Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4 Plates Solutions
4 Plates Solutions
Uploaded by
armanjeffryCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- FAQ Basic Accounting ConceptsDocument183 pagesFAQ Basic Accounting ConceptsNowmaster100% (20)
- Entwistle, K. M.-Basic Principles of The Finite Element Method-Maney Publishing For IOM3, The Institute of Materials, Minerals and Mining (2001)Document187 pagesEntwistle, K. M.-Basic Principles of The Finite Element Method-Maney Publishing For IOM3, The Institute of Materials, Minerals and Mining (2001)Golu PatelNo ratings yet
- Kubota V3600 85HP Engine ManualDocument75 pagesKubota V3600 85HP Engine Manualcoulibalyoumar100% (2)
- Steel Design CombineDocument4 pagesSteel Design CombineLenielle AmatosaNo ratings yet
- S130 - Peças PDFDocument525 pagesS130 - Peças PDFtiago100% (1)
- FP Diesel International Navistar Engines - DigipubZDocument212 pagesFP Diesel International Navistar Engines - DigipubZdavidbeju100% (7)
- Diagrama Electrico D6NDocument20 pagesDiagrama Electrico D6NKeiber Bastos100% (3)
- 1 Vessels Some SolutionsDocument13 pages1 Vessels Some SolutionsarmanjeffryNo ratings yet
- PreLab 06Document3 pagesPreLab 06Anonymous L21MIUqANo ratings yet
- CIVL2110 Tutorial 8 SolutionsDocument5 pagesCIVL2110 Tutorial 8 SolutionsShinobu KannaNo ratings yet
- OLMPDocument28 pagesOLMPSiyu LiuNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Dynamic Analysis and Control On Single Machine Infinite Bus SystemDocument10 pagesLab Report: Dynamic Analysis and Control On Single Machine Infinite Bus SystemJack SheehyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document15 pagesAssignment 3peterNo ratings yet
- Module 9aDocument3 pagesModule 9aVincentNo ratings yet
- Problema 6-23 ShigleyDocument7 pagesProblema 6-23 ShigleylosdesquiciadosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Forced and Damped Oscillations PDFDocument3 pagesLecture 7 Forced and Damped Oscillations PDFSahaj ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Doubly Reinforced BeamDocument18 pagesAnalysis and Design of Doubly Reinforced BeamKherstine Muyano TantayNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Concrete KippapDocument3 pagesPrestressed Concrete KippapFernandez DanielNo ratings yet
- DesignDocument13 pagesDesignGrigoriy KotNo ratings yet
- Image Compression Using SVD PDFDocument7 pagesImage Compression Using SVD PDFMariam HossamNo ratings yet
- Ce 201 - Fundamentals of Surveying: Cos SinDocument2 pagesCe 201 - Fundamentals of Surveying: Cos SinDaille Wroble GrayNo ratings yet
- Week 1 PDFDocument41 pagesWeek 1 PDFTanapat LapanunNo ratings yet
- CompressionDocument11 pagesCompressionkaisser091202No ratings yet
- Reporte ExtendidoDocument13 pagesReporte Extendidoluis rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Working Stress Design: Dr. Majed AshoorDocument12 pagesWorking Stress Design: Dr. Majed AshoorMuslim MahdiNo ratings yet
- PHYS 118 Formula SheetDocument2 pagesPHYS 118 Formula Sheetemmacont2060No ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document15 pagesChapter 13Avishka PriyanjanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document20 pagesChapter 10Avishka PriyanjanaNo ratings yet
- AC Power Analysis: School of Electrical InformationDocument20 pagesAC Power Analysis: School of Electrical InformationkamalNo ratings yet
- 4a - Simple Strain StudentsDocument16 pages4a - Simple Strain StudentsGisang IsdaNo ratings yet
- Contest Math Problem Solving #1Document4 pagesContest Math Problem Solving #1Darie MitulescuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 SolutionDocument3 pagesAssignment 5 Solutionsolai muruganNo ratings yet
- Final Exam تخلفات - Model Answer - Part 1Document6 pagesFinal Exam تخلفات - Model Answer - Part 1Maher Gomaa IsmaeelNo ratings yet
