Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Septic Shock For Site
Septic Shock For Site
Uploaded by
محمد زين0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesSeptic shock is a serious condition with a high mortality rate, especially in infants and those with comorbidities. It occurs when infection leads to systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and dysfunction of the cardiovascular system and multiple organs. Pathophysiologically, septic shock involves a cascade of metabolic, hematological and clinical changes mediated by microbial toxins and the host's inflammatory response. Treatment involves rapid identification, source control through drainage or debridement, appropriate antimicrobial therapy, and supportive care including fluid resuscitation and vasopressors to maintain adequate blood pressure and reverse cardiovascular dysfunction.
Original Description:
Original Title
Septic Shock for Site
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSeptic shock is a serious condition with a high mortality rate, especially in infants and those with comorbidities. It occurs when infection leads to systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and dysfunction of the cardiovascular system and multiple organs. Pathophysiologically, septic shock involves a cascade of metabolic, hematological and clinical changes mediated by microbial toxins and the host's inflammatory response. Treatment involves rapid identification, source control through drainage or debridement, appropriate antimicrobial therapy, and supportive care including fluid resuscitation and vasopressors to maintain adequate blood pressure and reverse cardiovascular dysfunction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesSeptic Shock For Site
Septic Shock For Site
Uploaded by
محمد زينSeptic shock is a serious condition with a high mortality rate, especially in infants and those with comorbidities. It occurs when infection leads to systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and dysfunction of the cardiovascular system and multiple organs. Pathophysiologically, septic shock involves a cascade of metabolic, hematological and clinical changes mediated by microbial toxins and the host's inflammatory response. Treatment involves rapid identification, source control through drainage or debridement, appropriate antimicrobial therapy, and supportive care including fluid resuscitation and vasopressors to maintain adequate blood pressure and reverse cardiovascular dysfunction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
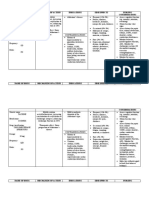
Septic shock MOD at subcellular level
Incidence 0.5: 1000 population. Result in CV dysfunction and MOF
Highest in infants. Depends on Organism
Orgs Staph all types Time to tx
Strept pneumo Host response to infection and tx
Pseudomonas Mediators IL1, 6, kinins, eicasanoids, platelet
NN HSV activating factor, NO
GBS Survival depends on speed &adequacy of resuscitation.
RF Injured children Hypovol - Incr microvasc perm
Neonates Arteriolar and venule dilatation, pooling blood
Chronic medical probs – CHD, UT abnormalities, Volume loss (poor input, v+d, 3rd spacing)
devices Abn Haemodynamic response
Fatality Highest for infants and comorbidities 80% kids present wLoc CI +/- abnormal vascular
Aetiology Combination of multiple types of shock – tone
Infection, 20% hyperdynamic state
relative and absolute hypovolaemia, Hypotension not required for diagnosis shock
maldistribution Progression – loss cardiac comp for ↓SVR
myocardial depression Cap leak, vd, toxin related cardiac
multiple metabolic, endocrine and depression
haematological problems. Impaired substrate us
Cascade of metabolic, haematological and clinical changes – decr tissue perfusion -> anaerobic metabolism ->
from invasive infection and microbial toxins. lactic acidosis. Deterioration in O2 consumption
SIRS is host dependant response. &extraction
Pathophysiological septic shock incompletely understood. Dysregulation glucose, fat, amino acids.
Direct effects microbiological agents Changes in glycolysis and gluconeogen early
Microbiological toxins
Pts inflam response to infection Assessment
Activation of endogenous mediators Hx, examination
Septic shock 1 JFICM 2010 Jan Kelly
Maintain adequate BP (no O2 debt) Restauration preload – incrementally,
Skin temperature gradient (>3ºC) attention to signs volume overload.
Peripheral perfusion index (variation in pulse Crystalloid vs colloid (SAFE, NEJM 2004-
pressure on pulse oximetry) ?alb better than NaCl in septic shock)
NIRS – MvSats and Cyt-aa3 saturation RBC if Hct <30% (Hb 8-10) (incr O2
TcO2 and CO3 - ↓TcO2 and ↑CO2 a/w ↓tissue carrying capacity)
perfusion Pressors Incr perfusion pressure and CO
Not validated Inodilators (dobu, milrinone incr flow)
Tissue capnography – sublingual/gastric –art CO2 gradient Inoconstrictors (adrenaline, NA, dopa ↑P)
Tx Vaspressin (incr survival adults, kids)
Goals Identification of shock state Infection source control
Rapid reversal of CV dysfunction and vital fns Culture Blood, urine, other pot infected sites
Antimicrobial tx Give adequate abs – narrow at 48-72h
Source control (debride, drainage) Ab choice Determined by Age, hx, comorbidity, clinical
Monitoring – ECG, pulse ox, BP/IABP, IDC syndrome, gm stain, local resistance patterns.
