Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3.0 Acid Base Imbalances ABGS
3.0 Acid Base Imbalances ABGS
Uploaded by
Ciara GonzalezCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Donovans Brain - Curt-Siodmak PDFDocument66 pagesDonovans Brain - Curt-Siodmak PDFBob AvocadoNo ratings yet
- Edn Quiz 1 - A2 2Document4 pagesEdn Quiz 1 - A2 2Je KirsteneNo ratings yet
- DYSRHYTHMIAS (A.k.a. Arrhythmias) Disorders in TheDocument3 pagesDYSRHYTHMIAS (A.k.a. Arrhythmias) Disorders in TheDarell M. Book100% (1)
- Case 2Document14 pagesCase 2Je KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Veco LetterDocument1 pageVeco LetterJe Kirstene100% (1)
- Zoology 100 Notes 2Document27 pagesZoology 100 Notes 2Bethany Jane Ravelo IsidroNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS ABG-InterpretationDocument1 pageNursing CS ABG-InterpretationJanaNo ratings yet
- EKG Quick ViewDocument1 pageEKG Quick ViewJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Ace Inhibitors 6Document10 pagesAce Inhibitors 6api-316574434No ratings yet
- 3 Step ABG Interpretation - 2Document1 page3 Step ABG Interpretation - 2Sibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Neurologic NursingDocument10 pagesNeurologic NursingAllisson Beckers100% (1)
- Https:Jetmapp - orbundsis.com:Einstein-freshair:Videos::102793DigitalDownload LabValues NurseInTheMaking 2pagesDocument5 pagesHttps:Jetmapp - orbundsis.com:Einstein-freshair:Videos::102793DigitalDownload LabValues NurseInTheMaking 2pagesamazonian005100% (1)
- Prof. Sandra M. Covarrubias - September 24, 2021: 5.2fluid & Electrolytes ImbalancesDocument5 pagesProf. Sandra M. Covarrubias - September 24, 2021: 5.2fluid & Electrolytes ImbalancesIvy VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Dysrhythmias 1: Cardiac Conduc1on System Rhythm Strip Recogni1onDocument4 pagesDysrhythmias 1: Cardiac Conduc1on System Rhythm Strip Recogni1ontantalizin marieNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology FreebieDocument3 pagesPharmacology FreebieMohammad Farooq KhanNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Problems in OxygenationDocument5 pagesCare of Clients With Problems in OxygenationSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- ABGs Respiratory/MetabolicDocument3 pagesABGs Respiratory/MetabolicJoe B100% (1)
- Cranial NervesDocument6 pagesCranial Nervesvienny kayeNo ratings yet
- PREPUMASTERKEY (Repaired)Document2,031 pagesPREPUMASTERKEY (Repaired)surviving nursing schoolNo ratings yet
- Ncle X Cheat SheetDocument24 pagesNcle X Cheat Sheet98b5jc5hgtNo ratings yet
- Nursing Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNursing Cheat Sheetnazbeen.ahmadiNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure PDFDocument9 pagesCongestive Heart Failure PDFSheryl Ann Mae BombalesNo ratings yet
- Nervous System AlterationsDocument45 pagesNervous System AlterationsMajesty ParkerNo ratings yet
- Adenosine: Rapid IV PushDocument4 pagesAdenosine: Rapid IV PushsabboNo ratings yet
- Condition Drug Class: Cardiovascular MedicationsDocument5 pagesCondition Drug Class: Cardiovascular MedicationsCasey Fioravante100% (1)
- Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument2 pagesElectrolyte ImbalanceRanita IvanaNo ratings yet
- ABG ExamDocument3 pagesABG ExamLoiegy PaetNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medication WorksheetDocument1 pageClinical Medication WorksheetSrkocher100% (1)
- ABG Tic Tac Toe Part 2Document2 pagesABG Tic Tac Toe Part 2C Caballero LobregasNo ratings yet
- Fluids Electrolytes and Acid Base ImbalancesDocument8 pagesFluids Electrolytes and Acid Base ImbalancesSamantha Bernardo UndaNo ratings yet
- Acidosis Vs AlkalosisDocument15 pagesAcidosis Vs Alkalosisdina sharafNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes ImbalancesDocument4 pagesElectrolytes ImbalancesPeter John Ruiz100% (1)