- Group12 Lab08Document20 pagesGroup12 Lab08Chayathorn DuangtongsukNo ratings yet
- Experimentales Circuito Rc Caso Resistivo Media Onda Onda Completa Media Onda Onda Completa τ (ms) Vmax (V) Vpp (V) Vcd (V) Vca (V) Vrms (V)Document7 pagesExperimentales Circuito Rc Caso Resistivo Media Onda Onda Completa Media Onda Onda Completa τ (ms) Vmax (V) Vpp (V) Vcd (V) Vca (V) Vrms (V)Raul Jose Guerrero QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 - 2022 - With Final AnsDocument8 pagesQuiz 1 - 2022 - With Final AnsRaraNo ratings yet
- F12 - 2023 - Statistical ModuleDocument30 pagesF12 - 2023 - Statistical ModuleAbdirahman NurNo ratings yet
- Word Tugas 3 Beplas ArgaDocument8 pagesWord Tugas 3 Beplas ArgaArgaYudhistiraNo ratings yet
- Connection Between Sharpe and Max-DrawdownDocument4 pagesConnection Between Sharpe and Max-DrawdownGaryNo ratings yet
- Longitudinal Data Analysis Instructor: Natasha SarkisianDocument31 pagesLongitudinal Data Analysis Instructor: Natasha SarkisianHe HNo ratings yet
- Shear Stress - A ReviewDocument16 pagesShear Stress - A ReviewAmogh SharmaNo ratings yet
- ENCV4GS - Test 1 - SolutionDocument6 pagesENCV4GS - Test 1 - Solution217005052No ratings yet
- Assignment SolutionDocument4 pagesAssignment SolutionosamaNo ratings yet
- Formulario 2da PDFDocument1 pageFormulario 2da PDFRichard LarinoNo ratings yet
- Formulario 2da PDFDocument1 pageFormulario 2da PDFMery Cristina Cahuana CáceresNo ratings yet
- 𝑓𝑐𝑟 = 2√𝑓′𝑐 Cuantía Mecánica Ac. 𝜌 = 𝜔. 𝑓′𝑐 𝑓𝑦 𝜌% → 𝜌 = 𝑝ℎ𝑜/100 𝐾𝑢 = 𝑀𝑢 𝑏. 𝑑 Resist. Nom. y Últ. f (ω) 𝑀𝑛 = 𝑓 𝑐. 𝑏. 𝑑 - 𝜔 (1 − 0.59𝜔) 𝜑. 𝑀𝑛 = 𝜑. 𝑓 𝑐. 𝑏. 𝑑 - 𝜔 (1 − 0.59𝜔)Document1 page𝑓𝑐𝑟 = 2√𝑓′𝑐 Cuantía Mecánica Ac. 𝜌 = 𝜔. 𝑓′𝑐 𝑓𝑦 𝜌% → 𝜌 = 𝑝ℎ𝑜/100 𝐾𝑢 = 𝑀𝑢 𝑏. 𝑑 Resist. Nom. y Últ. f (ω) 𝑀𝑛 = 𝑓 𝑐. 𝑏. 𝑑 - 𝜔 (1 − 0.59𝜔) 𝜑. 𝑀𝑛 = 𝜑. 𝑓 𝑐. 𝑏. 𝑑 - 𝜔 (1 − 0.59𝜔)Acero EliasNo ratings yet
- 5a - Generalized Hooke's Law Solved Problem 6.2020Document18 pages5a - Generalized Hooke's Law Solved Problem 6.2020Gisang IsdaNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Midterm Exam AnskeyDocument4 pagesReinforced Concrete Midterm Exam AnskeyAngelito AngelesNo ratings yet
- Transformers Numericals Vol. 2 Qtns and SolutionsDocument12 pagesTransformers Numericals Vol. 2 Qtns and SolutionsBaluku DavidNo ratings yet
- Xmas Tree in MATLABDocument8 pagesXmas Tree in MATLABMirzaNo ratings yet
- Kiran P B180894ee Pe Exp4Document7 pagesKiran P B180894ee Pe Exp4khyati patelNo ratings yet
- Homework ÇözümüDocument2 pagesHomework Çözümüenes arikanNo ratings yet
- Heat Conduction Equation: Heat Transfer 2021: Equations For Part ADocument9 pagesHeat Conduction Equation: Heat Transfer 2021: Equations For Part AMiguelKevinNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Transferencia de CalorDocument7 pagesEjercicios Transferencia de CalorAly HerreraNo ratings yet
- MSV 780 Exam 2020 MemoDocument24 pagesMSV 780 Exam 2020 MemoBesuidenhout Engineering Solutions and ConsultingNo ratings yet
- Design of Slab For Bridge 2: Dead LoadDocument2 pagesDesign of Slab For Bridge 2: Dead Loadjan janNo ratings yet
- Joint Design CalculationDocument21 pagesJoint Design Calculationjosephinelamsy0304No ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet PDFDocument4 pagesCheat Sheet PDFesenalieva03No ratings yet
- MD2 Ass4 ENG. Ahmad Assaf BDocument21 pagesMD2 Ass4 ENG. Ahmad Assaf BAmna AlenziNo ratings yet
- Formulário de Áreas e Volumes de SólidosDocument1 pageFormulário de Áreas e Volumes de SólidosmariaNo ratings yet
- For Combined Loading, Se' 0.5 SutDocument10 pagesFor Combined Loading, Se' 0.5 Sut154 ahmed ehabNo ratings yet
- Linear AlgebraDocument22 pagesLinear AlgebraMalcolmNo ratings yet
- Tut 8 DriveDocument10 pagesTut 8 Drivemennaabdelrazik848No ratings yet
- Trimmed Sample Means For Uniform Mean Estimation and RegressionDocument36 pagesTrimmed Sample Means For Uniform Mean Estimation and RegressionrimfoNo ratings yet
