Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Async Act
Async Act
Uploaded by
Ella Blanca BuyaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Async Act
Async Act
Uploaded by
Ella Blanca BuyaCopyright:
Available Formats
Ella Blanca Buya
1BSA
Async Activity
Requirement 1
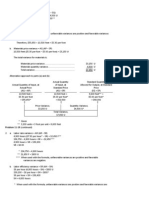
Actual Quantity of Inputs (AQ)
Actual Price (AP)
Standard Price (SP)
Standard Quantity Allowed for Output (SQ)
Actual Hours of Input (AH)
Actual Rate (AR)
Standard Rate (SR)
Standard Hours Allowed for Output (SH)
a.
Materials Price Variance
= AQ (AP – SP) 25,000 pounds (P2.95 per pound – P2.50 per pound)
= P11,250 U
Materials Quantity Variance
= SP (AQ – SQ) P2.50 per pound (19,800 pounds – 20,000 pounds)
= P500 F
b. Finished goods and work in process inventories are significant and can be ignored.
c.
Labor Rate Variance
= AH (AR – SR) 3,600 hours (P8.70 per hour – P9.00 per hour)
= P1,080 F
Labor Efficiency Variance
= SR (AH – SH) P9.00 per hour (3,600 hours – 3,000 hours)
= P5,400 U
d. Variable Overhead Spending Variance
= AH (AR – SR) 1,800 hours (P2.40 per hour* – P2.00 per hour)
= P720 U
* P4,320 ÷ 1,800 hours = P2.40 per hour
Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance
= SR (AH – SH) P2.00 per hour (1,800 hours – 1,500 hours)
= P600
Requirement 2 Requirement 3
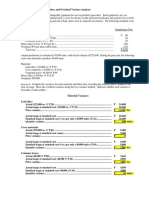
Summary of variances:
Material price variance............................................................................................P11,250 Unfavorable
Material quantity variance.......................................................................................500 Favorable
Labor rate variance..................................................................................................1,080 Favorable
Labor efficiency variance........................................................................................5,400 Unfavorable
Variable overhead spending variance......................................................................720 Unfavorable
Variable overhead efficiency variance..................................................................... 600 Unfavorable
Net variance.....................................................................................................P16,390 Unfavorable
The net unfavorable variance of P16,390 for the month caused the plant’s variable cost of goods sold to
increase from the budgeted level of P80,000 to P96,390:
Budgeted cost of goods sold at P16 per metal mold...............................................P80,000
Add the net unfavorable variance (as above).......................................................... 16,390
Actual cost of goods sold.............................................................................. ....P96,390
This P16,390 net unfavorable variance also accounts for the difference between the budgeted net
operating income and the actual net loss for the month.
Budgeted net operating income............................................................................... P15,000
Deduct the net unfavorable variance added to cost of goods
sold for the month..................................................................................................... 16,390
Net operating loss......................................................................................... ..... (P1,390)
You might also like
- CO12101E IP06 ProblemDocument5 pagesCO12101E IP06 ProblemHaydeeNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To Accounting For BSOA &1BSENTREPDocument21 pagesModule 1 Introduction To Accounting For BSOA &1BSENTREPjilliantrcieNo ratings yet
- 2M Cargo Notes by AnupamDocument87 pages2M Cargo Notes by AnupamAmaan MoyalNo ratings yet
- QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesQuestionnaireBishu BiswasNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Problem - SolutionDocument9 pagesQuiz 2 Problem - SolutionCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument9 pagesThis Study Resource Wasshivam chugh100% (2)
- Case 11-55Document3 pagesCase 11-55HETTYNo ratings yet
- Variance Analysis (Practice Problems)Document7 pagesVariance Analysis (Practice Problems)Godwin De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- MasDocument13 pagesMasHiroshi Wakato50% (2)
- Lesson 1Document7 pagesLesson 1Ma Aaron Gwyneth BalisacanNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems 2-Standard Costing and Variance Analysis-1Document2 pagesPractice Problems 2-Standard Costing and Variance Analysis-1Unknowingly AnonymousNo ratings yet
- Hilton MAcc Ch10 SolutionDocument8 pagesHilton MAcc Ch10 Solutionokquan33% (3)
- $3,200 Units X 3 Foot Per Unit $55,650 / 10,500 Feet $5.30 Per FootDocument41 pages$3,200 Units X 3 Foot Per Unit $55,650 / 10,500 Feet $5.30 Per FootLyra EscosioNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing or Variance AnalysisDocument11 pagesStandard Costing or Variance Analysisgull skNo ratings yet
- Accounting Khalil 198Document11 pagesAccounting Khalil 198Khalil JuttNo ratings yet
