Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geometry Unit Plan
Geometry Unit Plan
Uploaded by
api-485170066Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geometry Unit Plan
Geometry Unit Plan
Uploaded by
api-485170066Copyright:
Available Formats
Grade 7 Geometry
Rationale:
At all levels, students benefit from working with a variety of materials, tools and contexts when
constructing meaning about new mathematical ideas. Meaningful student discussions provide essential
links among concrete, pictorial and symbolic representations of mathematical concepts.
The main goals of mathematics education are to prepare students to:
use mathematics confidently to solve problems
communicate and reason mathematically
appreciate and value mathematics
make connections between mathematics and its applications Mathematics
commit themselves to lifelong learning
become mathematically literate adults, using mathematics to contribute to society
(Alberta K-9 Math Program of Studies, 2022)
Geometry is applicable to everyday life and can be seen in the construction of buildings, art, and sports.
Many different occupations require the use of geometry, from carpentry, welding, plumping, engineering,
architecture, design, artistry, etc. Students will explore these concepts through hands on learning with
manipulatives, and exploring around the school, projects, practice problems, and group work. Students
will explore new concepts and be encouraged to ask questions and make connections to the real world.
Assessment will be completed in the form of observation/ asking questions, writing questions with
markers on their desks, quizzes, assignments, projects, and textbook questions, and a unit test. There are 7
grade 7 students which allows me to have more one on one time with students and dedicate more time to
answering questions in depth.
Materials/ Resources:
Mirrors
Pearson Math Makes Sense 7 Textbook Unit 8
Geometry & Transformations | msayres (carolayres0.wixsite.com)
Geometry Drawing Challenge assignment
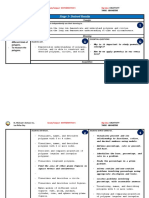
Established Goals – GLO(s):
GLO:
Describe the characteristics of 3-D objects and 2-D shapes, and analyze the relationships among them
Describe and analyze position and motion of objects and shape
Understandings: Essential Questions:
Students will understand that… Where in the world do you see aspects of geometry?
SLO:
Perform geometric constructions, including:
o Perpendicular line segments
o Parallel line segments
o Perpendicular bisectors
o Angle bisectors
Identify and plot points in the four quadrants of a Cartesian
plane, using integral ordered pairs
Perform and describe transformations (translations, rotations,
or reflections) of a 2-D shape in all four quadrants of a
Cartesian plane (limited to integral number vertices).
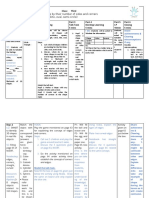
Prior understandings… Students will be able to…
Grade 6 Create and identify different types of line segments and
o Construct and compare triangles, including: bisectors
- Scalene, Isosceles, Equilateral, Right, Understand and use a cartesian plane to plot points in the
Obtuse, Acute in different orientations. four quadrants and apply transformations
o Describe and compare the sides and angles of regular
and irregular polygons.
o Perform a combination of translations, rotations
and/or reflections on a single 2-D shape, with and
without technology, and draw and describe the image
o Perform a combination of successive transformations
of 2-D shapes to create a design, and identify and
describe the transformations
o Identify and plot points in the first quadrant of a
Cartesian plane, using whole number ordered pairs.
o Perform and describe single transformations of a 2-D
shape in the first quadrant of a Cartesian plane
(limited to whole number vertices)
Where does this lead?
Describe the characteristic of 3-D objects and 2-D shapes, and analyze
the relationships among them
Draw and interpret top, front and side views of 3-D objects
composed of right rectangular prisms.
Describe and analyze position and motion of objects and shapes
Demonstrate an understanding of the congruence of polygons.
