Professional Documents
Culture Documents
U4L1 Student Guide
U4L1 Student Guide
Uploaded by
-Esha-Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
U4L1 Student Guide
U4L1 Student Guide
Uploaded by
-Esha-Copyright:
Available Formats
Unit 4: How Brain’s Differ
Student Guide Lesson 1: Anxiety
1. What are the objectives of today’s lesson?
Factors and variables present that cause an anxiety disorder
List the type of anxiety disorders, symptoms and general scientific understanding
Ways to reduce anxiety by having a growth mindset
2. Review the 5 things to know about stress.
● Stress affects everyone
● Not all stress is bad
● Long - Term stress can harm your health
● There are ways to manage stress
● If you feel overwhelmed by stress, ask for help from a health professional
3. Define anxiety.
Anxiety is an emotion characterized by feelings of tension, worried thoughts and physical
changes like increased Blood pressure
A Normal Reaction that everyone experiences from time to time in response to different
kinds of events and situations
- Examples: before a big Test big performance or decision
4. Are stress and anxiety the same?
- No, they are not the same; they are not Interchangeable terms
- There is an Overlap in two – both are related to fear Response
- Stress = external pressures
- Anxiety = worries or fear about things (especially things that we interpret) could
threaten us
5. Recall the concept of the fight or flight response.
U4L1 Student Guide 1
Anxiety = internal warning system, alerts us to danger or other threats and prepares our
bodies to fight back or get out of a dangerous situation
Fight = you take action
Flight = you avoid the situation
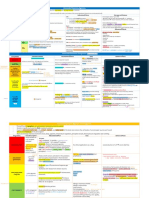
6. What is the difference between normal anxiety experiences and an anxiety disorder?
Normal Anxiety Experiences Experiencing an Anxiety Disorder
Related to a specific situation or Occurs unexpectedly
problem Anxiety feeling lasts a long time,
Lasts only as long as the situation or even when situation or problem has
problem resolved
Is proportional to the situation or Anxiety response to situation or
problem problem is much stronger than
Is a realistic response to problem or expected
situation Unrealistic experience of anxiety –
fear of a situation that likely will
never happen
Anxiety may feel impossible to
control or manage
7. According to the American Psychological Association, people experiencing anxiety disorders
usually have recurring intrusive thoughts or concerns
Avoid certain situations out of worry
May have physical symptoms such as:
- Sweating
- Trembling
- Dizziness
- Rapid Heart Beat
-
8. Why do anxiety disorders occur?
Many variables are possible such as:
U4L1 Student Guide 2
- Hereditary (genetic)
- External Factors (living environment, drugs/alcohol use, life events)
- Scientists believe that anxiety disorders occur when there are in the signaling of the
limbic system
9. Recall the responsibilities of the limbic system and frontal cortex.
- Limbic system circuit believed to handle most of our emotional Processing
-
Prefrontal cortex is responsible for integrating emotional Information into our decision
making
10. List the types of anxiety disorders?
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Characterized by Chromic anxiety
Social Anxiety Disorder
Anxiety in social or performance situations
Post- Traumatic Stress Disorder
- Experiencing severe anxiety after a traumatic event
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
A person has intrusive thoughts that produce feelings of uneasiness by repetitive behaviors
aimed at reducing anxiety
Panic disorder
An abrupt feeling of catastrophic fear
Phobia
An extreme irrational Fear
U4L1 Student Guide 3
11. What is the brain based reason for anxiety?
Fear and anxiety both play key roles across the anxiety disorder spectrum
Changes in amygdala and hippocampus are apparent across all anxiety disorders by multiple
studies
Majority of studies reporting hyperactive amygdala responses to threat across anxiety
disorders
12. What are some important statistics to note about anxiety?
Anxiety disorders are the most common mental Health concern in the United States
Over 50 million adults in the U.S have an anxiety disorder
Approximately 7% of children aged 3-17 experience issues with anxiety each year
Most people develop symptoms before age 21
According to the National Alliance on Mental Health, mental health conditions are common
among young teens and young adults
50% of all lifetime mental illnesses develop by age 14 and 75% develop by age 24
13. What are the treatments for anxiety disorders?
Cognitive Behavior Therapy
Medication
A Combination of both
14. List examples of prescription medicine known as Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
that prescribed to treat anxiety and depression.