- Materials Price Variance (AP - SP) X AQDocument8 pagesMaterials Price Variance (AP - SP) X AQRIZLE SOGRADIELNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8 Sheet Solved MGMT 2Document6 pagesTutorial 8 Sheet Solved MGMT 2Mohamed ManoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Homework MADocument13 pagesChapter 8 Homework MAErvin Jello Rosete RagonotNo ratings yet
- Sol. Ch. 8Document45 pagesSol. Ch. 8phoopoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 AnswerDocument7 pagesTutorial 4 AnswernajihahNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 Overhead VariancesDocument10 pagesUnit 14 Overhead VariancesZaki GustiNo ratings yet
- DM and DL Variances SolutionsDocument7 pagesDM and DL Variances SolutionsYuna OliveroNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing: 1. Single MaterialDocument7 pagesStandard Costing: 1. Single MaterialManisha KhatriNo ratings yet
- Acct Bah WDocument4 pagesAcct Bah WAbby Sta AnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Solutions - Inclass ExercisesDocument12 pagesChapter 10 Solutions - Inclass ExercisesSummerNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing With Solution-1Document11 pagesStandard Costing With Solution-1jikuenterprise789No ratings yet
- Cost Lesson 8.variancesDocument4 pagesCost Lesson 8.variancessanagustinveramaeNo ratings yet
- Solution Chapter 10: Exercise 10-1Document16 pagesSolution Chapter 10: Exercise 10-1AHMED MOHAMED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Zamil Industries (Q-7 Aut-16) SOLUTIONDocument2 pagesZamil Industries (Q-7 Aut-16) SOLUTION90 SHAMAZNo ratings yet
- HbjhjhjhujuhjDocument14 pagesHbjhjhjhujuhjnjkjhNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 StandardDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 9 Standardsarahayeesha1No ratings yet
- Ma Chapter 3 Standard Costing - LabourDocument60 pagesMa Chapter 3 Standard Costing - LabourMohd Zubair KhanNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Solution - Standard CostingDocument3 pages9.1 Solution - Standard CostingKendall Anne MendozaNo ratings yet
- Acctg201 Standard Cost and Variance Analysis2 AnsKeyDocument6 pagesAcctg201 Standard Cost and Variance Analysis2 AnsKeyJessa YuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Problem 34Document5 pagesChapter 14 Problem 34freaann03No ratings yet
- Standard Costing Quiz 2Document2 pagesStandard Costing Quiz 2Shafni DulnuanNo ratings yet
- Variance Analysis - 084249Document20 pagesVariance Analysis - 084249Adams JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Standard CostingDocument19 pagesStandard CostingCillian ReevesNo ratings yet
- ÔN THI CK KTQT2 - GiảiDocument7 pagesÔN THI CK KTQT2 - GiảiNguyễn Thùy LinhNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Kelompok 12 Bab 11 ADocument18 pagesPresentasi Kelompok 12 Bab 11 AsimsonNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing: Answer Key On Chapter 7Document5 pagesStandard Costing: Answer Key On Chapter 7Jaquelyn JacquesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 (Individu)Document13 pagesChapter 12 (Individu)Rahmatul MaghfirohNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing & Variance AnalysisDocument18 pagesStandard Costing & Variance AnalysisMahesh G VNo ratings yet
- Lê Thị Thùy Dương-Chương-3Document12 pagesLê Thị Thùy Dương-Chương-3duong leNo ratings yet
- Assignment On SC and VADocument12 pagesAssignment On SC and VAVixen Aaron EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing Presentation 091951Document5 pagesStandard Costing Presentation 091951Sofia BaguinatNo ratings yet
- Johanna Grace Singuran - Written Assignment No. 2Document3 pagesJohanna Grace Singuran - Written Assignment No. 2Johanna GraceNo ratings yet
- ACCT6008 2021S1 W9 Variances Homework SolutionDocument10 pagesACCT6008 2021S1 W9 Variances Homework Solutionwuzhen102110No ratings yet
- Exercise 9-10: Solutions (12/01)Document8 pagesExercise 9-10: Solutions (12/01)ppaulyni33No ratings yet
- Assignment #2 DM&DL L Variance With SolutionDocument9 pagesAssignment #2 DM&DL L Variance With SolutionJeannet LagcoNo ratings yet
- Answer For Question One: 19200 YardDocument4 pagesAnswer For Question One: 19200 Yardwossen gebremariamNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument38 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysisAlexis Kaye DayagNo ratings yet
- Name:: Standard Costs/Quantities: Per PuckDocument15 pagesName:: Standard Costs/Quantities: Per Puckpb3091No ratings yet
- BTVNDocument8 pagesBTVNTrâm PhươngNo ratings yet
- Cost ManagementDocument18 pagesCost ManagementGeo Rublico ManilaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Managerial Accounting Canadian 5th Edition Brewer Solutions Manual DownloadDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Managerial Accounting Canadian 5th Edition Brewer Solutions Manual DownloadWm Mcgranahan100% (28)
- SMA Chapter Four - Variance AnalysisDocument86 pagesSMA Chapter Four - Variance Analysisngandu100% (1)
- Total Project Cost Infrastructure CapitalDocument39 pagesTotal Project Cost Infrastructure CapitalAshish SinghNo ratings yet
- Class Questions PDFDocument5 pagesClass Questions PDFmanav tilokaniNo ratings yet
