Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Welding - Lecture1 1 2
Welding - Lecture1 1 2
Uploaded by
Edon MorinaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Welding - Lecture1 1 2
Welding - Lecture1 1 2
Uploaded by
Edon MorinaCopyright:
Available Formats
Welding
1. Introduction
Welding is the process for joining different materials.
Welding is used for making permanent joints.
In order to join two or more pieces of metal together by welding process the most essential
requirement is Heat. Pressure may also be employed.
It is used in the manufacture of automobile bodies, aircraft frames, railway wagons, machine
frames, structural works, tanks, furniture, boilers, general repair work and ship building
2. Welding Defined
Welding is defined by the American welding Society (AWS) as “a materials joining process
used in making welds”. A weld is defined as “a localized coalescence (the growing together
of the grain structure of the materials being welded) of metals or nonmetals produced either
by heating the materials to suitable temperatures, with or without application of pressure and
with or without the use of filler metal”.
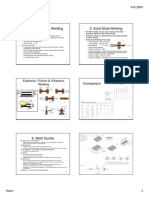
3. Types of Welding
• Plastic Welding or Pressure Welding
The piece of metal to be joined are heated to a plastic state and forced together by external
pressure
Example -Resistance welding
• Fusion Welding or Non-Pressure Welding
The material at the joint is heated to a molten state and allowed to solidify
Example-Gas welding, Arc welding
4. Classification of Welding Processes
There are about 35 welding processes used by industry today.
Welding can be classified on the basis of
(i) Source of heat i.e. flame, arc etc.
(ii) Type of interaction i.e. liquid/liquid (fusion welding) or solid/solid (solid state welding)
In general various welding processes are classified as below
1. Gas Welding
a) Air acetylene welding c) Oxyhydrogen welding
b) Oxyacetylene welding d) Prussure gas welding
2. Arc Welding
a) Carbon Arc Welding e) Metal Inert Gas (MIG) Welding
b) Shielded Metal Arc Welding f) Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
(SMAW) g) Plasma Arc Welding (PAW)
c) Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) h) Electroslag Welding
d) Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Welding
3. Resistance Welding
a) Spot Welding e) Flash Butt Welding
b) Projection Welding f) Percussion Welding
c) Seam Welding i) High Frequency Resistance Welding
d) Resistance Butt Welding (HFRW)
4. Solid State Welding
a) Cold Welding e) Friction Welding
b) Diffusion Welding f) Hot Pressure Welding
c) Explosive Welding g) Roll Welding
d) Forge Welding h) Ultrasonic Welding
5. Thermo-Chemical Welding Processes
a) Thermit Welding b) Atomic Hydrogen Welding
6. Radiant Energy Welding Processes
a) Electron Beam Welding (EBW) b) Laser Beam Welding (LBW)
5. Advantages, Disadvantages and Applications of Welding
Advantages of Welding
1. A good weld is as strong as the base metal.
2. General welding equipment is not very costly.
3. Portable welding equipments are available.
4. Welding permits considerable freedom in design.
5. Welding can be mechanized.
You might also like
- Cswip 3.2 MCQ-004Document5 pagesCswip 3.2 MCQ-004Moses_Jakkala80% (5)
- A Comparative Analysis On The Effectiveness of Star FruitDocument19 pagesA Comparative Analysis On The Effectiveness of Star FruitMaria Danica de Villa67% (3)
- Presantation On Reverse OsmosisDocument33 pagesPresantation On Reverse OsmosisAlhad Nigudkar82% (17)
- Welding Lecture1 2Document34 pagesWelding Lecture1 2Dr Abhijeet GangulyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Joining Processes-1Document9 pagesLecture 1 - Joining Processes-1Shaheer FarrukhNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1: Introduction To Metal Joining Process 1. WeldingDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 1: Introduction To Metal Joining Process 1. Weldingprasoon pathakNo ratings yet
- 2 Classification of Welding PDFDocument31 pages2 Classification of Welding PDFSiva Narendra100% (2)
- Introduction & Classification of WeldingDocument3 pagesIntroduction & Classification of WeldingZaky MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- Lecture NoteDocument93 pagesLecture Noteamit kumarNo ratings yet
- Advance Welding RME-081Document69 pagesAdvance Welding RME-081enjoy your dayNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Manufacturing Process - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument11 pagesUnit 2 - Manufacturing Process - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inIPL 2020 LIVE100% (1)