Prozac
- Celexa
Lexapro
- Zoloft
- Paxil
Luvox
U4L1 Student Guide 4
15. What do SSRI’s do?
● Block neurons from reabsorbing serotine through the reuptake transporter
● Leaves serotonin in the Synapse where it can repeatedly stimulate the receiving neuron
● This Readjust the serotonin levels
16. What are SNRI’s?
● SNRI = Serotonin Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors
● SNRI’s are like SSRI’s but instead of only blocking Reabsorption of serotonin – SNRI’s blocks
Neurons from reabsorbing both serotonin and norepinephrine
Norepinephrine is the neurotransmitter responsible for alertness and Attention
17. What are Benzodiazepines also known as “Benzos”?
Work Differently than SSRI’s and SNRI’s
Benzodiazepines are need for acute crisis such as panic attacks
- Fast acting medication
- Have sedative effect and can act as muscle relaxer
- Considered addictive because of the immediate relaxing effect and can be easily
abused
- prescription medicine
- Xanax Valium
18. What are some tips for teens to use to help reduce anxiety?
Lean on a Social Support Group
Be sure to get solid amounts of:
- Exercise
- Proper Nutrition_
- Sleep
- Consider Relaxation Techniques
Prepare for the “Big Event” in advance
Set Realistic goals
19. What is the summary?
U4L1 Student Guide 5
Anxiety is our internal Warning System alerts us to danger or other threats and prepares
out bodies to fight back or get out of a dangerous situation
An anxiety disorder is quite different than anxiety that occurs to warn us of a genuine
dangerous or threatening situation
People experiencing anxiety disorders usually have recurring intrusive thoughts or concerns,
avoid certain situations out of worry, and may experience physical symptoms as a result
Scientists believe that anxiety disorders occur when there are changes in the signaling of the
limbic System
Anxiety disorders are the most common mental health concern in the U.S
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and prescription medications such as SSRI’s, SNRI’s and
Benzodiazepines and a combination of both therapy and medication are the most common
treatments
Mental health services and supports are available and the earlier a person accesses them,
the better the result
U4L1 Student Guide 6
You might also like
- Psychopharmacology Drugs The Brain and Behavior 3Rd Edition Jerrold S Meyer All ChapterDocument67 pagesPsychopharmacology Drugs The Brain and Behavior 3Rd Edition Jerrold S Meyer All Chapterrita.strickland541100% (8)
- Student Guide Unit 4: How Brain's Differ Lesson 1: AnxietyDocument5 pagesStudent Guide Unit 4: How Brain's Differ Lesson 1: Anxietyria wu100% (2)
- AnxietyDocument40 pagesAnxietyhelperforeu100% (2)
- Anxiety DisordersDocument3 pagesAnxiety DisordersCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Panic & Bipolar Affective Disorders: Group 1Document33 pagesPanic & Bipolar Affective Disorders: Group 1AYO NELSONNo ratings yet
- 01 Session 05 Anxiety and FearDocument62 pages01 Session 05 Anxiety and FearMalakatete Mwaipojele-fNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Chapter EditedDocument19 pagesAnxiety Chapter EditedamarnehNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument45 pagesAnxiety DisordersAileen A. Monares100% (1)
- ATI Mental Health CH 11: Anxiety DisordersDocument4 pagesATI Mental Health CH 11: Anxiety DisordersRuthie BellaNo ratings yet
- Anxiolytic Lecture - PPTX 2020jsmuDocument125 pagesAnxiolytic Lecture - PPTX 2020jsmuraffia mahakNo ratings yet
- P$y C@$3 3Document11 pagesP$y C@$3 3Linds GoNo ratings yet
- AnxietyDocument36 pagesAnxietyRobert RevillasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Anxiety, Trauma and Stressor - Related, Obsessive Compulsive Related DisordersDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Anxiety, Trauma and Stressor - Related, Obsessive Compulsive Related DisordersAnnie SumacotNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorder LectureDocument17 pagesAnxiety Disorder Lecturealvaran.alliyah.0609No ratings yet
- Summary 8 - 16 KopieDocument33 pagesSummary 8 - 16 Kopielara.van.kemenadeNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument4 pagesAnxiety DisordersCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Generalized Anxiety DisorderDocument22 pagesGeneralized Anxiety DisorderAsqa KhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Anxiety-DisordersDocument74 pagesLesson 6 - Anxiety-DisordersKristian Dave DivaNo ratings yet
