Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pipe 03
Pipe 03
Uploaded by
AmrutaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Problem Set 8Document7 pagesProblem Set 8Sayyed Ali MirjafariNo ratings yet
- KNS2163 Week1Document32 pagesKNS2163 Week1Nurul QurratuNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 06 Dec 2023-2Document4 pagesAdobe Scan 06 Dec 2023-2GenNo ratings yet
- Recrete Water&sewerDocument4 pagesRecrete Water&sewerhanisNo ratings yet
- Liquids - Level 3Document6 pagesLiquids - Level 3demolition squadNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Third Exam 2011Document5 pagesFluid Mechanics: Third Exam 2011nageshNo ratings yet
- Sankalp - Phase Iii - FL - 7Document6 pagesSankalp - Phase Iii - FL - 7Anusha SinghalNo ratings yet
- The Physics of Fluids-2 PDFDocument20 pagesThe Physics of Fluids-2 PDFMellissa MungureNo ratings yet
- LPP-Fluid Mechanics: FiitjeeDocument5 pagesLPP-Fluid Mechanics: FiitjeeYash TandonNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 - HydrodynamicsDocument10 pagesAssignment 4 - HydrodynamicsluluNo ratings yet
- Chanana Institute of Physics: 326, Tilak Nagar, Amritsar. 9888190610 ViscosityDocument4 pagesChanana Institute of Physics: 326, Tilak Nagar, Amritsar. 9888190610 ViscosityAditya SallyNo ratings yet
- National University of Singapore Department of Mechanical Engineering ME2134 Fluid Mechanics I Tutorial 3Document5 pagesNational University of Singapore Department of Mechanical Engineering ME2134 Fluid Mechanics I Tutorial 3Cl SkyeNo ratings yet
- RESERVORIO CIRCULAR 20m3.es - enDocument22 pagesRESERVORIO CIRCULAR 20m3.es - enpravin mundeNo ratings yet
- GWH-PPT ch3 SumDocument41 pagesGWH-PPT ch3 SumMistireselassieNo ratings yet
- ME 326: Experiment No. 1Document32 pagesME 326: Experiment No. 1parvejNo ratings yet
- FluidMechanics TD Chaps 01-05Document14 pagesFluidMechanics TD Chaps 01-05Mamoudou Bah DialloNo ratings yet
- Me19b hw1Document2 pagesMe19b hw1Hugh HeNo ratings yet
- Pressure in FluidsDocument18 pagesPressure in FluidsSayantan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Exercise Using The Sand Tank Model: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesGroundwater Exercise Using The Sand Tank Model: ObjectivesIrsan BahutalaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Reci PumpDocument12 pagesFluid Reci PumpMaxiNo ratings yet
- RM1 Liquids in Relative Equilibrium Translation 1Document26 pagesRM1 Liquids in Relative Equilibrium Translation 1EmmanNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Well Drainage AreaDocument4 pagesHorizontal Well Drainage AreaJuhaina HeibaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (Part 4) - Fluid Flow in Closed ConduitsDocument2 pagesModule 3 (Part 4) - Fluid Flow in Closed Conduitstoriopeter350No ratings yet
- Flow NetsDocument5 pagesFlow NetsrreglosNo ratings yet
- Uniform Flow in Open Channels Economical SectionsDocument16 pagesUniform Flow in Open Channels Economical Sectionscarl ingariNo ratings yet
- Quiz 22-23 Sem1Document6 pagesQuiz 22-23 Sem1Dheemant RastogiNo ratings yet
- 3 2 Liquid Pressure 2012Document12 pages3 2 Liquid Pressure 2012ZaoiNo ratings yet
- HLP of The RebellionDocument3 pagesHLP of The RebellionCrewdex ProNo ratings yet
- Cls Aipmt 19 20 Xi Phy Study Package 4 Level 2 Chapter 10Document34 pagesCls Aipmt 19 20 Xi Phy Study Package 4 Level 2 Chapter 10sona babuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Hydro Electric CalculationsDocument22 pagesLecture 7 Hydro Electric CalculationsFikirini MmaleNo ratings yet
