Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LINUX
LINUX
Uploaded by
Reds Vharshan MahandrenCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- PowershellDocument4 pagesPowershellshortcutNo ratings yet
- Os ProjectDocument9 pagesOs ProjectVishal SharmaNo ratings yet
- 3CS LSP Unit 1Document20 pages3CS LSP Unit 1Deepak KumarNo ratings yet
- 3CS LSP Unit 1-1Document15 pages3CS LSP Unit 1-1Deepak KumarNo ratings yet
- 15877091881capse0401-Unit-4-App. of Os O.SDocument11 pages15877091881capse0401-Unit-4-App. of Os O.Sezhilarasu2k9No ratings yet
- Linux System ProgrammingDocument38 pagesLinux System ProgrammingStan MigsNo ratings yet
- Case Study On LinuxDocument40 pagesCase Study On LinuxDivyanshuNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Linux Prof. Sujata RizalDocument40 pagesCase Study On Linux Prof. Sujata RizalRupesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Linux Ms. Jaya GangwaniDocument40 pagesCase Study On Linux Ms. Jaya GangwaniArpit GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Linux Admin Lecture 1Document12 pagesLinux Admin Lecture 1bekesy7No ratings yet
- Operating SystemsDocument22 pagesOperating SystemsRajdeep BorgohainNo ratings yet
- Os FileDocument57 pagesOs Fileguptatulsi31No ratings yet
- Ashu Linux 1Document13 pagesAshu Linux 1Ashish SinghNo ratings yet
- Prajwal GaykwadDocument8 pagesPrajwal GaykwadVaibhav KokitkarNo ratings yet
- Unix V Case StudiesDocument24 pagesUnix V Case StudiesvenkatNo ratings yet
- LinusDocument15 pagesLinusAbel HaileNo ratings yet
- LINUX MODULE-1 - NewDocument66 pagesLINUX MODULE-1 - NewFausiya SalimNo ratings yet
- ITC 401 Lect Note2Document35 pagesITC 401 Lect Note24rgx7fmvg9No ratings yet
- LINUX Programming: INSTRUCTOR: Ms. M. KeerthikaDocument4 pagesLINUX Programming: INSTRUCTOR: Ms. M. KeerthikaKeerthika MNo ratings yet
- Case Study1Document15 pagesCase Study1Anshuman KashyapNo ratings yet
- Operating System - LinuxDocument3 pagesOperating System - LinuxTitus ThukuNo ratings yet
- HCIA-Cloud Computing-Chapter5Document20 pagesHCIA-Cloud Computing-Chapter5islemNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 LinuxDocument18 pagesUnit-1 LinuxNikhil GharatNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document36 pagesUnit 5seetha yuviNo ratings yet
- Unix V Case StudiesDocument36 pagesUnix V Case StudiesAnish A RNo ratings yet
- Linux MOD 1Document55 pagesLinux MOD 1www.noelabraham60No ratings yet
- Linux Operating SystemDocument11 pagesLinux Operating SystemNaval BihaniNo ratings yet
- Windows Vs LinuxDocument21 pagesWindows Vs LinuxrameshkkrliveNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Linux, Unix, WindowsDocument3 pagesIntroduction of Linux, Unix, Windowssanya gargNo ratings yet
- Linux KernelDocument9 pagesLinux KernelNavneetMishraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Linux OS: Nbkrist Iv B.Tech Cse-Ii SemDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Linux OS: Nbkrist Iv B.Tech Cse-Ii SemSiva Prathap MNo ratings yet
- Subject: Operating Systems: Topic: LinuxDocument26 pagesSubject: Operating Systems: Topic: LinuxB.C.H. ReddyNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument17 pagesCase StudySumeet KaurNo ratings yet
- LinuxDocument3 pagesLinuxrahul274274No ratings yet
- Os LinuxDocument2 pagesOs LinuxDavid D'bayuNo ratings yet
- What Is An Operating SystemDocument5 pagesWhat Is An Operating Systemrashmi rashmiNo ratings yet
- Linux OSDocument27 pagesLinux OSJowel VistaNo ratings yet
- LinuxDocument17 pagesLinuxAmal FahadNo ratings yet
- LinuxDocument3 pagesLinuxTejas JadhavNo ratings yet
- Null 9Document4 pagesNull 9Josue SipingNo ratings yet
- 3LINUX DocumentxDocument65 pages3LINUX DocumentxKalyan KNo ratings yet
- 01-Introduction To LinuxDocument24 pages01-Introduction To LinuxGeorge JNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument11 pagesChapter Onetigersiin4No ratings yet
