Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Tab
Drug Tab
Uploaded by
ATEHAN BORDSOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Tab
Drug Tab
Uploaded by
ATEHAN BORDSCopyright:
Available Formats
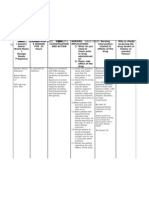
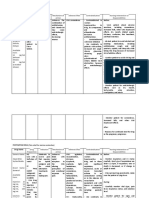
Name of Drug Action Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects/Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities
Magnesium Mineral/ Magnesium is the second the most Magnesium sulfate Flushing, sweating, sharply lowered
blood pressure, hypothermia, stupor Before the administration of drug:
Sulfate Anticonvulsant most plentiful cation of common should be given very
and ultimately, respiratory depression. Verify Doctor’s order
Injection the intracellular fluids. It medicine used cautiously in the presence
(Magnesium Magnesium is the is essential for the for preventing of serious impairment of Remember the 10R’s of Drug
Sulfate/ Epsom second most plentiful activity of many enzyme eclampsia renal function since it is administration
Salt) cation of the systems and plays an (seizures) during excreted almost entirely
intracellular fluids. It important role with pregnancy by the kidneys. This During the administration of drug:
is essential for the regard to neurochemical product contains Verify patient’s identification
activity of many transmission and aluminum that may be
enzyme systems and muscular excitability. toxic. Inform the patient with
plays an important Magnesium sulfate Aluminum may reach regards to drug administration
role with regard to reduces striated muscle toxic levels with Clean the IV port prior to
neurochemical contractions and blocks prolonged parenteral administration of the drug
transmission and peripheral administration if kidney
muscular excitability. neuromuscular function is impaired. After the administration of drug:
Deficits are transmission by reducing Monitor patient for adverse
accompanied by a acetylcholine release at Magnesium sulfate should effects
variety of structural and the myoneural junction. not be administered
functional disturbances. Additionally, parenterally in patients with Inform patient that easy
Magnesium inhibits heart block or myocardial bruising may occur
Ca2+ influx through damage.
Caution patient not to stop
dihydropyridine-
taking drug abruptly without
sensitive, voltage-
first consulting prescriber
dependent channels. This
accounts for much of its
relaxant action on
vascular smooth muscle.
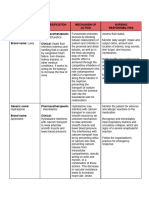
VI. Drug Tabulation
Name of Drug Action Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects/Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities
Hydralazine Anti-hypertensive Direct vasodilation of an intravenous MAO inhibitors should be (Common)\ Headache, anorexia, nausea,
Before the administration of drug:
(Apresoline) arterioles (with little medicine for used with caution in patients vomiting, diarrhea, palpitations,
receiving hydralazine. Used tachycardia, angina pectoris. Verify Doctor’s order
Hydralazine effect on veins) with quickly
apparently lowers lowering with caution in patients with Remember the 10R’s of Drug
decreased systemic suspected coronary artery
blood pressure by severely high administration
resistance. Although disease.
exerting a peripheral blood pressure
vasodilating effect
exact mechanism during
Apresoline should be used with During the administration of drug:
through a direct unknown, arterial pregnancy
caution in patients with Verify patient’s identification
vasodilation may advanced renal damage
relaxation of
vascular smooth occur via inhibition of Inform the patient with
muscle. calcium release from regards to drug administration
Hydralazine, by the sarcoplasmic Clean the IV port prior to
altering cellular reticulum and administration of the drug
calcium metabolism, inhibition of myosin
interferes with the phosphorylation in After the administration of drug:
calcium movements arterial smooth muscle Monitor patient for adverse
within effects
cells.
the vascular smooth
muscle that are Inform patient that easy
responsible for bruising may occur
initiating or maintaining
Caution patient not to stop
the contractile state.