- HW 3Document2 pagesHW 3Michael WendlNo ratings yet
- Open Channel Hydraulics2Document30 pagesOpen Channel Hydraulics2Chileshe Mulenga PhiriNo ratings yet
- Supplement Questions of FLUID MECHANICS: Paragraph For Question Nos. 1 To 3Document7 pagesSupplement Questions of FLUID MECHANICS: Paragraph For Question Nos. 1 To 3Tanuj Gupta0% (2)
- Matriz - Asistente Administrativo RegionalDocument27 pagesMatriz - Asistente Administrativo RegionalCliver Amanqui UminaNo ratings yet
- Velocity of Flow: Er. Sandip BudhathokiDocument64 pagesVelocity of Flow: Er. Sandip BudhathokiManmohan Singh KhadkaNo ratings yet
- DPP 2 18TH April 2020Document10 pagesDPP 2 18TH April 2020gauravNo ratings yet
- Assignment 10C-Flooding Hazard Evaluation - GuadalquivirDocument3 pagesAssignment 10C-Flooding Hazard Evaluation - Guadalquivirfranklin gdNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions DR YuanDocument5 pagesPractice Questions DR YuanSteven KuaNo ratings yet
- EECQ 3131 HYDRAULICS 1A OPEN CHANNELS Lecture 1 Classification of Channel FlowsDocument8 pagesEECQ 3131 HYDRAULICS 1A OPEN CHANNELS Lecture 1 Classification of Channel FlowsMomanyi AnthonyNo ratings yet
- N Into The Water Is (Zero Atmospheric Press.) : y y H y - yDocument2 pagesN Into The Water Is (Zero Atmospheric Press.) : y y H y - y木辛耳总No ratings yet
- (Antim Yudh) - SHM, Waves, Fluid Mechanics - 2nd MarDocument33 pages(Antim Yudh) - SHM, Waves, Fluid Mechanics - 2nd MarNamo KaulNo ratings yet
- Salt Water IntrusionDocument12 pagesSalt Water IntrusionAn Ho TaylorNo ratings yet
- Lodos ActivadosDocument32 pagesLodos Activadosjvan migvelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document29 pagesChapter 1Fong Pei TyngNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mech Exercise 4 MotionDocument3 pagesFluid Mech Exercise 4 MotionyashNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Design For Sub-Surface FlowDocument3 pagesHydraulic Design For Sub-Surface FlowSuktara-Drubatara TaritNo ratings yet
- Model Exit Exam For Hydraulic and Water Resources Engineering Students PDFDocument46 pagesModel Exit Exam For Hydraulic and Water Resources Engineering Students PDFAbdulbasit Aba Biya100% (4)
- Bunker Design With Horizontal StiffenersDocument38 pagesBunker Design With Horizontal StiffenersChetan SukteNo ratings yet
- Math IADocument9 pagesMath IASamruddhiSatav100% (2)
- Ce 322-15 Module 7 - Permeability of SoilsDocument10 pagesCe 322-15 Module 7 - Permeability of SoilsBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- F05 C02 PressureDocument35 pagesF05 C02 Pressure0.sherwieeve.0No ratings yet
- Exer. 1Document7 pagesExer. 1SureshNo ratings yet
- Break Water: Lokasi & Lebar Mulut PelabuhanDocument40 pagesBreak Water: Lokasi & Lebar Mulut PelabuhanHendra D'jackNo ratings yet
- FLUMACHDocument9 pagesFLUMACHKim BagotNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating PumpDocument5 pagesReciprocating Pumpahsanul haqueNo ratings yet
- Exercise Pressure in LiquidDocument3 pagesExercise Pressure in LiquidArezly HarunNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Exercises FINAL 1676700516410Document51 pagesFluid Mechanics Exercises FINAL 1676700516410Shahroz NomaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 Uniform Flow Open ChannelDocument43 pagesLesson 12 Uniform Flow Open ChannelXzk MallaboNo ratings yet