- Introduction and Overview-Getting Started: ChapterDocument10 pagesIntroduction and Overview-Getting Started: Chapterram_somalaNo ratings yet
- LinuxDocument3 pagesLinuxjagruthims100% (1)
- Oss Unit2Document20 pagesOss Unit2Akash ShuklaNo ratings yet
- A Brief Review On Linux: IndexDocument6 pagesA Brief Review On Linux: IndexSifat AnwarNo ratings yet
- Basic Command For Linux New PDFDocument102 pagesBasic Command For Linux New PDFGhost RiderNo ratings yet
- OS06Document19 pagesOS06Asghar Khattak FDCPNo ratings yet
- 3Document6 pages3lgugunashviliNo ratings yet
- Mscse 3 Oss Iset64Document178 pagesMscse 3 Oss Iset64Undergraduate LibraryNo ratings yet
- BCA Sem V - UnixDocument14 pagesBCA Sem V - Unixshri_dasari0% (1)
- Module 5 UnixDocument16 pagesModule 5 Unixshekhawatharsh54No ratings yet
- Practical Training Report: LinuxDocument31 pagesPractical Training Report: LinuxRohit ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Linux Introduction-TeamsDocument22 pagesLinux Introduction-TeamsNithish GowdaNo ratings yet
- Linux FundamentalsDocument4 pagesLinux FundamentalsPratham MishraNo ratings yet
- 01 135221 040 11122096165 20092023 014910pmDocument8 pages01 135221 040 11122096165 20092023 014910pmzainm7032No ratings yet
- Os 2 All Assignments2Document118 pagesOs 2 All Assignments2tp60120No ratings yet
- Os Ass1Document13 pagesOs Ass1Khushi sahuNo ratings yet
- Unit I LinuxDocument30 pagesUnit I LinuxRohan RathodNo ratings yet
- Linux: A Comprehensive Guide to Linux Operating System and Command LineFrom EverandLinux: A Comprehensive Guide to Linux Operating System and Command LineNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Shomesh Web ProgrammingDocument7 pagesAssignment 1 Shomesh Web ProgrammingReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- Futuristic Background - by SlidesgoDocument15 pagesFuturistic Background - by SlidesgoReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document4 pagesAssignment 3Reds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- Dus-Point 3Document3 pagesDus-Point 3Reds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity AnalystDocument2 pagesCybersecurity AnalystReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- Parapharasing PracticeDocument24 pagesParapharasing PracticeReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Avoiding Plagiarism PracticeDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Avoiding Plagiarism PracticeReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- Theory About Sea PowerDocument2 pagesTheory About Sea PowerReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- Kesh LampiranDocument2 pagesKesh LampiranReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- Lampiran: Menguji Atur Cara Yang Telah DibinaDocument2 pagesLampiran: Menguji Atur Cara Yang Telah DibinaReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- SEKOLAHDocument2 pagesSEKOLAHReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- LAMPIRAN A - Urus Niaga Tugasan 2019 - UpdatedDocument4 pagesLAMPIRAN A - Urus Niaga Tugasan 2019 - UpdatedReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- What Are The Major Components of A Web Browser - Draw A Neat Diagram To Explain Them.Document3 pagesWhat Are The Major Components of A Web Browser - Draw A Neat Diagram To Explain Them.Fer LeroyNo ratings yet
- User Manual: NVR/DVR/Hybrid NDVRDocument138 pagesUser Manual: NVR/DVR/Hybrid NDVRGeorge JR BagsaoNo ratings yet
- Emonitor Users GuideDocument392 pagesEmonitor Users GuideFadooollNo ratings yet
- Pocket MirrorDocument70 pagesPocket MirrorRob HilliardNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To DSpaceDocument17 pagesAn Introduction To DSpaceamenu_bizunehNo ratings yet
- Installation Instructions LabsoftDocument32 pagesInstallation Instructions LabsoftDragoi Mihai0% (2)
- How To Hack Facebook Accounts - 5 Common Vulnerabilities - Hacker NoonDocument6 pagesHow To Hack Facebook Accounts - 5 Common Vulnerabilities - Hacker NoonMohamed AmgadNo ratings yet