- Chapter 6 - WeldingDocument20 pagesChapter 6 - WeldingDipayan DasNo ratings yet
- Overview of Welding Technology The Weld Joint Physics of Welding Features of A Fusion Welded JointDocument109 pagesOverview of Welding Technology The Weld Joint Physics of Welding Features of A Fusion Welded JointMasa FuadNo ratings yet
- Module - IIDocument48 pagesModule - IIsivasaNo ratings yet
- Metal Joining Processes: Prof. Mayur S Modi Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department Ssasit, SuratDocument79 pagesMetal Joining Processes: Prof. Mayur S Modi Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department Ssasit, SuratPrateekNo ratings yet
- Welding MJ-1Document13 pagesWelding MJ-1P2109 Praphul HampapuramNo ratings yet
- Casing ProcessDocument18 pagesCasing ProcessManeesh TNo ratings yet
- Welding ProcessDocument52 pagesWelding Processakash.vd.1603No ratings yet
- Joining ProcessesDocument10 pagesJoining ProcessesSachin KhotNo ratings yet
- Welding Workshop PracticeDocument49 pagesWelding Workshop PracticedaveNo ratings yet
- NAME 345 Welding TechnologyDocument14 pagesNAME 345 Welding TechnologyHR TusherNo ratings yet
- Welding 1Document61 pagesWelding 1عبدالرحمن سيدNo ratings yet
- Welding and Types of WeldingDocument9 pagesWelding and Types of WeldingMunem ShahriarNo ratings yet
- Welding Dip ME MainDocument101 pagesWelding Dip ME MainSiamNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document13 pagesLec 1MUuhammed FikiNo ratings yet
- Welding Course PDFDocument46 pagesWelding Course PDFRogerio Salvagni100% (1)
- Course Name: NAME 301 Shipbuilding Technology-I: Md. Omar FarukDocument56 pagesCourse Name: NAME 301 Shipbuilding Technology-I: Md. Omar FarukMd. Omar FarukNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document47 pagesCH 1hailayNo ratings yet
- 5 WeldingDocument70 pages5 WeldingOmar KurdiNo ratings yet
- BMP SCJ Mj1 IntroDocument13 pagesBMP SCJ Mj1 IntroNimesh BhagatNo ratings yet
- Welding 171002150527Document40 pagesWelding 171002150527Sk SajedulNo ratings yet
- Cswip Qa 3 2Document8 pagesCswip Qa 3 2Koya ThangalNo ratings yet
- Chapter (9) WeldingDocument20 pagesChapter (9) Weldingarkarminkhant734No ratings yet
- Cswip 3.1 Difficul - Multichoice QuesDocument11 pagesCswip 3.1 Difficul - Multichoice QuesLuan Nguyen0% (1)
- Module 3a - Welding ProcessesDocument36 pagesModule 3a - Welding ProcessesMayur PatelNo ratings yet
- Welding MidsemDocument100 pagesWelding Midsemamit kumarNo ratings yet
- Welding SlidesDocument99 pagesWelding SlidesMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document30 pagesLec 1Serhat ManulboğaNo ratings yet
- Friction Stir Welding of Aluminium AlloysDocument46 pagesFriction Stir Welding of Aluminium AlloysBhupender LawaNo ratings yet
- CSWIP 3.2 Welding Inspector Exam: Signing Off A ProductDocument9 pagesCSWIP 3.2 Welding Inspector Exam: Signing Off A ProductAhmed NassarNo ratings yet
- Welding Inspection, Steels - WIS 5: Multi - Choice End of Course Assessment Question Paper (MSR-AWI-1)Document8 pagesWelding Inspection, Steels - WIS 5: Multi - Choice End of Course Assessment Question Paper (MSR-AWI-1)Le Tuan100% (1)
- Friction WeldingDocument25 pagesFriction WeldingBHAVESH JOSHI0% (1)
- Chapter Two (Welding)Document26 pagesChapter Two (Welding)mesfin snowNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions WELDING PROCESSES SOLUTIONSDocument3 pagesTutorial Questions WELDING PROCESSES SOLUTIONSJosephine BakewaNo ratings yet
- Types of WeldingDocument10 pagesTypes of WeldingMuhammad Tauseef ZafarNo ratings yet
- U4 - WeldingDocument59 pagesU4 - WeldingAnonymous LM9RaUA4yNo ratings yet
- Project Report of Mini ProjectDocument24 pagesProject Report of Mini ProjectpramodassNo ratings yet
- BMP Paper With SolutionDocument58 pagesBMP Paper With SolutionAtul GaurNo ratings yet
- Welding Inspection, Steels Multi - Choice Question Paper (MFY-007)Document7 pagesWelding Inspection, Steels Multi - Choice Question Paper (MFY-007)Moses_JakkalaNo ratings yet
- Welding Fundamentals PDFDocument33 pagesWelding Fundamentals PDFHusain AliNo ratings yet
- (D) A Transformer or Alternator and A Means To Change The CurrentDocument19 pages(D) A Transformer or Alternator and A Means To Change The Currentmohammed dallyNo ratings yet
- Basic Q A For Welding PDFDocument6 pagesBasic Q A For Welding PDFMadhan KannanNo ratings yet
- Need For WeldingDocument5 pagesNeed For Weldingvijayanandan thekkethodikayilNo ratings yet
- 112103263Document689 pages112103263Aakash TiwariNo ratings yet
- 7691IV - 4th Semester - Metallurgical and Materials EngineeringDocument18 pages7691IV - 4th Semester - Metallurgical and Materials EngineeringankNo ratings yet