- Electrolyte Imbalance Cause Signs and Symptoms Intervention ConnectionDocument6 pagesElectrolyte Imbalance Cause Signs and Symptoms Intervention ConnectionmkninnyNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte DisturbancesDocument7 pagesFluid and Electrolyte DisturbancesMarie Antionette MondragonNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet For Fluid Balance and ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet For Fluid Balance and ElectrolytesLiel TorresNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas AnalysisDocument43 pagesArterial Blood Gas AnalysisLoribel Coma100% (1)
- Dysrhythmias: Se Admin Anticoagulante, Cardioversion As PrescribedDocument10 pagesDysrhythmias: Se Admin Anticoagulante, Cardioversion As Prescribedyaneidys perezNo ratings yet
- NCM-112 Midterms BATCH 2023 College of Nursing-Adamson UniversityDocument13 pagesNCM-112 Midterms BATCH 2023 College of Nursing-Adamson UniversityjoanneNo ratings yet
- 60 Most Common DrugsDocument1 page60 Most Common DrugsNikkaLim100% (1)
- Nursing Cardiology: Rebound HypertensionDocument8 pagesNursing Cardiology: Rebound HypertensionVon R SemillaNo ratings yet
- 5 Step EKG InterpretationDocument1 page5 Step EKG InterpretationSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Med SurgDocument41 pagesMed SurgPrincess LabasanNo ratings yet
- CH 29 - Management of Patients With Structural, Infectious, and Inflmmatory Cardiac DisordersDocument15 pagesCH 29 - Management of Patients With Structural, Infectious, and Inflmmatory Cardiac DisordersPye Antwan Delva100% (1)
- Medical Surgical Nursing Pre-Test 2 RATIONALEDocument8 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Pre-Test 2 RATIONALEBlaine ManiegoNo ratings yet
- Shock NotesDocument5 pagesShock NotesAlyss Wallschleger100% (1)
- ABG Interpretation WorksheetDocument5 pagesABG Interpretation WorksheetArvee Caezar F. VizcarraNo ratings yet
- Visual Chart 1 - Developmental MilestonesDocument1 pageVisual Chart 1 - Developmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument9 pagesUrinary SystemCailah Sofia SelausoNo ratings yet
- Lab Values - Chart by PriorityDocument2 pagesLab Values - Chart by PriorityashleyNo ratings yet
- OB Med SheetDocument12 pagesOB Med SheetSam DanaNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs ChartDocument15 pagesCommon Drugs Chartforminsko100% (1)
- Sirs & ModsDocument5 pagesSirs & Modsmarlou agananNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of PlanDocument16 pagesNursing Care of PlanDbyNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes Cram SheetDocument8 pagesFluid and Electrolytes Cram SheetChrizley Shawn DeroniaNo ratings yet
- Med Surg 2 - 10 Nursing Care of Clients With Biliary DisordersDocument4 pagesMed Surg 2 - 10 Nursing Care of Clients With Biliary DisordersMaxinne RoseñoNo ratings yet
- Digestive Domain Guide 1Document31 pagesDigestive Domain Guide 1surviving nursing school100% (1)
- Formulas and DripsDocument6 pagesFormulas and DripsJsohna BelinaNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia and HyperglycemiaDocument1 pageHypoglycemia and HyperglycemiaMa Cheryll DueñasNo ratings yet
- EMS Calculating Drip RatesDocument17 pagesEMS Calculating Drip Ratesزهرة النرجسNo ratings yet
- Answers, Rationales, and Test Taking Strategies: The Client With Acute Coronary SyndromesDocument12 pagesAnswers, Rationales, and Test Taking Strategies: The Client With Acute Coronary SyndromesNursyNurseNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : Myocardial InfarctionDocument5 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : Myocardial InfarctionManju PillaiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Med Surg Memory Notebook of NursingDocument8 pagesCardiovascular Med Surg Memory Notebook of NursingdmsapostolNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Acid Based BalanceDocument11 pagesAcid Based BalanceAngellene GraceNo ratings yet