- Google Adwords Certification - Fundamentals Exam NotesDocument15 pagesGoogle Adwords Certification - Fundamentals Exam NotesAllison DiCicco BerlinNo ratings yet
- Latex GraphicsDocument122 pagesLatex GraphicslambfellerNo ratings yet
- XSS Filter Evasion Cheat SheetDocument43 pagesXSS Filter Evasion Cheat SheetYaseenNo ratings yet
- LT2203Document15 pagesLT2203Sharafat KabirNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DreamweaverDocument50 pagesIntroduction To DreamweaverIlyas A HuqqaniNo ratings yet
- Adminguides4hanaimpl Help enDocument52 pagesAdminguides4hanaimpl Help enbujjishaikNo ratings yet
- Step-By-Step Guide For AWS Virtual TrainingDocument6 pagesStep-By-Step Guide For AWS Virtual TrainingAdmin BakamaNo ratings yet
- Storyline 3: Create Interactive Courses For Any DeviceDocument9 pagesStoryline 3: Create Interactive Courses For Any DeviceHendra Tjahja100% (1)
- DataDocument226 pagesDataSamuel TerrellNo ratings yet
- CRD-33 Trouble Shooting Guide .: Vice/toptipsDocument3 pagesCRD-33 Trouble Shooting Guide .: Vice/toptipsjbloggs2007No ratings yet
- Niit MCQDocument10 pagesNiit MCQArun SomanNo ratings yet
- First Login in Uniflow and Card RegistrationDocument2 pagesFirst Login in Uniflow and Card RegistrationAndrew EvansNo ratings yet
- IitiDocument2 pagesIitiLiliana CondreaNo ratings yet
- Jmeter - Recording: Set Up For Script RecordingDocument11 pagesJmeter - Recording: Set Up For Script RecordingIfraH SuhailNo ratings yet
- Monochrome: Ineo 600/750Document6 pagesMonochrome: Ineo 600/750GabiNo ratings yet
- Google Dork 2011Document12 pagesGoogle Dork 2011offistarNo ratings yet
- Achieving Control Levels Functionality in Adobe FormsDocument13 pagesAchieving Control Levels Functionality in Adobe FormsRakesh RaiNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument3 pagesReadmeMassive MilkersNo ratings yet
- Installation ApS WindowsDocument10 pagesInstallation ApS WindowsHoracio TerragnoNo ratings yet
- External Data Recovery Services by TechchefDocument7 pagesExternal Data Recovery Services by TechchefKushal ShriNo ratings yet
- Aim 3.1Document3 pagesAim 3.1Basavanagowda GowdaNo ratings yet
- Six Weeks/months Industrial Training Report On IT CompanyDocument28 pagesSix Weeks/months Industrial Training Report On IT CompanySachin Rana100% (2)
LINUX
LINUX
Uploaded by
Reds Vharshan MahandrenOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LINUX
LINUX
Uploaded by
Reds Vharshan MahandrenCopyright:
Available Formats
ORGANIZATION
Linux operating system is one of the popular versions of the UNIX operating
system, which is designed to offer a free or low-cost operating system for
personal computer users. It gained a reputation as a fast performing and very
efficient system. This is a remarkably complete operating system, including a
GUI (graphical user interface), TCP/IP, the Emacs editor, can X Window
System, etc. The best Linux operating systems are Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora,
Red Hat Linux, SUSE Linux, Gentoo, Kali Linux & Centos.
Despite the fact that the Linux kernel is the key component in the operating
system, most of the components are open source. Linux is one of the only open
source operating systems, and the kernel is the hub of the operation. The
bootloader, graphical server, daemons, desktop environment, and application
software all play a part in the Linux operating system. Linux, unlike other
operating systems, is successful for its various advantages, including ease of use
and acquisition, higher security, more customization options, less maintenance,
available on any brand’ devices, and stable, to name a few.
A computer’s operating system interface to the hardware is referred to as a
software application. A number of software applications are run on operating
systems to manage hardware resources on a computer.