- 5 Creep and SolutionDocument1 page5 Creep and SolutionarmanjeffryNo ratings yet
- 1 Vessels Some SolutionsDocument13 pages1 Vessels Some SolutionsarmanjeffryNo ratings yet
- Esercizi Tipo Esame 13-01-2022Document15 pagesEsercizi Tipo Esame 13-01-2022armanjeffryNo ratings yet
- Esercizi Tipo Esame 13 - 01 - 2022Document11 pagesEsercizi Tipo Esame 13 - 01 - 2022armanjeffryNo ratings yet
- 1 Lindapter Maggio 2023Document84 pages1 Lindapter Maggio 2023CALGERINo ratings yet
- Abdul Rehman: Islamabad, PakistanDocument2 pagesAbdul Rehman: Islamabad, PakistanEngr Abdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- HP Cq41-Nal70 (NCL70) - Dis - La-4107p - 1109Document55 pagesHP Cq41-Nal70 (NCL70) - Dis - La-4107p - 1109Joshua SawyerNo ratings yet
- 3 Pin HD44780 LCD For Arduino - Works of Rowan SimmsDocument2 pages3 Pin HD44780 LCD For Arduino - Works of Rowan SimmsDenaiya Watton LeehNo ratings yet
- SICAM GridPass ProfileDocument2 pagesSICAM GridPass ProfileSerge RinaudoNo ratings yet
- Semester - 4 - HT - Term Paper Topics - Even - 2020Document3 pagesSemester - 4 - HT - Term Paper Topics - Even - 2020PradeepNo ratings yet
- MS PowerPoint Keyboard ShortcutsDocument22 pagesMS PowerPoint Keyboard Shortcutsapi-3754269100% (1)
- SEEPW Engineering BookDocument412 pagesSEEPW Engineering BookTudor MilchisNo ratings yet
- Canon Printer IX5000 & IX4000 - Service ManualDocument8 pagesCanon Printer IX5000 & IX4000 - Service ManualVaxsis SisvaxNo ratings yet
- What Is Deck Water Seal On Tanker and Its Types in DetailDocument5 pagesWhat Is Deck Water Seal On Tanker and Its Types in DetailRose AriantiNo ratings yet
- UB Beam DimensionDocument2 pagesUB Beam Dimensiontuan100% (1)
- Tib Tea User GuideDocument42 pagesTib Tea User GuidefvalmeidaNo ratings yet
- 8200-0859-01-A0 Intlx InstallConfig EN PDFDocument94 pages8200-0859-01-A0 Intlx InstallConfig EN PDFFrancisco Rodriguez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Eliminating Tablet Spots and SpecksDocument2 pagesEliminating Tablet Spots and SpecksMina Maher MikhailNo ratings yet
- Adaptive ControlDocument382 pagesAdaptive ControlAnonymous QakmLc3kTINo ratings yet
- Flow Control Valves: Catalog HY15-3502/USDocument51 pagesFlow Control Valves: Catalog HY15-3502/USPartsGopher.comNo ratings yet
- FiberHome Optical Network Overview Kntelecom IrDocument49 pagesFiberHome Optical Network Overview Kntelecom IrashuschandranNo ratings yet
- Design of Fluid Power Systems: - Stuart J. WilliamsDocument37 pagesDesign of Fluid Power Systems: - Stuart J. WilliamsAnonymous Ms8nYcbxY2No ratings yet
- Property Spectrum of Engineering MaterialsDocument4 pagesProperty Spectrum of Engineering MaterialsAriel Mark Pilotin50% (2)
- Danfoss Vane Tip LUG SylaxDocument18 pagesDanfoss Vane Tip LUG SylaxmaggamNo ratings yet
- A20 Datasheet v1.5 20150510Document36 pagesA20 Datasheet v1.5 20150510denis2xNo ratings yet
- 10 Accuracy of Prediction Methods For Sound Transmission LossDocument8 pages10 Accuracy of Prediction Methods For Sound Transmission LossJuan Ambrosio MartinezNo ratings yet
- MIL-S-38249 Superseded by AMS 3374Document13 pagesMIL-S-38249 Superseded by AMS 3374HenryNo ratings yet
- LEGO 8295 Telescopic Handler Set Parts InventoryDocument12 pagesLEGO 8295 Telescopic Handler Set Parts InventoryrlobetNo ratings yet
4 Plates Solutions
4 Plates Solutions
Uploaded by
armanjeffryOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4 Plates Solutions
4 Plates Solutions
Uploaded by
armanjeffryCopyright:
Available Formats
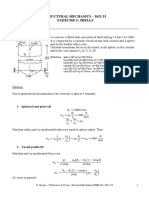
STRUCTURAL MECHANICS – 2022-23
EXERCISE 6: AXYSIMMETRIC PLATES
EXERCISE 1
An axisymmetric plate, which thickness is t= 50 mm and the radius is R=1000 mm, undergoes a uniform
pressure which varies between p1=0 MPa and p2= 0,5 MPa.
The material mechanical properties are: Rm= 420 MPa, Rp02= 280 MPa sD-1= 190 MPa.