- ABBREVIATIONSDocument5 pagesABBREVIATIONSJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- NS 1 QUIZ 3 For PrintingDocument4 pagesNS 1 QUIZ 3 For PrintingJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Leadership Exam 2Document51 pagesLeadership Exam 2Je Kirstene100% (1)
- Rle RequirementDocument101 pagesRle RequirementJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- OR - DR InstrumentsDocument7 pagesOR - DR InstrumentsJe Kirstene100% (2)
- Pre TestDocument10 pagesPre TestJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- EKG Quick ViewDocument1 pageEKG Quick ViewJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- MS P2 CompilationDocument451 pagesMS P2 CompilationJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Format NCP and Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFormat NCP and Drug StudyJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Questions:: Your Email Will Be Recorded When You Submit This FormDocument8 pagesQuestions:: Your Email Will Be Recorded When You Submit This FormJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Group 1 SDLDocument11 pagesGroup 1 SDLJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- MS - Periop POST TESTDocument19 pagesMS - Periop POST TESTJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Heart Sounds & 5 EKG Lead PlacementDocument1 pageHeart Sounds & 5 EKG Lead PlacementJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs by Age: Age HR SBP DBP RRDocument1 pageVital Signs by Age: Age HR SBP DBP RRJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Fabs and Onco Post TestDocument20 pagesFabs and Onco Post TestJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- LMR Quiz 2 - A2 Page 2Document6 pagesLMR Quiz 2 - A2 Page 2Je KirsteneNo ratings yet
- LMR Quiz 1Document5 pagesLMR Quiz 1Je KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Gi-Gu Post TestDocument21 pagesGi-Gu Post TestJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- LMR Quiz 2 - A2 Page 1Document5 pagesLMR Quiz 2 - A2 Page 1Je KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Edn Quiz 1 - A2 3Document5 pagesEdn Quiz 1 - A2 3Je KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Compre Exam 2 - StudentsDocument23 pagesCompre Exam 2 - StudentsJe Kirstene100% (1)
- Compre Exam 1 - StudentsDocument27 pagesCompre Exam 1 - StudentsJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Book Condition Guide PDFDocument7 pagesBook Condition Guide PDFJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- LMR QUIZ 1. Part 2Document5 pagesLMR QUIZ 1. Part 2Je KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Edn Quiz 1 - A2: Questions 1 To 10Document5 pagesEdn Quiz 1 - A2: Questions 1 To 10Je KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Morphology and Cell StructureDocument14 pagesBacterial Morphology and Cell StructureJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Sample Consent-Form PDFDocument4 pagesSample Consent-Form PDFJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Methods of Age Determination in FishDocument19 pagesMethods of Age Determination in FishWaqar Ul ArfeenNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics and Physiology in Active Manual Wheelchair PropulsionDocument21 pagesBiomechanics and Physiology in Active Manual Wheelchair PropulsionStanislas AchardNo ratings yet
- 40410-Article Text-198641-2-10-20221207Document11 pages40410-Article Text-198641-2-10-20221207Ahmad IhsanNo ratings yet
- Sexual Dimorphism in Morphological Traits and Food Habits of Rana TigrinaDocument10 pagesSexual Dimorphism in Morphological Traits and Food Habits of Rana TigrinaRyan Carlo CondeNo ratings yet