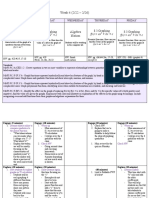
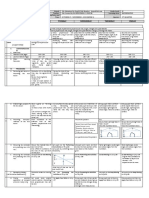
Lesson # Topic Activity # of Materials Needed
Periods
(80 mins)
1 Parallel Lines & -Definitions 1 Textbook
Perpendicular Lines -Finding different sets of lines around school Miras
(formative)
-Textbook questions
2 Perpendicular -3 ways to draw perpendicular bisector 1 Textbook
bisectors and angle -Real life examples Miras
bisectors -3 ways to draw angle bisectors
-Real life examples
-Textbook questions (formative)
3 Practice/ Review -Geometry Drawing Challenge (summative) 2 Worksheet
-Mid- Unit Review TB (formative) Textbook
-Quiz (summative) Quiz
4 Graphing on a grid -Review plotting points on a grid 2 Cartesian planes
-Introduce coordinate grids Textbook
-Vocab- x-axis, y-axis, origin, quadrants, Graphing picture
ordered pair (how to write an ordered pair) worksheet
Poster (summative Textbook
-Explore pg. 315
-Graphing Picture Worksheet (formative)
-Textbook pages (formative)
5 Translations & -Definitions 2 Cartesian planes
Reflections -How to translations & reflections (describe, Textbook
label, draw) Miras
-Practice- Explore pg. 320
-Textbook questions (formative)
6 Rotations -Definitions 2 Transparent sheet
-How to rotations (describe (degrees, Protractor
directions), label, draw) on white board and Textbook
transparent sheet
-Textbook questions in partners(formative)
7 Unit Review -Review package (summative) 2 Review package
-Study notes (formative)
-Review game (formative)
8 -Unit test (summative) 1 Test
Assessment
Assignments
o Textbook questions: Used to practice content learned in class and track progress and
learning
o Geometric drawing challenge
o Review Package
Quizzes
o Mid-unit review quizzes
Unit Exams
o End of unit test
Formative
o Practice problems (individual and group)
o School examples
o Study notes
o Graphing picture worksheet
o Desk questions
o Textbook questions
o Textbook question reviews
o Review game
Assignments- (35%) projects, questions, reviews, study guide, activities, homework checks, etc.
Quizzes- (15%)
Unit Exams-(25%)
Final Exam/Project-(25%)
You might also like
- MYP3 Math Unit Planner - GeometryDocument12 pagesMYP3 Math Unit Planner - GeometryKelly OroszNo ratings yet
- Process Validation ReportDocument4 pagesProcess Validation ReportSUBODHH100% (1)
- Reading Exercise 1Document5 pagesReading Exercise 1Ghazy Muammar Fawwaz Fawwaz67% (3)
- Course Outline in Analytic gEO.Document4 pagesCourse Outline in Analytic gEO.raymart zalun100% (1)
- 50 Strategies For Differentiated InstructionDocument19 pages50 Strategies For Differentiated InstructionMisael AmoraNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Unit 2 Assessment PlanDocument2 pagesMath 9 Unit 2 Assessment Planapi-336705424No ratings yet
- Grade 11 Quadratics Unit PlanDocument20 pagesGrade 11 Quadratics Unit Planapi-381868432No ratings yet
- Plane and Solid GeometryDocument38 pagesPlane and Solid GeometryMichael FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Unit PlanDocument24 pagesMath 7 Unit Planapi-436565505No ratings yet
- Geometry Unit 2nd Grade RevisedDocument56 pagesGeometry Unit 2nd Grade Revisedapi-609099537100% (1)
- Stage 1 - Identify Desired Results: y A (X - P) + QDocument12 pagesStage 1 - Identify Desired Results: y A (X - P) + Qapi-438357152No ratings yet
- Technical Drawing Unit PlanDocument46 pagesTechnical Drawing Unit PlantereveNo ratings yet
- Geometry PlansDocument7 pagesGeometry Plansapi-485170066No ratings yet
- Scheme of Work TemplateDocument2 pagesScheme of Work TemplateBadrul HishamNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map - Math 6 q3Document3 pagesCurriculum Map - Math 6 q3Dhevy LibanNo ratings yet