Calculate in two cases: simply supported and blocked on the external edge:
• radial and circumferential maximum stresses on axis and on edge and plot the corresponding
bending moments per unit length diagram
• static and fatigue safety factor
• verify that the maximum displacement is lower than 5 mm
Solution
The stiffness of the plate is:
𝐸 ∙ 𝑡! 200000 ∙ (50)!
𝐷= = = 2,29 ∙ 10# 𝑁𝑚𝑚
12 ∙ (1 − 𝜈 " ) 12(1 − 0,3" )
Simply supported plate:
The moment per unit length is maximum in the centre of the plate and it is:
(3 + 𝜈)𝑝𝑅"
𝑚$%& = − = 1,03 ∙ 10' 𝑁
16
The corresponding stresses are:
6𝑚$%&
𝜎($%& = 𝜎)$%& = = 247,5 𝑀𝑃𝑎
𝑡"
t
0,5 247,5 s
𝜎*+ = |𝜎, − 𝜎! | = |𝜎( − 𝑝| = 248 𝑀𝑃𝑎
The static safety factor is:
𝑅./" 280
𝐶𝑆- = = 1,3
𝜎*+ 248
The maximum displacement is:
(5 + 𝜈)𝑝𝑅2
𝜔0%&,% = = 13,9 𝑚𝑚
64𝐷(1 + 𝜈)
R. Sesana – DIMEAS Axisymmetric plates 1
Fatigue stresses
Amplitude [MPa] Mean [MPa]
Radial stress 124 124
Axial stress 0,25 -0,25
Circumferential stress 124 124
1 " " "
𝜎%,34 = D E𝜎%,) − 𝜎%,5 F + E𝜎%,5 − 𝜎%,( F + E𝜎%,) − 𝜎%,( F = 124 𝑀𝑃𝑎
√2
𝜎$,34 = 𝜎),$ + 𝜎(,$ + 𝜎5,$ = 247 𝑀𝑃𝑎
sa
sD-1=135
sa,L
sa,eq=124
sm,eq=247 sm
UTS=420
To find the fatigue limit when a mean stress is present, the Goodman line in Haigh diagram is used
𝜎%,6 𝜎$,6
+ =1
G𝜎78, 𝑈𝑇𝑆
𝜎$,6 = 𝜎$,34
Then
𝜎$,6 247
𝜎%,6 = J1 − K 𝜎78, = L1 − M 190 = 78 𝑀𝑃𝑎
𝑈𝑇𝑆 420
Then the fatigue safety factor is:
𝜎%,6 78
𝑆𝐹9 = = <1
𝜎78,%,34 124
Fatigue requirements are not verified
Blocked plate
The moment per unit length is maximum in the edge of the plate and it is:
𝑝𝑅3"
𝑚( = 𝑚$%& = − = 62500 𝑁
8
𝜈𝑝𝑅3"
𝑚: = 𝜈𝑚$%& =− = 18750 𝑁
8
The corresponding stresses are:
6𝑚$%&
𝜎($%& == = 150𝑀𝑃𝑎
𝑡"
𝜈6𝑚$%&
𝜎)$%& = = 45𝑀𝑃𝑎
𝑡"
R. Sesana – DIMEAS Axisymmetric plates 2
t
0,5 45 150 s
𝜎*+ = |𝜎, − 𝜎! | = |𝜎( − 𝑝| = 150,5
The static safety factor is:
𝑅./" 280
𝐶𝑆- = = 1,4
𝜎*+ 150
The maximum displacement is:
𝑝𝑅2
𝜔0%&,% = = 3,41 𝑚𝑚
64𝐷
Amplitude [MPa] Mean [MPa]
Radial stress 75 75
Axial stress 0,25 0,25
Circumferential stress 23 23
1 " " "
𝜎%,34 = D E𝜎%,) − 𝜎%,5 F + E𝜎%,5 − 𝜎%,( F + E𝜎%,) − 𝜎%,( F = 66,5 𝑀𝑃𝑎
√2
𝜎$,34 = 𝜎),$ + 𝜎(,$ + 𝜎5,$ = 99 𝑀𝑃𝑎
sa
sD-1=135
sa,L
sa,eq=124
sm,eq=247 sm
UTS=420
To find the fatigue limit when a mean stress is present, the Goodman line in Haigh diagram is used
𝜎%,6 𝜎$,6
+ =1
G𝜎78, 𝑈𝑇𝑆
𝜎$,6 = 𝜎$,34
Then
𝜎$,6 99
𝜎%,6 = J1 − K 𝜎78, = L1 − M 190 = 145 𝑀𝑃𝑎
𝑈𝑇𝑆 420
Then the fatigue safety factor is:
R. Sesana – DIMEAS Axisymmetric plates 3
𝜎%,6 145
𝑆𝐹9 = = = 1,5
𝜎78,%,34 99
EXERCISE 2
A circular plate has radius R=2000 mm. It is made of three plates of the same material
(steel, Rm=210MPa, ReH=180 MPa).
The thicknesses are: t1=12.5 mm, t2=25 mm and t3=37,5 mm.