- JC-2 Tutorial-1 Immunology Practice MCQ'sDocument14 pagesJC-2 Tutorial-1 Immunology Practice MCQ'shelamahjoubmounirdmo100% (5)
- A Quick Representation of Body MovementsDocument16 pagesA Quick Representation of Body MovementsAkshainee SenNo ratings yet
- Writing Assignment Week TwoDocument3 pagesWriting Assignment Week TwoyesihavenNo ratings yet
- SBL 1023 Exp 3 ProteinDocument7 pagesSBL 1023 Exp 3 Proteinapi-384057570No ratings yet
- VITAL SIGNS ReviewDocument4 pagesVITAL SIGNS ReviewA CNo ratings yet
- Stewart'S Easy Way Acid-Base: To UnderstandDocument40 pagesStewart'S Easy Way Acid-Base: To UnderstandTaufiq GemawanNo ratings yet
- What Is Quantiferon-Tb Gold?Document12 pagesWhat Is Quantiferon-Tb Gold?Seph LiwanagNo ratings yet
- Biology Exemplar ProblemsDocument4 pagesBiology Exemplar ProblemsAkshatha NayakNo ratings yet
- Stimuli & Responses in PlantsDocument3 pagesStimuli & Responses in PlantsNasiruddin KutatNo ratings yet
- Seeley 6e 2004 CH 28 Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesSeeley 6e 2004 CH 28 Reproductive SystemNinoamelia OrikkuNo ratings yet
- Womersley1977 Article AContextualEffectInFeatureDeteDocument5 pagesWomersley1977 Article AContextualEffectInFeatureDeteTasya aqimarNo ratings yet
- Circulation Management: Hypovolemic Shock: Hemorrhagic Shock, Dehydration and CombustionDocument23 pagesCirculation Management: Hypovolemic Shock: Hemorrhagic Shock, Dehydration and CombustionYuni Sulistiyo WardhaniNo ratings yet
- HHWC Stress Management Manual FinalDocument33 pagesHHWC Stress Management Manual FinalSiraj ShaikhNo ratings yet
- P So As SequenceDocument2 pagesP So As SequencethiagomorettiNo ratings yet
- Health Benefits of Tea Drinking: Camellia Sinensis "Tea sutra:Cha-Kyou" Written by Lu Yu inDocument6 pagesHealth Benefits of Tea Drinking: Camellia Sinensis "Tea sutra:Cha-Kyou" Written by Lu Yu inDan George IIINo ratings yet
- Embriologia Humana y Biologia Del Desarrollo CarlsonDocument14 pagesEmbriologia Humana y Biologia Del Desarrollo CarlsonJulio AbarzuaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Subjective: "Apat Na Araw Na SiyangDocument2 pagesAssessment Subjective: "Apat Na Araw Na Siyangmarlon_taycoNo ratings yet
- Zoology Generic ElectiveDocument18 pagesZoology Generic Electivemaharanauma466No ratings yet
- 4bi1 2b Que 20230117Document20 pages4bi1 2b Que 20230117ah6643242No ratings yet
- Module 5 Death 3Document25 pagesModule 5 Death 3Nhelly Anne NiedoNo ratings yet
- This Protocol Describes The Production of Competent Yeast Cells For Lithium AcetateDocument7 pagesThis Protocol Describes The Production of Competent Yeast Cells For Lithium AcetateMohd AimanNo ratings yet
- The Science Behind Dreams - 2Document32 pagesThe Science Behind Dreams - 2Farah ZureikatNo ratings yet
- MCDS 02 036Document10 pagesMCDS 02 036Sinly ReginaNo ratings yet
- Keratinization SeminarDocument38 pagesKeratinization Seminarbands85100% (2)
3.0 Acid Base Imbalances ABGS
3.0 Acid Base Imbalances ABGS
Uploaded by
Ciara GonzalezCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3.0 Acid Base Imbalances ABGS
3.0 Acid Base Imbalances ABGS
Uploaded by
Ciara GonzalezCopyright:
Available Formats
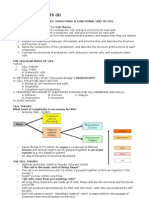
Acid Base Imbalances + ABGs
Pathophysiology Course
Pathophysiology pH
Acid base imbalances are the balance of Acid & Base in the body, Acidotic NORMAL pH
NORMAL pH Alkalotic
kind of like a tug of war the body loves to keep pH in balance. 7.35
7.35 pHpH 7.45
7.45pHpH
- Normal pH: 7.35 - 7.45
- Acidosis: Less than 7.35 pH
- Alkalosis (base): Over 7.45 pH
MEMORY TRICKS
• Full compensation = FULLY Normal pH 7.35 - 7.45 Base = Bicarbonate Carbon diACID
• Partial compensation = pH is not normal
Hydrogen ions = HIGH acid
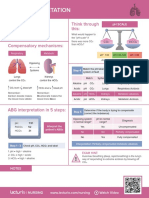
Controlling Organs
KEY PLAYERS