taking drug abruptly without
first consulting prescriber
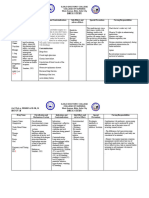
Name of Action Mechanism of Indication Contraindica Side Effects/Adverse Nursing Responsibilities
Drug Action tions Effects
Methyldop Anti-hypertensive The exact an oral medicine With sedation, usually Before the administration of drug:
a (Aldomet) mechanism of for controlling active transient, may occur
Verify Doctor’s order
Methyldop ALDOMET is an aromatic- methyldopa is not high blood hepatic during the initial period
a amino- acid decarboxylase fully elucidated; pressure during disease, of therapy or whenever Remember the 10R’s of Drug administration
(Aldomet)) inhibitor in animals and in however, the main pregnancy such as the dose is increased.
man. Although the mechanisms of acute Headache, asthenia, or During the administration of drug:
mechanism of action has methyldopa involve hepatitis weakness may be noted as Verify patient’s identification
yet to be conclusively its actions on alpha- and active early and transient
demonstrated, the adrenergic receptor cirrhosis. symptoms. Inform the patient with regards to drug administration
antihypertensive effect of and the aromatic L- With Clean the IV port prior to administration of the drug
methyldopa probably is amino acid liver
due to its metabolism to decarboxylase disorders After the administration of drug:
alpha- methylnorepinephr enzyme, to a lesser previousl Monitor patient for adverse effects
ine, which then lowers extent. The y
arterial pressure by sympathetic outflow associate Inform patient that easy bruising may occur
stimulation of central is regulated by alpha d with
Caution patient not to stop taking drug abruptly without first
inhibitory alpha-adrenergic (α)-2 adrenergic methyldo
consulting prescriber
receptors, false receptors and pa
neurotransmission, and/or imidazoline therapy.
reduction of plasma renin receptors expressed With
activity. on adrenergic hypersen
Methyldopa has been neurons within the sitivity to
shown to cause a net rostral ventrolateral any
reduction in the tissue medulla compone
concentration of nt of
serotonin, dopamine, these
norepinephrine, and products.
epinephrine.
On therapy
with
monoamine
oxidase
(MAO)
inhibitors.
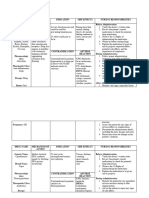
Name of Action Mechanism of Indication Contraindications Side Effects/Adverse Nursing Responsibilities
Drug Action Effects
Labetalol Anti-hypertensive Labetalol non- an The drug is contraindicated in Body as a Whole: Fever. Before the administration of drug:
(Trandate) selectively intravenous bronchial asthma, overt cardiac
Verify Doctor’s order
Labetalol HCl antagonizes beta- medicine for failure, greater- than-first-degree Cardiovascular:
combines both adrenergic quickly heart block, cardiogenic shock, Hypotension, and rarely, Remember the 10R’s of Drug administration
selective, competitive, receptors, and lowering severe bradycardia, other syncope, bradycardia,
alpha1-adrenergic selectively severely conditions associated with severe heart block. During the administration of drug:
blocking and antagonizes alpha- high blood and prolonged hypotension, and in Verify patient’s identification
nonselective, 1-adrenergic pressure in patients with a history of Central and Peripheral
competitive, beta- receptors. Followin the hospital, hypersensitivity to any component Inform the patient with regards to drug
Nervous Systems:
adrenergic blocking g oral and also an of the product. administration
Paresthesia, most
activity in a single administration, oral frequently Clean the IV port prior to administration of
substance. In man, the labetalol has 3 medicine for described as scalp tingling. the drug
ratios times the beta- controlling In most cases, it was mild
of alpha- to beta- blocking ability high blood and transient and usually After the administration of drug:
blockade have been than alpha- pressure occurred at the beginning Monitor patient for adverse effects
estimated to be blocking ability. during of treatment.
approximately 1:3 and pregnancy Inform patient that easy bruising may occur
1:7 following oral and Collagen Disorders: Caution patient not to stop taking drug
intravenous (IV) Systemic lupus abruptly without first consulting prescriber
administration, erythematosus, positive
respectively. antinuclear factor.