Calculate the maximum stress in the three layers assuming that they are solidal and that the plate
undergoes a uniform pressure which resultant is F=200 kN.
Compare the maximum stress obtained with the maximum pressure, with the stress of the monolithic
plate.
t1
t2
t3
Solution
The distributed pressure is:
𝐹 𝐹
𝑝= = = 0,016 𝑀𝑃𝑎
𝐴 𝜋 𝑅"R
4
The plate stiffness general formulation is
𝐸 ∙ 𝑡!
𝐷= = 18315 ∙ 𝑡 !
12 ∙ (1 − 𝜈 " )
The stiffness of each plate is:
𝐸 ∙ 𝑡,!
𝐷, = 357715 𝑁𝑚𝑚
12 ∙ (1 − 𝜈 " )
𝐸 ∙ 𝑡"!
𝐷" = = 286171870 𝑁𝑚𝑚
12 ∙ (1 − 𝜈 " )
𝐸 ∙ 𝑡!!
𝐷! = = 965830070𝑁𝑚𝑚
12 ∙ (1 − 𝜈 " )
The total stiffness is the sum of the single stiffnesses:
𝐷;<; = 𝐷, + 𝐷" + 𝐷! = 1287773400 𝑁𝑚𝑚
The monolithic plate stiffness is
𝐸 ∙ 𝑡!
𝐷= = 18315 ∙ (𝑡, + 𝑡" + 𝑡! )! = 7593750000 𝑁𝑚𝑚
12 ∙ (1 − 𝜈 " )
R. Sesana – DIMEAS Axisymmetric plates 4
In a simply supported plate of homogeneous material, undergoing a uniform pressure, the maximum
moment per unit length (thickness) is in the center of the plate
(3 + 𝜈)𝑝𝑅" 𝑁𝑚𝑚
𝑚$%& = = 13130,3
16 𝑚𝑚
This total moment per unit length is then distributed to each plate according to its stiffness:
𝐷,
𝑚, = 𝑚$%& = 364,7 𝑁𝑚𝑚
𝐷;<;
𝐷"
𝑚" = 𝑚$%& = 2917,8 𝑁𝑚𝑚
𝐷;<;
𝐷!
𝑚! = 𝑚$%& = 9847,7 𝑁𝑚𝑚
𝐷;<;
The corresponding maximum stresses are:
6𝑚,
𝜎, = = 14 𝑀𝑃𝑎
𝑡,"
6𝑚"
𝜎" = " = 28 𝑀𝑃𝑎
𝑡,
6𝑚!
𝜎! = " = 42 𝑀𝑃𝑎
𝑡,
If the plate is monolitic then the corresponding maximum stress is:
6𝑚$%&
𝜎$<= = " = 14 𝑀𝑃𝑎
𝑡;<;
EXERCISE 3
A circular holed plate is simply supported. It has external radius Re=125 mm, internal radius Ri= 100
mm and thickness s=18 mm. It is on the external edge and it undergoes a uniform pressure p=1 MPa on
the upper surface. Calculate the maximum stress and the maximum axial displacement.
The plate is made of steel, Rm=210MPa, ReH=180 MPa.
Ri
Re
Solution
The stiffness D of the plate is:
R. Sesana – DIMEAS Axisymmetric plates 5
𝐸𝑠 ! 200000 ∙ 18!
𝐷= = = 106813 𝑁𝑚𝑚
12(1 − 𝜈 " ) 12(1 − 0,3" )
The general formulation for a plate undergoing uniform pressure, for the moments per unit length is:
are:
0 B 3+ ν 2 1+ ν $r'
2mr = A − + pr + F ln && ))
2 r 2 16 4π % re (
1
2 B 1+ 3ν 2 F * $r' -
m
2 c = A + 2
+ pr + ,(1+ ν)ln &
&r )) − (1− ν) /
3 r 16 4π ,
+ % e ( /.
Rotation and displacement are:
A B 1 pr 3 F + %r( .