CVL (CVP), pulse pressure variation (preload Hypoglycaemia 0.5-1g/kg glucose =5-10ml/kg D10
dependant till PPV <10%) HCO3 Tx of shock induced met acidosis showed no
Lab ABG improvement in CO / decr inotropes.
Lactate (adequacy of global O2ation) APC Incr CNS bleeding in kids, no benefit.
MvO2Sats
Echo Glucocorticoids
Up to date 2010: Adults: Beneficial in pts w severe septic
Supportive measures shock (systolic BP <90 despite fluids and inotropes for 1h)
O2 and ventilator support in adults (grade2B recommended).
CV support No good evidence for steroids in mod septic shock.
Incr O2 delivery, decr O2 requirements Response to ACTH testing should not be used to select
Vol Impr CO by maximizing Starling curve patients as unreliable.
Administer for 5-7 days (grade 2C), taper optional.
Septic shock 2 JFICM 2010 Jan Kelly
Fludrocortisone not beneficial (COITTS – grade 2C) Amp + gent cefotaxime Cefotaxime
HPA axis may be disturbed in sepsis. CNS susp Cef +vanc
Absolute adrenal insufficiency (random cortisol<500nmol/L Pneumonia Fluclox & Fluclox &
and incr post ACTH stimulation test <240), relative adrenal gentamicin gentamicin &
insufficiency (incr post ACTH stimulation test <240) may roxithromycin
GU –No abn Amp & gent Amp and gentamicin
benefit from steroids (inconclusive evidence). Low dose Timentin gent Timentin and gentamicin
GUT
ACTH test probably more sensitive than high dose. Abn GUT
Skin/soft Clindamycin, penicillin and gentamicin
Kids Appears to benefit some. tissue
Limited date in children. Improved outcomes in Orbital Cefotaxime & fluclox
dengue shock. Incr mort in heterogeneous cellulitis
retrospective cohort. IC / febrile neutropenic Timentin and gentamicin
Dose 1-2mg/kg/dose
Expert consensus – catecholamine resistant shock /
suspected adrenal insufficiency (random cortisol
<500nmol/L) defines absolute adrenal insufficiency,
indicates need for continued glucocorticoid tx.
Calculated free and total cortisol may be more accurate.
Dex may be better if ACTH stimulation test planned
(hydrocortisone is pharmacological cortisol, binds cortisol
binding protein well – other steroids don’t ->?less
interference w ACTH stimulation test)
Susp source Neonate Infant 1-3m Ped <3m
<1m
Source unk, no Amp & gent Fluclox and gent (vanc if CVL
meningitis (vanc if CVL) or EVD) & cefotaxime
& cefotaxime
Source unk Cefotax and Amp and Fluclox and
Septic shock 3 JFICM 2010 Jan Kelly
You might also like
- Gastroenterology Medical Records SampleDocument1 pageGastroenterology Medical Records SampleMarisol Jane JomayaNo ratings yet
- M4 Revision Spreadsheet - Crit CareDocument7 pagesM4 Revision Spreadsheet - Crit CareandrewNo ratings yet
- Reaksi Transfusi PDTDI NWDocument32 pagesReaksi Transfusi PDTDI NWDevi AndrianiNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Monitoring in Critically Ill PatientsDocument46 pagesHemodynamic Monitoring in Critically Ill PatientsDipo Mas SuyudiNo ratings yet
- Joe Carcillo - Hemodynamic Managemnet in Peidtric SepsisDocument92 pagesJoe Carcillo - Hemodynamic Managemnet in Peidtric SepsisMega SeptianaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Shock (PICUCOURSE)Document40 pagesPediatric Shock (PICUCOURSE)surasuarezlopezNo ratings yet
- 02-03-21 - Impending Thyroid Storm PerioperativeDocument4 pages02-03-21 - Impending Thyroid Storm PerioperativeWilujeng AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- PSGNDocument23 pagesPSGNalpha mae beltranNo ratings yet
- Contora, Isah TblrenalDocument7 pagesContora, Isah TblrenalisahNo ratings yet