Lungs control Kidneys control
Carbon Dioxide CO2 Acid Base
Breath in O2 & breath out CO2 Hydrogen H+ ions (acid)
Found in the urine
H⁺
Hypoventilation leads to
HIGHER CO2 Bicarbonate HCO3 (base)
Hyperventilation leads to Found in the intestines
Hydrogen Acid
O
lower CO2
C
C H
O O
O O
Bicarb
Carbon dioxide Acid
Metabolic Acidosis & Alkalosis - Causes MEMORY TRICKS
Metabolic
Over 7.45 pH Under 7.35 pH ALKalosis
Metabolic ALKalosis Metabolic Acidosis
H⁺
H⁺
H⁺
H⁺
Vomiting Diarrhea
NGT suction Renal Failure
Hypokalemia DKA - Diabetic Ketoacidosis
• Low K+ Potassium (below 3.5) Lactic AcidOSIS Vomiting sounds like
• LOW K+ = AlKaLOWsis • Shock (low perfusion) “ALKKK-alosis”
Compensation • Sepsis (severe infection)
• Slow Compensation
• Shallow respirations • Rapid, deep respirations Metabolic
ACIDosis
K
Memory tricks Memory tricks
Base out the Butt DKA - Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Metabolic ACIDosis
< 3.5
Diarrhea: if it comes
LOW K+ out of your a$$idosis
AlKaLOWsis Renal Failure: when the
kidneys fail, acid prevails!
You might also like
- Donovans Brain - Curt-Siodmak PDFDocument66 pagesDonovans Brain - Curt-Siodmak PDFBob AvocadoNo ratings yet
- Edn Quiz 1 - A2 2Document4 pagesEdn Quiz 1 - A2 2Je KirsteneNo ratings yet
- DYSRHYTHMIAS (A.k.a. Arrhythmias) Disorders in TheDocument3 pagesDYSRHYTHMIAS (A.k.a. Arrhythmias) Disorders in TheDarell M. Book100% (1)
- Case 2Document14 pagesCase 2Je KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Veco LetterDocument1 pageVeco LetterJe Kirstene100% (1)
- Zoology 100 Notes 2Document27 pagesZoology 100 Notes 2Bethany Jane Ravelo IsidroNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS ABG-InterpretationDocument1 pageNursing CS ABG-InterpretationJanaNo ratings yet
- EKG Quick ViewDocument1 pageEKG Quick ViewJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Ace Inhibitors 6Document10 pagesAce Inhibitors 6api-316574434No ratings yet
- 3 Step ABG Interpretation - 2Document1 page3 Step ABG Interpretation - 2Sibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Neurologic NursingDocument10 pagesNeurologic NursingAllisson Beckers100% (1)
- Https:Jetmapp - orbundsis.com:Einstein-freshair:Videos::102793DigitalDownload LabValues NurseInTheMaking 2pagesDocument5 pagesHttps:Jetmapp - orbundsis.com:Einstein-freshair:Videos::102793DigitalDownload LabValues NurseInTheMaking 2pagesamazonian005100% (1)
- Prof. Sandra M. Covarrubias - September 24, 2021: 5.2fluid & Electrolytes ImbalancesDocument5 pagesProf. Sandra M. Covarrubias - September 24, 2021: 5.2fluid & Electrolytes ImbalancesIvy VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Dysrhythmias 1: Cardiac Conduc1on System Rhythm Strip Recogni1onDocument4 pagesDysrhythmias 1: Cardiac Conduc1on System Rhythm Strip Recogni1ontantalizin marieNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology FreebieDocument3 pagesPharmacology FreebieMohammad Farooq KhanNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Problems in OxygenationDocument5 pagesCare of Clients With Problems in OxygenationSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- ABGs Respiratory/MetabolicDocument3 pagesABGs Respiratory/MetabolicJoe B100% (1)
- Cranial NervesDocument6 pagesCranial Nervesvienny kayeNo ratings yet
- PREPUMASTERKEY (Repaired)Document2,031 pagesPREPUMASTERKEY (Repaired)surviving nursing schoolNo ratings yet
- Ncle X Cheat SheetDocument24 pagesNcle X Cheat Sheet98b5jc5hgtNo ratings yet
- Nursing Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNursing Cheat Sheetnazbeen.ahmadiNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure PDFDocument9 pagesCongestive Heart Failure PDFSheryl Ann Mae BombalesNo ratings yet
- Nervous System AlterationsDocument45 pagesNervous System AlterationsMajesty ParkerNo ratings yet