- The Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisFrom EverandThe Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisNo ratings yet
- Pipe 20Document2 pagesPipe 20AmrutaNo ratings yet
- Pipe 11Document7 pagesPipe 11AmrutaNo ratings yet
- Lec31 InClassDocument1 pageLec31 InClassAmrutaNo ratings yet
- Pipe 09Document3 pagesPipe 09AmrutaNo ratings yet
- Pipe 08Document3 pagesPipe 08AmrutaNo ratings yet
- Pipe 05Document3 pagesPipe 05AmrutaNo ratings yet
- Project LightweightDocument2 pagesProject LightweightAmrutaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 2Document14 pagesResearch Paper 2AmrutaNo ratings yet
- Pipe 04Document3 pagesPipe 04AmrutaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentAmrutaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 3Document9 pagesResearch Paper 3AmrutaNo ratings yet
- CompaniesDocument1 pageCompaniesAmrutaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 1Document11 pagesResearch Paper 1AmrutaNo ratings yet
Pipe 03
Pipe 03
Uploaded by
AmrutaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pipe 03
Pipe 03
Uploaded by
AmrutaCopyright:
Available Formats
pipe_03
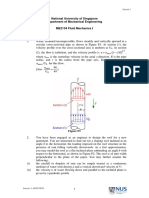
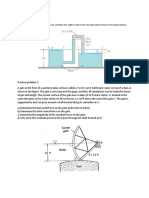
It rains during the construction of a building and water fills a recently excavated pit to a depth, h=0.5m.
In order to continue construction, the water must first be pumped out of the pit. A hose with a length of
L=50m, a diameter of D=2.5*10-2m, and a surface roughness of e=5.0*10-5m is attached to a pump.
Note that the kinematic viscosity of the water is n=1.005*10-6 m2/s and the density is r=1000 kg/m3.
a. If the pump is placed at the pit’s surface (figure a), what is the maximum depth of the pit, H, for
which water can be pumped out at a velocity of V=1 m/s without causing cavitation in the pipe? The
vapor pressure of water for the current temperature is pv=2.337 kPa (absolute pressure) and
atmospheric pressure is patm=101 kPa (absolute pressure).
b. If the pump is placed at the bottom of the pit (figure b), what is the maximum depth of the pit, H, for
which water can be pumped out at a velocity of V=1 m/s? Assume that the pump supplies a power of
P=200 W to the fluid.
pump water velocity, V
water velocity, V
hose of length, L, hose of length, L,
diameter, D, and diameter, D, and
surface roughness, e surface roughness, e
H=? H=?
pump
h h
Figure b
Figure a
Page 1 of 3
You might also like
- Problem Set 8Document7 pagesProblem Set 8Sayyed Ali MirjafariNo ratings yet
- KNS2163 Week1Document32 pagesKNS2163 Week1Nurul QurratuNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 06 Dec 2023-2Document4 pagesAdobe Scan 06 Dec 2023-2GenNo ratings yet
- Recrete Water&sewerDocument4 pagesRecrete Water&sewerhanisNo ratings yet
- Liquids - Level 3Document6 pagesLiquids - Level 3demolition squadNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Third Exam 2011Document5 pagesFluid Mechanics: Third Exam 2011nageshNo ratings yet
- Sankalp - Phase Iii - FL - 7Document6 pagesSankalp - Phase Iii - FL - 7Anusha SinghalNo ratings yet
- The Physics of Fluids-2 PDFDocument20 pagesThe Physics of Fluids-2 PDFMellissa MungureNo ratings yet
- LPP-Fluid Mechanics: FiitjeeDocument5 pagesLPP-Fluid Mechanics: FiitjeeYash TandonNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 - HydrodynamicsDocument10 pagesAssignment 4 - HydrodynamicsluluNo ratings yet