α= r+ + + -(1+ ν)ln '' ** −10 r
D(1+ ν) D(1− ν) r 16D 4πD(1+ ν) -, & re ) 0/
𝐴 𝐵 𝑟 𝑝𝑟 2
𝑤 = 𝑟" + 𝑙𝑛 L M + 𝐶 +
2𝐷(1 + 𝜈) 𝐷(1 − 𝜈) 𝑟3 64𝐷
To obtain the A and B coefficients values boundary conditions are applied:
𝑚(3 = 0
G 𝑚(* = 0
𝑤(3 = 0
𝐵 3+𝜈 "
⎧ 𝑚(3 = 𝐴 − + 𝑝𝑟3 = 0
⎪ 𝑟3" 16
⎪ 𝐵 3+𝜈 "
𝑚(* = 𝐴 − " + 𝑝𝑟* = 0
⎨ 𝑟* 16
⎪
⎪𝑤 𝐴 "
𝐵 𝑟3 𝑝𝑟3"
= 𝑟 + 𝑙𝑛 L M + 𝐶 + =0
⎩ (3 2𝐷(1 + 𝜈) 3 𝐷(1 − 𝜈) 𝑟3 64𝐷
And then:
3−𝜈 𝑟3" 𝑟*"
𝑝(𝑟3" − 𝑟*" ) " "
𝐵=−
16 𝑟3 +𝑟*
𝐵 3+𝜈 " 3−𝜈 𝑝 " "
𝑟3" 𝑟*" 3+𝜈 "
𝐴= "− 𝑝𝑟3 = − "
(𝑟3 − 𝑟* ) " − 𝑝𝑟3
𝑟3 16 16 𝑟3 "
𝑟3 +𝑟* 16
𝐴 𝑝𝑟3"
𝐶=− 𝑟3" −
2𝐷(1 + 𝜈) 64𝐷
R. Sesana – DIMEAS Axisymmetric plates 6
You might also like
- FAQ Basic Accounting ConceptsDocument183 pagesFAQ Basic Accounting ConceptsNowmaster100% (20)
- Entwistle, K. M.-Basic Principles of The Finite Element Method-Maney Publishing For IOM3, The Institute of Materials, Minerals and Mining (2001)Document187 pagesEntwistle, K. M.-Basic Principles of The Finite Element Method-Maney Publishing For IOM3, The Institute of Materials, Minerals and Mining (2001)Golu PatelNo ratings yet
- Kubota V3600 85HP Engine ManualDocument75 pagesKubota V3600 85HP Engine Manualcoulibalyoumar100% (2)
- Steel Design CombineDocument4 pagesSteel Design CombineLenielle AmatosaNo ratings yet
- S130 - Peças PDFDocument525 pagesS130 - Peças PDFtiago100% (1)
- FP Diesel International Navistar Engines - DigipubZDocument212 pagesFP Diesel International Navistar Engines - DigipubZdavidbeju100% (7)
- Diagrama Electrico D6NDocument20 pagesDiagrama Electrico D6NKeiber Bastos100% (3)
- 1 Vessels Some SolutionsDocument13 pages1 Vessels Some SolutionsarmanjeffryNo ratings yet
- PreLab 06Document3 pagesPreLab 06Anonymous L21MIUqANo ratings yet
- CIVL2110 Tutorial 8 SolutionsDocument5 pagesCIVL2110 Tutorial 8 SolutionsShinobu KannaNo ratings yet
- OLMPDocument28 pagesOLMPSiyu LiuNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Dynamic Analysis and Control On Single Machine Infinite Bus SystemDocument10 pagesLab Report: Dynamic Analysis and Control On Single Machine Infinite Bus SystemJack SheehyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document15 pagesAssignment 3peterNo ratings yet
- Module 9aDocument3 pagesModule 9aVincentNo ratings yet
- Problema 6-23 ShigleyDocument7 pagesProblema 6-23 ShigleylosdesquiciadosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Forced and Damped Oscillations PDFDocument3 pagesLecture 7 Forced and Damped Oscillations PDFSahaj ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Doubly Reinforced BeamDocument18 pagesAnalysis and Design of Doubly Reinforced BeamKherstine Muyano TantayNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Concrete KippapDocument3 pagesPrestressed Concrete KippapFernandez DanielNo ratings yet
- DesignDocument13 pagesDesignGrigoriy KotNo ratings yet
- Image Compression Using SVD PDFDocument7 pagesImage Compression Using SVD PDFMariam HossamNo ratings yet
- Ce 201 - Fundamentals of Surveying: Cos SinDocument2 pagesCe 201 - Fundamentals of Surveying: Cos SinDaille Wroble GrayNo ratings yet
- Week 1 PDFDocument41 pagesWeek 1 PDFTanapat LapanunNo ratings yet
- CompressionDocument11 pagesCompressionkaisser091202No ratings yet
- Reporte ExtendidoDocument13 pagesReporte Extendidoluis rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Working Stress Design: Dr. Majed AshoorDocument12 pagesWorking Stress Design: Dr. Majed AshoorMuslim MahdiNo ratings yet
- PHYS 118 Formula SheetDocument2 pagesPHYS 118 Formula Sheetemmacont2060No ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document15 pagesChapter 13Avishka PriyanjanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document20 pagesChapter 10Avishka PriyanjanaNo ratings yet
- AC Power Analysis: School of Electrical InformationDocument20 pagesAC Power Analysis: School of Electrical InformationkamalNo ratings yet