- Adenosine: Rapid IV PushDocument4 pagesAdenosine: Rapid IV PushsabboNo ratings yet
- Condition Drug Class: Cardiovascular MedicationsDocument5 pagesCondition Drug Class: Cardiovascular MedicationsCasey Fioravante100% (1)
- Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument2 pagesElectrolyte ImbalanceRanita IvanaNo ratings yet
- ABG ExamDocument3 pagesABG ExamLoiegy PaetNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medication WorksheetDocument1 pageClinical Medication WorksheetSrkocher100% (1)
- ABG Tic Tac Toe Part 2Document2 pagesABG Tic Tac Toe Part 2C Caballero LobregasNo ratings yet
- Fluids Electrolytes and Acid Base ImbalancesDocument8 pagesFluids Electrolytes and Acid Base ImbalancesSamantha Bernardo UndaNo ratings yet
- Acidosis Vs AlkalosisDocument15 pagesAcidosis Vs Alkalosisdina sharafNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes ImbalancesDocument4 pagesElectrolytes ImbalancesPeter John Ruiz100% (1)
- Electrolyte Imbalance Cause Signs and Symptoms Intervention ConnectionDocument6 pagesElectrolyte Imbalance Cause Signs and Symptoms Intervention ConnectionmkninnyNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte DisturbancesDocument7 pagesFluid and Electrolyte DisturbancesMarie Antionette MondragonNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet For Fluid Balance and ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet For Fluid Balance and ElectrolytesLiel TorresNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas AnalysisDocument43 pagesArterial Blood Gas AnalysisLoribel Coma100% (1)
- Dysrhythmias: Se Admin Anticoagulante, Cardioversion As PrescribedDocument10 pagesDysrhythmias: Se Admin Anticoagulante, Cardioversion As Prescribedyaneidys perezNo ratings yet
- NCM-112 Midterms BATCH 2023 College of Nursing-Adamson UniversityDocument13 pagesNCM-112 Midterms BATCH 2023 College of Nursing-Adamson UniversityjoanneNo ratings yet
- 60 Most Common DrugsDocument1 page60 Most Common DrugsNikkaLim100% (1)
- Nursing Cardiology: Rebound HypertensionDocument8 pagesNursing Cardiology: Rebound HypertensionVon R SemillaNo ratings yet
- 5 Step EKG InterpretationDocument1 page5 Step EKG InterpretationSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Med SurgDocument41 pagesMed SurgPrincess LabasanNo ratings yet
- CH 29 - Management of Patients With Structural, Infectious, and Inflmmatory Cardiac DisordersDocument15 pagesCH 29 - Management of Patients With Structural, Infectious, and Inflmmatory Cardiac DisordersPye Antwan Delva100% (1)
- Medical Surgical Nursing Pre-Test 2 RATIONALEDocument8 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Pre-Test 2 RATIONALEBlaine ManiegoNo ratings yet
- Shock NotesDocument5 pagesShock NotesAlyss Wallschleger100% (1)
- ABG Interpretation WorksheetDocument5 pagesABG Interpretation WorksheetArvee Caezar F. VizcarraNo ratings yet
- Visual Chart 1 - Developmental MilestonesDocument1 pageVisual Chart 1 - Developmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument9 pagesUrinary SystemCailah Sofia SelausoNo ratings yet
- Lab Values - Chart by PriorityDocument2 pagesLab Values - Chart by PriorityashleyNo ratings yet
- OB Med SheetDocument12 pagesOB Med SheetSam DanaNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs ChartDocument15 pagesCommon Drugs Chartforminsko100% (1)
- Sirs & ModsDocument5 pagesSirs & Modsmarlou agananNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of PlanDocument16 pagesNursing Care of PlanDbyNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes Cram SheetDocument8 pagesFluid and Electrolytes Cram SheetChrizley Shawn DeroniaNo ratings yet
- Med Surg 2 - 10 Nursing Care of Clients With Biliary DisordersDocument4 pagesMed Surg 2 - 10 Nursing Care of Clients With Biliary DisordersMaxinne RoseñoNo ratings yet