- Chanana Institute of Physics: 326, Tilak Nagar, Amritsar. 9888190610 ViscosityDocument4 pagesChanana Institute of Physics: 326, Tilak Nagar, Amritsar. 9888190610 ViscosityAditya SallyNo ratings yet
- National University of Singapore Department of Mechanical Engineering ME2134 Fluid Mechanics I Tutorial 3Document5 pagesNational University of Singapore Department of Mechanical Engineering ME2134 Fluid Mechanics I Tutorial 3Cl SkyeNo ratings yet
- RESERVORIO CIRCULAR 20m3.es - enDocument22 pagesRESERVORIO CIRCULAR 20m3.es - enpravin mundeNo ratings yet
- GWH-PPT ch3 SumDocument41 pagesGWH-PPT ch3 SumMistireselassieNo ratings yet
- ME 326: Experiment No. 1Document32 pagesME 326: Experiment No. 1parvejNo ratings yet
- FluidMechanics TD Chaps 01-05Document14 pagesFluidMechanics TD Chaps 01-05Mamoudou Bah DialloNo ratings yet
- Me19b hw1Document2 pagesMe19b hw1Hugh HeNo ratings yet
- Pressure in FluidsDocument18 pagesPressure in FluidsSayantan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Exercise Using The Sand Tank Model: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesGroundwater Exercise Using The Sand Tank Model: ObjectivesIrsan BahutalaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Reci PumpDocument12 pagesFluid Reci PumpMaxiNo ratings yet
- RM1 Liquids in Relative Equilibrium Translation 1Document26 pagesRM1 Liquids in Relative Equilibrium Translation 1EmmanNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Well Drainage AreaDocument4 pagesHorizontal Well Drainage AreaJuhaina HeibaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (Part 4) - Fluid Flow in Closed ConduitsDocument2 pagesModule 3 (Part 4) - Fluid Flow in Closed Conduitstoriopeter350No ratings yet
- Flow NetsDocument5 pagesFlow NetsrreglosNo ratings yet
- Uniform Flow in Open Channels Economical SectionsDocument16 pagesUniform Flow in Open Channels Economical Sectionscarl ingariNo ratings yet
- Quiz 22-23 Sem1Document6 pagesQuiz 22-23 Sem1Dheemant RastogiNo ratings yet
- 3 2 Liquid Pressure 2012Document12 pages3 2 Liquid Pressure 2012ZaoiNo ratings yet
- HLP of The RebellionDocument3 pagesHLP of The RebellionCrewdex ProNo ratings yet
- Cls Aipmt 19 20 Xi Phy Study Package 4 Level 2 Chapter 10Document34 pagesCls Aipmt 19 20 Xi Phy Study Package 4 Level 2 Chapter 10sona babuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Hydro Electric CalculationsDocument22 pagesLecture 7 Hydro Electric CalculationsFikirini MmaleNo ratings yet
- HW 3Document2 pagesHW 3Michael WendlNo ratings yet
- Open Channel Hydraulics2Document30 pagesOpen Channel Hydraulics2Chileshe Mulenga PhiriNo ratings yet
- Supplement Questions of FLUID MECHANICS: Paragraph For Question Nos. 1 To 3Document7 pagesSupplement Questions of FLUID MECHANICS: Paragraph For Question Nos. 1 To 3Tanuj Gupta0% (2)
- Matriz - Asistente Administrativo RegionalDocument27 pagesMatriz - Asistente Administrativo RegionalCliver Amanqui UminaNo ratings yet
- Velocity of Flow: Er. Sandip BudhathokiDocument64 pagesVelocity of Flow: Er. Sandip BudhathokiManmohan Singh KhadkaNo ratings yet
- DPP 2 18TH April 2020Document10 pagesDPP 2 18TH April 2020gauravNo ratings yet
- Assignment 10C-Flooding Hazard Evaluation - GuadalquivirDocument3 pagesAssignment 10C-Flooding Hazard Evaluation - Guadalquivirfranklin gdNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions DR YuanDocument5 pagesPractice Questions DR YuanSteven KuaNo ratings yet