- Chp1 QuestionsOnStandardCostingDocument9 pagesChp1 QuestionsOnStandardCostingNur HidayahNo ratings yet
- Labor Variance: By: Group 2Document24 pagesLabor Variance: By: Group 2Kris BayronNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument15 pagesDocxAhsan IqbalNo ratings yet
- Budgets For Control, Part 2Document29 pagesBudgets For Control, Part 2vukicevic.ivan5No ratings yet
- E-mini Futures Trading Earning: Cognitive Energy Since 2016-01-01 Through 2020-05-14From EverandE-mini Futures Trading Earning: Cognitive Energy Since 2016-01-01 Through 2020-05-14No ratings yet
- Notes CostDocument44 pagesNotes CostElla Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- Position Paper BlancoDocument7 pagesPosition Paper BlancoElla Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4 FarDocument1 pageQuiz 4 FarElla Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Far PR2Document1 pageChapter 5 Far PR2Ella Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - ELLA BUYADocument3 pagesAssignment - ELLA BUYAElla Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- Buya - Ella Blanca - Prelim1&2Document2 pagesBuya - Ella Blanca - Prelim1&2Ella Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 SeatworkDocument2 pagesChapter 6 SeatworkElla Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- Feasibility EngDocument4 pagesFeasibility EngElla Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- CritiqueDocument4 pagesCritiqueElla Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- Concept PaperDocument15 pagesConcept PaperElla Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- Blanco Act10Document1 pageBlanco Act10Ella Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- Abstract Et AlDocument2 pagesAbstract Et AlElla Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- Cwts ReviewDocument5 pagesCwts ReviewElla Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- To PrintDocument4 pagesTo PrintElla Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- Mid UnderDocument2 pagesMid UnderElla Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- Under RevDocument5 pagesUnder RevElla Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- Review PaperDocument3 pagesReview PaperElla Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- CritiqueDocument3 pagesCritiqueElla Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Accounting 1 (Week 4) OnlineDocument14 pagesFundamentals of Accounting 1 (Week 4) OnlineElla Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental - Exer, Week1Document1 pageFundamental - Exer, Week1Ella Blanca BuyaNo ratings yet
- Ch08 Roth3eDocument86 pagesCh08 Roth3etaghavi1347No ratings yet
- Tanishq and Mia OffersDocument2 pagesTanishq and Mia OffersAkshay RanganathkumarNo ratings yet
- MIC15691-CAL-Md Riyad HasanDocument2 pagesMIC15691-CAL-Md Riyad Hasanmonir.saseduNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standard - 4Document6 pagesAccounting Standard - 4api-298918505No ratings yet
- Hire Purchase System: By:Ca Parveen JindalDocument27 pagesHire Purchase System: By:Ca Parveen Jindalphani chowdaryNo ratings yet
- Monday QantasDocument35 pagesMonday QantasKornel GokinsonNo ratings yet
- Soal Tutor Sislog 2021Document8 pagesSoal Tutor Sislog 2021Rusli Saga100% (1)
- Lean Manufacturing OverviewDocument252 pagesLean Manufacturing OverviewDebashishDolon100% (1)
- To Islamic Finance: DR Masahina SarabdeenDocument20 pagesTo Islamic Finance: DR Masahina SarabdeenNouf ANo ratings yet
- Abm G3Document32 pagesAbm G3Chrizelle Mariece Escalante KaguingNo ratings yet
- CEI Planet Winter 2021Document16 pagesCEI Planet Winter 2021CEINo ratings yet
- PESTEL ScotiabankDocument3 pagesPESTEL ScotiabankSridhar PantNo ratings yet
- Revision For Test 2Document3 pagesRevision For Test 2Raudhatun Nisa'No ratings yet
- Annual Report 2015Document300 pagesAnnual Report 2015Iqbal H Biplob100% (1)
- Disruptive InnovationDocument12 pagesDisruptive InnovationArghadeep HazraNo ratings yet
- Birquttes SantoiDocument21 pagesBirquttes SantoiEdward UyNo ratings yet
- UNIT 6 Import ExportDocument14 pagesUNIT 6 Import Exportprayana smartwisetechNo ratings yet
- BFC5935 - Final Exam Information PDFDocument2 pagesBFC5935 - Final Exam Information PDFXue XuNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 - Investment PlanningDocument55 pagesTopic 9 - Investment PlanningArun GhatanNo ratings yet
- Indian Banking .. ..SECTORDocument30 pagesIndian Banking .. ..SECTORShakshi Arvind GuptaNo ratings yet
- FM CaseDocument3 pagesFM CaseROSHAN KUMAR SAHOONo ratings yet
- Donghua Double Pitch ChainDocument611 pagesDonghua Double Pitch ChainErliana IndahNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Ca/Sv/Rs 4,750,000 7,750,000 3,000,000Document3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Ca/Sv/Rs 4,750,000 7,750,000 3,000,000lana del reyNo ratings yet
- Đường giới hạn khả năng sản xuất - Production possibility frontierDocument11 pagesĐường giới hạn khả năng sản xuất - Production possibility frontierNguyễn Bá Tài AnhNo ratings yet
- Ifrs Edition: Preview ofDocument28 pagesIfrs Edition: Preview ofwtf100% (1)