- Design Topic: - Geometry - Subject(s) : - Math - Grade(s) 4th - Designer(s) - Arrykka Jackson - Understanding by DesignDocument9 pagesDesign Topic: - Geometry - Subject(s) : - Math - Grade(s) 4th - Designer(s) - Arrykka Jackson - Understanding by Designapi-344056965No ratings yet
- LP - Math9 - 3rd QuarterDocument15 pagesLP - Math9 - 3rd QuarterMark FerrerNo ratings yet
- Curtis Groupuwa 5e Lesson Plan Ed 405 2 1Document4 pagesCurtis Groupuwa 5e Lesson Plan Ed 405 2 1api-725011686No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics 8 Date: Content StandardDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Mathematics 8 Date: Content StandardDynna Marie Vera100% (1)
- Design Topic - Lines and Geometry - Subject(s) - Math - Grade(s) 4th Designer(s) - Doucette Understanding by DesignDocument8 pagesDesign Topic - Lines and Geometry - Subject(s) - Math - Grade(s) 4th Designer(s) - Doucette Understanding by Designapi-300677834No ratings yet
- Week 4Document5 pagesWeek 4api-430230722No ratings yet
- 2021 Output3 MathadvanceDocument20 pages2021 Output3 MathadvanceZamanoden D. UndaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Coordinates and Design Unit PlanDocument8 pagesGrade 7 Coordinates and Design Unit Planapi-308494023No ratings yet
- Year 10 Mathematics CurriculumDocument2 pagesYear 10 Mathematics CurriculumJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- Stage 1 - Identify Desired Results: Title of Unit Grade Level Subject Time Frame Developed byDocument15 pagesStage 1 - Identify Desired Results: Title of Unit Grade Level Subject Time Frame Developed byapi-438357152No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For RankingDocument3 pagesLesson Plan For RankingRonieta VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Final LPDocument7 pagesFinal LPtorresjunakzNo ratings yet
- Maths D (Normal Track) Year 10 (3 YEARS)Document23 pagesMaths D (Normal Track) Year 10 (3 YEARS)Yenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Adzema 3Document3 pagesAdzema 3api-563599311No ratings yet
- tp2 M 2567177 Year 6 Position and Direction Planit Maths Steps To Progression Overview - Ver - 2Document5 pagestp2 M 2567177 Year 6 Position and Direction Planit Maths Steps To Progression Overview - Ver - 2Omii ConsultantNo ratings yet
- Maths - Syllabus Class 1Document24 pagesMaths - Syllabus Class 1Saravana PerumalNo ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics 4 q3 w1Document4 pagesDLL Mathematics 4 q3 w1Ireene Pocong100% (1)
- Draft JuswaDocument8 pagesDraft JuswatorresjunakzNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Shapes and Space Transformations Unit PlanDocument6 pagesMath 8 Shapes and Space Transformations Unit Planapi-697430197No ratings yet
- Math 5.4 SLRP For Acquisition Group 1Document9 pagesMath 5.4 SLRP For Acquisition Group 1JV Isn't EnoughNo ratings yet
- CM - Mathematics 9Document6 pagesCM - Mathematics 9Emalyn CataytayNo ratings yet
- Angles and Triangles Unit Plan 2021Document12 pagesAngles and Triangles Unit Plan 2021api-453015805No ratings yet
- Track 1 - ShapesDocument2 pagesTrack 1 - Shapesapi-535074162No ratings yet
- G7 AlgDocument12 pagesG7 AlgNeha SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Coordinate Geometry Parallel N Perperndicular Lines and EquationsDocument27 pagesUnit 1 Coordinate Geometry Parallel N Perperndicular Lines and Equationsalbert corbillaNo ratings yet
- Time Frame Topics Learning Competencies Assessment: Classroom OrientationDocument15 pagesTime Frame Topics Learning Competencies Assessment: Classroom OrientationElaine AringNo ratings yet