- Consultationliaison Psychiatry IcuDocument56 pagesConsultationliaison Psychiatry IcuChrisAlipioNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit 4Document21 pagesAp Unit 4Vaishnavi RaveendranNo ratings yet
- What Me Worry - 01 - Overview of Generalised Anxiety-2Document7 pagesWhat Me Worry - 01 - Overview of Generalised Anxiety-2장채윤No ratings yet
- Mental HealthDocument96 pagesMental HealthTinaHo100% (4)
- Anxiety and Panic DisordersDocument6 pagesAnxiety and Panic DisordersNo OneNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders: Ab SalgadoDocument44 pagesAnxiety Disorders: Ab SalgadoLoggerz ArckNo ratings yet
- U4L2 Student GuideDocument5 pagesU4L2 Student Guide-Esha-No ratings yet
- Anxious Patient Amended 21.2.2011Document122 pagesAnxious Patient Amended 21.2.2011Yogesh Malam100% (1)
- GAD, OCD and OCD Related DisordersDocument21 pagesGAD, OCD and OCD Related DisordersAkshita ZuzzanneNo ratings yet
- US MentalHealth HowToDealWithAnxietyDocument3 pagesUS MentalHealth HowToDealWithAnxietyAvinashNo ratings yet
- Practical 2 3P1Document16 pagesPractical 2 3P1Kz ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Handout Ab PsychDocument8 pagesHandout Ab PsychJoyAMCNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument11 pagesAnxiety DisorderBiswas AruNo ratings yet
- Postnatal Anxiety - Consumer Fact SheetDocument3 pagesPostnatal Anxiety - Consumer Fact SheetjosawoodNo ratings yet
- Anxiety & Anxiety Disorders ClassDocument27 pagesAnxiety & Anxiety Disorders Classbrianmuthomi851No ratings yet
- 6anxiety DisordersDocument40 pages6anxiety Disorderswwamed18No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Anxiety Trauma and Stressor Related and Obsessive Compulsive and Related DisorderDocument43 pagesChapter 5 Anxiety Trauma and Stressor Related and Obsessive Compulsive and Related DisorderGabriel Jeremy OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Session-1-Mental-Health-Act Pinaka FinalDocument41 pagesSession-1-Mental-Health-Act Pinaka FinalFrances Vale BasanNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument40 pagesAnxiety Disordersamal abdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- AP Psychology Module 66+67Document5 pagesAP Psychology Module 66+67kyuuNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument30 pagesAnxiety DisordersAbelNo ratings yet
- 02 Anxiety DisordersDocument9 pages02 Anxiety DisorderskayalvizhiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 & 5 Assignment Saif UllahDocument30 pagesUnit 3 & 5 Assignment Saif UllahMuhammad Saif UllahNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument43 pagesAnxiety DisorderRibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mental HealthDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Mental HealthXo Yem100% (2)
- Antenatal Anxiety Consumer Fact SheetDocument3 pagesAntenatal Anxiety Consumer Fact SheetjosawoodNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Problems in Young People - Part 2Document71 pagesMental Health Problems in Young People - Part 2elaineNo ratings yet
- Learn Psychology With Vishal Pandey: Term 2Document17 pagesLearn Psychology With Vishal Pandey: Term 2Labhanshi BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument36 pagesAnxiety DisorderRujuta BaramateNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument40 pagesAnxiety DisorderJemi LoriNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument19 pagesAnxiety DisordersGreysi AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument43 pagesAnxiety DisordersShivam SoniNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Crisis: Members: Justine F. Canceran Marvilyn R. Ancheta Nica Jane M. Asis Mary Jane C. Mabazza Reymar TaluganDocument38 pagesBehavioral Crisis: Members: Justine F. Canceran Marvilyn R. Ancheta Nica Jane M. Asis Mary Jane C. Mabazza Reymar TaluganMary Grace Recaña AgustinNo ratings yet
- What Me Worry - 01 - Overview of Generalised AnxietyDocument7 pagesWhat Me Worry - 01 - Overview of Generalised AnxietyManda BlaževićNo ratings yet
- Mental HealthDocument10 pagesMental HealthMohammed SaqibNo ratings yet
- Stress and CopingDocument47 pagesStress and CopingAitzaz IjazNo ratings yet
- Urooj Zafar (Assignment)Document8 pagesUrooj Zafar (Assignment)Urooj ZafarNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument24 pagesAnxiety DisordersSusan MaglaquiNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument116 pagesAnxiety DisordersusamanurahmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Module AnxietyDocument6 pagesChapter 14 Module AnxietyJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- 3 EmotionsDocument23 pages3 EmotionsaliNo ratings yet