Beta2-agonist activity
has been
demonstrated in
animals with minimal
beta1- agonist (ISA)
activity detected. In
animals, at doses
greater than those
required for alpha- or
beta- adrenergic
blockade, a
membrane stabilizing
effect has been
demonstrated.
Name of Action Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects/Adverse Nursing Responsibilities
Drug Effects
Nifedipine Anti-hypertensive Nifedipine blocks an oral Concomitant Body as a Before the administration of drug:
(Adalat) voltage gated L-type medicine for administration with strong Whole/Systemic: chest
The mechanism by which Verify Doctor’s order
calcium channels in controlling P450 inducers, such as pain, leg pain
nifedipine reduces arterial vascular smooth muscle high blood rifampin, are
blood pressure involves Remember the 10R’s of Drug administration
peripheral arterial
and myocardial pressure during contraindicated since the Central Nervous
cells.This blockage pregnancy efficacy of nifedipine System: paresthesia, During the administration of drug:
vasodilatation and,
consequently, a reduction prevents the entry of tablets could be vertigo Verify patient’s identification
in peripheral vascular calcium ions into cells significantly reduced.
during depolarization, Inform the patient with regards to drug
resistance. The increased Dermatologic: rash
peripheral vascular reducing peripheral Nifedipine must not be administration
resistance, an underlying arterial vascular used in cases of Gastrointestinal:
cause of hypertension, Clean the IV port prior to administration of the
resistance and dilating cardiogenic shock. constipation drug
results from an increase in
coronary arteries. These
active tension in the
vascular smooth muscle. actions reduce blood Musculoskeletal: leg After the administration of drug:
Studies have demonstrated pressure and increase Known hypersensitivity to cramps Monitor patient for adverse effects
that the increase in active the supply of oxygen to nifedipine.
tension reflects an increase the heart, alleviating Respiratory: Inform patient that easy bruising may occur
in cytosolic free calcium. angina. epistaxis, rhinitis Caution patient not to stop taking drug abruptly
without first consulting prescriber
Urogenital:
impotence, urinary
frequency
You might also like
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Case PresentationDocument46 pagesGestational Diabetes Mellitus: Case PresentationATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- OfloxacinDocument2 pagesOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- AlanervDocument3 pagesAlanervCen Janber CabrillosNo ratings yet
- Tourism Planning Development The Jed'S Island Resort: Inquiries, Investigation, and ImmersionDocument25 pagesTourism Planning Development The Jed'S Island Resort: Inquiries, Investigation, and ImmersionWhotfis Maysie100% (1)
- Lauren Herr Nsg-432cc-Care-Plan-ExemplarDocument11 pagesLauren Herr Nsg-432cc-Care-Plan-Exemplarapi-520453750100% (1)
- Hypothyroidism Lesson PlanDocument20 pagesHypothyroidism Lesson PlanDimpal Choudhary33% (3)
- Drug Study On AnestheticsDocument9 pagesDrug Study On AnestheticsKalvinArtRazalanCelebradosNo ratings yet
- Amikacin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmikacin Drug StudyRussel Kate SulangNo ratings yet
- Jara 2Document14 pagesJara 2John Kenneth DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Drug Name MagsnDocument3 pagesDrug Name MagsnBryant Von Andrew EstradaNo ratings yet
- Beecroft 2010 KDocument3 pagesBeecroft 2010 KCati JurcaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Furosemide and MidazolamDocument2 pagesDrug Study Furosemide and MidazolamCuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyfortunelobsterNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Sulfate: Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMagnesium Sulfate: Drug StudyMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- Mfe, Ferrous Sulfate, Calcium Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMfe, Ferrous Sulfate, Calcium Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeNo ratings yet