- Q1 Week 1-9 Pre-CalculusDocument84 pagesQ1 Week 1-9 Pre-CalculusJONELL PADONGAONo ratings yet
- Parent Newsletter - Second Grade Math mp4 Part 2Document2 pagesParent Newsletter - Second Grade Math mp4 Part 2api-281541436No ratings yet
- Section 5Document4 pagesSection 5api-436843543No ratings yet
- Math LOs For 3 YearsDocument51 pagesMath LOs For 3 Yearsahmedelmelegy850No ratings yet
- MYP G9 Syllabus 2019-20 - MathematicsDocument3 pagesMYP G9 Syllabus 2019-20 - MathematicsLlama jennerNo ratings yet
- Digital Unit Plan Template Unit Title: Triangles Name: Mackenzie Sheppard Content Area: Math - Geometry Grade Level: 9 & 10Document2 pagesDigital Unit Plan Template Unit Title: Triangles Name: Mackenzie Sheppard Content Area: Math - Geometry Grade Level: 9 & 10api-403395161No ratings yet
- Shapes and Symmetry LessonplanDocument5 pagesShapes and Symmetry LessonplananilbajnathNo ratings yet
- Apprentice Teaching: Lesson Plan Summary TemplateDocument2 pagesApprentice Teaching: Lesson Plan Summary Templateapi-389591300No ratings yet
- 2d Shapes Term 1Document3 pages2d Shapes Term 1api-277245562No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - MAAM SUKIEDocument4 pagesLesson Plan - MAAM SUKIEJenefer Suspeñe FernandezNo ratings yet
- Stations Document.) Look For Evidence of Math Practices (MP) Indicated While Students WorkDocument2 pagesStations Document.) Look For Evidence of Math Practices (MP) Indicated While Students WorkJaniene BathanNo ratings yet
- Stage 1-Desired Results: Established GoalsDocument8 pagesStage 1-Desired Results: Established GoalsMark Anthony EspañolaNo ratings yet
- G.7-G.9 BMathDocument13 pagesG.7-G.9 BMathMa Paola Theresa MortillaNo ratings yet
- Grade K Unit 2 Outline Overview 2017Document23 pagesGrade K Unit 2 Outline Overview 2017api-401628488No ratings yet
- 3 RD Mathwk 7Document4 pages3 RD Mathwk 7EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- Final Observation Math LessonDocument4 pagesFinal Observation Math Lessonapi-545129087No ratings yet
- Module7 Graph TheoryDocument27 pagesModule7 Graph Theoryreigoraoul56No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - MathDocument3 pagesLesson Plan - Mathapi-584171630No ratings yet
- Maligaya Central Elementary School - DLPDocument4 pagesMaligaya Central Elementary School - DLPStarga WhiteNo ratings yet
- Form5 - 2008 Yearly Plan MathDocument17 pagesForm5 - 2008 Yearly Plan MathsuryantyNo ratings yet
- LP - G3 - M - Geometry - 2 D - 3 D Shapes and PatternsDocument5 pagesLP - G3 - M - Geometry - 2 D - 3 D Shapes and PatternsRashmi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Pre AssessmentDocument1 pagePre Assessmentapi-485170066No ratings yet
- Design A Quiz - Suface Area and VolumeDocument1 pageDesign A Quiz - Suface Area and Volumeapi-485170066No ratings yet
- What Is The Better Deal - Ratio PosterDocument1 pageWhat Is The Better Deal - Ratio Posterapi-485170066No ratings yet
- Gym 1-6 Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesGym 1-6 Lesson Planapi-485170066No ratings yet
- PD Session Seminar 2Document11 pagesPD Session Seminar 2api-485170066No ratings yet
- Student Self AssessmentDocument2 pagesStudent Self Assessmentapi-485170066No ratings yet
- Long Range PlanDocument4 pagesLong Range Planapi-485170066No ratings yet
- Percent Ratio and Rate Unit PlanDocument4 pagesPercent Ratio and Rate Unit Planapi-485170066No ratings yet
- Archery LessonDocument2 pagesArchery Lessonapi-485170066No ratings yet
- Geometry PlansDocument7 pagesGeometry Plansapi-485170066No ratings yet