- 4a - Simple Strain StudentsDocument16 pages4a - Simple Strain StudentsGisang IsdaNo ratings yet
- Contest Math Problem Solving #1Document4 pagesContest Math Problem Solving #1Darie MitulescuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 SolutionDocument3 pagesAssignment 5 Solutionsolai muruganNo ratings yet
- Final Exam تخلفات - Model Answer - Part 1Document6 pagesFinal Exam تخلفات - Model Answer - Part 1Maher Gomaa IsmaeelNo ratings yet
- Group12 Lab08Document20 pagesGroup12 Lab08Chayathorn DuangtongsukNo ratings yet
- Experimentales Circuito Rc Caso Resistivo Media Onda Onda Completa Media Onda Onda Completa τ (ms) Vmax (V) Vpp (V) Vcd (V) Vca (V) Vrms (V)Document7 pagesExperimentales Circuito Rc Caso Resistivo Media Onda Onda Completa Media Onda Onda Completa τ (ms) Vmax (V) Vpp (V) Vcd (V) Vca (V) Vrms (V)Raul Jose Guerrero QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 - 2022 - With Final AnsDocument8 pagesQuiz 1 - 2022 - With Final AnsRaraNo ratings yet
- F12 - 2023 - Statistical ModuleDocument30 pagesF12 - 2023 - Statistical ModuleAbdirahman NurNo ratings yet
- Word Tugas 3 Beplas ArgaDocument8 pagesWord Tugas 3 Beplas ArgaArgaYudhistiraNo ratings yet
- Connection Between Sharpe and Max-DrawdownDocument4 pagesConnection Between Sharpe and Max-DrawdownGaryNo ratings yet
- Longitudinal Data Analysis Instructor: Natasha SarkisianDocument31 pagesLongitudinal Data Analysis Instructor: Natasha SarkisianHe HNo ratings yet
- Shear Stress - A ReviewDocument16 pagesShear Stress - A ReviewAmogh SharmaNo ratings yet
- ENCV4GS - Test 1 - SolutionDocument6 pagesENCV4GS - Test 1 - Solution217005052No ratings yet
- Assignment SolutionDocument4 pagesAssignment SolutionosamaNo ratings yet
- Formulario 2da PDFDocument1 pageFormulario 2da PDFRichard LarinoNo ratings yet
- Formulario 2da PDFDocument1 pageFormulario 2da PDFMery Cristina Cahuana CáceresNo ratings yet
- 𝑓𝑐𝑟 = 2√𝑓′𝑐 Cuantía Mecánica Ac. 𝜌 = 𝜔. 𝑓′𝑐 𝑓𝑦 𝜌% → 𝜌 = 𝑝ℎ𝑜/100 𝐾𝑢 = 𝑀𝑢 𝑏. 𝑑 Resist. Nom. y Últ. f (ω) 𝑀𝑛 = 𝑓 𝑐. 𝑏. 𝑑 - 𝜔 (1 − 0.59𝜔) 𝜑. 𝑀𝑛 = 𝜑. 𝑓 𝑐. 𝑏. 𝑑 - 𝜔 (1 − 0.59𝜔)Document1 page𝑓𝑐𝑟 = 2√𝑓′𝑐 Cuantía Mecánica Ac. 𝜌 = 𝜔. 𝑓′𝑐 𝑓𝑦 𝜌% → 𝜌 = 𝑝ℎ𝑜/100 𝐾𝑢 = 𝑀𝑢 𝑏. 𝑑 Resist. Nom. y Últ. f (ω) 𝑀𝑛 = 𝑓 𝑐. 𝑏. 𝑑 - 𝜔 (1 − 0.59𝜔) 𝜑. 𝑀𝑛 = 𝜑. 𝑓 𝑐. 𝑏. 𝑑 - 𝜔 (1 − 0.59𝜔)Acero EliasNo ratings yet
- 5a - Generalized Hooke's Law Solved Problem 6.2020Document18 pages5a - Generalized Hooke's Law Solved Problem 6.2020Gisang IsdaNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Midterm Exam AnskeyDocument4 pagesReinforced Concrete Midterm Exam AnskeyAngelito AngelesNo ratings yet
- Transformers Numericals Vol. 2 Qtns and SolutionsDocument12 pagesTransformers Numericals Vol. 2 Qtns and SolutionsBaluku DavidNo ratings yet
- Xmas Tree in MATLABDocument8 pagesXmas Tree in MATLABMirzaNo ratings yet
- Kiran P B180894ee Pe Exp4Document7 pagesKiran P B180894ee Pe Exp4khyati patelNo ratings yet
- Homework ÇözümüDocument2 pagesHomework Çözümüenes arikanNo ratings yet
- Heat Conduction Equation: Heat Transfer 2021: Equations For Part ADocument9 pagesHeat Conduction Equation: Heat Transfer 2021: Equations For Part AMiguelKevinNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Transferencia de CalorDocument7 pagesEjercicios Transferencia de CalorAly HerreraNo ratings yet
- MSV 780 Exam 2020 MemoDocument24 pagesMSV 780 Exam 2020 MemoBesuidenhout Engineering Solutions and ConsultingNo ratings yet
- Design of Slab For Bridge 2: Dead LoadDocument2 pagesDesign of Slab For Bridge 2: Dead Loadjan janNo ratings yet
- Joint Design CalculationDocument21 pagesJoint Design Calculationjosephinelamsy0304No ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet PDFDocument4 pagesCheat Sheet PDFesenalieva03No ratings yet
- MD2 Ass4 ENG. Ahmad Assaf BDocument21 pagesMD2 Ass4 ENG. Ahmad Assaf BAmna AlenziNo ratings yet