- Specific ActionDocument3 pagesSpecific Actionmoritashinobu2011No ratings yet
- Gantala Drug Stusy-TabhsoDocument8 pagesGantala Drug Stusy-TabhsoHey it's FerdyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DRDocument3 pagesDrug Study DRGershom Perez AcaboNo ratings yet
- Medical ManagementDocument3 pagesMedical ManagementMark Jefferson LunaNo ratings yet
- Druggggggg StudyDocument8 pagesDruggggggg StudyAcob, Jean LykaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study orDocument3 pagesDrug Study orJuvanni SantosNo ratings yet
- LidocaineDocument2 pagesLidocaineLeigh Marie LastimosaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyChuchai AmbongNo ratings yet
- Hernandez Ob Drug StudyDocument7 pagesHernandez Ob Drug StudyEliza Joyce HernandezNo ratings yet
- Lisinopril Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLisinopril Drug StudyKristinelou Marie Reyna100% (1)
- Ismael Jaani - DRUG STUDY On Cardiovascular DrugsDocument2 pagesIsmael Jaani - DRUG STUDY On Cardiovascular DrugsIsmael JaaniNo ratings yet
- Drug study-FIRST TWO MEDICAL WARDDocument2 pagesDrug study-FIRST TWO MEDICAL WARDErryl Justine AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Rle Final 1Document18 pagesDrug Study Rle Final 1YBH Construction SupplyNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Brand Name: BeforeDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name: BeforeArt russelNo ratings yet
- LevetiracetamDocument3 pagesLevetiracetamGwyn Rosales100% (2)
- PPD's Better Pharmacy Drug Hand Book 9 Edition 2009: Marquez, Crystal Queen CDocument1 pagePPD's Better Pharmacy Drug Hand Book 9 Edition 2009: Marquez, Crystal Queen CCrystal Queen MarquezNo ratings yet
- Marfori - Activity 3 Antineoplastic Agents Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMarfori - Activity 3 Antineoplastic Agents Drug Studyckkyle0% (1)
- Drug Study: Meclizine Is An Antagonist atDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Meclizine Is An Antagonist atJayson Ray AbellarNo ratings yet
- Silbert, Sara May L. (BSN 2-H) DRUG STUDYDocument4 pagesSilbert, Sara May L. (BSN 2-H) DRUG STUDYSara May SilbertNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology NMB Ds and Anti Cholinesterase S FinalDocument8 pagesPharmacology NMB Ds and Anti Cholinesterase S FinalPamella Kusuma WerdanieNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Atracurium: RecommendedDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Atracurium: RecommendedShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Silbert, Sara May L. (BSN 2-h) Drug StudyDocument4 pagesSilbert, Sara May L. (BSN 2-h) Drug StudySara May SilbertNo ratings yet
- Er-Drug StudyDocument41 pagesEr-Drug Studyrc_lacampuinganyahooNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Drug Classificati ON Mechanism of Action Rationale Common Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Drug Classificati ON Mechanism of Action Rationale Common Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyChristine Mae BandiolaNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis CEACCP 2004Document3 pagesAnaphylaxis CEACCP 2004kuruppukarlNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Brand Name Generic Name Classification Dosage Action MechanismDocument4 pagesDrug Study Brand Name Generic Name Classification Dosage Action MechanismJudith D. DSantosNo ratings yet
- Propofol Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPropofol Drug Studygersalia.christiennikkiNo ratings yet
- Devanni Shane-Hiyas Drugstudy Po PDFDocument3 pagesDevanni Shane-Hiyas Drugstudy Po PDFDeva HiyasNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs and AntidoteDocument114 pagesEmergency Drugs and AntidoteAlexa BelderolNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Blocking Drugs and Anticholinesterases UpdateDocument4 pagesNeuromuscular Blocking Drugs and Anticholinesterases UpdateAuliaNo ratings yet
- Antiarthritic Drug StudiesDocument15 pagesAntiarthritic Drug StudiesSaidinaNo ratings yet