- EECQ 3131 HYDRAULICS 1A OPEN CHANNELS Lecture 1 Classification of Channel FlowsDocument8 pagesEECQ 3131 HYDRAULICS 1A OPEN CHANNELS Lecture 1 Classification of Channel FlowsMomanyi AnthonyNo ratings yet
- N Into The Water Is (Zero Atmospheric Press.) : y y H y - yDocument2 pagesN Into The Water Is (Zero Atmospheric Press.) : y y H y - y木辛耳总No ratings yet
- (Antim Yudh) - SHM, Waves, Fluid Mechanics - 2nd MarDocument33 pages(Antim Yudh) - SHM, Waves, Fluid Mechanics - 2nd MarNamo KaulNo ratings yet
- Salt Water IntrusionDocument12 pagesSalt Water IntrusionAn Ho TaylorNo ratings yet
- Lodos ActivadosDocument32 pagesLodos Activadosjvan migvelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document29 pagesChapter 1Fong Pei TyngNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mech Exercise 4 MotionDocument3 pagesFluid Mech Exercise 4 MotionyashNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Design For Sub-Surface FlowDocument3 pagesHydraulic Design For Sub-Surface FlowSuktara-Drubatara TaritNo ratings yet
- Model Exit Exam For Hydraulic and Water Resources Engineering Students PDFDocument46 pagesModel Exit Exam For Hydraulic and Water Resources Engineering Students PDFAbdulbasit Aba Biya100% (4)
- Bunker Design With Horizontal StiffenersDocument38 pagesBunker Design With Horizontal StiffenersChetan SukteNo ratings yet
- Math IADocument9 pagesMath IASamruddhiSatav100% (2)
- Ce 322-15 Module 7 - Permeability of SoilsDocument10 pagesCe 322-15 Module 7 - Permeability of SoilsBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- F05 C02 PressureDocument35 pagesF05 C02 Pressure0.sherwieeve.0No ratings yet
- Exer. 1Document7 pagesExer. 1SureshNo ratings yet
- Break Water: Lokasi & Lebar Mulut PelabuhanDocument40 pagesBreak Water: Lokasi & Lebar Mulut PelabuhanHendra D'jackNo ratings yet
- FLUMACHDocument9 pagesFLUMACHKim BagotNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating PumpDocument5 pagesReciprocating Pumpahsanul haqueNo ratings yet
- Exercise Pressure in LiquidDocument3 pagesExercise Pressure in LiquidArezly HarunNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Exercises FINAL 1676700516410Document51 pagesFluid Mechanics Exercises FINAL 1676700516410Shahroz NomaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 Uniform Flow Open ChannelDocument43 pagesLesson 12 Uniform Flow Open ChannelXzk MallaboNo ratings yet
- The Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisFrom EverandThe Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisNo ratings yet
- Pipe 20Document2 pagesPipe 20AmrutaNo ratings yet
- Pipe 11Document7 pagesPipe 11AmrutaNo ratings yet
- Lec31 InClassDocument1 pageLec31 InClassAmrutaNo ratings yet
- Pipe 09Document3 pagesPipe 09AmrutaNo ratings yet
- Pipe 08Document3 pagesPipe 08AmrutaNo ratings yet
- Pipe 05Document3 pagesPipe 05AmrutaNo ratings yet
- Project LightweightDocument2 pagesProject LightweightAmrutaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 2Document14 pagesResearch Paper 2AmrutaNo ratings yet
- Pipe 04Document3 pagesPipe 04AmrutaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentAmrutaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 3Document9 pagesResearch Paper 3AmrutaNo ratings yet
- CompaniesDocument1 pageCompaniesAmrutaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 1Document11 pagesResearch Paper 1AmrutaNo ratings yet