteMa Jessica Allequer LlanoNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To EndocrinologyDocument47 pagesAn Introduction To EndocrinologyAmeng GosimNo ratings yet
- Agri Paper 2Document6 pagesAgri Paper 2VikasNo ratings yet
- Commercial Production of HormonesDocument2 pagesCommercial Production of HormonessumayyaNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth RegulatorsDocument55 pagesPlant Growth RegulatorsXimena Libano0% (1)
- Growth and Development of CropsDocument17 pagesGrowth and Development of CropsSUSHMA PRIYANo ratings yet
- Gamete Formation BIO 101Document3 pagesGamete Formation BIO 101Esther EkengNo ratings yet
- Meaning, Tools and Relevance of PhilosophyDocument3 pagesMeaning, Tools and Relevance of PhilosophyEsther EkengNo ratings yet
- The Need To Move From Fossil Fuel To Alternative EnergyDocument3 pagesThe Need To Move From Fossil Fuel To Alternative EnergyEsther EkengNo ratings yet
- Ossification Centres of The Upper Limb, Importance, and Greenstick FracturesDocument3 pagesOssification Centres of The Upper Limb, Importance, and Greenstick FracturesEsther EkengNo ratings yet