- Prenatal DrugDocument4 pagesPrenatal DrugJorgie Ann ReyNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesKarl Lourenz DeysolongNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyAbie Jewel Joy Roque100% (1)
- Assignment 1 - PHARMACOLOGYDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 - PHARMACOLOGYJewel SebastianNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 2058534921000172Document6 pagesPi Is 2058534921000172Yader Enrique Altamirano RamirezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CaDocument3 pagesDrug Study - Casaint_ronald8No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyTRIXY MAE HORTILLANONo ratings yet
- Pharma Coven IDocument9 pagesPharma Coven IJocel LongosNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesGeneric Name:: Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTONo ratings yet
- Biperiden HCLDocument2 pagesBiperiden HCLivy_tan_6No ratings yet
- Arcega, Romar DRUGSDocument3 pagesArcega, Romar DRUGSR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CytotecDocument2 pagesDrug Study CytotecJahmil DulatreNo ratings yet
- Gloria DS Module 2Document1 pageGloria DS Module 2z6cc9vgg6nNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (First Meet - RLE)Document5 pagesDrug Study (First Meet - RLE)Pauline AñesNo ratings yet
- BeclomethasoneDocument2 pagesBeclomethasoneDiane Bonita HerreraNo ratings yet
- Inhalation Anesthetic Drug StudyDocument4 pagesInhalation Anesthetic Drug StudyElisse RodulfoNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Prayers 1Document4 pagesPrayers 1ATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- Or Instruments Set 3Document3 pagesOr Instruments Set 3ATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- Amantillo ParkinsonsDocument14 pagesAmantillo ParkinsonsATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- CARDS AutoRecoveredDocument3 pagesCARDS AutoRecoveredATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension Case StudyDocument77 pagesPregnancy Induced Hypertension Case StudyATEHAN BORDS100% (1)
- Prayer Before Surgery: (Surgeon)Document1 pagePrayer Before Surgery: (Surgeon)ATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- Niel SJWDocument13 pagesNiel SJWATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- Family Case StudyDocument57 pagesFamily Case StudyATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- Final Group A BSN 3A 2Document91 pagesFinal Group A BSN 3A 2ATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- My JournalDocument4 pagesMy JournalATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument50 pagesResearchATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity No.1Document4 pagesLearning Activity No.1ATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- NIEL JournalDocument1 pageNIEL JournalATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- Self Awareness AmantilloDocument6 pagesSelf Awareness AmantilloATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- Final Draft Group A BSN 3ADocument59 pagesFinal Draft Group A BSN 3AATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer PPT 1Document127 pagesBreast Cancer PPT 1ATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- Catholic Social TeachingDocument2 pagesCatholic Social TeachingATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- Journal (Belle)Document1 pageJournal (Belle)ATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- Family Case Study: By: Kian Ivan F. BialenDocument19 pagesFamily Case Study: By: Kian Ivan F. BialenATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- Information Technology System Applicable in Nursing PracticeDocument92 pagesInformation Technology System Applicable in Nursing PracticeATEHAN BORDS100% (1)
- The Natural Law: Group 5Document39 pagesThe Natural Law: Group 5ATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- Catholic Social Teachings-It Includes Issues, Principles, Church Documents and Scriptural Bases ButDocument3 pagesCatholic Social Teachings-It Includes Issues, Principles, Church Documents and Scriptural Bases ButATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Bronchial Asthma in Acute ExacerbationDocument71 pagesA Case Study On Bronchial Asthma in Acute ExacerbationATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- GDM Case PresentationDocument20 pagesGDM Case PresentationATEHAN BORDS100% (1)