- Math 8 Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesMath 8 Lesson Planapi-485170066No ratings yet
- ComplimentsDocument5 pagesComplimentsapi-485170066No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2 - IndigenousDocument3 pagesLesson Plan 2 - Indigenousapi-485170066No ratings yet
- GR 6 Voc Words 4th QTRDocument5 pagesGR 6 Voc Words 4th QTRAzlynn Courtney FernandezNo ratings yet
- Queues: Chapter 6 - Principles of Data Structures Using C by Vinu V DasDocument25 pagesQueues: Chapter 6 - Principles of Data Structures Using C by Vinu V DasAamir ChohanNo ratings yet
- How Can Apologetics Help Me Defend My Faith?Document16 pagesHow Can Apologetics Help Me Defend My Faith?Regina D. RogersNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Lesson 2 Tongue TwistersDocument14 pagesWeek 1 Lesson 2 Tongue Twistersapi-246058425No ratings yet
- Moyang 2007Document11 pagesMoyang 2007Clarina TitusNo ratings yet
- CMRL.12.18 : Section A: New Business, Regulatory and Sales-Related RequirementsDocument2 pagesCMRL.12.18 : Section A: New Business, Regulatory and Sales-Related RequirementsJovelyn ArgeteNo ratings yet
- Essay On Corruption in in IndiaDocument1 pageEssay On Corruption in in IndiaGaurav ThakurNo ratings yet
- English Presentations - Useful PhrasesDocument2 pagesEnglish Presentations - Useful PhrasesNitish Nagar100% (1)
- Tia HistoryDocument11 pagesTia HistoryTiara AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Six Examples of Large-Scale ProgramsDocument7 pagesSix Examples of Large-Scale ProgramsPhilcas LiNo ratings yet
- On Children: About The AuthorDocument3 pagesOn Children: About The AuthorVinayak VKNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Manual2Document106 pagesGreenhouse Manual2Amit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Annexure 6.0 Candidate InstructionsDocument8 pagesAnnexure 6.0 Candidate Instructionschiluverushivaprasad02No ratings yet
- Britannica Childrens Encyclopedia 2007Document1 pageBritannica Childrens Encyclopedia 2007Marius AndreiNo ratings yet
- Rephrasing Exercises Second TermDocument6 pagesRephrasing Exercises Second TermLulu SancNo ratings yet
- 10 Female Superheroes Who Depict Women EmpowermentDocument3 pages10 Female Superheroes Who Depict Women EmpowermentSharjeel ZamanNo ratings yet
- Angular With NodeJS - The MEAN Stack Training Guide - UdemyDocument15 pagesAngular With NodeJS - The MEAN Stack Training Guide - UdemyHarsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- (With Script) June 2021 Saturday WSF Teaching GuideDocument3 pages(With Script) June 2021 Saturday WSF Teaching GuideMichael T. BelloNo ratings yet
- CDHA Infection ControlDocument2 pagesCDHA Infection ControlAliaa El WakeelNo ratings yet
- Motor Claim Form THE ORIENTAL INSURANCE CO. LTD.Document4 pagesMotor Claim Form THE ORIENTAL INSURANCE CO. LTD.rajiv.surveyor7145No ratings yet
- SDO Navotas Project-Assist - MAPEH Grade-8..Document17 pagesSDO Navotas Project-Assist - MAPEH Grade-8..Vanessa AsyaoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument9 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelharpritahingoraniNo ratings yet
- Q4FY23 HMCL Transcript-230711-085731Document19 pagesQ4FY23 HMCL Transcript-230711-085731vishwesh gautamNo ratings yet
- Koran Textcode PDFDocument115 pagesKoran Textcode PDFAboubacar Sompare0% (1)
- Kyrgyzstan. ReportDocument27 pagesKyrgyzstan. Report200211555No ratings yet
- Riko Technical Brochure PDFDocument29 pagesRiko Technical Brochure PDFGrigoreOzonNo ratings yet
- Mirantis CKA ExamDocument10 pagesMirantis CKA ExamvNo ratings yet