- EGDT - PICU-NICU-Bandung-2016-DadangHDocument63 pagesEGDT - PICU-NICU-Bandung-2016-DadangHvillnachintyaNo ratings yet
- Septic Shock: Dr. Dr. Hori Hariyanto, Span, Kic, KMNDocument89 pagesSeptic Shock: Dr. Dr. Hori Hariyanto, Span, Kic, KMNPander MadonNo ratings yet
- Treatment of SepsisDocument52 pagesTreatment of SepsisUmmulAklaNo ratings yet
- Bagian Ilmu Kesehatan Anak FK UNSRAT/ RSU. Prof. Dr. R.D. Kandou-ManadoDocument29 pagesBagian Ilmu Kesehatan Anak FK UNSRAT/ RSU. Prof. Dr. R.D. Kandou-ManadoAmarantoNo ratings yet
- Adverse Effects of Blood Transfusion and Alternatives 2021aDocument9 pagesAdverse Effects of Blood Transfusion and Alternatives 2021ahcp8s6tmn9No ratings yet
- Sirs and Sepsis Pasca TraumaDocument61 pagesSirs and Sepsis Pasca TraumahermanfirdausNo ratings yet
- Resuscitare Sepsis RezidentiDocument51 pagesResuscitare Sepsis RezidentiMihai PopescuNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of ShockDocument28 pagesDiagnosis and Management of ShockAgus MahendraNo ratings yet
- SepsisDocument26 pagesSepsisWulan MulyaniNo ratings yet
- Department of Surgery G.R. Medical College, Gwalior: Septic Shock and Its ManagementDocument31 pagesDepartment of Surgery G.R. Medical College, Gwalior: Septic Shock and Its ManagementNitin AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Biotti 2011Document3 pagesBiotti 2011nathalia_pastasNo ratings yet
- All Forms of Shock - Lactic Acid Via Tissue Hypoxia Tubulare Nec Via Coagulation in PT TALDocument10 pagesAll Forms of Shock - Lactic Acid Via Tissue Hypoxia Tubulare Nec Via Coagulation in PT TALlynk787No ratings yet
- Shock States in ChildrenDocument37 pagesShock States in ChildrenjuanitaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical - Multiorgan Failure ReviewerDocument15 pagesMedical Surgical - Multiorgan Failure ReviewerNatricia TrondilloNo ratings yet
- PQCNC Treatment of Maternal Sepsis - Luis D Pacheco, MDDocument32 pagesPQCNC Treatment of Maternal Sepsis - Luis D Pacheco, MDkcochranNo ratings yet
- Tuberculous Pericarditis Leading To Cardiac Tamponade Importance of Screening Prior To ImmunosuppressionDocument3 pagesTuberculous Pericarditis Leading To Cardiac Tamponade Importance of Screening Prior To ImmunosuppressionLink BuiNo ratings yet
- 4.5 LP 6 Septic ShockDocument40 pages4.5 LP 6 Septic ShockCamelia A. ParuschiNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Shock: Dr. Lilia Dewiyanti, Spa, MsimedDocument40 pagesPediatric Shock: Dr. Lilia Dewiyanti, Spa, MsimedLa Ode RinaldiNo ratings yet
- Proof Only: Is Severe Hypocalcemia Immediately Life Threatening?Document8 pagesProof Only: Is Severe Hypocalcemia Immediately Life Threatening?Ursula MalauNo ratings yet
- Shock: Clinical ManifestationsDocument3 pagesShock: Clinical ManifestationsJean ReyesNo ratings yet
- MCQs 1Document10 pagesMCQs 1Mostafa MahmoudNo ratings yet
- SYOKDocument76 pagesSYOKRiri EltadezaNo ratings yet
- Golden Period Septic ChildDocument32 pagesGolden Period Septic ChildcallNo ratings yet
- Fluid Dss PKB - RsDocument39 pagesFluid Dss PKB - RsancillaagraynNo ratings yet
- Final Hem and Onc Slides39 EndDocument50 pagesFinal Hem and Onc Slides39 EndiniidzniNo ratings yet
- Sirs, Sepsis, and Mods: Claudio Martin, MSC, MDDocument32 pagesSirs, Sepsis, and Mods: Claudio Martin, MSC, MDMohamad ZulfikarNo ratings yet
- SepsisDocument54 pagesSepsisStayOnSundayNo ratings yet
- SHOCKDocument24 pagesSHOCKAngela mitaNo ratings yet
- SepsisDocument54 pagesSepsisStayOnSundayNo ratings yet
- Toxic Shock SyndromeDocument5 pagesToxic Shock Syndromeمحمد زينNo ratings yet