- Edited MCN Case PresentationDocument24 pagesEdited MCN Case PresentationATEHAN BORDSNo ratings yet
- ReferenceMaterials O'SullivanDocument141 pagesReferenceMaterials O'SullivanAntonio tapiaNo ratings yet
- 118 A Chapter 2 - Responses To Altered Ventilatory Function (Edited) Handout #3 (Sir Marvin)Document14 pages118 A Chapter 2 - Responses To Altered Ventilatory Function (Edited) Handout #3 (Sir Marvin)Joanna TaylanNo ratings yet
- THE FIRST TERM TEST (E10) - No.5Document6 pagesTHE FIRST TERM TEST (E10) - No.5Thanh GàNo ratings yet
- Devlin2020 PDFDocument8 pagesDevlin2020 PDFMatias FlammNo ratings yet
- Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction: Guidelines OnDocument52 pagesNeurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction: Guidelines OnPatrascu CristiNo ratings yet
- Body Image and Media Use Among AdolescentsDocument26 pagesBody Image and Media Use Among AdolescentsWhitney CampbellNo ratings yet
- Gallstone Pancreatitis - CST PDFDocument5 pagesGallstone Pancreatitis - CST PDFDaniel Rosero CadenaNo ratings yet
- 3.2.schizo Bipolar DelusionDocument112 pages3.2.schizo Bipolar DelusionAmar Nur Arif ZazuliNo ratings yet
- Book 6413 Introduction To Inclsuive EducationDocument372 pagesBook 6413 Introduction To Inclsuive EducationKhurram GulzarNo ratings yet
- Hilot (Wellness) NC IiDocument71 pagesHilot (Wellness) NC IiShella Mae TudioNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Ruminant Herpesvirus Infections: Monika Engels, Mathias AckermannDocument13 pagesPathogenesis of Ruminant Herpesvirus Infections: Monika Engels, Mathias AckermannRosafina SetyantariNo ratings yet
- Pubmed Pneumonias SetDocument107 pagesPubmed Pneumonias SetWALTERNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1: Nursing Interventions To Promote Healthy Physiologic Responses: Comfort and PainDocument14 pagesUNIT 1: Nursing Interventions To Promote Healthy Physiologic Responses: Comfort and Painlouie tibarNo ratings yet
- Ms 1 Lec Integumentary Disorders 1Document35 pagesMs 1 Lec Integumentary Disorders 1Denise LacapNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders Part I Hyperthyroidism Little 2006Document9 pagesThyroid Disorders Part I Hyperthyroidism Little 2006Jing XueNo ratings yet
- RT 312 Prelim NotesDocument20 pagesRT 312 Prelim NotesGiralph NikkoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Education & Working ExperienceDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Education & Working Experienceapotek hegarNo ratings yet
- Acute & Chronic Pancreatitis - DoneDocument7 pagesAcute & Chronic Pancreatitis - DoneAriana ValenciaNo ratings yet
- TM1-Environmental EpidemiologyDocument17 pagesTM1-Environmental EpidemiologyFarahAzzahraAnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Long-QT Syndrome From Genetics To ManagementDocument10 pagesLong-QT Syndrome From Genetics To ManagementDiogo Botelho Medeiros BrilhanteNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Stress - Why People Get TattoosDocument2 pagesThe Effects of Stress - Why People Get TattoosRicardo Monserrat Castro100% (1)
- Wound Care: Section I: Assessing Your UnderstandingDocument12 pagesWound Care: Section I: Assessing Your Understandingkeyona100% (1)
- Rough Draft Research Paper 11Document14 pagesRough Draft Research Paper 11api-549217680No ratings yet
- PR2 Chap 2Document14 pagesPR2 Chap 2Grace SumagueNo ratings yet
- Tools For Assessment: - IDB (Initial Data Base) : Family Nursing ProcessDocument6 pagesTools For Assessment: - IDB (Initial Data Base) : Family Nursing ProcessKath ArabisNo ratings yet
- Bleaching Part 1Document6 pagesBleaching Part 1Hamad KayaniNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis: by DR Haris Gul Senior Registrar Rheumatology Fauji Foundation Hospital RawalpindiDocument32 pagesBronchiectasis: by DR Haris Gul Senior Registrar Rheumatology Fauji Foundation Hospital RawalpindiAamer NaeemNo ratings yet