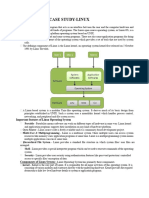
ARCHIECHTURE
The Linux architecture is largely composed of elements such as the Kernel,
System Library, Hardware layer, System, and Shell functions
The Linux architecture is largely composed of elements such as the Kernel,
System Library, Hardware layer, System, and Shell functions.
Kernel: The kernel is one of the fundamental parts of an operating system. It is
responsible for each of the primary duties of the Linux OS. Each of the major
procedures of Linux is coordinated with hardware directly. The kernel is in charge
of creating an appropriate abstraction for concealing trivial hardware or
application strategies. The following kernel varieties are mentioned:
1. Monolithic Kernel
2. Micro kernels
3. Exo kernels
4. Hybrid kernels
System Libraries: A set of library functions may be specified as these functions.
These functions are implemented by the operating system and do not require
code access rights on the kernel modules.
System Utility Programs: A system utility program performs specific and
individual jobs.
Hardware layer: The hardware layer of Linux is made up of several peripheral
devices such as a CPU, HDD, and RAM.
Shell: Different operating systems are classified as graphical shells and
command-line shells. A graphical shell is an interface between the kernel and the
user. It provides kernel services, and it runs kernel operations. There are two
types of graphical shells, which differ in appearance. These operating systems
are divided into two categories, which are the graphical shells and command-line
shells.
The graphical line shells allow for graphical user interfaces, while the command
line shells enable for command line interfaces. As a result, both of these shells
operate. However, graphical user interfaces performed using the graphical line
shells are faster than those using the command line shells.
You might also like
- PowershellDocument4 pagesPowershellshortcutNo ratings yet
- Os ProjectDocument9 pagesOs ProjectVishal SharmaNo ratings yet
- 3CS LSP Unit 1Document20 pages3CS LSP Unit 1Deepak KumarNo ratings yet
- 3CS LSP Unit 1-1Document15 pages3CS LSP Unit 1-1Deepak KumarNo ratings yet
- 15877091881capse0401-Unit-4-App. of Os O.SDocument11 pages15877091881capse0401-Unit-4-App. of Os O.Sezhilarasu2k9No ratings yet
- Linux System ProgrammingDocument38 pagesLinux System ProgrammingStan MigsNo ratings yet
- Case Study On LinuxDocument40 pagesCase Study On LinuxDivyanshuNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Linux Prof. Sujata RizalDocument40 pagesCase Study On Linux Prof. Sujata RizalRupesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Linux Ms. Jaya GangwaniDocument40 pagesCase Study On Linux Ms. Jaya GangwaniArpit GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Linux Admin Lecture 1Document12 pagesLinux Admin Lecture 1bekesy7No ratings yet
- Operating SystemsDocument22 pagesOperating SystemsRajdeep BorgohainNo ratings yet
- Os FileDocument57 pagesOs Fileguptatulsi31No ratings yet
- Ashu Linux 1Document13 pagesAshu Linux 1Ashish SinghNo ratings yet
- Prajwal GaykwadDocument8 pagesPrajwal GaykwadVaibhav KokitkarNo ratings yet
- Unix V Case StudiesDocument24 pagesUnix V Case StudiesvenkatNo ratings yet
- LinusDocument15 pagesLinusAbel HaileNo ratings yet
- LINUX MODULE-1 - NewDocument66 pagesLINUX MODULE-1 - NewFausiya SalimNo ratings yet
- ITC 401 Lect Note2Document35 pagesITC 401 Lect Note24rgx7fmvg9No ratings yet
- LINUX Programming: INSTRUCTOR: Ms. M. KeerthikaDocument4 pagesLINUX Programming: INSTRUCTOR: Ms. M. KeerthikaKeerthika MNo ratings yet
- Case Study1Document15 pagesCase Study1Anshuman KashyapNo ratings yet
- Operating System - LinuxDocument3 pagesOperating System - LinuxTitus ThukuNo ratings yet
- HCIA-Cloud Computing-Chapter5Document20 pagesHCIA-Cloud Computing-Chapter5islemNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 LinuxDocument18 pagesUnit-1 LinuxNikhil GharatNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document36 pagesUnit 5seetha yuviNo ratings yet