- Irreversible ShockDocument50 pagesIrreversible ShockAnonymous YWmEwCNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Shock StatesDocument32 pagesPediatric Shock StatessavasNo ratings yet
- Correos Electrónicos 1. Optimizacion Cardiovascular, FluidosDocument29 pagesCorreos Electrónicos 1. Optimizacion Cardiovascular, FluidosKaren PMNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow Aplasia: A Rare Complication of Disseminated TuberculosisDocument3 pagesBone Marrow Aplasia: A Rare Complication of Disseminated TuberculosisayuNo ratings yet
- MaternalDocument29 pagesMaternalJim XieNo ratings yet
- Massa Kat 2019Document17 pagesMassa Kat 2019nayyarNo ratings yet
- 11 - Management Post Operative Low Cardiac Output SyndromeDocument46 pages11 - Management Post Operative Low Cardiac Output SyndromeNat SNo ratings yet
- Efek Samping Kolkisin, 2020Document3 pagesEfek Samping Kolkisin, 2020Shared LifeNo ratings yet
- Pediatric ShockDocument19 pagesPediatric ShockdarlingcarvajalduqueNo ratings yet
- DR - Nursamsu, SpPD-KGH-Penggunaan Cairan Koloid Pada Kondisi Syok PDFDocument38 pagesDR - Nursamsu, SpPD-KGH-Penggunaan Cairan Koloid Pada Kondisi Syok PDFNONANo ratings yet
- Sepsis & SirsDocument55 pagesSepsis & SirsMuhamad Agung SupriyantoNo ratings yet
- 7.goal Directed Fluid and Volume Therapy - Static and Volume - CVP, PAOP, GEDI (DR IYAN)Document24 pages7.goal Directed Fluid and Volume Therapy - Static and Volume - CVP, PAOP, GEDI (DR IYAN)MuhammadHazmiAnzhariNo ratings yet
- GHHH HHHH HHHH K SssDocument4 pagesGHHH HHHH HHHH K SssgabriellcvieiraNo ratings yet
- Week 4. ARFDocument50 pagesWeek 4. ARFAira EspleguiraNo ratings yet
- Sirspresent 130118235951 Phpapp01Document41 pagesSirspresent 130118235951 Phpapp01Princess BubblegumNo ratings yet
- Syock & ManagementDocument34 pagesSyock & ManagementIndra Anwari RukmanNo ratings yet
- Peds Heme-Onc FlashcardsDocument15 pagesPeds Heme-Onc FlashcardsRodrigo FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Sepsis Imec 2019 RevisiDocument56 pagesSepsis Imec 2019 RevisiBhisma D. SyaputraNo ratings yet
- Transplant Registrar BookletDocument9 pagesTransplant Registrar BookletSamiaNazNo ratings yet
- Pages From STS-2 - 1Document43 pagesPages From STS-2 - 1mostaw safNo ratings yet
- Anaphylactic ShockDocument2 pagesAnaphylactic Shockمحمد زينNo ratings yet
- Toxic Shock SyndromeDocument5 pagesToxic Shock Syndromeمحمد زينNo ratings yet
- DD ShockDocument34 pagesDD Shockمحمد زينNo ratings yet
- Septic ShockDocument2 pagesSeptic Shockمحمد زينNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia and Sedation Outside TheatresDocument15 pagesAnaesthesia and Sedation Outside Theatresمحمد زينNo ratings yet
- ECG Monitoring and Rhythm RecognitionDocument36 pagesECG Monitoring and Rhythm Recognitionمحمد زينNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Assessment of Airway: by Dr. T.Varsha Moderator: Dr.C.N.Chandrasekhar SirDocument21 pagesPreoperative Assessment of Airway: by Dr. T.Varsha Moderator: Dr.C.N.Chandrasekhar Sirمحمد زينNo ratings yet
- #Dr. Lora Ecg PDFDocument53 pages#Dr. Lora Ecg PDFمحمد زينNo ratings yet
- 2 Summary of ECGDocument14 pages2 Summary of ECGمحمد زين100% (1)
- Supervisor: Dr. H. Doddy A. K., Spog (K) Medical Students:: Rian, FebriDocument12 pagesSupervisor: Dr. H. Doddy A. K., Spog (K) Medical Students:: Rian, FebriRian Segal HidajatNo ratings yet
- 12.0 Emergency Protocol Allergic ReactionsDocument9 pages12.0 Emergency Protocol Allergic ReactionsConstantin BudinNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Basic Human Anatomy, Physiology & Fitness ConceptsDocument30 pagesWeek 3 - Basic Human Anatomy, Physiology & Fitness ConceptsJohn Cailen Barceñas IINo ratings yet