- Formulário de Áreas e Volumes de SólidosDocument1 pageFormulário de Áreas e Volumes de SólidosmariaNo ratings yet
- For Combined Loading, Se' 0.5 SutDocument10 pagesFor Combined Loading, Se' 0.5 Sut154 ahmed ehabNo ratings yet
- Linear AlgebraDocument22 pagesLinear AlgebraMalcolmNo ratings yet
- Tut 8 DriveDocument10 pagesTut 8 Drivemennaabdelrazik848No ratings yet
- Trimmed Sample Means For Uniform Mean Estimation and RegressionDocument36 pagesTrimmed Sample Means For Uniform Mean Estimation and RegressionrimfoNo ratings yet
- 5 Creep and SolutionDocument1 page5 Creep and SolutionarmanjeffryNo ratings yet
- 1 Vessels Some SolutionsDocument13 pages1 Vessels Some SolutionsarmanjeffryNo ratings yet
- Esercizi Tipo Esame 13-01-2022Document15 pagesEsercizi Tipo Esame 13-01-2022armanjeffryNo ratings yet
- Esercizi Tipo Esame 13 - 01 - 2022Document11 pagesEsercizi Tipo Esame 13 - 01 - 2022armanjeffryNo ratings yet
- 1 Lindapter Maggio 2023Document84 pages1 Lindapter Maggio 2023CALGERINo ratings yet
- Abdul Rehman: Islamabad, PakistanDocument2 pagesAbdul Rehman: Islamabad, PakistanEngr Abdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- HP Cq41-Nal70 (NCL70) - Dis - La-4107p - 1109Document55 pagesHP Cq41-Nal70 (NCL70) - Dis - La-4107p - 1109Joshua SawyerNo ratings yet
- 3 Pin HD44780 LCD For Arduino - Works of Rowan SimmsDocument2 pages3 Pin HD44780 LCD For Arduino - Works of Rowan SimmsDenaiya Watton LeehNo ratings yet
- SICAM GridPass ProfileDocument2 pagesSICAM GridPass ProfileSerge RinaudoNo ratings yet
- Semester - 4 - HT - Term Paper Topics - Even - 2020Document3 pagesSemester - 4 - HT - Term Paper Topics - Even - 2020PradeepNo ratings yet
- MS PowerPoint Keyboard ShortcutsDocument22 pagesMS PowerPoint Keyboard Shortcutsapi-3754269100% (1)
- SEEPW Engineering BookDocument412 pagesSEEPW Engineering BookTudor MilchisNo ratings yet
- Canon Printer IX5000 & IX4000 - Service ManualDocument8 pagesCanon Printer IX5000 & IX4000 - Service ManualVaxsis SisvaxNo ratings yet
- What Is Deck Water Seal On Tanker and Its Types in DetailDocument5 pagesWhat Is Deck Water Seal On Tanker and Its Types in DetailRose AriantiNo ratings yet
- UB Beam DimensionDocument2 pagesUB Beam Dimensiontuan100% (1)
- Tib Tea User GuideDocument42 pagesTib Tea User GuidefvalmeidaNo ratings yet
- 8200-0859-01-A0 Intlx InstallConfig EN PDFDocument94 pages8200-0859-01-A0 Intlx InstallConfig EN PDFFrancisco Rodriguez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Eliminating Tablet Spots and SpecksDocument2 pagesEliminating Tablet Spots and SpecksMina Maher MikhailNo ratings yet
- Adaptive ControlDocument382 pagesAdaptive ControlAnonymous QakmLc3kTINo ratings yet
- Flow Control Valves: Catalog HY15-3502/USDocument51 pagesFlow Control Valves: Catalog HY15-3502/USPartsGopher.comNo ratings yet
- FiberHome Optical Network Overview Kntelecom IrDocument49 pagesFiberHome Optical Network Overview Kntelecom IrashuschandranNo ratings yet
- Design of Fluid Power Systems: - Stuart J. WilliamsDocument37 pagesDesign of Fluid Power Systems: - Stuart J. WilliamsAnonymous Ms8nYcbxY2No ratings yet
- Property Spectrum of Engineering MaterialsDocument4 pagesProperty Spectrum of Engineering MaterialsAriel Mark Pilotin50% (2)
- Danfoss Vane Tip LUG SylaxDocument18 pagesDanfoss Vane Tip LUG SylaxmaggamNo ratings yet
- A20 Datasheet v1.5 20150510Document36 pagesA20 Datasheet v1.5 20150510denis2xNo ratings yet
- 10 Accuracy of Prediction Methods For Sound Transmission LossDocument8 pages10 Accuracy of Prediction Methods For Sound Transmission LossJuan Ambrosio MartinezNo ratings yet
- MIL-S-38249 Superseded by AMS 3374Document13 pagesMIL-S-38249 Superseded by AMS 3374HenryNo ratings yet
- LEGO 8295 Telescopic Handler Set Parts InventoryDocument12 pagesLEGO 8295 Telescopic Handler Set Parts InventoryrlobetNo ratings yet