- Unix V Case StudiesDocument36 pagesUnix V Case StudiesAnish A RNo ratings yet
- Linux MOD 1Document55 pagesLinux MOD 1www.noelabraham60No ratings yet
- Linux Operating SystemDocument11 pagesLinux Operating SystemNaval BihaniNo ratings yet
- Windows Vs LinuxDocument21 pagesWindows Vs LinuxrameshkkrliveNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Linux, Unix, WindowsDocument3 pagesIntroduction of Linux, Unix, Windowssanya gargNo ratings yet
- Linux KernelDocument9 pagesLinux KernelNavneetMishraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Linux OS: Nbkrist Iv B.Tech Cse-Ii SemDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Linux OS: Nbkrist Iv B.Tech Cse-Ii SemSiva Prathap MNo ratings yet
- Subject: Operating Systems: Topic: LinuxDocument26 pagesSubject: Operating Systems: Topic: LinuxB.C.H. ReddyNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument17 pagesCase StudySumeet KaurNo ratings yet
- LinuxDocument3 pagesLinuxrahul274274No ratings yet
- Os LinuxDocument2 pagesOs LinuxDavid D'bayuNo ratings yet
- What Is An Operating SystemDocument5 pagesWhat Is An Operating Systemrashmi rashmiNo ratings yet
- Linux OSDocument27 pagesLinux OSJowel VistaNo ratings yet
- LinuxDocument17 pagesLinuxAmal FahadNo ratings yet
- LinuxDocument3 pagesLinuxTejas JadhavNo ratings yet
- Null 9Document4 pagesNull 9Josue SipingNo ratings yet
- 3LINUX DocumentxDocument65 pages3LINUX DocumentxKalyan KNo ratings yet
- 01-Introduction To LinuxDocument24 pages01-Introduction To LinuxGeorge JNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument11 pagesChapter Onetigersiin4No ratings yet
- Introduction and Overview-Getting Started: ChapterDocument10 pagesIntroduction and Overview-Getting Started: Chapterram_somalaNo ratings yet
- LinuxDocument3 pagesLinuxjagruthims100% (1)
- Oss Unit2Document20 pagesOss Unit2Akash ShuklaNo ratings yet
- A Brief Review On Linux: IndexDocument6 pagesA Brief Review On Linux: IndexSifat AnwarNo ratings yet
- Basic Command For Linux New PDFDocument102 pagesBasic Command For Linux New PDFGhost RiderNo ratings yet
- OS06Document19 pagesOS06Asghar Khattak FDCPNo ratings yet
- 3Document6 pages3lgugunashviliNo ratings yet
- Mscse 3 Oss Iset64Document178 pagesMscse 3 Oss Iset64Undergraduate LibraryNo ratings yet
- BCA Sem V - UnixDocument14 pagesBCA Sem V - Unixshri_dasari0% (1)
- Module 5 UnixDocument16 pagesModule 5 Unixshekhawatharsh54No ratings yet
- Practical Training Report: LinuxDocument31 pagesPractical Training Report: LinuxRohit ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Linux Introduction-TeamsDocument22 pagesLinux Introduction-TeamsNithish GowdaNo ratings yet
- Linux FundamentalsDocument4 pagesLinux FundamentalsPratham MishraNo ratings yet
- 01 135221 040 11122096165 20092023 014910pmDocument8 pages01 135221 040 11122096165 20092023 014910pmzainm7032No ratings yet
- Os 2 All Assignments2Document118 pagesOs 2 All Assignments2tp60120No ratings yet
- Os Ass1Document13 pagesOs Ass1Khushi sahuNo ratings yet
- Unit I LinuxDocument30 pagesUnit I LinuxRohan RathodNo ratings yet
- Linux: A Comprehensive Guide to Linux Operating System and Command LineFrom EverandLinux: A Comprehensive Guide to Linux Operating System and Command LineNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Shomesh Web ProgrammingDocument7 pagesAssignment 1 Shomesh Web ProgrammingReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- Futuristic Background - by SlidesgoDocument15 pagesFuturistic Background - by SlidesgoReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document4 pagesAssignment 3Reds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- Dus-Point 3Document3 pagesDus-Point 3Reds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity AnalystDocument2 pagesCybersecurity AnalystReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- Parapharasing PracticeDocument24 pagesParapharasing PracticeReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Avoiding