- Mesalazine: Mesalazine (INN, BAN), Also Known As Mesalamine (USAN) or 5-Aminosalicylic AcidDocument4 pagesMesalazine: Mesalazine (INN, BAN), Also Known As Mesalamine (USAN) or 5-Aminosalicylic AcidAnkan PalNo ratings yet
- Benchmark LettersDocument11 pagesBenchmark LettersRavy KiranNo ratings yet
- Asa Difficult Airway AlgorithmDocument20 pagesAsa Difficult Airway AlgorithmspidymahiNo ratings yet
- AutoimmunityDocument40 pagesAutoimmunityKarl RobleNo ratings yet
- IV Therapy ChecklistDocument3 pagesIV Therapy ChecklistJestoni SalvadorNo ratings yet
- 1428 Progyluton 1329836451Document5 pages1428 Progyluton 1329836451sole_dentistNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing TransesDocument17 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing Transesmainek42No ratings yet
- Muse 123, Fall 2014 Breathing For Singing (James Mckinney, Kimberly James, Costanza Cuccaro)Document2 pagesMuse 123, Fall 2014 Breathing For Singing (James Mckinney, Kimberly James, Costanza Cuccaro)MerrillLeeRasmussenNo ratings yet
- 2009TweedProfile PDFDocument48 pages2009TweedProfile PDFAndré Louiz FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Gut and Psychology SyndromeDocument12 pagesGut and Psychology SyndromeJhanan NaimeNo ratings yet
- Clinics in SurgeryDocument5 pagesClinics in SurgeryShahrukh ali khanNo ratings yet
- Region Iv-A Calabarzon Department of Education Bitin Integrated National High SchoolDocument4 pagesRegion Iv-A Calabarzon Department of Education Bitin Integrated National High SchoolAlbert Ian Casuga100% (1)
- ECG PresentationDocument52 pagesECG PresentationShah NahidNo ratings yet
- Neurology Signs and Symptoms Managements/Disposition 3 Drug Study FDAR Charting With Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesNeurology Signs and Symptoms Managements/Disposition 3 Drug Study FDAR Charting With Nursing DiagnosisEmergency Room DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) : Pembimbing: Dr. Sondang M Lumban Batu, Sp.ADocument36 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) : Pembimbing: Dr. Sondang M Lumban Batu, Sp.AWinda Oktavia PakpahanNo ratings yet
- Drugs To Watch With WARFARINDocument3 pagesDrugs To Watch With WARFARINRajendra RaiNo ratings yet
- Case Study:: CholelithiasisDocument19 pagesCase Study:: CholelithiasisGillarhymesNo ratings yet
- Gida Profiling Tool PDFDocument4 pagesGida Profiling Tool PDFRaym AvilaNo ratings yet
- Mobile PTH Testing: Tosoh SolutionsDocument2 pagesMobile PTH Testing: Tosoh SolutionsAhmed LarbiNo ratings yet
- Contraception After AbortionDocument11 pagesContraception After AbortionLaurențiu LucaNo ratings yet
- DRG Overview of All Patient Refined Diagostic Related GroupsDocument42 pagesDRG Overview of All Patient Refined Diagostic Related Groupsjaypee pengNo ratings yet
- Gonorrhea SlidesDocument54 pagesGonorrhea SlidesYonathanHasudunganNo ratings yet
- STD Facts - Human Papillomavirus (HPV)Document3 pagesSTD Facts - Human Papillomavirus (HPV)MUNIRAH SUHAIBAH BINTI SULAIMAN STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Medical Parasitology, 6th EditionDocument45 pagesTextbook of Medical Parasitology, 6th EditionDaniel Austria50% (2)
- Crash Cart Supplies and DrugsDocument3 pagesCrash Cart Supplies and DrugsShrutiNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument9 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsJaysellePuguonTabije100% (1)