- 2 Pharmacology I, Anxiolytic Hypnotics TrimmedDocument55 pages2 Pharmacology I, Anxiolytic Hypnotics TrimmedYasser IsteitiehNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Chap 5 (Due 29)Document1 pageModule 3 - Chap 5 (Due 29)-Esha-No ratings yet
- U4L4 3 2 1 Wrap Up WorksheetDocument6 pagesU4L4 3 2 1 Wrap Up Worksheet-Esha-No ratings yet
- World Civ Chapter 18Document22 pagesWorld Civ Chapter 18-Esha-No ratings yet
- U4L2 Student GuideDocument5 pagesU4L2 Student Guide-Esha-No ratings yet
- Volleyball Sports Analysis - Esha Pradeshik (11 - 16-17 - 2022)Document9 pagesVolleyball Sports Analysis - Esha Pradeshik (11 - 16-17 - 2022)-Esha-No ratings yet
- Brain Gut Connection: Anil K. RajvanshiDocument2 pagesBrain Gut Connection: Anil K. RajvanshijulfukarNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants Pharmacology LectureDocument19 pagesAntidepressants Pharmacology LectureHomman TommanNo ratings yet
- 109 Questions and Rationale On Psychotic Disorders IIIDocument32 pages109 Questions and Rationale On Psychotic Disorders IIIChaelo SantosNo ratings yet
- 30 10 201sdsdDocument10 pages30 10 201sdsdLuis_Javier_To_1572No ratings yet
- Penggolongan Kelas Terapi PsikotropikaDocument3 pagesPenggolongan Kelas Terapi Psikotropikapkm curugNo ratings yet
- BY Doon Psychothearaputic CentreDocument33 pagesBY Doon Psychothearaputic CentreRujuta BaramateNo ratings yet
- The Definitive Guide To 120+ Nootropic Supplements & DrugsDocument70 pagesThe Definitive Guide To 120+ Nootropic Supplements & DrugselshikarNo ratings yet
- Surya VigyanDocument41 pagesSurya Vigyanpradeepnagda100% (2)
- 3 - Antidepressants DrugsDocument27 pages3 - Antidepressants DrugsHadeelNo ratings yet
- Dark Classics in Chemical Neuroscience PsilocybinDocument33 pagesDark Classics in Chemical Neuroscience Psilocybindaniel_jose_skateNo ratings yet
- Drug AbreviationDocument14 pagesDrug AbreviationGlenn Suerte100% (1)
- An Interdisciplinary Investigation Into Alcohol Caffeine and ProzacDocument85 pagesAn Interdisciplinary Investigation Into Alcohol Caffeine and ProzacMa. Chantal Anjelika RamirezNo ratings yet
- The Reasons of DepressionDocument2 pagesThe Reasons of DepressionĐỗ Thị Ngân HàNo ratings yet
- Ann Blake SSRI DepressionDocument17 pagesAnn Blake SSRI Depressionthings3100% (1)
- Use of Paracetamol During Pregnancy and Child Neurological DevelopmentDocument7 pagesUse of Paracetamol During Pregnancy and Child Neurological DevelopmentLabontu IustinaNo ratings yet
- Dysthymia Clinical Picture, Extent of Overlap With Chronic Fatigue PDFDocument16 pagesDysthymia Clinical Picture, Extent of Overlap With Chronic Fatigue PDFRiham AmmarNo ratings yet
- TRA Psychiatric NursingDocument10 pagesTRA Psychiatric NursingGil GanibanNo ratings yet
- MagnesolDocument5 pagesMagnesolMisheelito MachaNo ratings yet
- TryptophanDocument4 pagesTryptophanAmit AnirudhNo ratings yet
- Ninja - Autacoids PDFDocument3 pagesNinja - Autacoids PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- CimicifugaDocument34 pagesCimicifugaNutricionista Ingrid AraújoNo ratings yet
- 22 Ways To Increase Serotonin Levels - CarexDocument1 page22 Ways To Increase Serotonin Levels - Carexshers xtrustxNo ratings yet
- Drug Interactions Results - MICROMEDEX - MAYODocument10 pagesDrug Interactions Results - MICROMEDEX - MAYOMARIA JULIANA RENGIFO LARANo ratings yet
- The Enteric Nervous System: Stuart Brierley Marcello Costa EditorsDocument236 pagesThe Enteric Nervous System: Stuart Brierley Marcello Costa EditorsJAVIERNo ratings yet
- MDMA PowerpointDocument16 pagesMDMA Powerpointapi-26938624No ratings yet
- Horowitz Taylor A Method of Tapering SSRI Treatment To Mitigate Withdrawal SymptomsDocument17 pagesHorowitz Taylor A Method of Tapering SSRI Treatment To Mitigate Withdrawal SymptomsDonaNo ratings yet
- What We Feel and Think Depends On Neural Connections PDFDocument1 pageWhat We Feel and Think Depends On Neural Connections PDFSoumya BurmaNo ratings yet
- Ananda Bosman - Akasha Somagenic and SomajeticsDocument19 pagesAnanda Bosman - Akasha Somagenic and Somajeticstheherbsmith100% (1)
- Dapoxetine For The Management of Premature EjaculationDocument5 pagesDapoxetine For The Management of Premature EjaculationMohammad Mesbaul HaqueNo ratings yet