- Digestive Domain Guide 1Document31 pagesDigestive Domain Guide 1surviving nursing school100% (1)
- Formulas and DripsDocument6 pagesFormulas and DripsJsohna BelinaNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia and HyperglycemiaDocument1 pageHypoglycemia and HyperglycemiaMa Cheryll DueñasNo ratings yet
- EMS Calculating Drip RatesDocument17 pagesEMS Calculating Drip Ratesزهرة النرجسNo ratings yet
- Answers, Rationales, and Test Taking Strategies: The Client With Acute Coronary SyndromesDocument12 pagesAnswers, Rationales, and Test Taking Strategies: The Client With Acute Coronary SyndromesNursyNurseNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : Myocardial InfarctionDocument5 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : Myocardial InfarctionManju PillaiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Med Surg Memory Notebook of NursingDocument8 pagesCardiovascular Med Surg Memory Notebook of NursingdmsapostolNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Acid Based BalanceDocument11 pagesAcid Based BalanceAngellene GraceNo ratings yet
- ABBREVIATIONSDocument5 pagesABBREVIATIONSJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- NS 1 QUIZ 3 For PrintingDocument4 pagesNS 1 QUIZ 3 For PrintingJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Leadership Exam 2Document51 pagesLeadership Exam 2Je Kirstene100% (1)
- Rle RequirementDocument101 pagesRle RequirementJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- OR - DR InstrumentsDocument7 pagesOR - DR InstrumentsJe Kirstene100% (2)
- Pre TestDocument10 pagesPre TestJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- EKG Quick ViewDocument1 pageEKG Quick ViewJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- MS P2 CompilationDocument451 pagesMS P2 CompilationJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Format NCP and Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFormat NCP and Drug StudyJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Questions:: Your Email Will Be Recorded When You Submit This FormDocument8 pagesQuestions:: Your Email Will Be Recorded When You Submit This FormJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Group 1 SDLDocument11 pagesGroup 1 SDLJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- MS - Periop POST TESTDocument19 pagesMS - Periop POST TESTJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Heart Sounds & 5 EKG Lead PlacementDocument1 pageHeart Sounds & 5 EKG Lead PlacementJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs by Age: Age HR SBP DBP RRDocument1 pageVital Signs by Age: Age HR SBP DBP RRJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Fabs and Onco Post TestDocument20 pagesFabs and Onco Post TestJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- LMR Quiz 2 - A2 Page 2Document6 pagesLMR Quiz 2 - A2 Page 2Je KirsteneNo ratings yet
- LMR Quiz 1Document5 pagesLMR Quiz 1Je KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Gi-Gu Post TestDocument21 pagesGi-Gu Post TestJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- LMR Quiz 2 - A2 Page 1Document5 pagesLMR Quiz 2 - A2 Page 1Je KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Edn Quiz 1 - A2 3Document5 pagesEdn Quiz 1 - A2 3Je KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Compre Exam 2 - StudentsDocument23 pagesCompre Exam 2 - StudentsJe Kirstene100% (1)