Plagiarism PracticeDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Avoiding Plagiarism PracticeReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- Theory About Sea PowerDocument2 pagesTheory About Sea PowerReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- Kesh LampiranDocument2 pagesKesh LampiranReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- Lampiran: Menguji Atur Cara Yang Telah DibinaDocument2 pagesLampiran: Menguji Atur Cara Yang Telah DibinaReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- SEKOLAHDocument2 pagesSEKOLAHReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- LAMPIRAN A - Urus Niaga Tugasan 2019 - UpdatedDocument4 pagesLAMPIRAN A - Urus Niaga Tugasan 2019 - UpdatedReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- What Are The Major Components of A Web Browser - Draw A Neat Diagram To Explain Them.Document3 pagesWhat Are The Major Components of A Web Browser - Draw A Neat Diagram To Explain Them.Fer LeroyNo ratings yet
- User Manual: NVR/DVR/Hybrid NDVRDocument138 pagesUser Manual: NVR/DVR/Hybrid NDVRGeorge JR BagsaoNo ratings yet
- Emonitor Users GuideDocument392 pagesEmonitor Users GuideFadooollNo ratings yet
- Pocket MirrorDocument70 pagesPocket MirrorRob HilliardNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To DSpaceDocument17 pagesAn Introduction To DSpaceamenu_bizunehNo ratings yet
- Installation Instructions LabsoftDocument32 pagesInstallation Instructions LabsoftDragoi Mihai0% (2)
- How To Hack Facebook Accounts - 5 Common Vulnerabilities - Hacker NoonDocument6 pagesHow To Hack Facebook Accounts - 5 Common Vulnerabilities - Hacker NoonMohamed AmgadNo ratings yet
- Google Adwords Certification - Fundamentals Exam NotesDocument15 pagesGoogle Adwords Certification - Fundamentals Exam NotesAllison DiCicco BerlinNo ratings yet
- Latex GraphicsDocument122 pagesLatex GraphicslambfellerNo ratings yet
- XSS Filter Evasion Cheat SheetDocument43 pagesXSS Filter Evasion Cheat SheetYaseenNo ratings yet
- LT2203Document15 pagesLT2203Sharafat KabirNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DreamweaverDocument50 pagesIntroduction To DreamweaverIlyas A HuqqaniNo ratings yet
- Adminguides4hanaimpl Help enDocument52 pagesAdminguides4hanaimpl Help enbujjishaikNo ratings yet
- Step-By-Step Guide For AWS Virtual TrainingDocument6 pagesStep-By-Step Guide For AWS Virtual TrainingAdmin BakamaNo ratings yet
- Storyline 3: Create Interactive Courses For Any DeviceDocument9 pagesStoryline 3: Create Interactive Courses For Any DeviceHendra Tjahja100% (1)
- DataDocument226 pagesDataSamuel TerrellNo ratings yet
- CRD-33 Trouble Shooting Guide .: Vice/toptipsDocument3 pagesCRD-33 Trouble Shooting Guide .: Vice/toptipsjbloggs2007No ratings yet
- Niit MCQDocument10 pagesNiit MCQArun SomanNo ratings yet
- First Login in Uniflow and Card RegistrationDocument2 pagesFirst Login in Uniflow and Card RegistrationAndrew EvansNo ratings yet
- IitiDocument2 pagesIitiLiliana CondreaNo ratings yet
- Jmeter - Recording: Set Up For Script RecordingDocument11 pagesJmeter - Recording: Set Up For Script RecordingIfraH SuhailNo ratings yet
- Monochrome: Ineo 600/750Document6 pagesMonochrome: Ineo 600/750GabiNo ratings yet
- Google Dork 2011Document12 pagesGoogle Dork 2011offistarNo ratings yet
- Achieving Control Levels Functionality in Adobe FormsDocument13 pagesAchieving Control Levels Functionality in Adobe FormsRakesh RaiNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument3 pagesReadmeMassive MilkersNo ratings yet
- Installation ApS WindowsDocument10 pagesInstallation ApS WindowsHoracio TerragnoNo ratings yet
- External Data Recovery Services by TechchefDocument7 pagesExternal Data Recovery Services by TechchefKushal ShriNo ratings yet
- Aim 3.1Document3 pagesAim 3.1Basavanagowda GowdaNo ratings yet
- Six Weeks/months Industrial Training Report On IT CompanyDocument28 pagesSix Weeks/months Industrial Training Report On IT CompanySachin Rana100% (2)