- Joining AND Assembly Processes:: WeldingDocument27 pagesJoining AND Assembly Processes:: Weldingravi00098No ratings yet
- Welding Inspector ExamDocument7 pagesWelding Inspector ExamEhab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Welding NotesDocument47 pagesWelding NotesAparna KumarNo ratings yet
- Solid State Welding and Application in Aeronautical IndustryDocument8 pagesSolid State Welding and Application in Aeronautical Industrymaster002 XDNo ratings yet
- API 571 2nd 2011 Unlocked - 051Document1 pageAPI 571 2nd 2011 Unlocked - 051nguyenNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Welding ProcessDocument57 pagesUnit 5 Welding Processmahammad kamaluddeenNo ratings yet
- Welding Terminology: A Guide to MIG, TIG, Stick, Gas, and Spot Welding TermsFrom EverandWelding Terminology: A Guide to MIG, TIG, Stick, Gas, and Spot Welding TermsNo ratings yet
- Welding 4Document1 pageWelding 4Edon MorinaNo ratings yet
- Welding 3Document1 pageWelding 3Edon MorinaNo ratings yet
- Welding 2Document1 pageWelding 2Edon MorinaNo ratings yet
- Welding 1Document1 pageWelding 1Edon MorinaNo ratings yet
- Preparing Laboratory Solutions and ReagentsDocument61 pagesPreparing Laboratory Solutions and ReagentsAlmira Kaye CuadraNo ratings yet
- Asl 6 217Document27 pagesAsl 6 217SaliniNo ratings yet
- Crude Distillation Unit - OdtDocument32 pagesCrude Distillation Unit - OdtfaresNo ratings yet
- Delayen A. Heterocycle 2005, 65 - 1673Document6 pagesDelayen A. Heterocycle 2005, 65 - 1673nileshshitole619No ratings yet
- Bonding in SolidsDocument24 pagesBonding in SolidsMahesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Balancing Redox Reactions Equations Practice With AnswersDocument4 pagesBalancing Redox Reactions Equations Practice With AnswersphilippepreanNo ratings yet
- Class 9th. Che-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesClass 9th. Che-WPS Officemr467051No ratings yet
- The Characterization of Saponifiable LipidsDocument7 pagesThe Characterization of Saponifiable LipidsREYMAR CASAREONo ratings yet
- FiIllers and Additives of Plastics PDFDocument53 pagesFiIllers and Additives of Plastics PDFAnishMendisNo ratings yet
- Dulux Spalling DocumentDocument3 pagesDulux Spalling Documentashish100% (1)
- Jurnal SemestaDocument7 pagesJurnal SemestaSteven Raynaldo HNo ratings yet
- 2 1 The Diagrams Show Four Different Methods of Collecting GasesDocument12 pages2 1 The Diagrams Show Four Different Methods of Collecting GasesMujeeb SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Parametri Za Laser 100WDocument3 pagesParametri Za Laser 100WIvan MarjanovićNo ratings yet
- Hull Cell IntroductionDocument4 pagesHull Cell IntroductionR.Subramanian0% (1)
- Apm 2018 PDFDocument408 pagesApm 2018 PDFRitesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Biofuel Production From Mesua Ferrea L Seed OilDocument6 pagesBiofuel Production From Mesua Ferrea L Seed OilerpublicationNo ratings yet
- Flotation in Inorganic Electrolytes The Relationship Between Recover of Hydrophobic Particles, Surface Tension, Bubble Coalescence and Gas SolubiDocument14 pagesFlotation in Inorganic Electrolytes The Relationship Between Recover of Hydrophobic Particles, Surface Tension, Bubble Coalescence and Gas SolubiJose Luis Barrientos RiosNo ratings yet
- ReferenceDocument4 pagesReferenceMaries San PedroNo ratings yet
- D 15 - 72 ScanDocument24 pagesD 15 - 72 Scanمهندس فهمي عبدالعزيزNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Review - pdf-1Document8 pagesExam 1 Review - pdf-1ANN BEATRICE GONo ratings yet
- NiAll-HX-M290-400W Material Data Sheet 10-15 enDocument5 pagesNiAll-HX-M290-400W Material Data Sheet 10-15 enAmit PowarNo ratings yet
- P8-4 (Page 572 Fogler 4th Ed.) : K M V VDocument15 pagesP8-4 (Page 572 Fogler 4th Ed.) : K M V VSILPA ASTI NURANo ratings yet
- Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0043279 A1Document13 pagesPatent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0043279 A1vitorio netoNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic ExamDocument12 pagesDiagnostic ExamAnabel AbulenciaNo ratings yet
- Fibre - Synthetic Fibres and Their UsesDocument4 pagesFibre - Synthetic Fibres and Their UsesAjay SatijaNo ratings yet
- Bond EnthalpyDocument10 pagesBond EnthalpyPartha SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Structure and Synthesis of AlkenesDocument40 pagesChapter 7 - Structure and Synthesis of Alkenesrareair213No ratings yet
- Maraging Steel: Sandeep NairDocument20 pagesMaraging Steel: Sandeep NairVysakh VasudevanNo ratings yet