- Compre Exam 1 - StudentsDocument27 pagesCompre Exam 1 - StudentsJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Book Condition Guide PDFDocument7 pagesBook Condition Guide PDFJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- LMR QUIZ 1. Part 2Document5 pagesLMR QUIZ 1. Part 2Je KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Edn Quiz 1 - A2: Questions 1 To 10Document5 pagesEdn Quiz 1 - A2: Questions 1 To 10Je KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Morphology and Cell StructureDocument14 pagesBacterial Morphology and Cell StructureJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Sample Consent-Form PDFDocument4 pagesSample Consent-Form PDFJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Methods of Age Determination in FishDocument19 pagesMethods of Age Determination in FishWaqar Ul ArfeenNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics and Physiology in Active Manual Wheelchair PropulsionDocument21 pagesBiomechanics and Physiology in Active Manual Wheelchair PropulsionStanislas AchardNo ratings yet
- 40410-Article Text-198641-2-10-20221207Document11 pages40410-Article Text-198641-2-10-20221207Ahmad IhsanNo ratings yet
- Sexual Dimorphism in Morphological Traits and Food Habits of Rana TigrinaDocument10 pagesSexual Dimorphism in Morphological Traits and Food Habits of Rana TigrinaRyan Carlo CondeNo ratings yet
- JC-2 Tutorial-1 Immunology Practice MCQ'sDocument14 pagesJC-2 Tutorial-1 Immunology Practice MCQ'shelamahjoubmounirdmo100% (5)
- A Quick Representation of Body MovementsDocument16 pagesA Quick Representation of Body MovementsAkshainee SenNo ratings yet
- Writing Assignment Week TwoDocument3 pagesWriting Assignment Week TwoyesihavenNo ratings yet
- SBL 1023 Exp 3 ProteinDocument7 pagesSBL 1023 Exp 3 Proteinapi-384057570No ratings yet
- VITAL SIGNS ReviewDocument4 pagesVITAL SIGNS ReviewA CNo ratings yet
- Stewart'S Easy Way Acid-Base: To UnderstandDocument40 pagesStewart'S Easy Way Acid-Base: To UnderstandTaufiq GemawanNo ratings yet
- What Is Quantiferon-Tb Gold?Document12 pagesWhat Is Quantiferon-Tb Gold?Seph LiwanagNo ratings yet
- Biology Exemplar ProblemsDocument4 pagesBiology Exemplar ProblemsAkshatha NayakNo ratings yet
- Stimuli & Responses in PlantsDocument3 pagesStimuli & Responses in PlantsNasiruddin KutatNo ratings yet
- Seeley 6e 2004 CH 28 Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesSeeley 6e 2004 CH 28 Reproductive SystemNinoamelia OrikkuNo ratings yet
- Womersley1977 Article AContextualEffectInFeatureDeteDocument5 pagesWomersley1977 Article AContextualEffectInFeatureDeteTasya aqimarNo ratings yet
- Circulation Management: Hypovolemic Shock: Hemorrhagic Shock, Dehydration and CombustionDocument23 pagesCirculation Management: Hypovolemic Shock: Hemorrhagic Shock, Dehydration and CombustionYuni Sulistiyo WardhaniNo ratings yet
- HHWC Stress Management Manual FinalDocument33 pagesHHWC Stress Management Manual FinalSiraj ShaikhNo ratings yet
- P So As SequenceDocument2 pagesP So As SequencethiagomorettiNo ratings yet
- Health Benefits of Tea Drinking: Camellia Sinensis "Tea sutra:Cha-Kyou" Written by Lu Yu inDocument6 pagesHealth Benefits of Tea Drinking: Camellia Sinensis "Tea sutra:Cha-Kyou" Written by Lu Yu inDan George IIINo ratings yet
- Embriologia Humana y Biologia Del Desarrollo CarlsonDocument14 pagesEmbriologia Humana y Biologia Del Desarrollo CarlsonJulio AbarzuaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Subjective: "Apat Na Araw Na SiyangDocument2 pagesAssessment Subjective: "Apat Na Araw Na Siyangmarlon_taycoNo ratings yet
- Zoology Generic ElectiveDocument18 pagesZoology Generic Electivemaharanauma466No ratings yet
- 4bi1 2b Que 20230117Document20 pages4bi1 2b Que 20230117ah6643242No ratings yet
- Module 5 Death 3Document25 pagesModule 5 Death 3Nhelly Anne NiedoNo ratings yet
- This Protocol Describes The Production of Competent Yeast Cells For Lithium AcetateDocument7 pagesThis Protocol Describes The Production of Competent Yeast Cells For Lithium AcetateMohd AimanNo ratings yet
- The Science Behind Dreams - 2Document32 pagesThe Science Behind Dreams - 2Farah ZureikatNo ratings yet
- MCDS 02 036Document10 pagesMCDS 02 036Sinly ReginaNo ratings yet
- Keratinization SeminarDocument38 pagesKeratinization Seminarbands85100% (2)